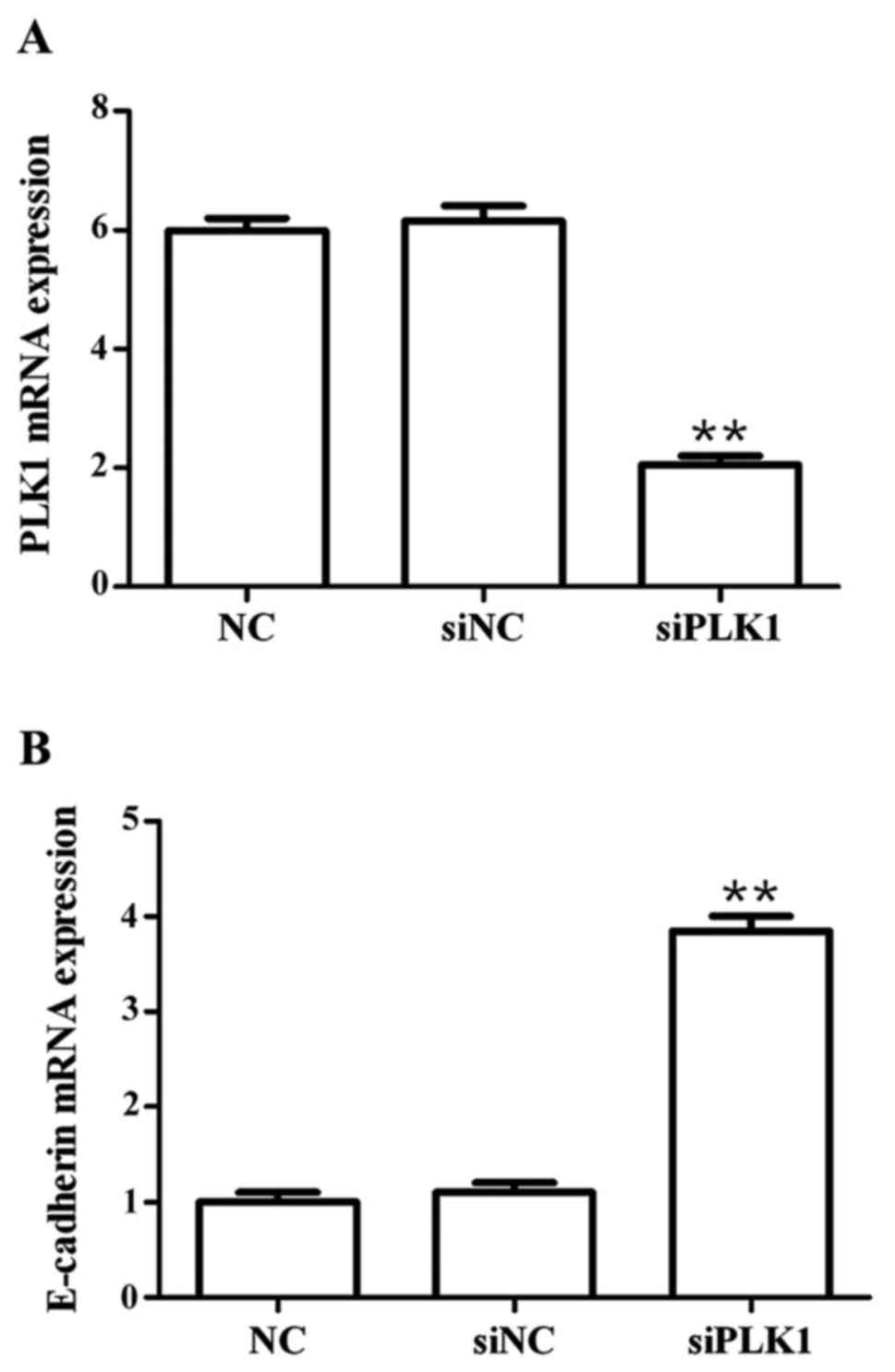
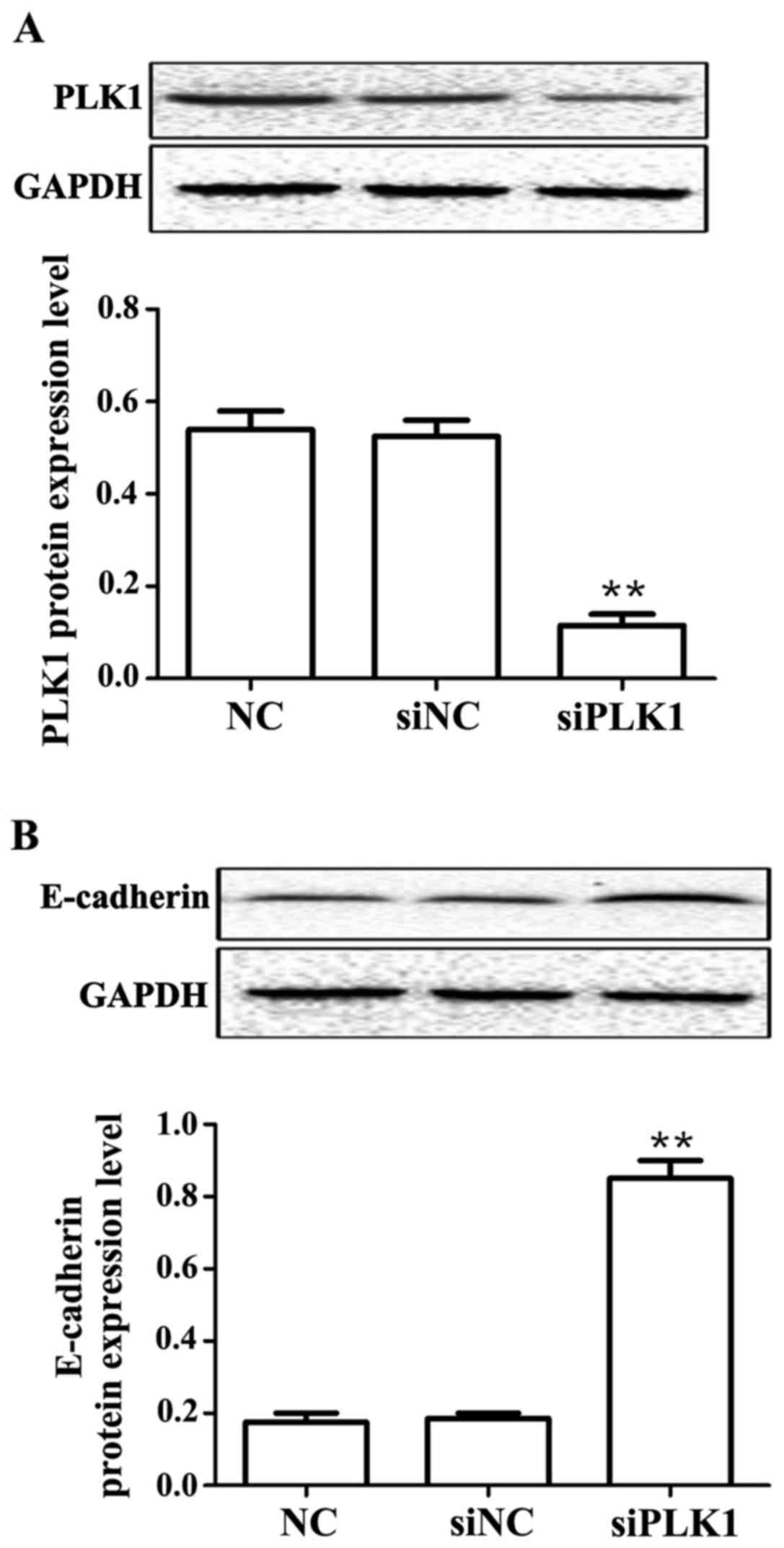
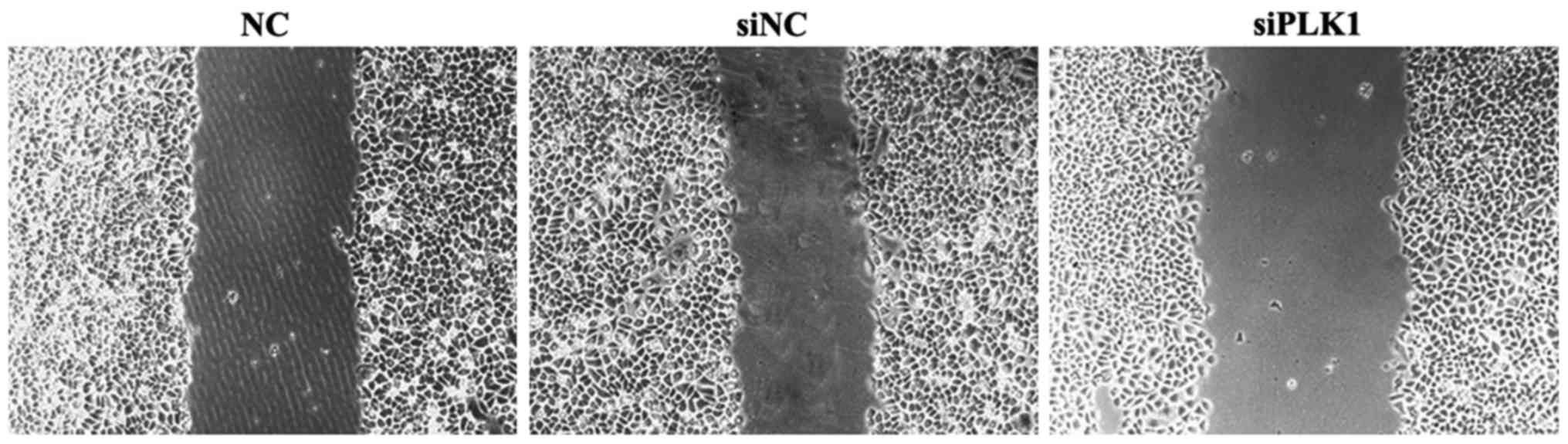
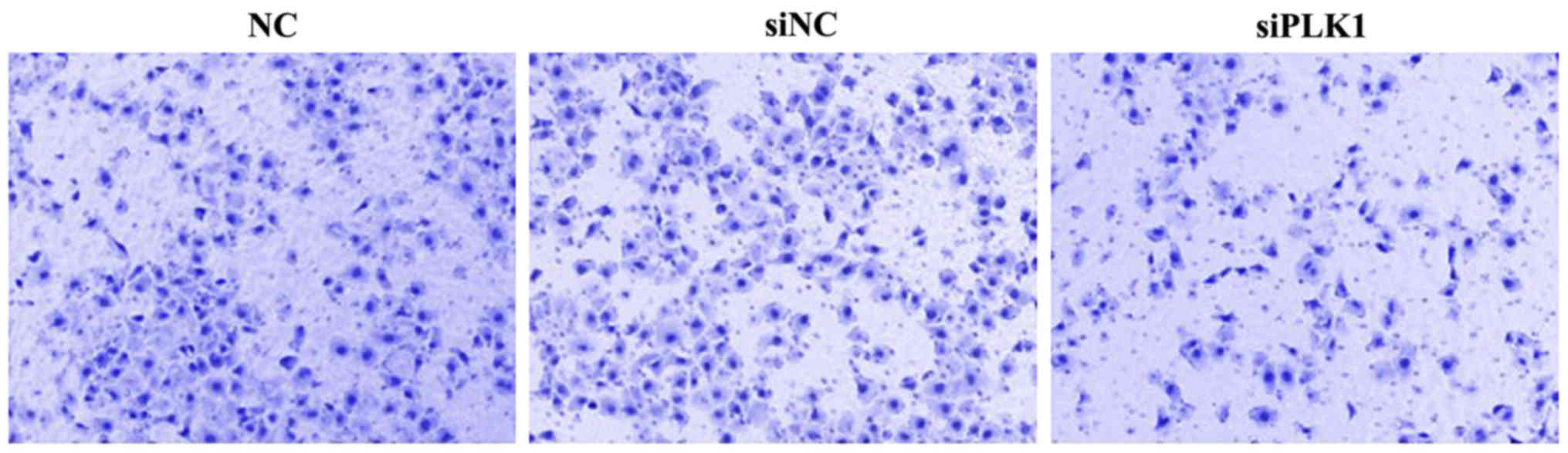
|
1
|
Brenner H, Rothenbacher D and Arndt V:
Epidemiology of stomach cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 472:467–477.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ryu MH and Kang YK: ML17032 trial:
Capecitabine/cisplatin versus 5-fluorouracil/cisplatin as
first-line therapy in advanced gastric cancer. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 9:1745–1751. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
De Vita F, Vecchione L, Galizia G, Di
Martino N, Fabozzi T, Catalano G, Ciardiello F and Orditura M:
Perspectives in adjuvant therapy of gastric cancer. Oncology. 77
Suppl 1:38–42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mlkvý P: Multimodal therapy of gastric
cancer. Dig Dis. 28:615–618. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mello BS, Lucena AF, Echer IC and Luzia
MF: Patients with gastric cancer submitted to gastrectomy: An
integrative review. Rev Gaúcha Enferm. 31:803–811. 2010.(In
Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A,
Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T,
et al: ToGA Trial Investigators: Trastuzumab in combination with
chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of
HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction
cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial.
Lancet. 376:687–697. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
de Cárcer G, Escobar B, Higuero AM, García
L, Ansón A, Pérez G, Mollejo M, Manning G, Meléndez B,
Abad-Rodríguez J, et al: Plk5, a polo box domain-only protein with
specific roles in neuron differentiation and glioblastoma
suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 31:1225–1239. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak and Schmittgen: Analysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2-ΔΔCq method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Crew KD and Neugut AI: Epidemiology of
upper gastrointestinal malignancies. Semin Oncol. 31:450–464. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Spiegel S and Milstien S: Functions of the
multifaceted family of sphingosine kinases and some close
relatives. J Biol Chem. 282:2125–2129. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ando K, Ozaki T, Yamamoto H, Furuya K,
Hosoda M, Hayashi S, Fukuzawa M and Nakagawara A: Polo-like kinase
1 (Plk1) inhibits p53 function by physical interaction and
phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 279:25549–25561. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Steinhauser I, Langer K, Strebhardt K and
Spänkuch B: Uptake of plasmid-loaded nanoparticles in breast cancer
cells and effect on Plk1 expression. J Drug Target. 17:627–637.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim SA, Kwon SM, Yoon JH and Ahn SG: The
antitumor effect of PLK1 and HSF1 double knockdown on human oral
carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 36:867–872. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Takai N, Hamanaka R, Yoshimatsu J and
Miyakawa I: Polo-like kinases (Plks) and cancer. Oncogene.
24:287–291. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang G, Zhang Z and Liu Z: Polo-like
kinase 1 is overexpressed in renal cancer and participates in the
proliferation and invasion of renal cancer cells. Tumour Biol.
34:1887–1894. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Smith MR, Wilson ML, Hamanaka R, Chase D,
Kung H, Longo DL and Ferris DK: Malignant transformation of
mammalian cells initiated by constitutive expression of the
polo-like kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 234:397–405. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Petrelli A, Perra A, Schernhuber K,
Cargnelutti M, Salvi A, Migliore C, Ghiso E, Benetti A, Barlati S,
Ledda-Columbano GM, et al: Sequential analysis of multistage
hepatocarcinogenesis reveals that miR-100 and PLK1 dysregulation is
an early event maintained along tumor progression. Oncogene.
31:4517–4526. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Voulgari A and Pintzas A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: Mechanisms,
markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:75–90. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smits VA, Klompmaker R, Arnaud L, Rijksen
G, Nigg EA and Medema RH: Polo-like kinase-1 is a target of the DNA
damage check point. Nat Cell Biol. 2:672–676. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tokumitsu Y, Mori M, Tanaka S, Akazawa K,
Nakano S and Niho Y: Prognostic significance of polo-like kinase
expression in esophageal carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 15:687–692.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|