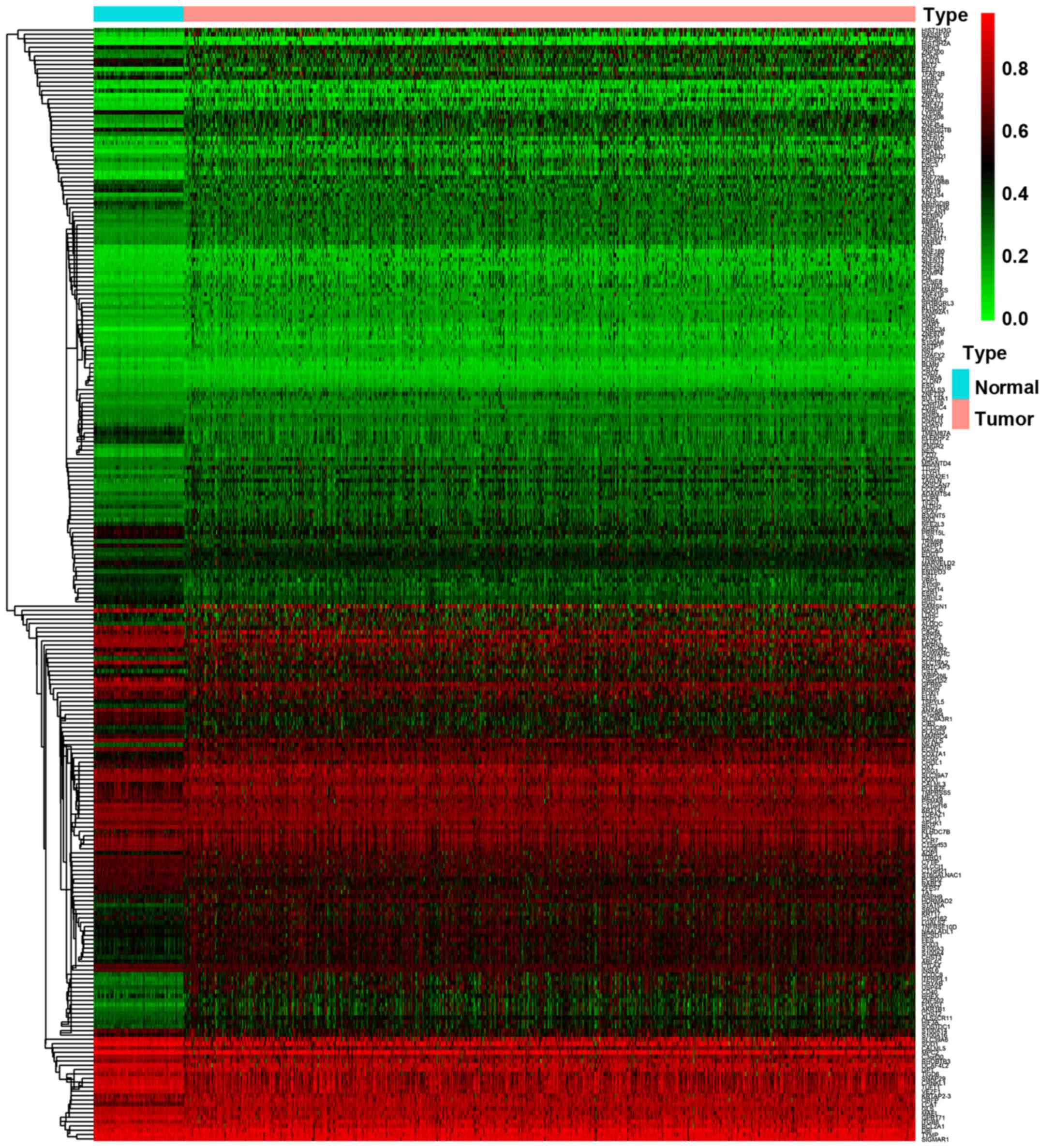
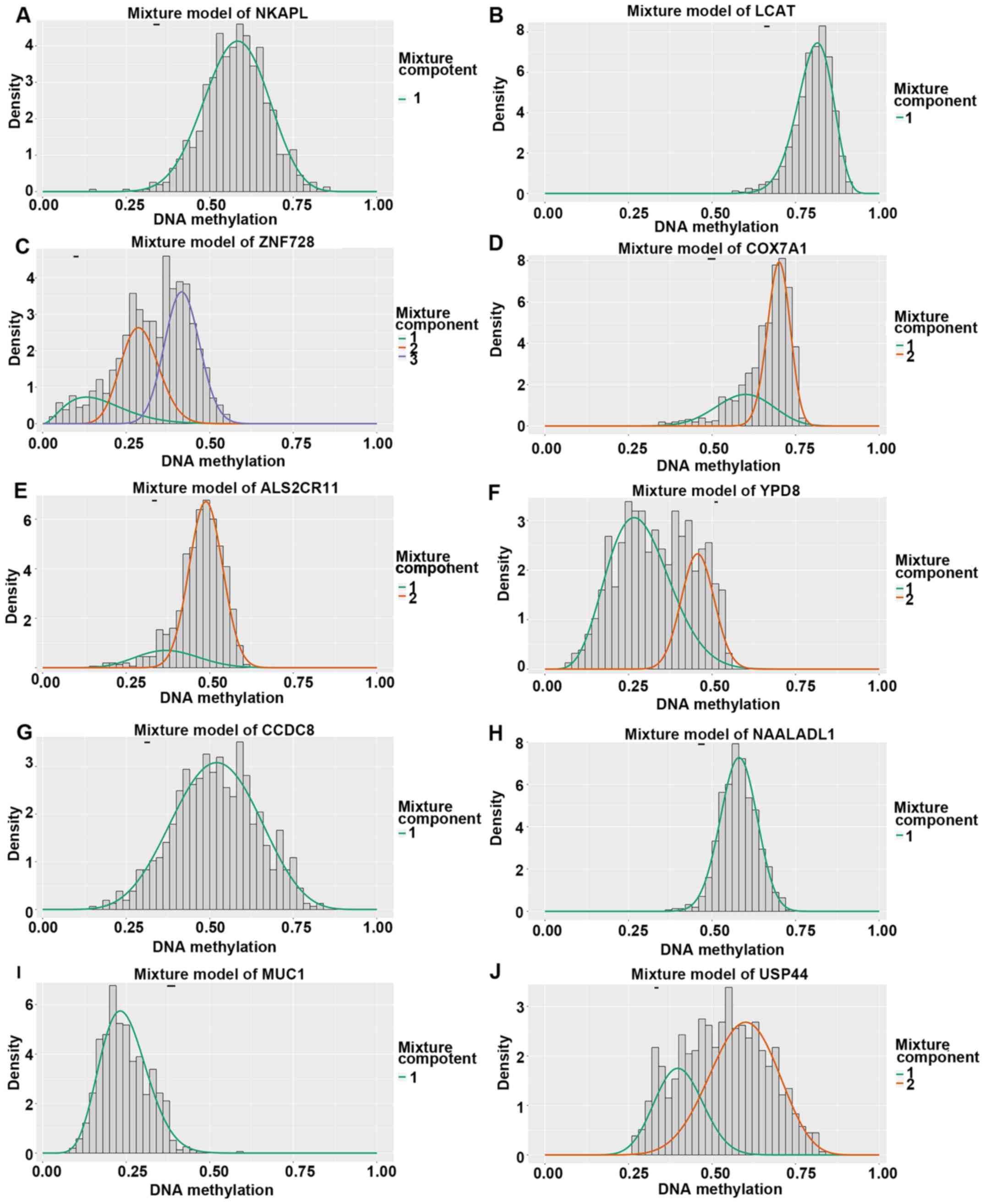
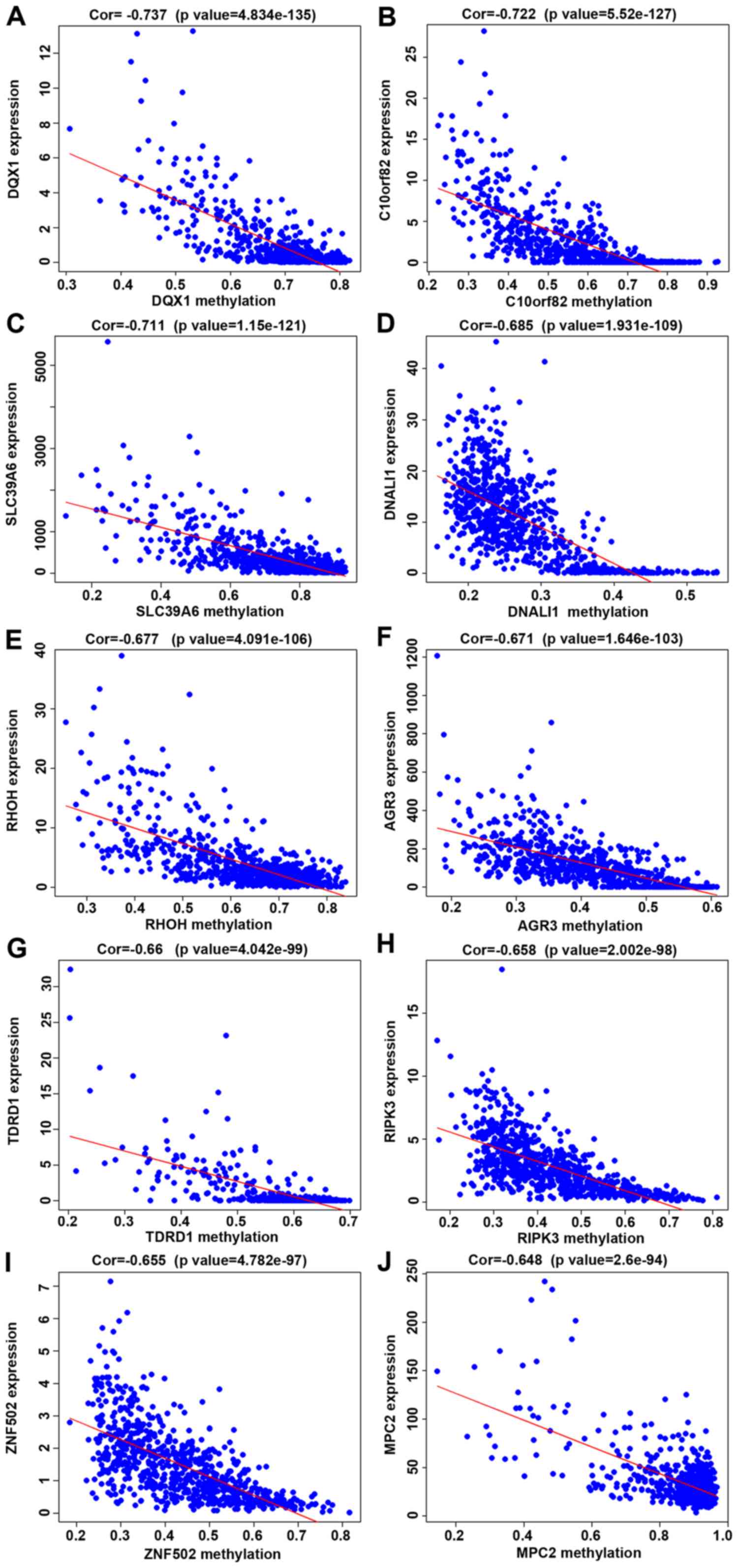
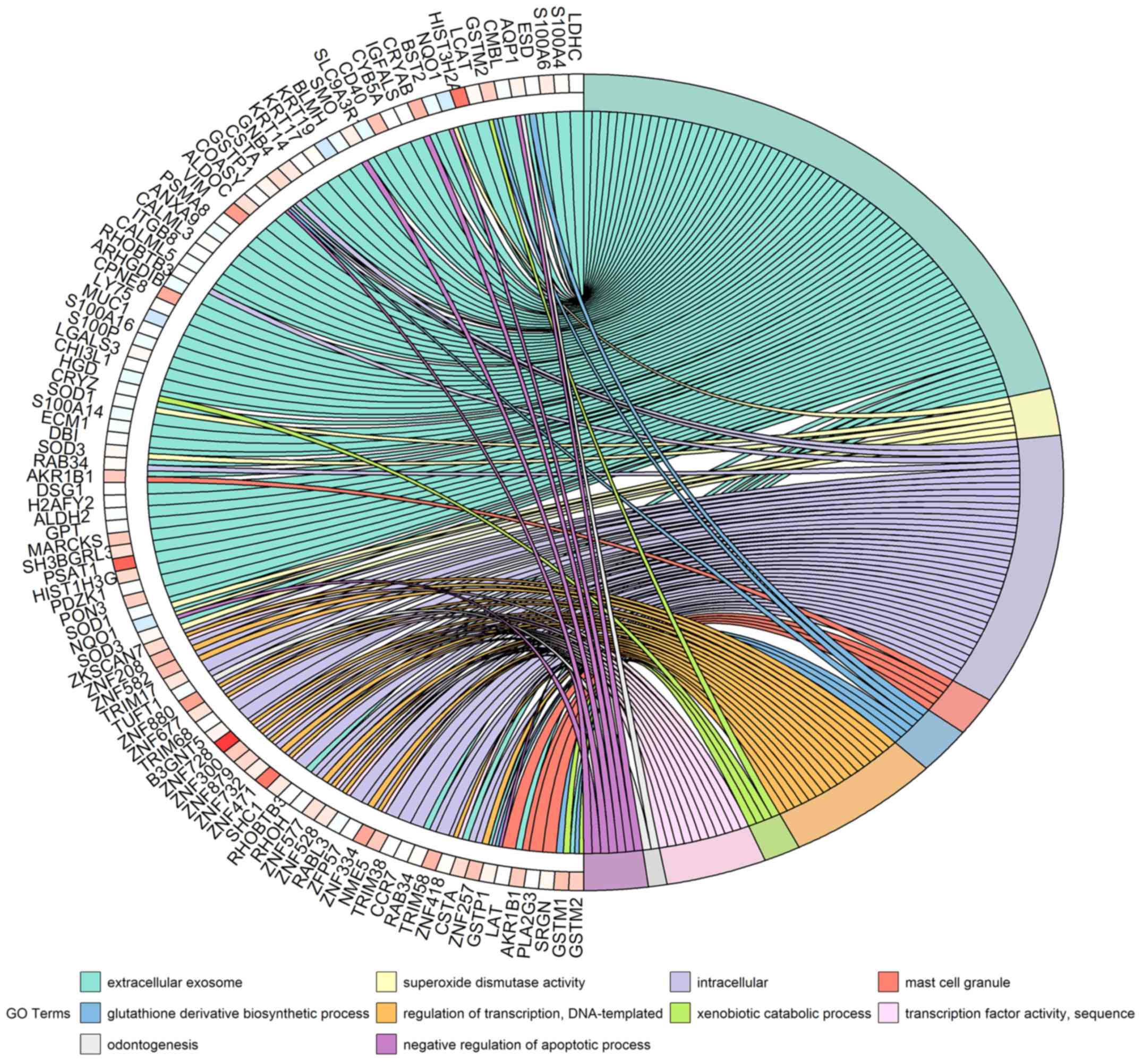
|
1
|
Inoue M, Nakagomi H, Nakada H, Furuya K,
Ikegame K, Watanabe H, Omata M and Oyama T: Specific sites of
metastases in invasive lobular carcinoma: A retrospective cohort
study of metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 24:667–672. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yates LR, Knappskog S, Wedge D, Farmery
JHR, Gonzalez S, Martincorena I, Alexandrov LB, Van Loo P, Haugland
HK, Lilleng PK, et al: Genomic evolution of breast cancer
metastasis and relapse. Cancer Cell. 32:169–184.e7. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
DeSantis CE, Ma J, Sauer Goding A, Newman
LA and Jemal A: Breast cancer statistics, 2017, racial disparity in
mortality by state. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:439–448. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xing P, Dong H, Liu Q, Yao F, Xu Y, Chen
B, Zheng X, Wu Y, Jin F and Li J: Impact of persistence on survival
of patients with breast cancer treated with endocrine therapy in
Northeast China: A prospective study. Oncotarget. 8:102499–102510.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zuo TT, Zheng RS, Zeng HM, Zhang SW and
Chen WQ: Female breast cancer incidence and mortality in China,
2013. Thorac Cancer. 8:214–218. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McGrath KG: An earlier age of breast
cancer diagnosis related to more frequent use of
antiperspirants/deodorants and underarm shaving. Eur J Cancer Prev.
12:479–485. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Widschwendter M, Siegmund KD, Müller HM,
Fiegl H, Marth C, Müller-Holzner E, Jones PA and Laird PW:
Association of breast cancer DNA methylation profiles with hormone
receptor status and response to tamoxifen. Cancer Res.
64:3807–3813. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Flanagan JM, Wilson A, Koo C, Masrour N,
Gallon J, Loomis E, Flower K, Wilhelm-Benartzi C, Hergovich A,
Cunnea P, et al: Platinum-based chemotherapy induces methylation
changes in blood DNA associated with overall survival in patients
with ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 23:2213–2222. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shu R, He J, Wu C and Gao J: The
association between RARβ and FHIT promoter methylation and the
carcinogenesis of patients with cervical carcinoma: A
meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177091262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Udali S, Guarini P, Ruzzenente A,
Ferrarini A, Guglielmi A, Lotto V, Tononi P, Pattini P, Moruzzi S,
Campagnaro T, et al: DNA methylation and gene expression profiles
show novel regulatory pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin
Epigenetics. 7:432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
An N, Shi Y, Ye P, Pan Z and Long X:
Association between MGMT promoter methylation and breast cancer: A
meta-analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 42:2430–2440. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hao X, Luo H, Krawczyk M, Wei W, Wang W,
Wang J, Flagg K, Hou J, Zhang H, Yi S, et al: DNA methylation
markers for diagnosis and prognosis of common cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 114:7414–7419. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weinstein JN, Collisson EA, Mills GB, Shaw
KR, Ozenberger BA, Ellrott K, Shmulevich I, Sander C and Stuart JM;
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, : The Cancer Genome Atlas
Pan-Cancer analysis project. Nat Genet. 45:1113–1120. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xie ZC, Dang YW, Wei DM, Chen P, Tang RX,
Huang Q, Liu JH and Luo DZ: Clinical significance and prospective
molecular mechanism of MALAT1 in pancreatic cancer exploration: A
comprehensive study based on the GeneChip, GEO, Oncomine, and TCGA
databases. OncoTargets Ther. 10:3991–4005. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Aho K, Derryberry D and Peterson T: Model
selection for ecologists: The worldviews of AIC and BIC. Ecology.
95:631–636. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stirzaker C, Song JZ, Ng W, Du Q,
Armstrong NJ, Locke WJ, Statham AL, French H, Pidsley R,
Valdes-Mora F, et al: Methyl-CpG-binding protein MBD2 plays a key
role in maintenance and spread of DNA methylation at CpG islands
and shores in cancer. Oncogene. 36:1328–1338. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kakizaki F, Sonoshita M, Miyoshi H,
Itatani Y, Ito S, Kawada K, Sakai Y and Taketo MM: Expression of
metastasis suppressor gene AES driven by a Yin Yang (YY) element in
a CpG island promoter and transcription factor YY2. Cancer Sci.
107:1622–1631. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Das S, Moran B and Perry AS: Assessing DNA
methylation in cancer stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 1692:157–178.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ng PKS, Lau CPY, Lam EKY, Li SSK, Lui VWY,
Yeo W, Ng YK, Lai PBS and Tsui SKW: Hypermethylation of
NF-κB-activating protein-like (NKAPL) promoter in hepatocellular
carcinoma suppresses its expression and predicts a poor prognosis.
Dig Dis Sci. 63:676–686. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roy S, Hochberg FH and Jones PS:
Extracellular vesicles: The growth as diagnostics and therapeutics;
a survey. J Extracell Vesicles. 7:14387202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Urabe F, Kosaka N, Kimura T, Egawa S and
Ochiya T: Extracellular vesicles: Toward a clinical application in
urological cancer treatment. Int J Urol. 25:533–543. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen L, Guo P, He Y, Chen Z, Chen L, Luo
Y, Qi L, Liu Y, Wu Q, Cui Y, et al: HCC-derived exosomes elicit HCC
progression and recurrence by epithelial-mesenchymal transition
through MAPK/ERK signalling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 9:5132018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Landeen KC, Spanos WC and Gromer L:
Topical superoxide dismutase in posttreatment fibrosis in patients
with head and neck cancer. Head Neck. May 13–2018.(Epub ahead of
print). doi: 10.1002/hed.25119. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kocot J, Kiełczykowska M, Dąbrowski W,
Piłat J, Rudzki S and Musik I: Total antioxidant status value and
superoxide dismutase activity in human colorectal cancer tissue
depending on the stage of the disease: A pilot study. Adv Clin Exp
Med. 22:431–437. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Caris AV, Da Silva ET, Dos Santos SA,
Tufik S and Dos Santos RVT: Effects of carbohydrate and glutamine
supplementation on oral mucosa immunity after strenuous exercise at
high altitude: A double-blind randomized trial. Nutrients.
9:6922017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Pavlova NN, Hui S, Ghergurovich JM, Fan J,
Intlekofer AM, White RM, Rabinowitz JD, Thompson CB and Zhang J: As
extracellular glutamine levels decline, asparagine becomes an
essential amino acid. Cell Metab. 27:428–438.e5. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aboud Abu O, Habib SL, Trott J, Stewart B,
Liang S, Chaudhari AJ, Sutcliffe J and Weiss RH: Glutamine
addiction in kidney cancer suppresses oxidative stress and can be
exploited for real-time imaging. Cancer Res. 77:6746–6758. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chiu M, Taurino G, Bianchi MG, Ottaviani
L, Andreoli R, Ciociola T, Lagrasta CAM, Tardito S and Bussolati O:
Oligodendroglioma cells lack glutamine synthetase and are
auxotrophic for glutamine, but do not depend on glutamine
anaplerosis for growth. Int J Mol Sci. 19:192018. View Article : Google Scholar
|