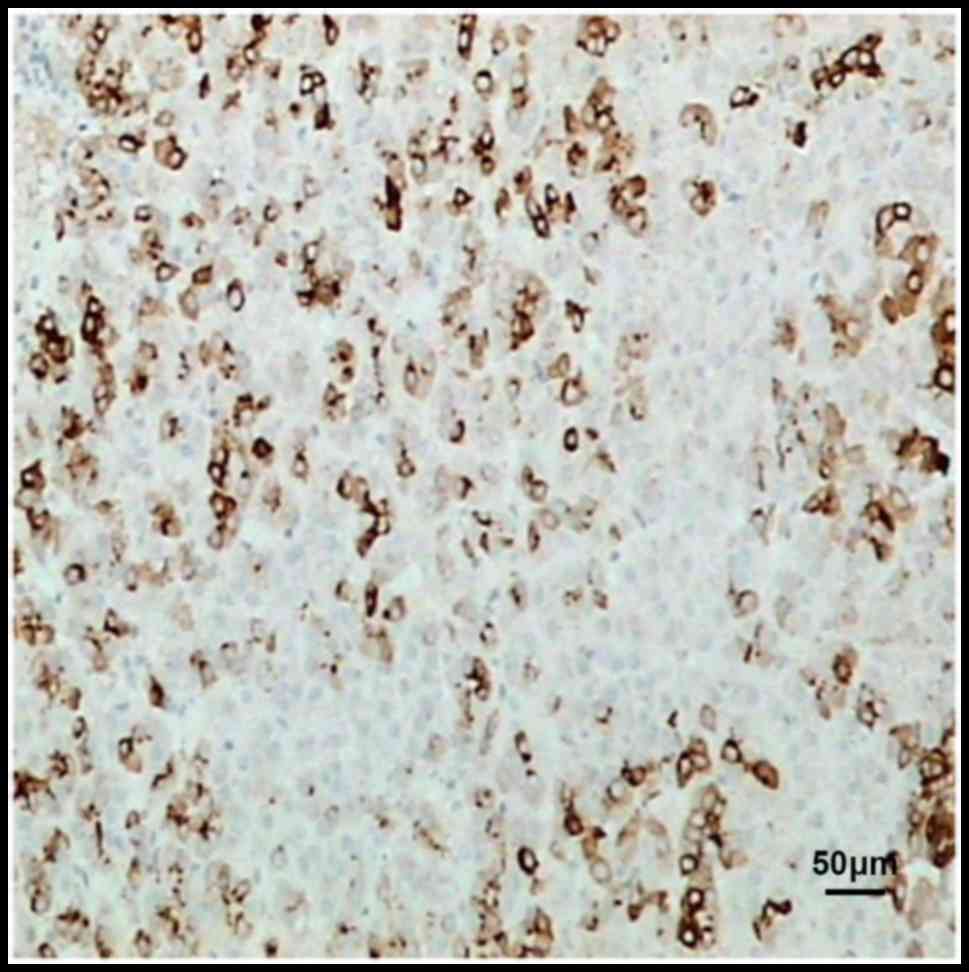
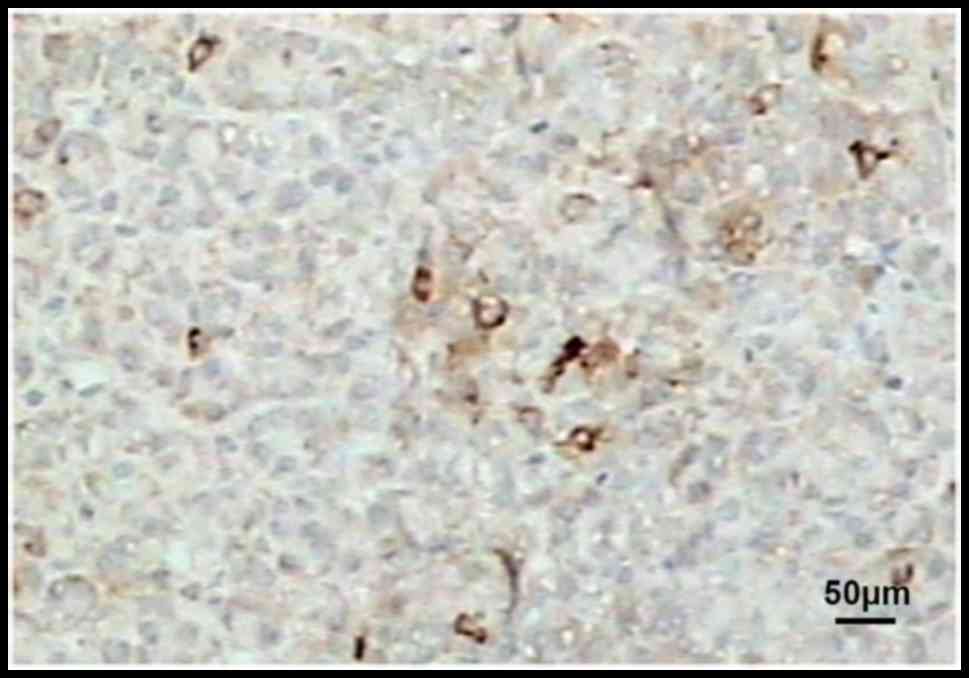
|
1
|
Gravitz L: Liver cancer. Nature.
516:S12014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shibata T, Chuma M, Kokubu A, Sakamoto M
and Hirohashi S: EBP50, a beta-catenin-associating protein,
enhances Wnt signaling and is over-expressed in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 38:178–186. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alioui A, Dufour J, Leoni V, Loregger A,
Moeton M, Iuliano L, Zerbinati C, Septier A, Val P, Fouache A, et
al: Liver X receptors constrain tumor development and metastasis
dissemination in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer. Nat Commun.
8:4452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Seo JH, Ahn Y, Lee SR, Yeo Yeol C and Hur
Chung K: The major target of the endogenously generated reactive
oxygen species in response to insulin stimulation is phosphatase
and tensin homolog and not phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI-3 kinase)
in the PI-3 kinase/Akt pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 16:348–357. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Furnari FB, Lin H, Huang HS and Cavenee
WK: Growth suppression of glioma cells by PTEN requires a
functional phosphatase catalytic domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:12479–12484. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dahia PL: PTEN, a unique tumor suppressor
gene. Endocr Relat Cancer. 7:115–129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Steck PA, Pershouse MA, Jasser SA, Yung
WKA, Lin H, Ligon AH, Langford LA, Baumgard ML, Hattier T, Davis T,
et al: Identification of a candidate tumour suppressor gene, MMAC1,
at chromosome 10q23.3 that is mutated in multiple advanced cancers.
Nat Genet. 15:356–362. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shearn CT and Petersen DR: Understanding
the tumor suppressor PTEN in chronic alcoholism and hepatocellular
carcinoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 815:173–184. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu DD, Zhang XR and Cao XR: Expression and
significance of new tumor suppressor gene PTEN in primary liver
cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 7:67–71. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose
S, Wang SI, Puc J, Miliaresis C, Rodgers L, McCombie R, et al:
PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human
brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science. 275:1943–1947. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Weng L, Brown J and Eng C: PTEN induces
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through
phosphoinositol-3-kinase/Akt-dependent and -independent pathways.
Hum Mol Genet. 10:237–242. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tamura M, Gu J, Takino T and Yamada KM:
Tumor suppressor PTEN inhibition of cell invasion, migration, and
growth: Differential involvement of focal adhesion kinase and
p130Cas. Cancer Res. 59:442–449. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang L, Yu Q, He J and Zha X: Study of
the PTEN gene expression and FAK phosphorylation in human
hepatocarcinoma tissues and cell lines. Mol Cell Biochem.
262:25–33. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Weng LP, Smith WM, Brown JL and Eng C:
PTEN inhibits insulin-stimulated MEK/MAPK activation and cell
growth by blocking IRS-1 phosphorylation and IRS-1/Grb-2/Sos
complex formation in a breast cancer model. Hum Mol Genet.
10:605–616. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuan XJ and Whang YE: PTEN sensitizes
prostate cancer cells to death receptor-mediated and drug-induced
apoptosis through a FADD-dependent pathway. Oncogene. 21:319–327.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rahman MA, Kyriazanos ID, Ono T, Yamanoi
A, Kohno H, Tsuchiya M and Nagasue N: Impact of PTEN expression on
the outcome of hepatitis C virus-positive cirrhotic hepatocellular
carcinoma patients: Possible relationship with COX II and inducible
nitric oxide synthase. Int J Cancer. 100:152–157. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wan XW, Jiang M, Cao HF, He YQ, Liu SQ,
Qiu XH, Wu MC and Wang HY: The alteration of PTEN tumor suppressor
expression and its association with the histopathological features
of human primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
129:100–106. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ginn-Pease ME and Eng C: Increased nuclear
phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 is
associated with G0-G1 in MCF-7 cells. Cancer
Res. 63:282–286. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yeh KT, Chang JG, Chen YJ, Chen ST, Yu SY,
Shih MC, Perng LI, Wang JC, Tsai M and Chang CP: Mutation analysis
of the putative tumor suppressor gene PTEN/MMAC1 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Invest. 18:123–129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yao YJ, Ping XL, Zhang H, Chen FF, Lee PK,
Ahsan H, Chen CJ, Lee PH, Peacocke M, Santella RM, et al:
PTEN/MMAC1 mutations in hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncogene.
18:3181–3185. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|