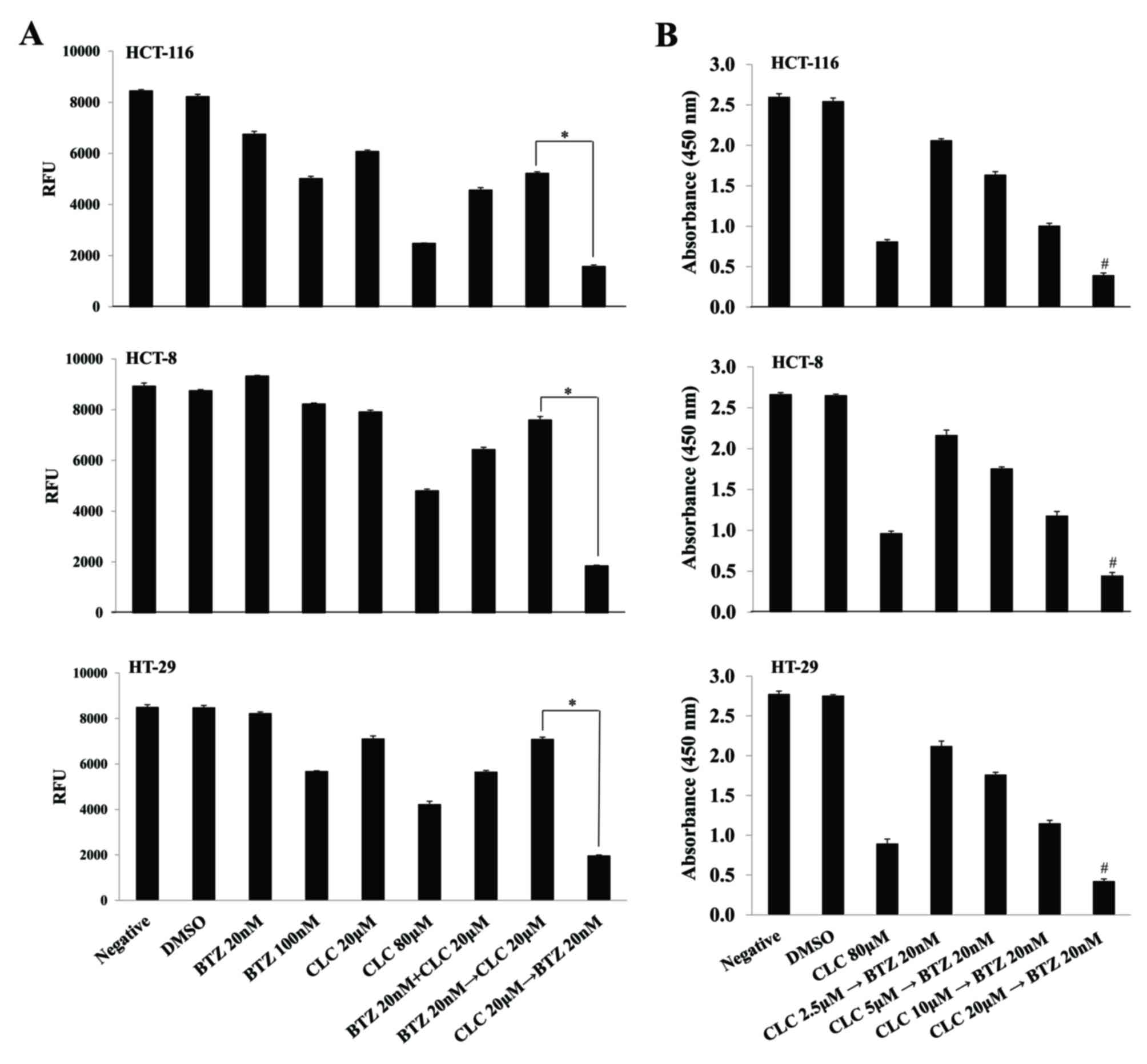
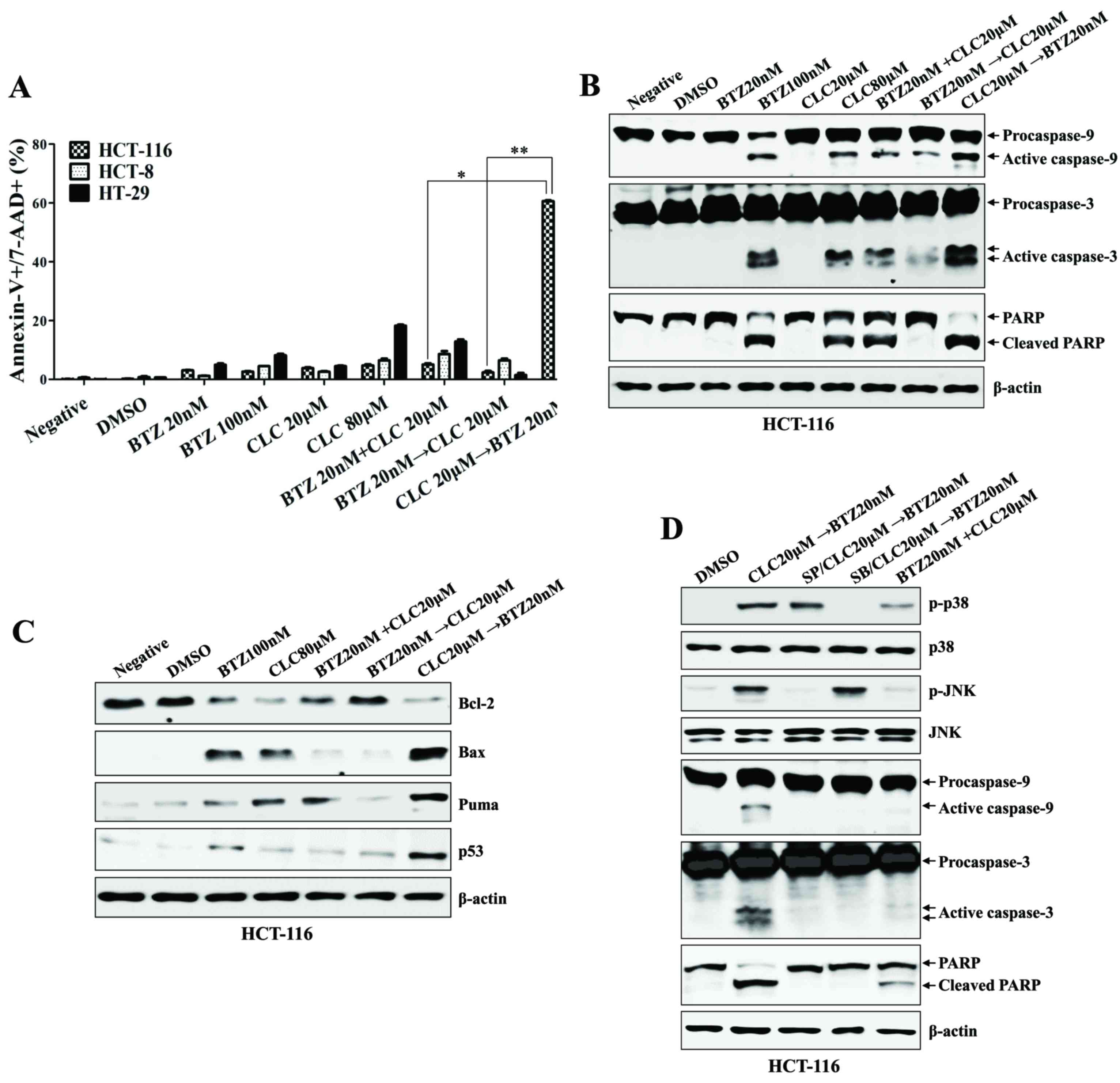
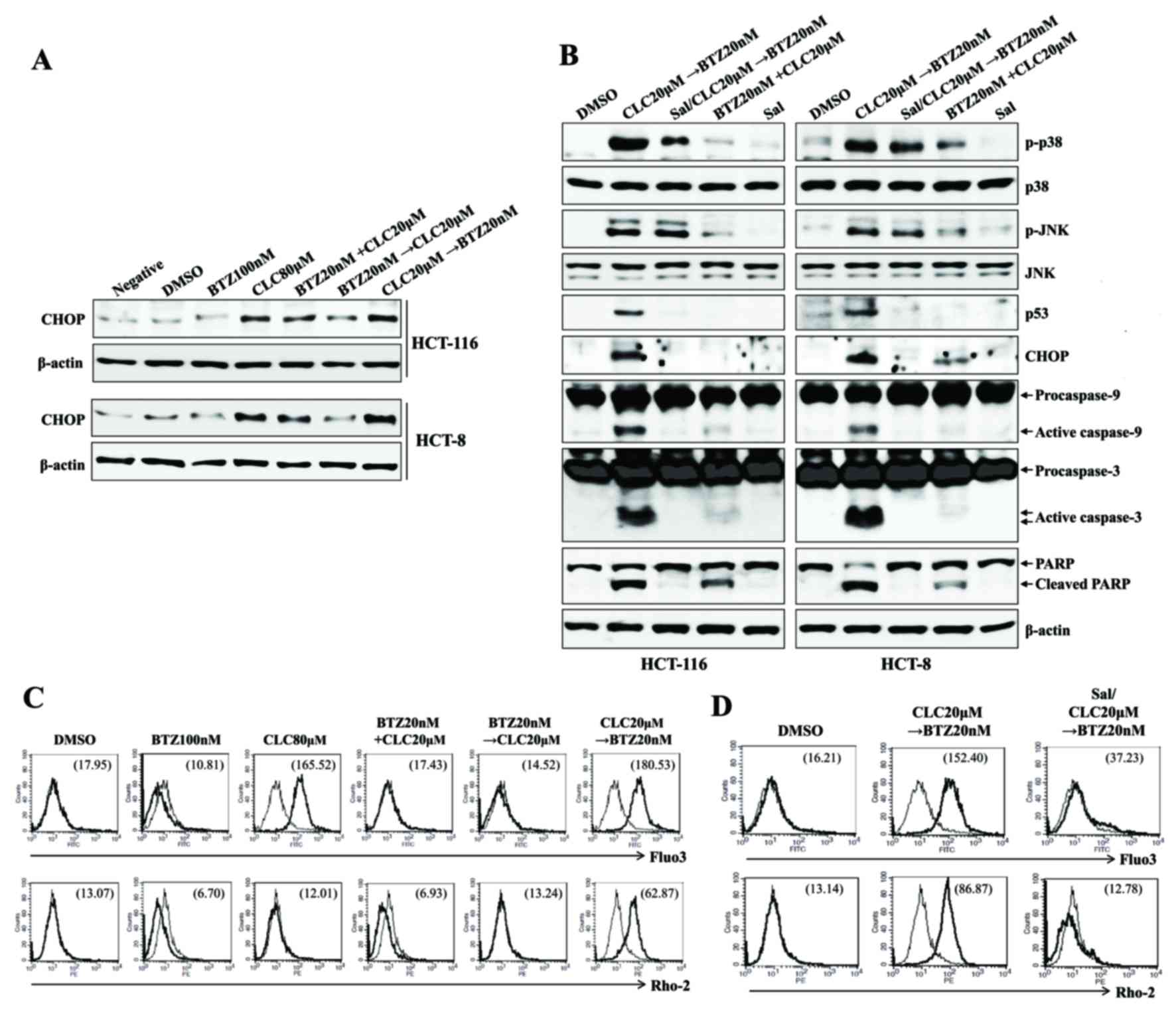
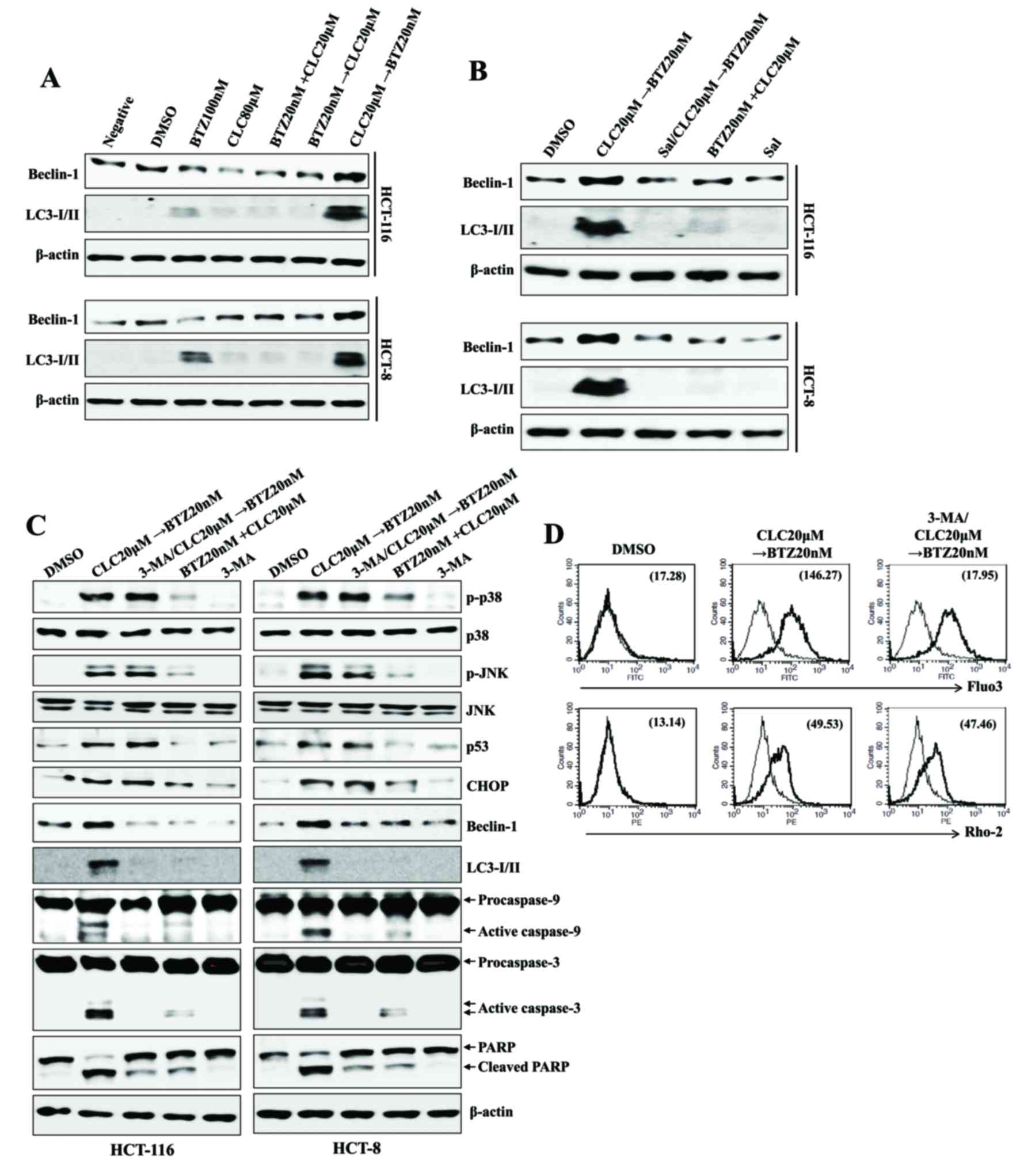
|
1
|
Arico S, Pattingre S, Bauvy C, Gane P,
Barbat A, Codogno P and Ogier-Denis E: Celecoxib induces apoptosis
by inhibiting 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1
activity in the human colon cancer HT-29 cell line. J Biol Chem.
277:27613–27621. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lynch PM, Ayers GD, Hawk E, Richmond E,
Eagle C, Woloj M, Church J, Hasson H, Patterson S, Half E and Burke
CA: The safety and efficacy of celecoxib in children with familial
adenomatous polyposis. Am J Gastroenterol. 105:1437–1443. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsutsumi S, Namba T, Tanaka KI, Arai Y,
Ishihara T, Aburaya M, Mima S, Hoshino T and Mizushima T: Celecoxib
upregulates endoplasmic reticulum chaperones that inhibit
celecoxib-induced apoptosis in human gastric cells. Oncogene.
25:1018–1029. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tsutsumi S, Gotoh T, Tomisato W, Mima S,
Hoshino T, Hwang HJ, Takenaka H, Tsuchiya T, Mori M and Mizushima
T: Endoplasmic reticulum stress response is involved in
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 11:1009–1016. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin WC, Chuang YC, Chang YS, Lai MD, Teng
YN, Su IJ, Wang CC, Lee KH and Hung JH: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress stimulates p53 expression through NF-κB activation. PLoS
One. 7:e391202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Edagawa M, Kawauchi J, Hirata M, Goshima
H, Inoue M, Okamoto T, Murakami A, Maehara Y and Kitajima S: Role
of activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) in endoplasmic
reticulum (ER) stress-induced sensitization of p53-deficient human
colon cancer cells to tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis through
up-regulation of death receptor 5 (DR5) by zerumbone and celecoxib.
J Biol Chem. 289:21544–21561. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ludwig H, Khayat D, Giaccone G and Facon
T: Proteasome inhibition and its clinical prospects in the
treatment of hematologic and solid malignancies. Cancer.
104:1794–1807. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nawrocki ST, Carew JS, Pino MS, Highshaw
RA, Dunner K Jr, Huang P, Abbruzzese JL and McConkey DJ: Bortezomib
sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Res. 65:11658–11666. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu J, Tiwari S, Steiner P and Zhang L:
Differential apoptotic response to the proteasome inhibitor
Bortezomib [VELCADE, PS-341] in Bax-deficient and p21-deficient
colon cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2:694–699. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lum JJ, Bauer DE, Kong M, Harris MH, Li C,
Lindsten T and Thompson CB: Growth factor regulation of autophagy
and cell survival in the absence of apoptosis. Cell. 120:237–248.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ogata M, Hino S, Saito A, Morikawa K,
Kondo S, Kanemoto S, Murakami T, Taniguchi M, Tanii I, Yoshinaga K,
et al: Autophagy is activated for cell survival after endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol. 26:9220–9231. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang Z and Klionsky DJ: Eaten alive: A
history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 12:814–822. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kao C, Chao A, Tsai CL, Chuang WC, Huang
WP, Chen GC, Lin CY, Wang TH, Wang HS and Lai CH: Bortezomib
enhances cancer cell death by blocking the autophagic flux through
stimulating ERK phosphorylation. Cell Death Dis. 5:e15102014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang S and Sinicrope FA:
Celecoxib-induced apoptosis is enhanced by ABT-737 and by
inhibition of autophagy in human colorectal cancer cells.
Autophagy. 6:256–269. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deniaud A, el dein Sharaf O, Maillier E,
Poncet D, Kroemer G, Lemaire C and Brenner C: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress induces calcium-dependent permeability transition,
mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis.
Oncogene. 27:285–299. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li J, Lee B and Lee AS: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced apoptosis: Multiple pathways and
activation of p53-up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) and
NOXA by p53. J Biol Chem. 281:7260–7270. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Giorgi C, Bonora M, Sorrentino G,
Missiroli S, Poletti F, Suski JM, Ramirez Galindo F, Rizzuto R, Di
Virgilio F, Zito E, et al: p53 at the endoplasmic reticulum
regulates apoptosis in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 112:1779–1784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kardosh A, Golden EB, Pyrko P, Uddin J,
Hofman FM, Chen TC, Louie SG, Petasis NA and Schönthal AH:
Aggravated endoplasmic reticulum stress as a basis for enhanced
glioblastoma cell killing by bortezomib in combination with
celecoxib or its non-coxib analogue, 2,5-dimethyl-celecoxib. Cancer
Res. 68:843–851. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim JE, Lee JI, Jin DH, Lee WJ, Park GB,
Kim S, Kim YS, Wu TC, Hur DY and Kim D: Sequential treatment of HPV
E6 and E7-expressing TC-1 cells with bortezomib and celecoxib
promotes apoptosis through p-p38 MAPK-mediated downregulation of
cyclin D1 and CDK2. Oncol Rep. 31:2429–2437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Altorki NK, Keresztes RS, Port JL, Libby
DM, Korst RJ, Flieder DB, Ferrara CA, Yankelevitz DF, Subbaramaiah
K, Pasmantier MW and Dannenberg AJ: Celecoxib, a selective
cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitor, enhances the response to preoperative
paclitaxel and carboplatin in early-stage non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 21:2645–2650. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Masferrer JL, Leahy KM, Koki AT, Zweifel
BS, Settle SL, Woerner BM, Edwards DA, Flickinger AG, Moore RJ and
Seibert K: Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Cancer Res. 60:1306–1311.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sacchetti A: Cancer cell killing by
Celecoxib: Reality or just in vitro precipitation-related artifact?
J Cell Biochem. 114:1434–1444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cho HY, Thomas S, Golden EB, Gaffney KJ,
Hofman FM, Chen TC, Louie SG, Petasis NA and Schönthal AH: Enhanced
killing of chemo-resistant breast cancer cells via controlled
aggravation of ER stress. Cancer Lett. 282:87–97. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Solomon SD, McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA,
Wittes J, Fowler R, Finn P, Anderson WF, Zauber A, Hawk E and
Bertagnolli M: Adenoma Prevention with Celecoxib (APC) Study
Investigators: Cardiovascular risk associated with celecoxib in a
clinical trial for colorectal adenoma prevention. N Engl J Med.
352:1071–1080. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Milani M, Rzymski T, Mellor HR, Pike L,
Bottini A, Generali D and Harris AL: The role of ATF4 stabilization
and autophagy in resistance of breast cancer cells treated with
Bortezomib. Cancer Res. 69:4415–4423. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boyce M and Yuan J: Cellular response to
endoplasmic reticulum stress: A matter of life or death. Cell Death
Differ. 13:363–373. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cuervo AM: Autophagy: In sickness and in
health. Trends Cell Biol. 14:70–77. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oakes SA, Scorrano L, Opferman JT, Bassik
MC, Nishino M, Pozzan T and Korsmeyer SJ: Proapoptotic BAX and BAK
regulate the type 1 inositol trisphosphate receptor and calcium
leak from the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:105–110. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pinton P, Giorgi C and Pandolfi PP: The
role of PML in the control of apoptotic cell fate: A new key player
at ER-mitochondria sites. Cell Death Differ. 18:1450–1456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Levine B, Sinha S and Kroemer G: Bcl-2
family members: Dual regulators of apoptosis and autophagy.
Autophagy. 4:600–606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|