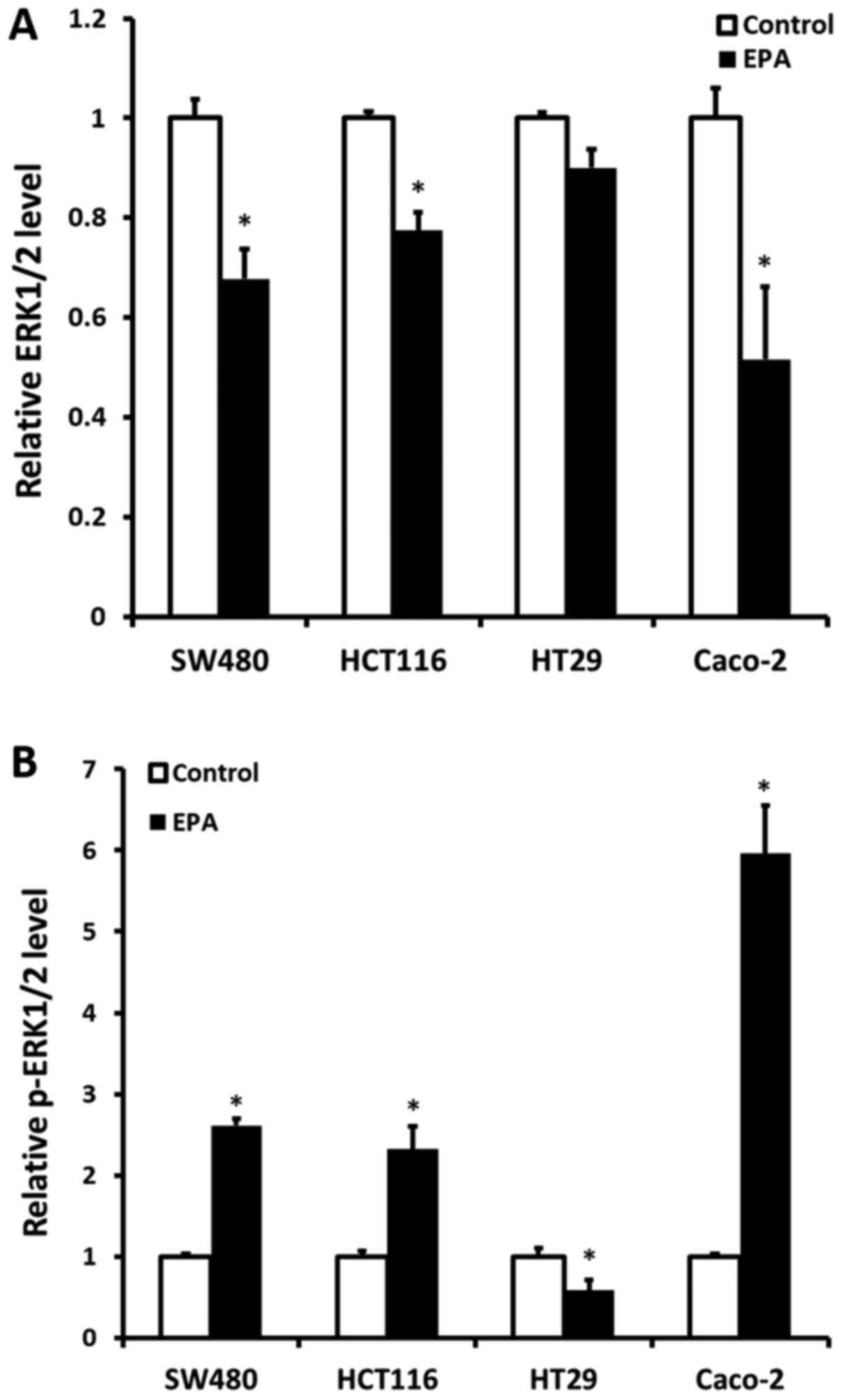
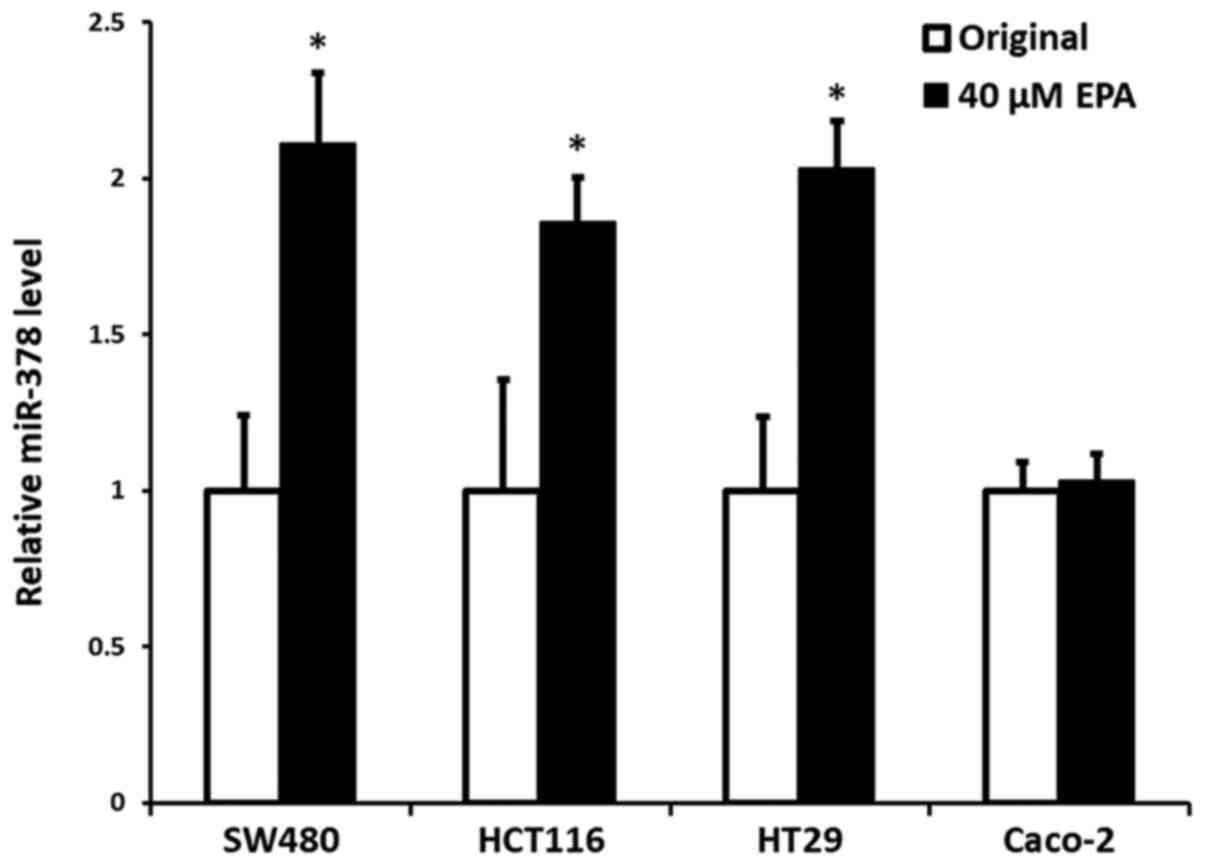
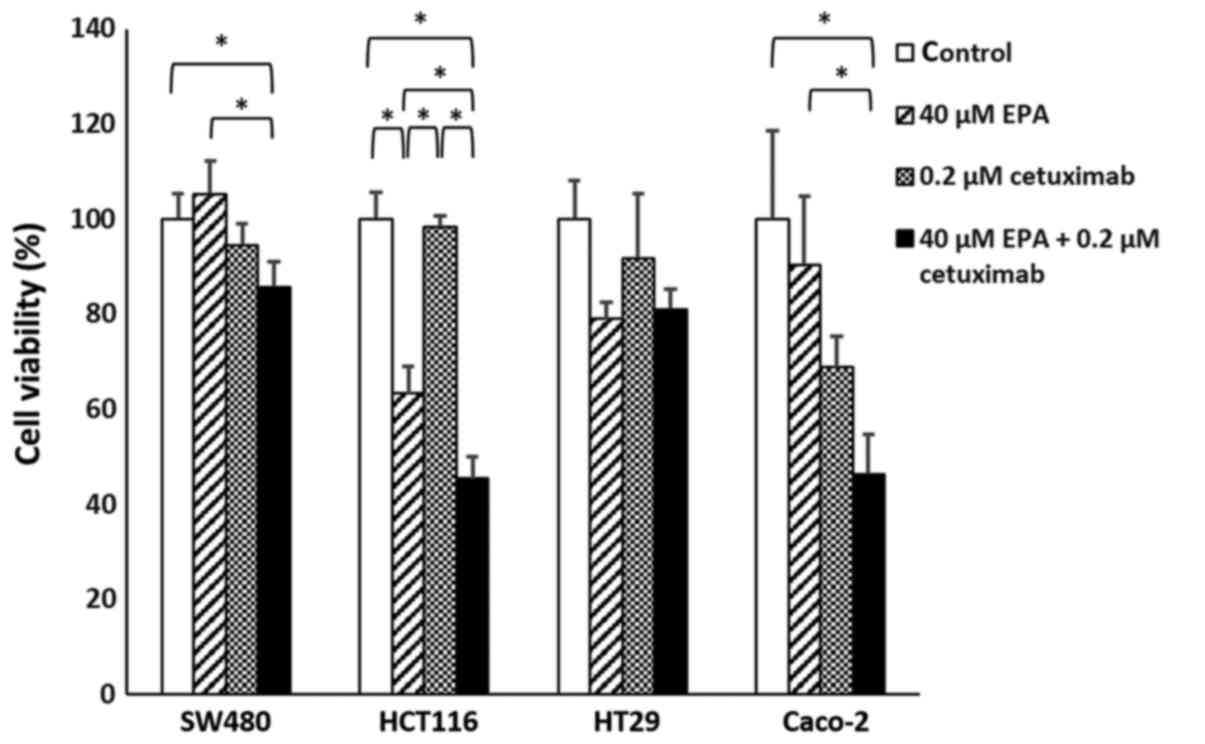
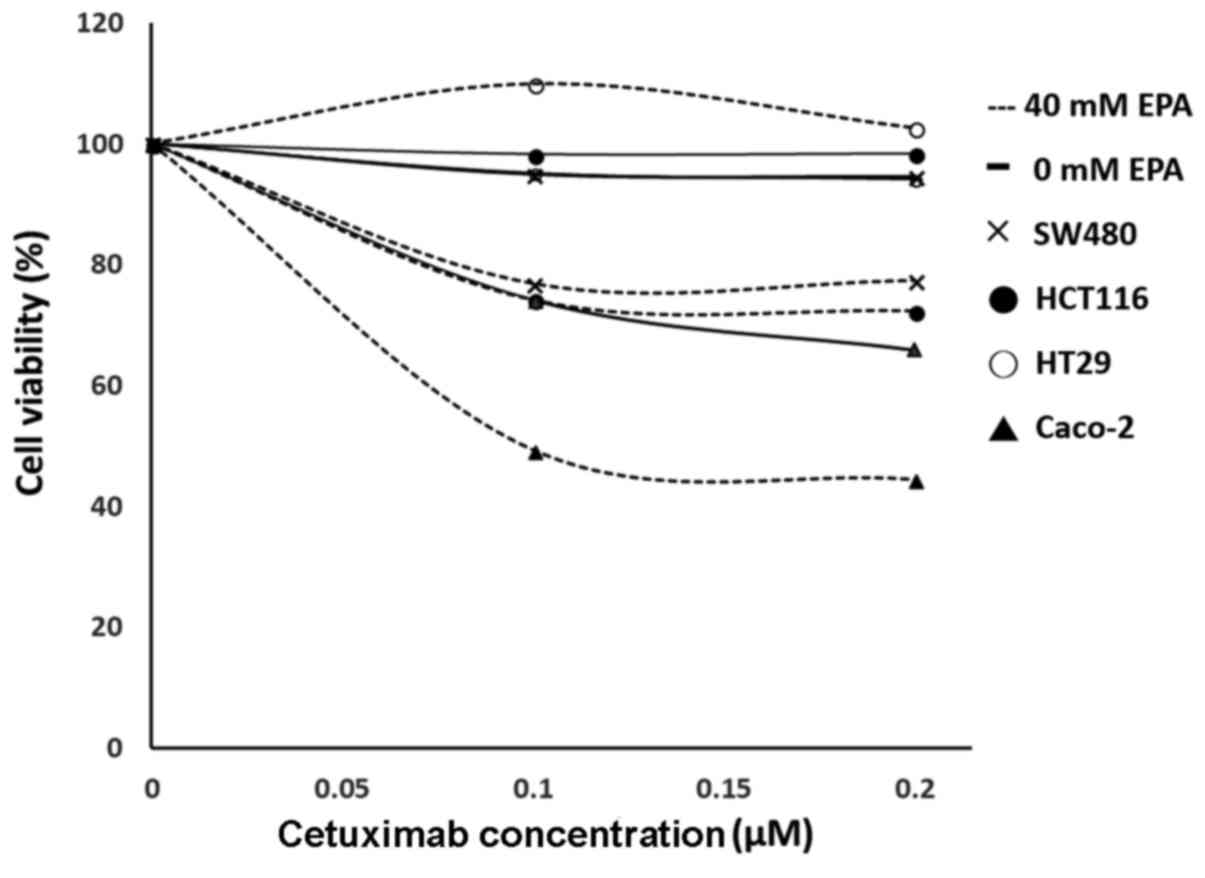
|
1
|
Lièvre A, Bachet JP, Le Corre D, Boige V,
Landi B, Emile JF, Côté JF, Tomasic G, Penna C, Ducreux M, et al:
KRAS mutation status is predictive of response to cetuximab therapy
in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 66:3992–3995. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Makhson A,
Hartmann JT, Aparicio J, de Braud F, Donea S, Ludwig H, Schuch G,
Stroh C, et al: Fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin with and
without cetuximab in the first-line treatment of metastatic
colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:663–671. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Hitre E, Zaluski
J, Chien Chang CR, Makhson A, D'Haens G, Pintér T, Lim R, Bodoky G,
et al: Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for
metastatic colorectal cancer. NEJM. 360:1408–1417. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tol J, Nagtegaal ID and Punt CJ: BRAF
mutation in metastatic colorectal cancer. NEJM. 361:98–99. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Di Nicolantonio F, Martini M, Molinari F,
Sartore-Bianchi A, Arena S, Saletti P, De Dosso S, Mazzucchelli L,
Frattini M, Siena S and Bardelli A: Wild-type BRAF is required for
response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:5705–5712. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baldus SE, Schaefer KL, Engers R, Hartleb
D, Stoecklein NH and Gabbert HE: Prevalence and heterogeneity of
KRAS, BRAF, and PIK3CA mutations in primary colorectal
adenocarcinomas and their corresponding metastases. Clin Cancer
Res. 16:790–799. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Di Fiore F, Blanchard F, Charbonnier F, Le
Pessot F, Lamy A, Galais MP, Bastit L, Killian A, Sesboüé R, Tuech
JJ, et al: Clinical relevance of KRAS mutation detection in
metastatic colorectal cancer treated by Cetuximab plus
chemotherapy. Br J Cancer. 96:1166–1169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Frattini M, Saletti P, Romagnani E, Martin
V, Molinari F, Ghisletta M, Camponovo A, Etienne LL, Cavalli F and
Mazzucchelli L: PTEN loss of expression predicts cetuximab efficacy
in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer.
97:1139–1145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E,
Siena S, Freeman DJ, Juan T, Sikorski R, Suggs S, Radinsky R, et
al: Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients
with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:1626–1634.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
De Roock W, Piessevaux H, De Schutter J,
Janssens M, De Hertogh G, Personeni N, Biesmans B, Van Laethem JL,
Peeters M, Humblet Y, et al: KRAS wild-type state predicts survival
and is associated to early radiological response in metastatic
colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. Ann Oncol. 19:508–515.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Láng I, Folprecht
G, Nowacki MP, Cascinu S, Shchepotin I, Maurel J, Cunningham D,
Tejpar S, et al: Cetuximab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal
cancer: Updated analysis of overall survival according to tumor
KRAS and BRAF mutation status. J Clin Oncol. 29:2011–2019. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Watzinger F, Mayr B, Haring E and Lion T:
High sequence similarity within ras exons 1 and 2 in different
mammalian species and phylogenetic divergence of the ras gene
family. Mamm Genome. 9:214–219. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Andreyev HJ, Ross PJ, Cunningham D and
Clarke PA: Antisense treatment directed against mutated Ki-ras in
human colorectal adenocarcinoma. Gut. 48:230–237. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bazan V, Migliavacca M, Zanna I, Tubiolo
C, Grassi N, Latteri MA, La Farina M, Albanese I, Dardanoni G,
Salerno S, et al: Specific codon 13 K-ras mutations are predictive
of clinical outcome in colorectal cancer patients, whereas codon 12
K-ras mutations are associated with mucinous histotype. Ann Oncol.
13:1438–1446. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Benvenuti S, Sartore-Bianchi A, Di
Nicolantonio F, Zanon C, Moroni M, Veronese S, Siena S and Bardelli
A: Oncogenic activation of the RAS/RAF signaling pathway impairs
the response of metastatic colorectal cancers to anti-epidermal
growth factor receptor antibody therapies. Cancer Res.
67:2643–2648. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Esteller M, Gonzalez S, Risques RA,
Marcuello E, Mangues R, Germà JR, Herman JG, Capellà G and Peinado
MA: K-ras and p16 aberrations confer poor prognosis in human
colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 19:299–304. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roskoski R Jr: RAF
protein-serine/threonine kinases: Structure and regulation. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 399:313–317. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pakneshan S, Salajegheh A, Smith RA and
Lam AK: Clinicopathological relevance of BRAF mutations in human
cancer. Pathology. 45:346–356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deng G, Bell I, Crawley S, Gum J, Terdiman
JP, Allen BA, Truta B, Sleisenger MH and Kim YS: BRAF mutation is
frequently present in sporadic colorectal cancer with methylated
hMLH1, but not in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:191–195. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Callari M, Dugo M, Musella V, Marchesi E,
Chiorino G, Grand MM, Pierotti MA, Daidone MG, Canevari S and De
Cecco L: Comparison of microarray platforms for measuring
differential microRNA expression in paired normal/cancer colon
tissues. PLoS One. 7:e451052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Faltejskova P, Svoboda M, Srutova K,
Mlcochova J, Besse A, Nekvindova J, Radova L, Fabian P, Slaba K,
Kiss I, et al: Identification and functional screening of microRNAs
highly deregulated in colorectal cancer. J Cell Mol Med.
16:2655–2666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mosakhani N, Sarhadi VK, Borze I,
Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Sundström J, Ristamäki R, Osterlund P and
Knuutila S: MicroRNA profiling differentiates colorectal cancer
according to KRAS status. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 51:1–9. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang YX, Zhang XY, Zhang BF, Yang CQ, Chen
XM and Gao HJ: Initial study of microRNA expression profiles of
colonic cancer without lymph node metastasis. J Dig Dis. 11:50–54.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ganesan J, Ramanujam D, Sassi Y, Ahles A,
Jentzsch C, Werfel S, Leierseder S, Loyer X, Giacca M, Zentilin L,
et al: MiR-378 controls cardiac hypertrophy by combined repression
of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway factors. Circulation.
127:2097–2106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weng WH, Leung WH, Pang YJ and Hsu HH:
Lauric acid can improve the sensitization of cetuximab in KRA/BRAF
mutated colorectal cancer cells by retrivable microRNA-378
expression. Oncol Rep. 35:107–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feng M, Li Z, Aau M, Wong CH, Yang X and
Yu Q: Myc/miR-378/TOB2/cyclin D1 functional module regulates
oncogenic transformation. Oncogene. 30:2242–2251. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Carrer M, Liu N, Grueter CE, Williams AH,
Frisard MI, Hulver MW, Bassel-Duby R and Olson EN: Control of
mitochondrial metabolism and systemic energy homeostasis by
microRNAs 378 and 378*. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:15330–15335.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chambers KT, Chen Z, Crawford PA, Fu X,
Burgess SC, Lai L, Leone TC, Kelly DP and Finck BN: Liver-specific
PGC-1beta deficiency leads to impaired mitochondrial function and
lipogenic response to fasting-refeeding. PLoS One. 7:e526452012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gerin I, Bommer GT, McCoin CS, Sousa KM,
Krishnan V and MacDougald OA: Roles for miRNA-378/378* in adipocyte
gene expression and lipogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
299:E198–E206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Crunkhorn S, Dearie F, Mantzoros C, Gami
H, da Silva WS, Espinoza D, Faucette R, Barry K, Bianco AC and
Patti ME: Peroxisome proliferator activator receptor gamma
coactivator-1 expression is reduced in obesity: Potential
pathogenic role of saturated fatty acids and p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 282:15439–15450. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
EFSA: Scientific option on the tolerable
upper intake level of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic
acid (DHA) and docosapentaenoic acid (EPA). European Food Safety
Authority Journal. 10:28152012.
|
|
32
|
Ijzerman RG, Stehouwer CD, Serné EH,
Voordouw JJ, Smulders YM, Delemarre-van de Waal HA and van
Weissenbruch MM: Incorporation of the fasting free fatty acid
concentration into quantitative insulin sensitivity check index
improves its association with insulin sensitivity in adults, but
not in children. Eur J Endocrinol. 160:59–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mensink RP, Zock PL, Kester AD and Katan
MB: Effects of dietary fatty acids and carbohydrates on the ratio
of serum total to HDL cholesterol and on serum lipids and
apolipoproteins: A meta-analysis of 60 controlled trials. Am J Clin
Nutr. 77:1146–1155. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Giros A, Grzybowski M, Sohn VR, Pons E,
Fernandez-Morales J, Xicola RM, Sethi P, Grzybowski J, Goel A,
Boland CR, Gassull MA, Llor X, et al: Regulation of colorectal
cancer cell apoptosis by the n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
Docosahexaenoic and Eicosapentaenoic. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
2:732–742. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fukui M, Kang KS, Okada K and Zhu BT: EPA,
an omega-3 fatty acid, induces apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer
cells: Role of ROS accumulation, caspase-8 activation, and
autophagy induction. J Cell Biochem. 114:192–203. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nikolakopoulou Z, Nteliopoulos G,
Michael-Titus AT and Parkinson EK: Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty
acids selectively inhibit growth in neoplastic oral keratinocytes
by differentially activating ERK1/2. Carcinogenesis. 34:2716–2725.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ding N, Sun X, Wang T, Huang L, Wen J and
Zhou Y: miR-378a-3p exerts tumor suppressive function on the
tumorigenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting
Rab10. Int J Mol Med. 42:381–391. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bai B, Liu H and Laiho M: Small RNA
expression and deep sequencing analyses of the nucleolus reveal the
presence of nucleolus-associated microRNAs. FEBS Open Bio.
4:441–449. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD.: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang L, Su T, Lv D, Xie F, Liu W, Cao J,
Sheikh IA, Qin X, Li L and Chen L: ERK1/2 mediates lung
adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and autophagy induced by
apelin-13. Acta Biochmm Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 46:100–111. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Randhawa H, Kibble K, Zeng H, Moyer MP and
Reindl KM: Activation of ERK signaling and induction of colon
cancer cell death by piperlongumine. Toxicol In Vitro.
27:1626–1633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu Y, Yang Y, Ye YC, Shi QF, Chai K,
Tashiro S, Onodera S and Ikejima T: Activation of ERK-p53 and
ERK-mediated phosphorylation of Bcl-2 are involved in autophagic
cell death induced by the c-Met inhibitor SU11274 in human lung
cancer A549 cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 118:423–432. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Singh S, Upadhyay AK, Ajay AK and Bhat MK:
p53 regulates ERK activation in carboplatin induced apoptosis in
cervical carcinoma: A novel target of p53 in apoptosis. FEBS Lett.
581:289–295. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schweyer S, Soruri A, Meschter O, Heintze
A, Zschunke F, Miosge N, Thelen P, Schlott T, Radzun HJ and Fayyazi
A: Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human malignant testicular germ
cell lines depends on MEK/ERK activation. Br J Cancer. 91:589–598.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu W, Ren H, Ren J, Yin T, Hu B, Xie S,
Dai Y, Wu W, Xiao Z, Yang X and Xie D: The role of
EGFR/PI3K/Akt/cyclinD1 signaling pathway in acquired middle ear
cholesteatoma. Mediators Inflamm. 2013:6512072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lo HW and Hung MC: Nuclear EGFR signalling
network in cancers: Linking EGFR pathway to cell cycle progression,
nitric oxide pathway and patient survival. Br J Cancer. 94:184–188.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|