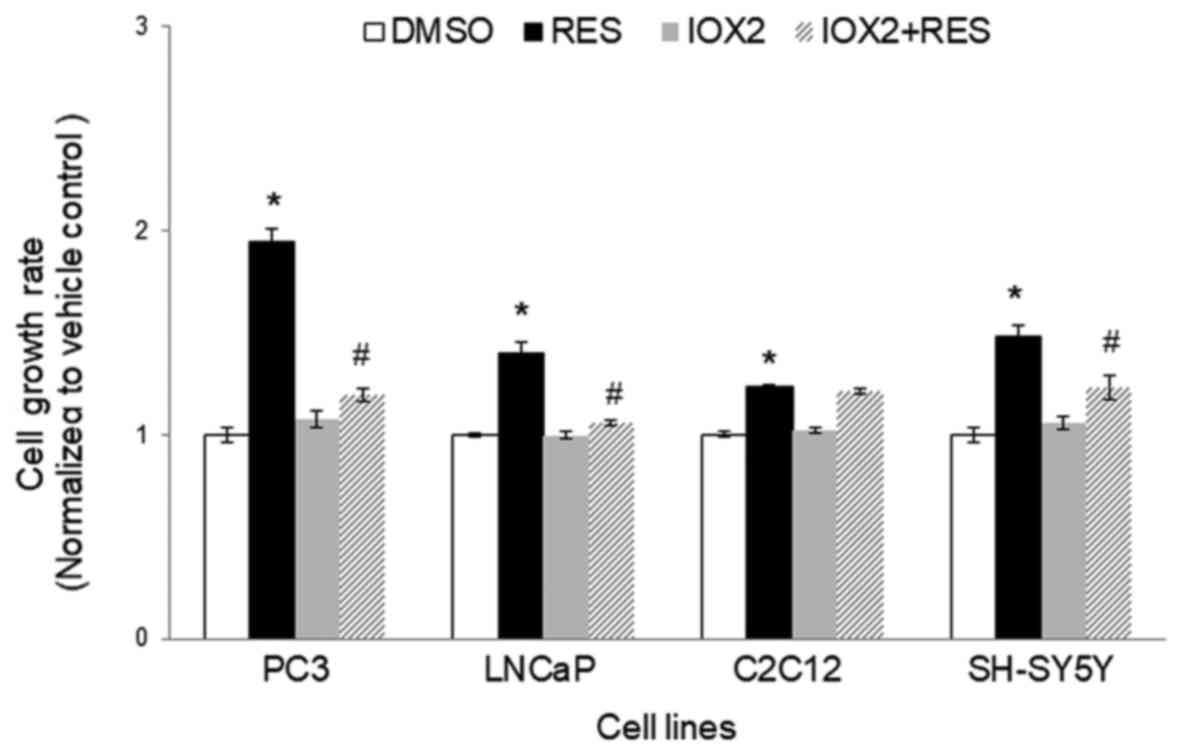
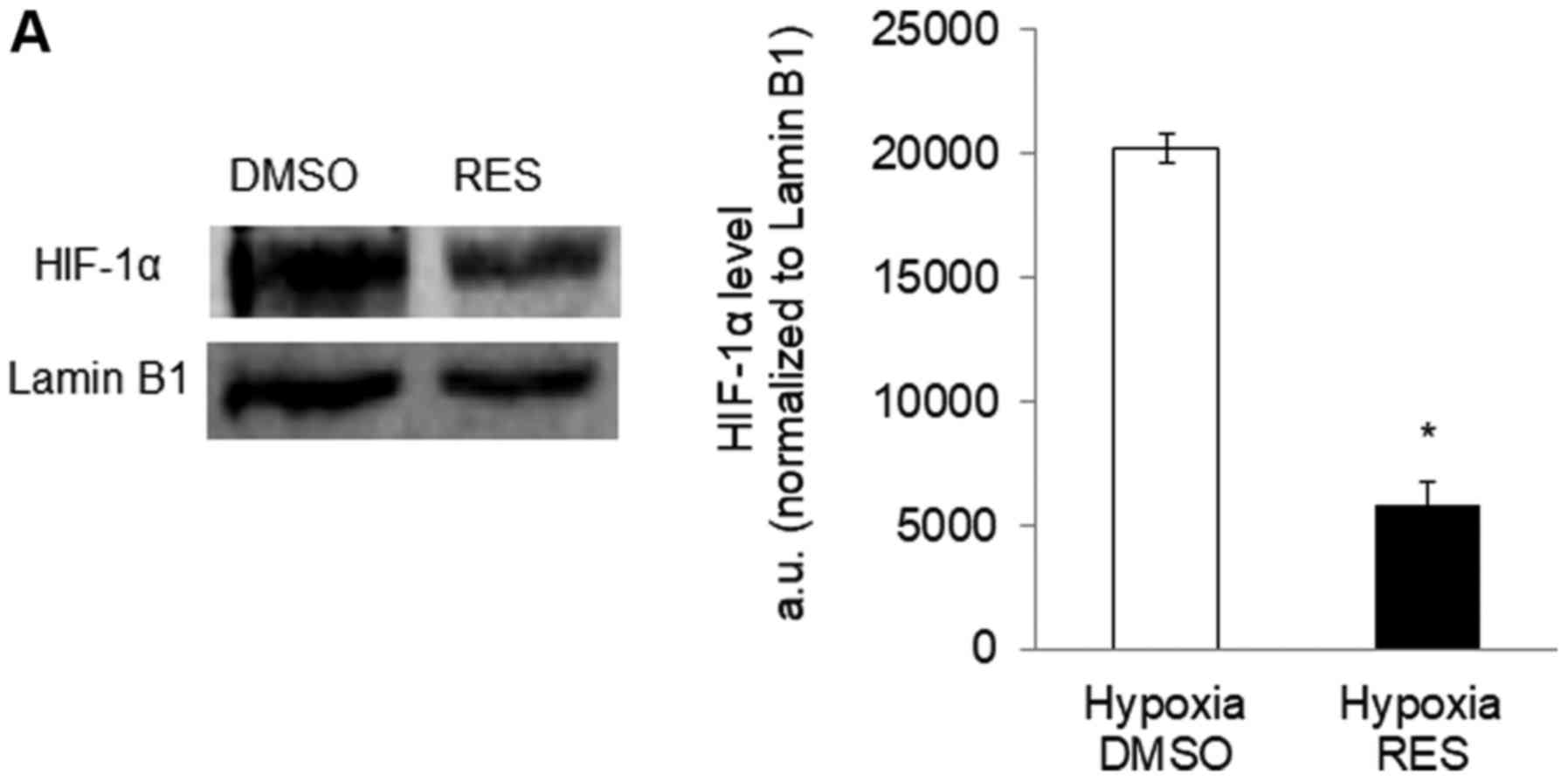
|
1
|
Diaz-Ruiz R, Rigoulet M and Devin A: The
warburg and crabtree effects: On the origin of cancer cell energy
metabolism and of yeast glucose repression. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1807:568–576. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pavlova NN and Thompson CB: The emerging
hallmarks of cancer metabolism. Cell Metab. 23:27–47. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Koppenol WH, Bounds PL and Dang CV: Otto
Warburg's contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism.
Nat Rev Cancer. 11:325–337. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fantin VR, St-Pierre J and Leder P:
Attenuation of LDH-A expression uncovers a link between glycolysis,
mitochondrial physiology, and tumor maintenance. Cancer Cell.
9:425–434. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Le A, Cooper CR, Gouw AM, Dinavahi R,
Maitra A, Deck LM, Royer RE, Vander Jagt DL, Semenza GL and Dang
CV: Inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase A induces oxidative stress
and inhibits tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:2037–2042. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Greer SN, Metcalf JL, Wang Y and Ohh M:
The updated biology of hypoxia-inducible factor. EMBO J.
31:2448–2460. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Masoud GN and Li W: HIF-1α pathway: Role,
regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B.
5:378–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han G, Xia J, Gao J, Inagaki Y, Tang W and
Kokudo N: Anti-tumor effects and cellular mechanisms of
resveratrol. Drug Discov Ther. 9:1–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stuart JA and Robb EL: Bioactive
polyphenols from wine grapes. Springer Press; New York, NY: pp.
772013
|
|
11
|
Robb EL, Moradi F, Maddalena LA, Valente
AJF, Fonseca J and Stuart JA: Resveratrol stimulates mitochondrial
fusion by a mechanism requiring mitofusin-2. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 485:249–254. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
de Oliveira MR, Nabavi SF, Manaya A,
Daglia M, Hajheydari Z and Nabavi SM: Resveratrol and the
mitochondria: From triggering the intrinsic apoptotic pathway to
inducing biogenesis, a mechanistic view. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1860:727–745. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Q, Tang X, Lu QY, Zhang ZF, Brown J
and Le AD: Resveratrol inhibits hypoxia-induced accumulation of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and VEGF expression in human tongue
squamous cell carcinoma and hepatoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
4:1465–1474. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang M, Li W, Yu L and Wu S: The
suppressive effect of resveratrol on HIF-1α and VEGF expression
after warm ischemia and reperfusion in rat liver. PLoS One.
9:e1095892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rossignol R, Gilerson R, Aggeler R,
Yamagata K, Remington SJ and Capaldi RA: Energy substrate modulates
mitochondrial structure and oxidative capacity in cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 64:985–993. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Valente AJ, Maddalena LA, Robb EL, Moradi
F and Stuart JA: A simple ImageJ macro tool for analyzing
mitochondrial network morphology in mammalian cell culture. Acta
Histochem. 119:315–326. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang X, Zhou J, Liu J, Tang B, Zhao F and
Qu Y: Biological characteristics of prostate cancer cells are
regulated by hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Oncol Lett. 8:1217–1221.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang H, Benzonana LL, Zhao H, Watts HR,
Perry NJ, Bevan C, Brown R and Ma D: Prostate cancer cell
malignancy via modulation of HIF-1α pathway with isoflurane and
propofol alone and in combination. Br J Cancer. 111:1338–1349.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yan Q, Bartz S, Mao M, Li L and Kaelin WG
Jr: The hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha N-terminal and C-terminal
transactivation domains cooperate to promote renal tumorigenesis in
vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 27:2092–2102. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sen A, Ren S, Lerchenmüller C, Sun J,
Weiss N, Most P and Peppel K: MicroRNA-138 regulates
hypoxia-induced endothelial cell dysfunction by targeting S100A1.
PLoS One. 8:e786842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Muz B, de la Puente P, Azab F and Azab AK:
The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis,
metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia (Auckl). 3:83–92.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hirschey MD, DeBerardinis RJ, Diehl AME,
Drew JE, Frezza C, Green MF, Jones LW, Ko YH, Le A, Lea MA, et al:
Dysregulated metabolism contributes to oncogenesis. Semin Cancer
Biol. 35 Suppl:S129–S150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Amoedo ND, Obre E and Rossignol R: Drug
discovery strategies in the field of tumor energy metabolism:
Limitations by metabolic flexibility and metabolic resistance to
chemotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 1858:674–685. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kankotia S and Stacpoole PW:
Dichloroacetate and cancer: New home for an orphan drug? Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1846:617–629. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Holden HM, Rayment I and Thoden JB:
Structure and function of enzymes of the Leloir pathway for
galactose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 278:43885–43888. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Robb EL and Stuart JA: The stilbenes
resveratrol, pterostilbene and piceid affect growth and stress
resistance in mammalian cells via a mechanism requiring estrogen
receptor beta and the induction of Mn-superoxide dismutase.
Phytochemistry. 98:164–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Courtnay R, Ngo DC, Malik N, Ververis K,
Tortorell SM and Kargiannis TC: Cancer metabolism and the Warburg
effect: The role of HIF-1 and PI3K. Mol Biol Rep. 42:841–851. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boulahbel H, Durán RV and Gottlieb E:
Prolyl hydroxylases as regulators of cell metabolism. Biochem Soc
Trans. 37:291–294. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jokilehto T and Jaakola PM: The role of
HIF prolyl hydroxylases in tumour growth. J Cell Mol Med.
14:758–770. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nguyen TL and Durán RV: Prolyl hydroxylase
domain enzymes and their role in cell signaling and cancer
metabolism. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 80:71–80. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li G, Rivas P, Bedolla R, Thapa D, Reddick
RL, Ghosh R and Kumar AP: Dietary resveratrol prevents development
of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplastic lesions:
Involvement of SIRT1-S6K axis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 6:27–39.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen L, Shi Y, Yuan J, Han Y, Qin R, Wu Q,
Jia B, Wei B, Wei L, Dai G and Jiao S: HIF-1 alpha overexpression
correlates with poor overall survival and disease-free survival in
gastric cancer patients post-gastrectomy. PLoS One. 9:e906782014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|