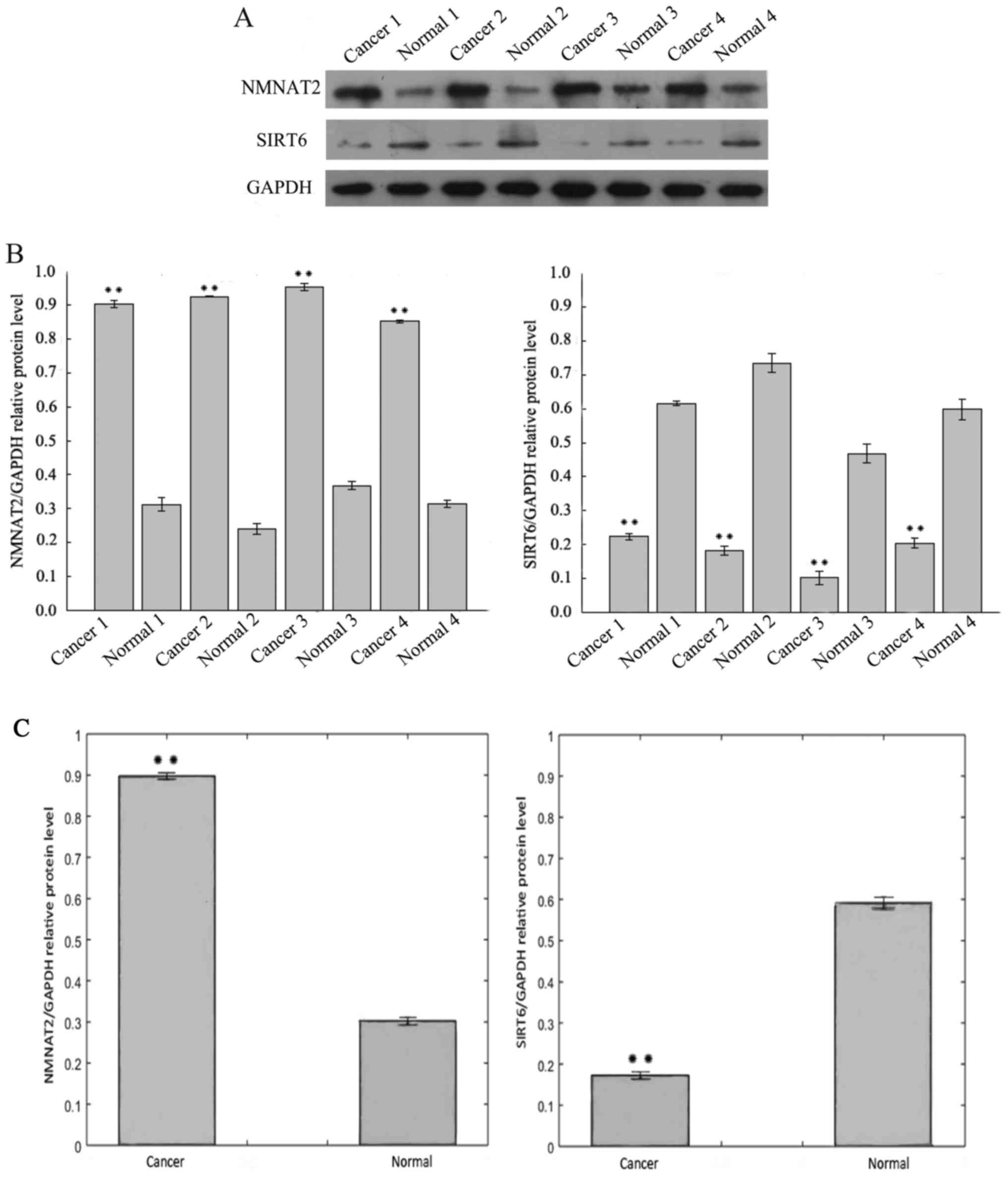
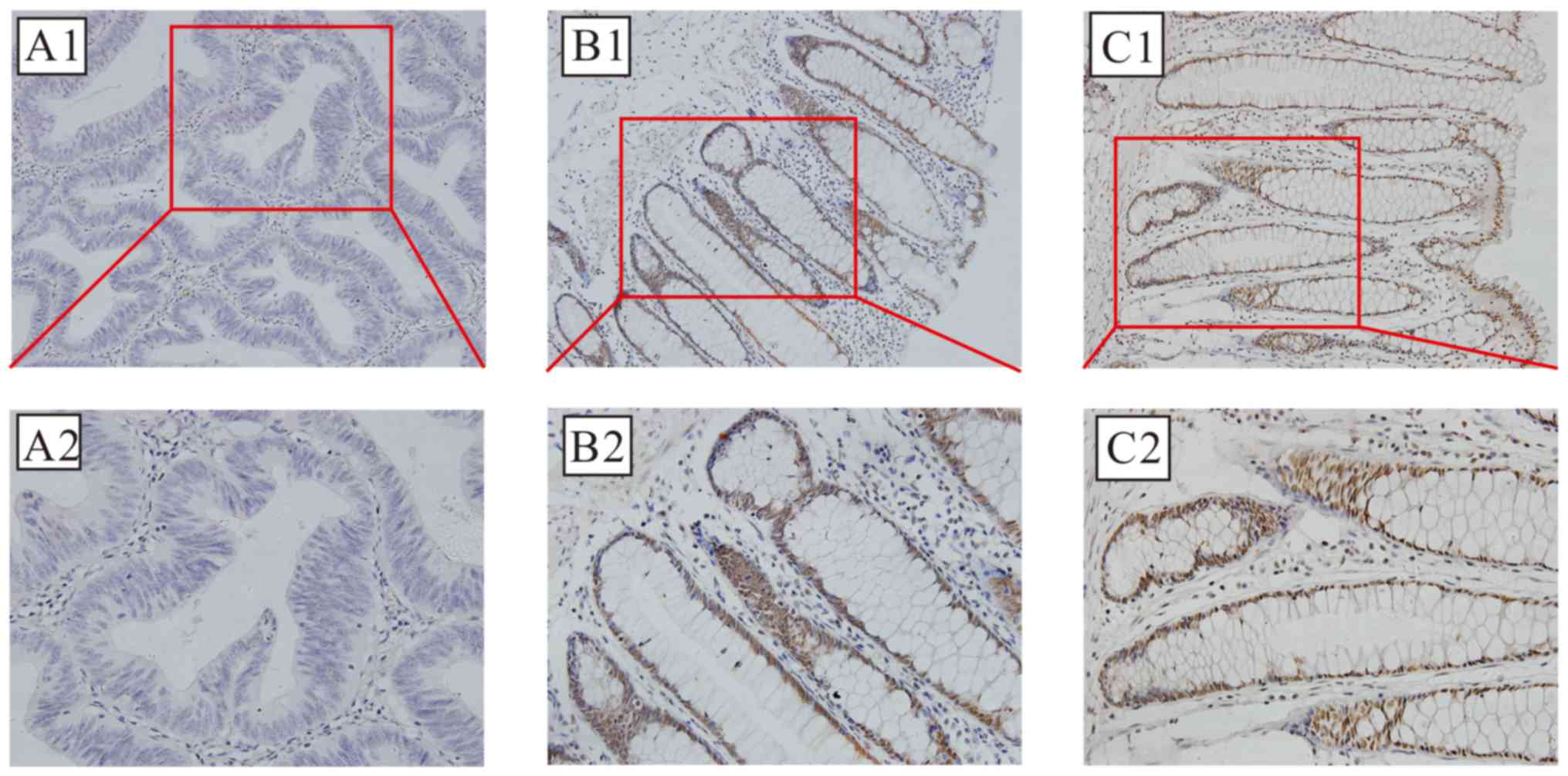
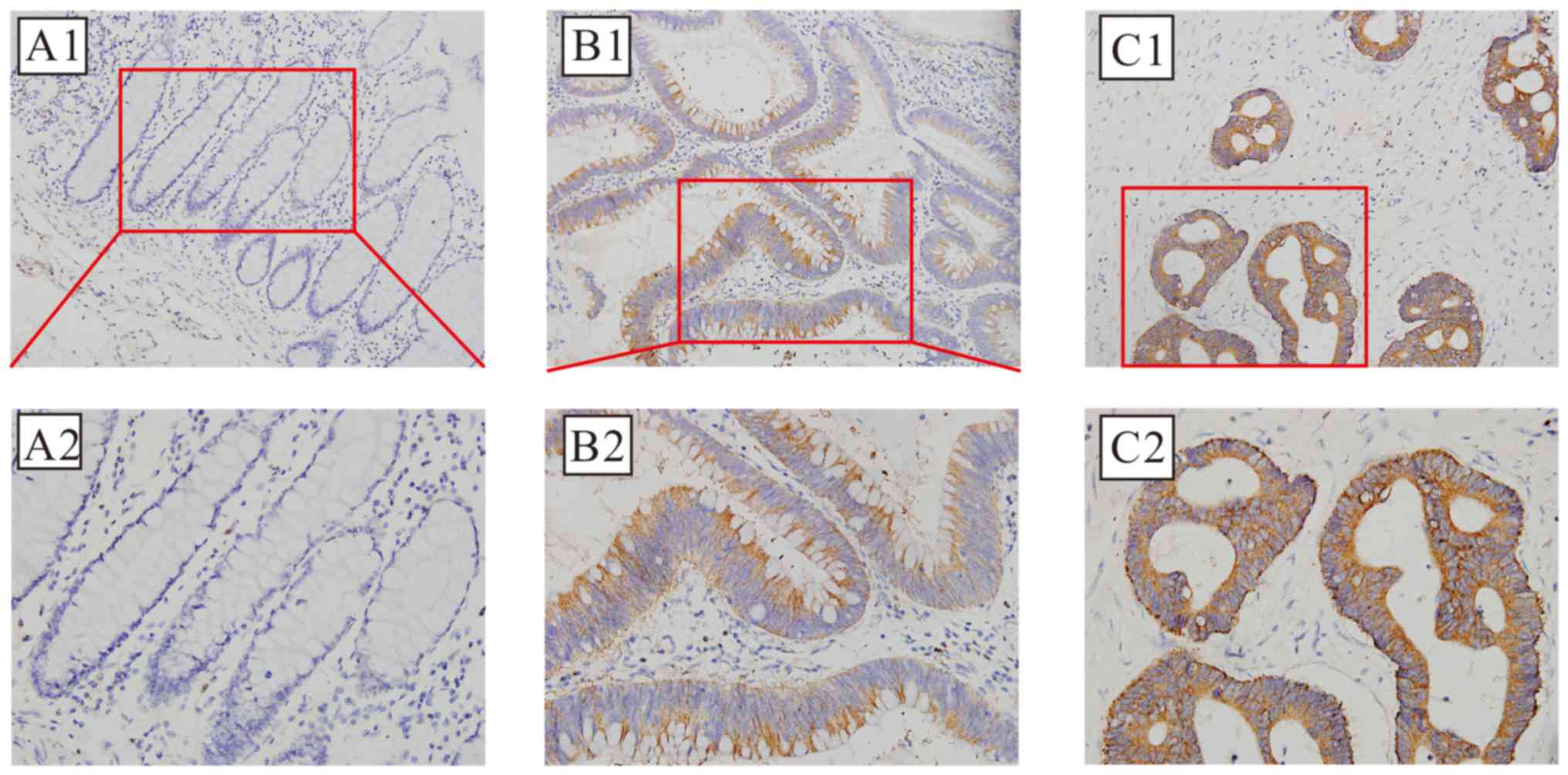
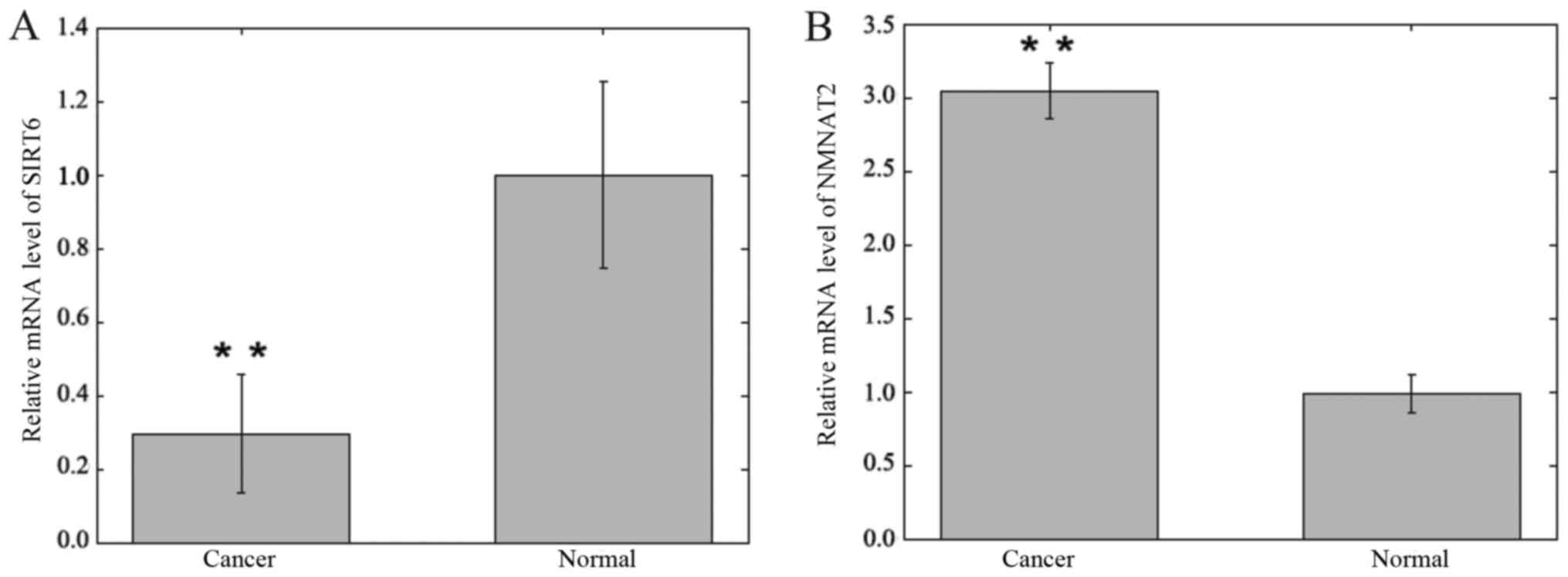
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Favoriti P, Carbone G, Greco M, Pirozzi F,
Pirozzi RE and Corcione F: Worldwide burden of colorectal cancer: A
review. Updates Surg. 68:7–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rabeneck L, Horton S, Zauber AG and Earle
C: Colorectal Cancer. In: Cancer: Disease Control Priorities, Third
Edition (Volume 3)Gelband H, Jha P, Sankaranarayanan R and Horton
S: The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The
World Bank (C) 2015 International Bank for Reconstruction and
Development/The World Bank. Washington (DC): 2015
|
|
6
|
Zhu AX, Kudo M, Assenat E, Cattan S, Kang
YK, Lim HY, Poon RT, Blanc JF, Vogel A, Chen CL, et al: Effect of
everolimus on survival in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma after
failure of sorafenib: The EVOLVE-1 randomized clinical trial. JAMA.
312:57–67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Michan S and Sinclair D: Sirtuins in
mammals: Insights into their biological function. Biochem J.
404:1–13. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bruzzone S, Parenti MD, Grozio A,
Ballestrero A, Bauer I, Del Rio A and Nencioni A: Rejuvenating
sirtuins: The rise of a new family of cancer drug targets. Curr
Pharm Des. 19:614–623. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lerrer B, Gertler AA and Cohen HY: The
complex role of SIRT6 in carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis.
37:108–118. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Michishita E, McCord RA, Berber E, Kioi M,
Padilla-Nash H, Damian M, Cheung P, Kusumoto R, Kawahara TL,
Barrett JC, et al: SIRT6 is a histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylase that
modulates telomeric chromatin. Nature. 452:492–496. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tennen RI and Chua KF: Chromatin
regulation and genome maintenance by mammalian SIRT6. Trends
Biochem Sci. 36:39–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Toiber D, Erdel F, Bouazoune K, Silberman
DM, Zhong L, Mulligan P, Sebastian C, Cosentino C, Martinez-Pastor
B, Giacosa S, et al: SIRT6 recruits SNF2H to DNA break sites,
preventing genomic instability through chromatin remodeling. Mol
Cell. 51:454–468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cea M, Cagnetta A, Adamia S, Acharya C,
Tai YT, Fulciniti M, Ohguchi H, Munshi A, Acharya P, Bhasin MK, et
al: Evidence for a role of the histone deacetylase SIRT6 in DNA
damage response of multiple myeloma cells. Blood. 127:1138–1150.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang G, Liu Z, Qin S and Li K: Decreased
expression of SIRT6 promotes tumor cell growth correlates closely
with poor prognosis of ovarian cancer. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol.
36:629–632. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu SS, Cai Y, Ye JT, Pi RB, Chen SR, Liu
PQ, Shen XY and Ji Y: Sirtuin 6 protects cardiomyocytes from
hypertrophy in vitro via inhibition of NF-κB-dependent
transcriptional activity. Br J Pharmacol. 168:117–128. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sundaresan NR, Vasudevan P, Zhong L, Kim
G, Samant S, Parekh V, Pillai VB, Ravindra PV, Gupta M, Jeevanandam
V, et al: The sirtuin SIRT6 blocks IGF-Akt signaling and
development of cardiac hypertrophy by targeting c-Jun. Nat Med.
18:1643–1650. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sebastian C, Zwaans BM, Silberman DM,
Gymrek M, Goren A, Zhong L, Ram O, Truelove J, Guimaraes AR, Toiber
D, et al: The histone deacetylase SIRT6 is a tumor suppressor that
controls cancer metabolism. Cell. 151:1185–1199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barretina J, Caponigro G, Stransky N,
Venkatesan K, Margolin AA, Kim S, Wilson CJ, Lehár J, Kryukov GV,
Sonkin D, et al: The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables
predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature.
483:603–607. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mayer PR, Huang N, Dewey CM, Dries DR,
Zhang H and Yu G: Expression, localization, and biochemical
characterization of nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase
2. J Biol Chem. 285:40387–40396. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jayaram HN, Kusumanchi P and Yalowitz JA:
NMNAT expression and its relation to NAD metabolism. Curr Med Chem.
18:1962–1972. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mouchiroud L, Houtkooper RH and Auwerx J:
NAD+ metabolism: A therapeutic target for age-related
metabolic disease. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 48:397–408. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cairns RA, Harris IS and Mak TW:
Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:85–95.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhong L, D'Urso A, Toiber D, Sebastian C,
Henry RE, Vadysirisack DD, Guimaraes A, Marinelli B, Wikstrom JD,
Nir T, et al: The histone deacetylase Sirt6 regulates glucose
homeostasis via Hif1alpha. Cell. 140:280–293. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bauer I, Grozio A, Lasigliè D, Basile G,
Sturla L, Magnone M, Sociali G, Soncini D, Caffa I, Poggi A, et al:
The NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase SIRT6 promotes cytokine
production and migration in pancreatic cancer cells by regulating
Ca2+ responses. J Biol Chem. 287:40924–40937. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Resch A and Langner C: Lymph node staging
in colorectal cancer: Old controversies and recent advances. World
J Gastroenterol. 19:8515–8526. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Van Cutsem E and Ducreux M: Colorectal and
gastric cancer in 2015: The development of new agents and molecular
classifications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 13:69–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fukuda T, Wada-Hiraike O, Oda K, Tanikawa
M, Makii C, Inaba K, Miyasaka A, Miyamoto Y, Yano T, Maeda D, et
al: Putative tumor suppression function of SIRT6 in endometrial
cancer. FEBS Lett. 589:2274–2281. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang ZG and Qin CY: Sirt6 suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth via inhibiting the
extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 9:882–888. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin Z, Yang H, Tan C, Li J, Liu Z, Quan Q,
Kong S, Ye J, Gao B and Fang D: USP10 antagonizes c-Myc
transcriptional activation through SIRT6 stabilization to suppress
tumor formation. Cell Rep. 5:1639–1649. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kleszcz R, Paluszczak J and Baer-Dubowska
W: Targeting aberrant cancer metabolism-The role of sirtuins.
Pharmacol Rep. 67:1068–1080. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xiong X, Wang G, Tao R, Wu P, Kono T, Li
K, Ding WX, Tong X, Tersey SA, Harris RA, et al: Sirtuin 6
regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic
beta cells. Diabetologia. 59:151–160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vander Heiden MG, Locasale JW, Swanson KD,
Sharfi H, Heffron GJ, Amador-Noguez D, Christofk HR, Wagner G,
Rabinowitz JD, Asara JM and Cantley LC: Evidence for an alternative
glycolytic pathway in rapidly proliferating cells. Science.
329:1492–1499. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hsu PP and Sabatini DM: Cancer cell
metabolism: Warburg and beyond. Cell. 134:703–707. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li H, Feng Z, Wu W, Li J, Zhang J and Xia
T: SIRT3 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis related to
energy metabolism in non-small cell lung cancer cells through
deacetylation of NMNAT2. Int J Oncol. 43:1420–1430. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Marquardt JU, Fischer K, Baus K, Kashyap
A, Ma S, Krupp M, Linke M, Teufel A, Zechner U, Strand D, et al:
Sirtuin-6-dependent genetic and epigenetic alterations are
associated with poor clinical outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma
patients. Hepatology. 58:1054–1064. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Locasale JW, Grassian AR, Melman T,
Lyssiotis CA, Mattaini KR, Bass AJ, Heffron G, Metallo CM, Muranen
T, Sharfi H, et al: Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase diverts
glycolytic flux and contributes to oncogenesis. Nat Genet.
43:869–874. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Possemato R, Marks KM, Shaul YD, Pacold
ME, Kim D, Birsoy K, Sethumadhavan S, Woo HK, Jang HG, Jha AK, et
al: Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is
essential in breast cancer. Nature. 476:346–350. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang WC, Shyh-Chang N, Yang H, Rai A,
Umashankar S, Ma S, Soh BS, Sun LL, Tai BC, Nga ME, et al: Glycine
decarboxylase activity drives non-small cell lung cancer
tumor-initiating cells and tumorigenesis. Cell. 148:259–272. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cantó C, Houtkooper RH, Pirinen E, Youn
DY, Oosterveer MH, Cen Y, Fernandez-Marcos PJ, Yamamoto H, Andreux
PA, Cettour-Rose P, et al: The NAD(+) precursor nicotinamide
riboside enhances oxidative metabolism and protects against
high-fat diet-induced obesity. Cell Metab. 15:838–847. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mégnin-Chanet F, Bollet MA and Hall J:
Targeting poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity for cancer therapy.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:3649–3662. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|