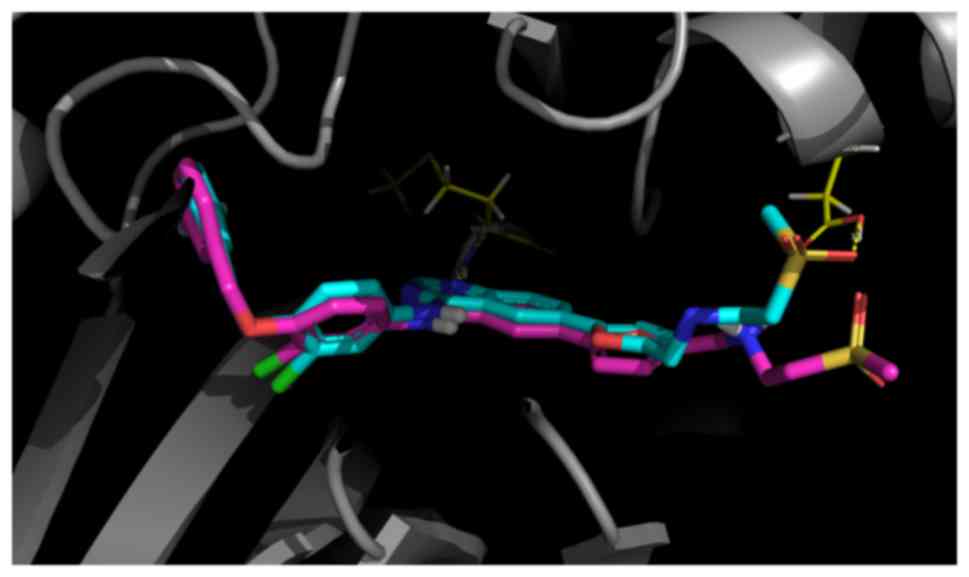
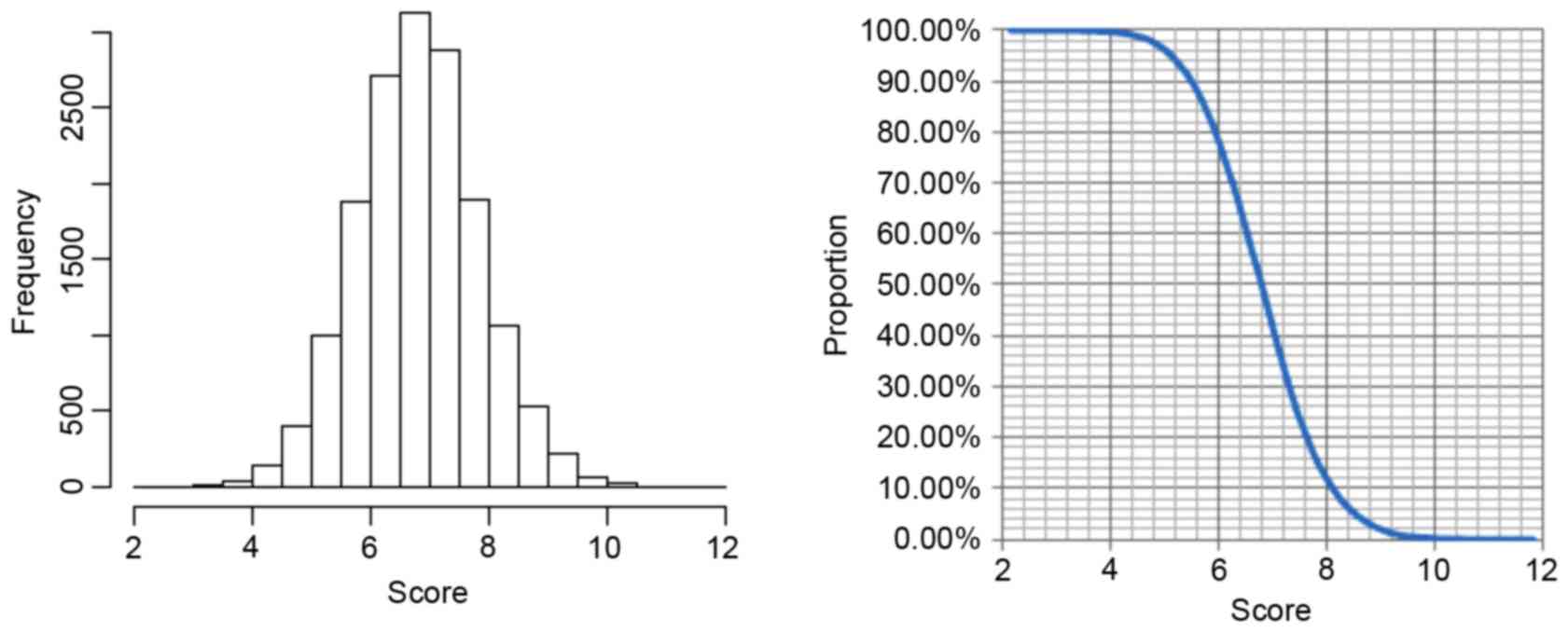
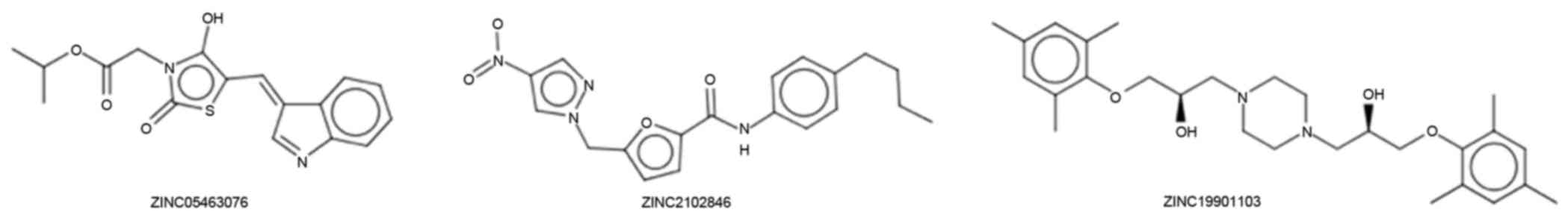
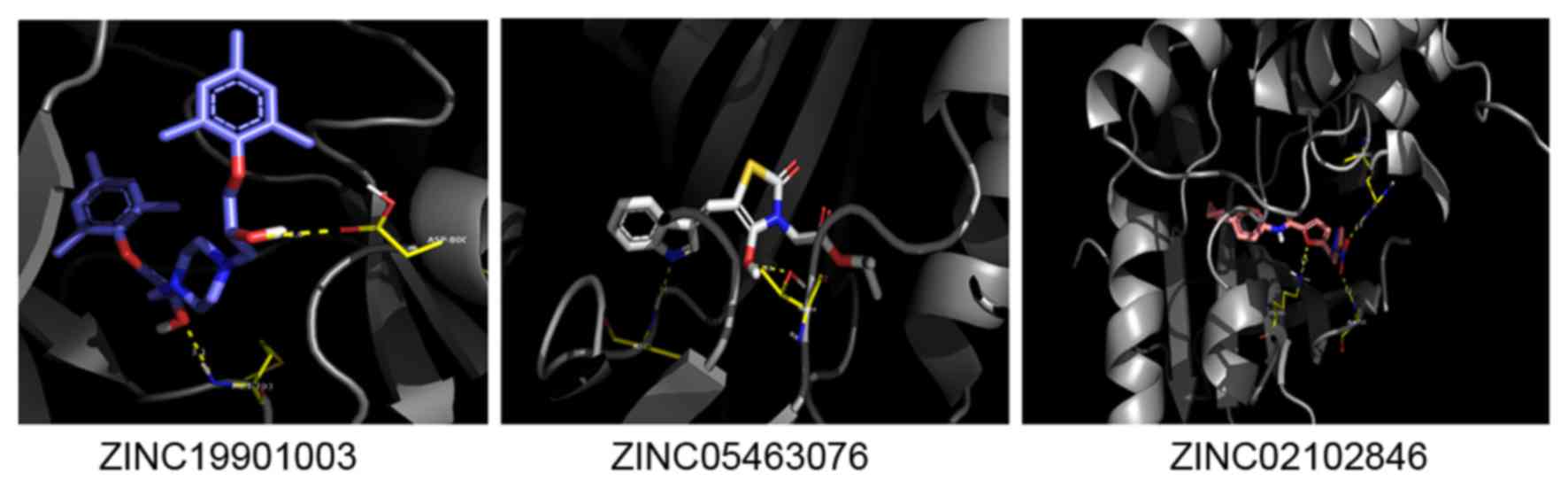
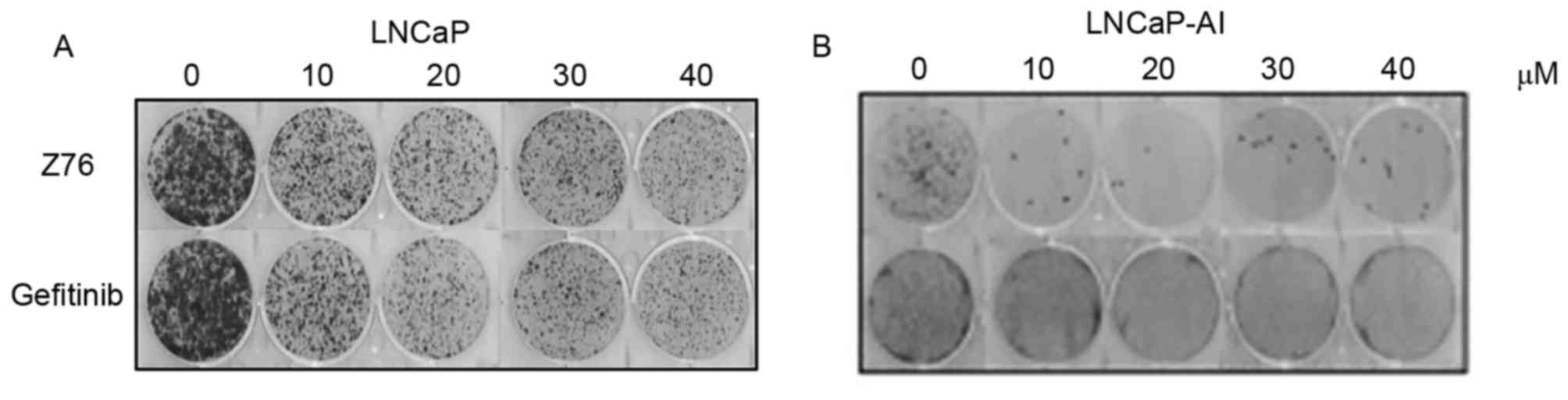
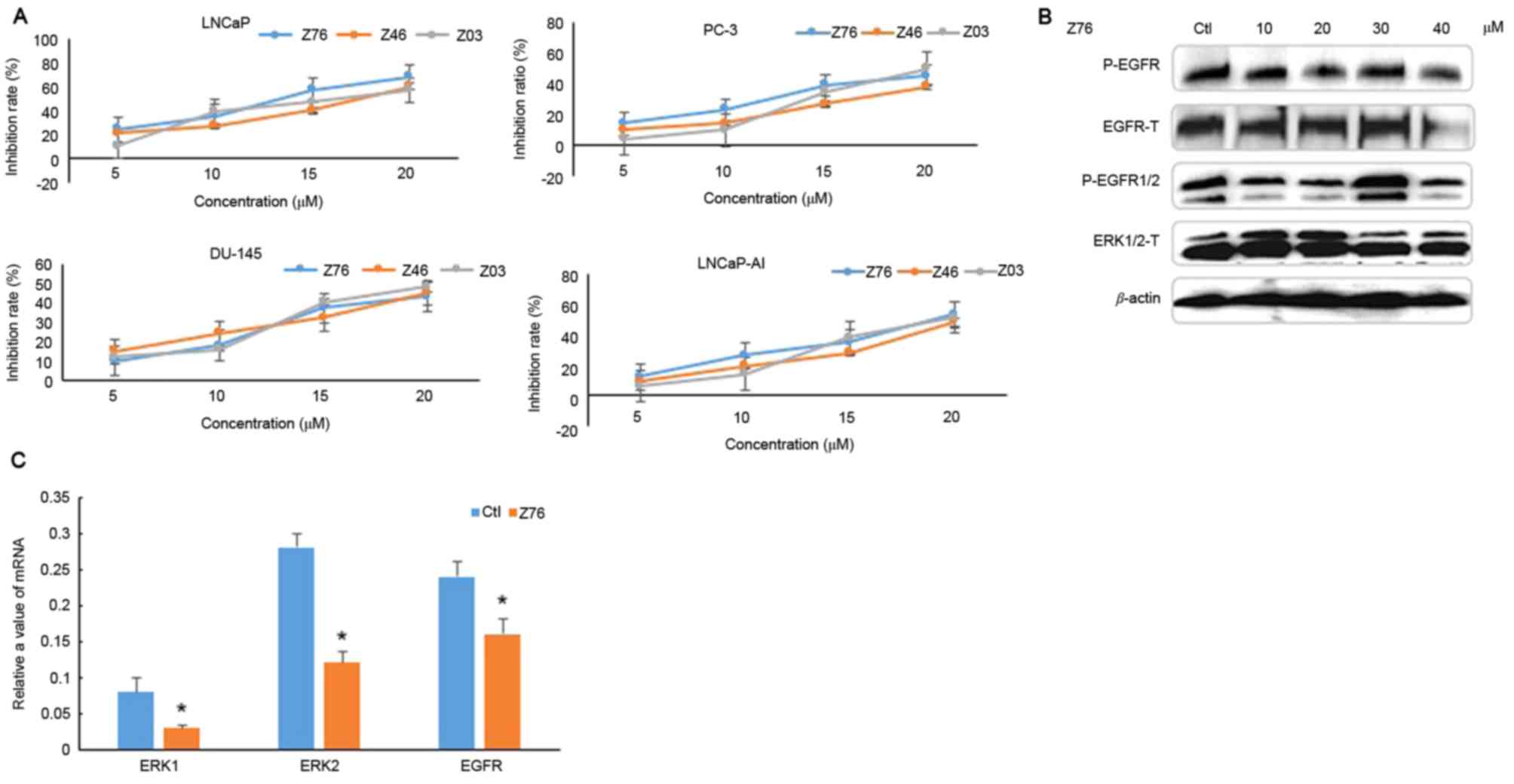
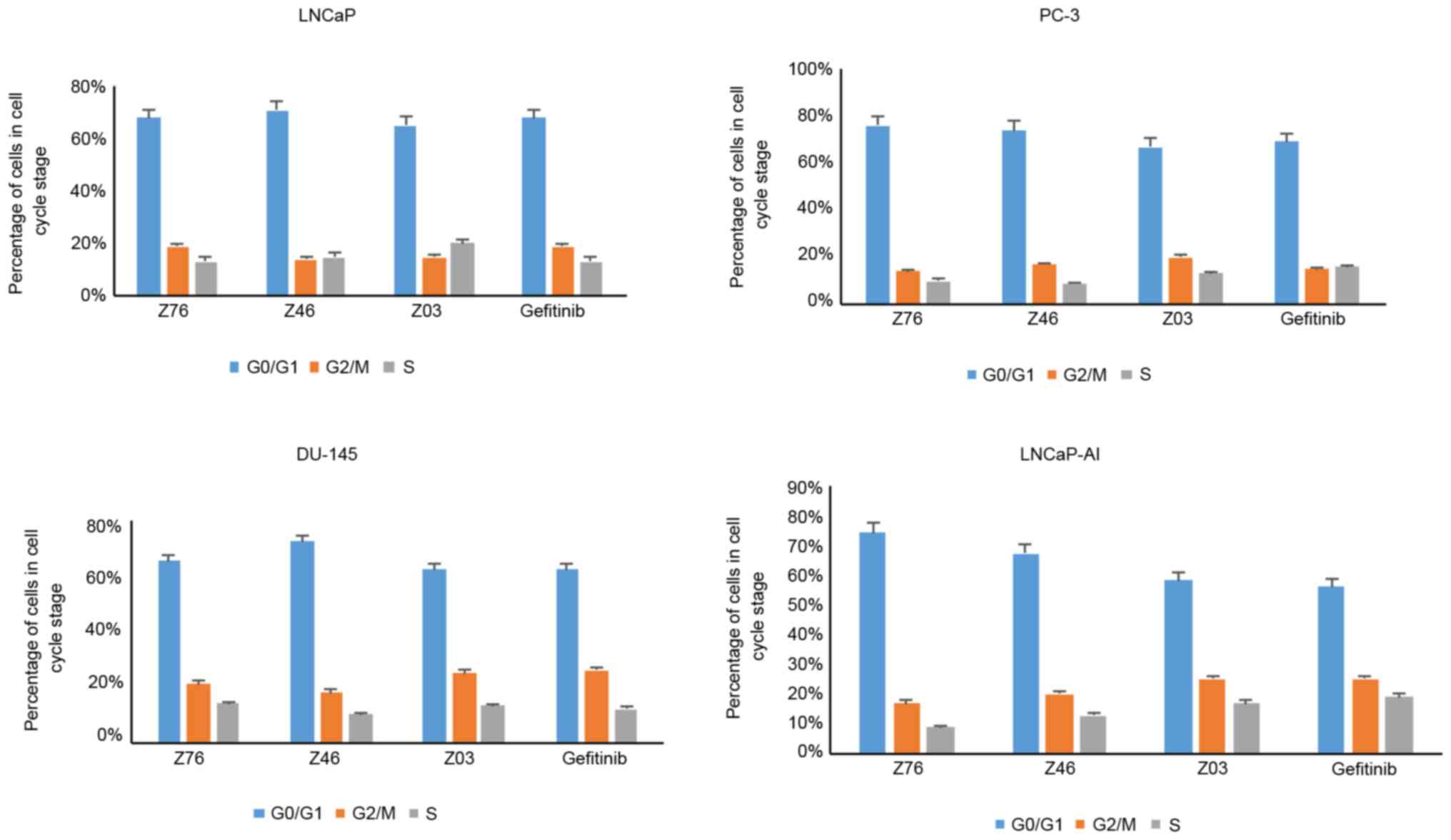
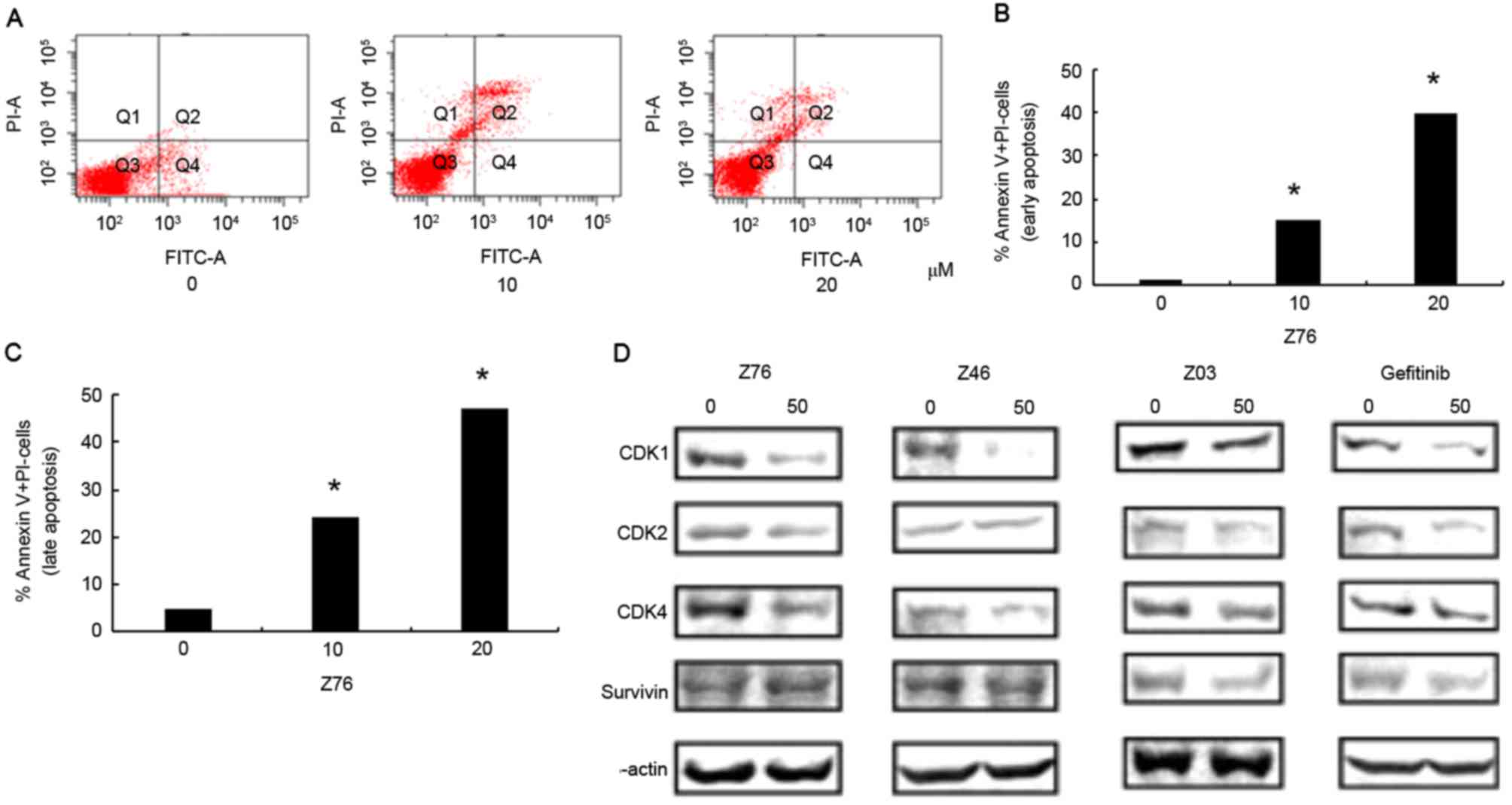
|
1
|
Gaudreau PO, Stagg J, Soulières D and Saad
F: The present and future of biomarkers in prostate cancer:
Proteomics, genomics, and immunology advancements. Biomark Cancer.
8 Suppl 2:S15–S33. 2016.
|
|
2
|
Hong JH and Kim IY: Nonmetastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Korean J Urol. 55:153–160.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang Y, Kreisberg JI and Ghosh PM:
Cross-talk between the androgen receptor and the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in prostate cancer. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 7:591–604. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Feitelson MA, Arzumanyan A, Kulathinal RJ,
Blain SW, Holcombe RF, Mahajna J, Marino M, Martinez-Chantar ML,
Nawroth R, Sanchez-Garcia I, et al: Sustained proliferation in
cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Semin Cancer
Biol. 35 Suppl:S25–S54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kwabi-Addo B, Ozen M and Ittmann M: The
role of fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in prostate
cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 11:709–724. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Corn PG, Wang F, McKeehan WL and Navone N:
Targeting fibroblast growth factor pathways in prostate cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 19:5856–5866. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen H, Zhou L, Wu X, Li R, Wen J, Sha J
and Wen X: The PI3K/AKT pathway in the pathogenesis of prostate
cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 21:1084–1091. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Proverbs-Singh T, Feldman JL, Morris MJ,
Autio KA and Traina TA: Targeting the androgen receptor in prostate
and breast cancer: Several new agents in development. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 22:R87–R106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cozza G, Pinna LA and Moro S: Protein
kinase CK2 inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat.
22:1081–1097. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mahapatra DK, Asati V and Bharti SK: MEK
inhibitors in oncology: A patent review (2015-Present). Expert Opin
Ther Pat. 27:887–906. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hospital A, Goñi JR, Orozco M and Gelpí
JL: Molecular dynamics simulations: Advances and applications. Adv
Appl Bioinform Chem. 8:37–47. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ferreira LG, Dos Santos RN, Oliva G and
Andricopulo AD: Molecular docking and structure-based drug design
strategies. Molecules. 20:13384–13421. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rao CM, Yejella RP, Rehman RS and Basha
SH: Molecular docking based screening of novel designed chalcone
series of compounds for their anti-cancer activity targeting EGFR
kinase domain. Bioinformation. 11:322–329. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li S, Sun X, Zhao H, Tang Y and Lan M:
Discovery of novel EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors by
structure-based virtual screening. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
22:4004–4009. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun XQ, Chen L, Li YZ, Li WH, Liu GX, Tu
YQ and Tang Y: Structure-based ensemble-QSAR model: A novel
approach to the study of the EGFR tyrosine kinase and its
inhibitors. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:301–310. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Singh VK and Coumar MS: Ensemble-based
virtual screening: Identification of a potential allosteric
inhibitor of Bcr-Abl. J Mol Model. 23:2182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kellenberger E, Rodrigo J, Muller P and
Rognan D: Comparative evaluation of eight docking tools for docking
and virtual screening accuracy. Proteins. 57:225–242. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang N, Shoichet BK and Irwin JJ:
Benchmarking sets for molecular docking. J Med Chem. 49:6789–6801.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McNaughton M, Pitman M, Pitson SM, Pyne NJ
and Pyne S: Proteasomal degradation of sphingosine kinase 1 and
inhibition of dihydroceramide desaturase by the sphingosine kinase
inhibitors, SKi or ABC294640, induces growth arrest in
androgen-independent LNCaP-AI prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget.
7:16663–16675. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lokadasan R, James FV, Narayanan G and
Prabhakaran PK: Targeted agents in epithelial ovarian cancer:
Review on emerging therapies and future developments.
Ecancermedicalscience. 10:6262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huskey NE, Guo T, Evason KJ, Momcilovic O,
Pardo D, Creasman KJ, Judson RL, Blelloch R, Oakes SA, Hebrok M and
Goga A: CDK1 inhibition targets the p53-NOXA-MCL1 axis, selectively
kills embryonic stem cells, and prevents teratoma formation. Stem
Cell Reports. 4:374–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen X, Guo D, Zhu Y, Xian F, Liu S, Wu L
and Lou X: Nuclear phosphoproteomics analysis reveals that CDK1/2
are involved in EGF-regulated constitutive pre-mRNA splicing in
MDA-MB-468 cells. J Proteomics. 141:77–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiao X, Wu J, Zhu X, Zhao P, Zhou J, Liu
QQ, Zheng L, Zeng M, Liu R and Huang W: Induction of cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by
ZD6474, an inhibitor of VEGFR tyrosine kinase with additional
activity against EGFR tyrosine kinase. Int J Cancer. 121:2095–2104.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rigas AC, Robson CN and Curtin NJ:
Therapeutic potential of CDK inhibitor NU2058 in
androgen-independent prostate cancer. Oncogene. 26:7611–7619. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hurtado A, Pinós T, Barbosa-Desongles A,
López-Avilés S, Barquinero J, Petriz J, Santamaria-Martínez A,
Morote J, de Torres I, Bellmunt J, et al: Estrogen receptor beta
displays cell cycle-dependent expression and regulates the G1 phase
through a non-genomic mechanism in prostate carcinoma cells. Cell
Oncol. 30:349–365. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang H, Zhang C, Rorick A, Wu D, Chiu M,
Thomas-Ahner J, Chen Z, Chen H, Clinton SK, Chan KK and Wang Q:
CCI-779 inhibits cell-cycle G2-M progression and invasion of
castration-resistant prostate cancer via attenuation of UBE2C
transcription and mRNA stability. Cancer Res. 71:4866–4876. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Comstock CE, Augello MA, Goodwin JF, de
Leeuw R, Schiewer MJ, Ostrander WF Jr, Burkhart RA, McClendon AK,
McCue PA, Trabulsi EJ, et al: Targeting cell cycle and hormone
receptor pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 32:5481–5491. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen J: The cell-cycle arrest and
apoptotic functions of p53 in tumor initiation and progression.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 6:a0261042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Purev E, Cai D, Miller E, Swoboda R, Mayer
T, Klein-Szanto A, Marincola FM, Mick R, Otvos L, Wunner W, et al:
Immune responses of breast cancer patients to mutated epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGF-RvIII, Delta EGF-R, and de2-7 EGF-R). J
Immunol. 173:6472–6480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Werry TD, Christopoulos A and Sexton PM:
Mechanisms of ERK1/2 regulation by seven-transmembrane-domain
receptors. Curr Pharm Des. 12:1683–1702. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Uribe P and Gonzalez S: Epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin:
Molecular bases for EGFR-targeted therapy. Pathol Res Pract.
207:337–342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Karandish F and Mallik S: Biomarkers and
targeted therapy in pancreatic cancer. Biomark Cancer. 8 Suppl
1:S27–S35. 2016.
|
|
34
|
Rivadeneira DB, Caino MC, Seo JH, Angelin
A, Wallace DC, Languino LR and Altieri DC: Survivin promotes
oxidative phosphorylation, subcellular mitochondrial repositioning,
and tumor cell invasion. Sci Signal. 8:ra802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen X, Duan N, Zhang C and Zhang W:
Survivin and tumorigenesis: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic
strategies. J Cancer. 7:314–323. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lim EJ, Heo J and Kim YH: Tunicamycin
promotes apoptosis in leukemia cells through ROS generation and
downregulation of survivin expression. Apoptosis. 20:1087–1098.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Garg H, Suri P, Gupta JC, Talwar GP and
Dubey S: Survivin: A unique target for tumor therapy. Cancer Cell
Int. 16:492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hakonen E, Ustinov J, Palgi J, Miettinen
PJ and Otonkoski T: EGFR signaling promotes β-cell proliferation
and survivin expression during pregnancy. PLoS One. 9:e936512014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|