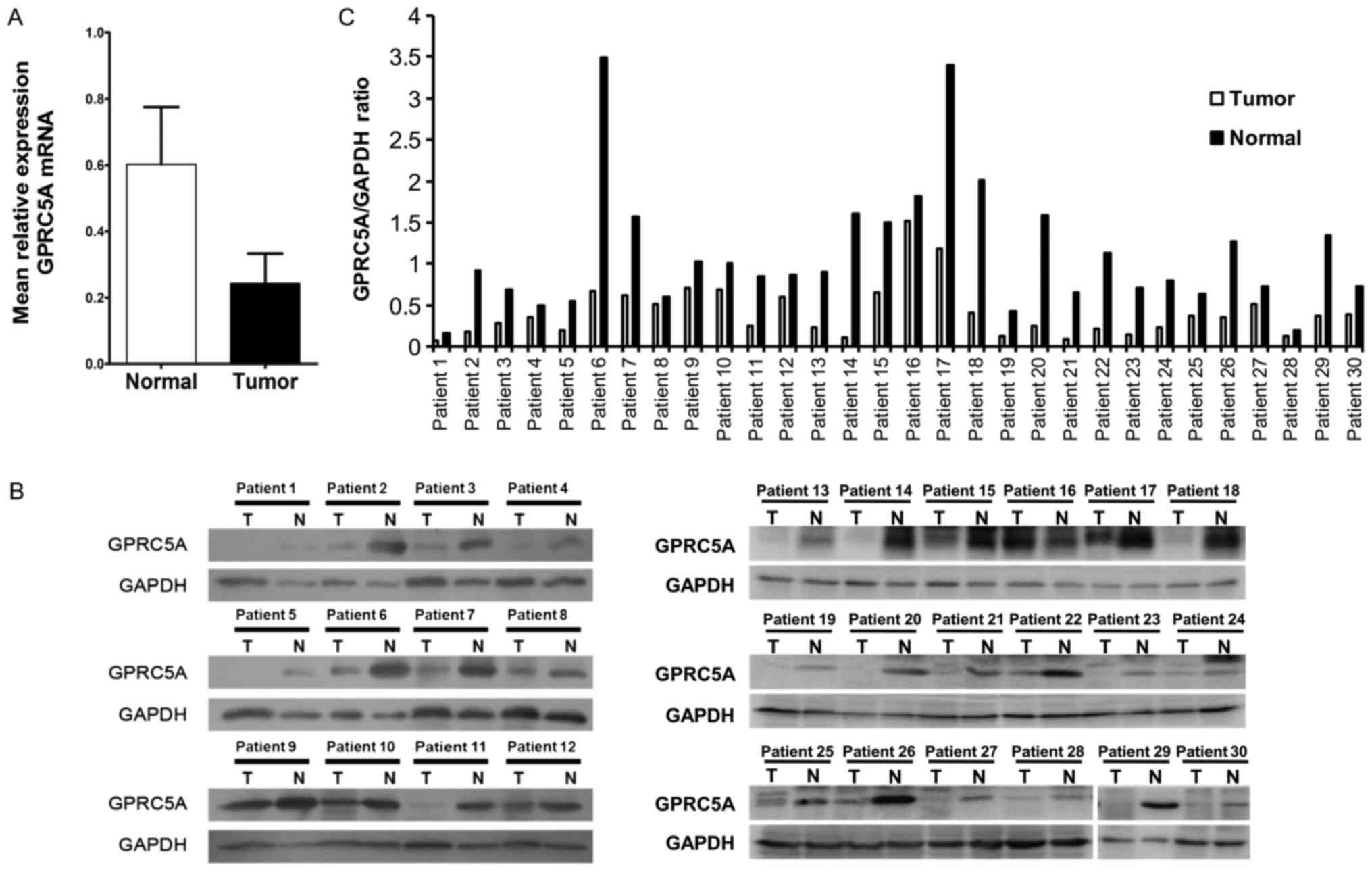
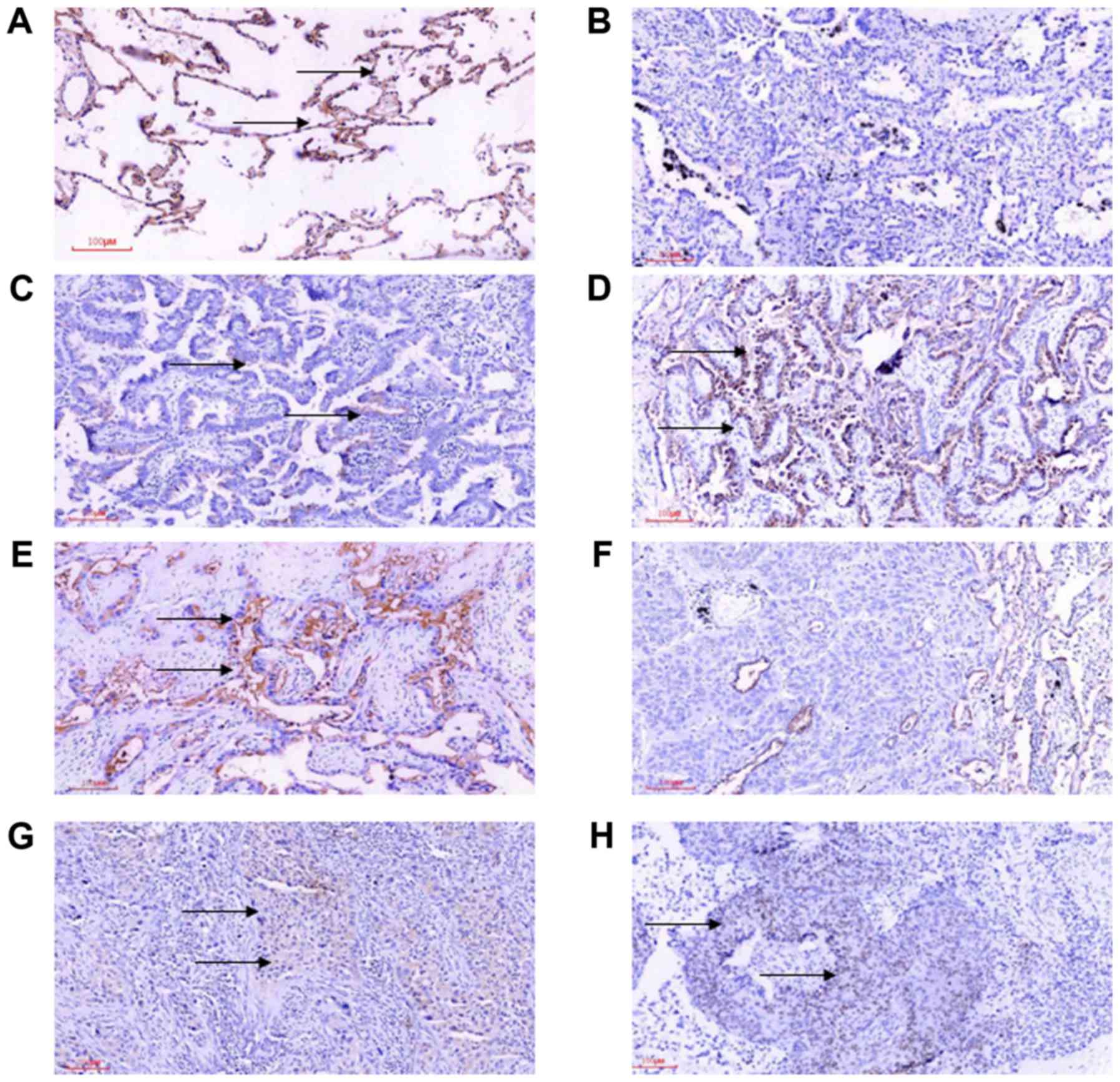
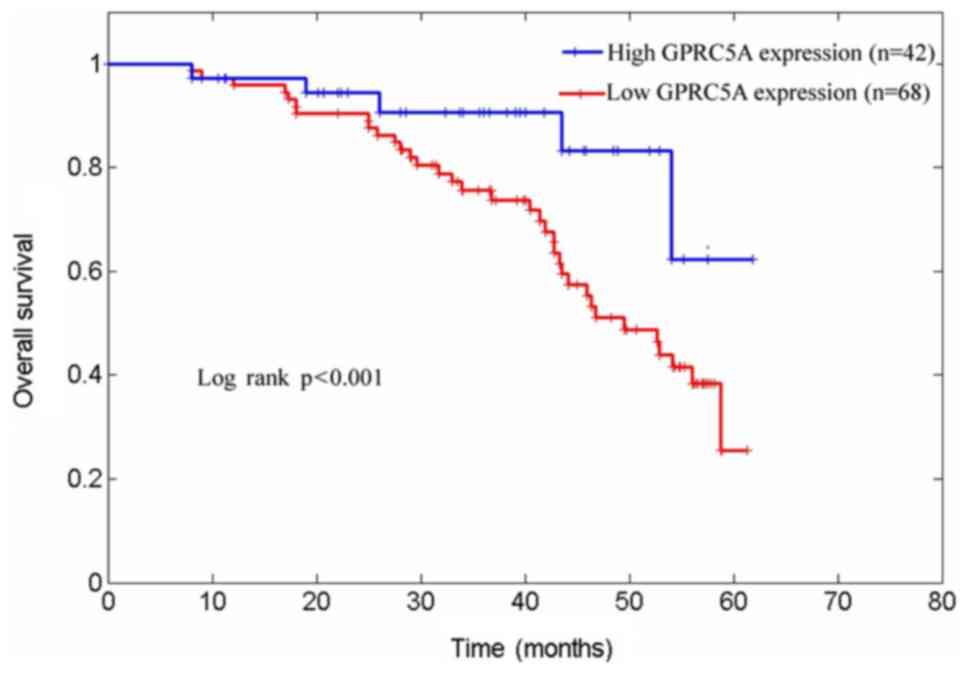
|
1
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cheng Y and Lotan R: Molecular cloning and
characterization of a novel retinoic acid-inducible gene that
encodes a putative G protein-coupled receptor. J Biol Chem.
273:35008–35015. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li S, Huang S and Peng SB: Overexpression
of G protein-coupled receptors in cancer cells: Involvement in
tumor progression. Int J Oncol. 27:1329–1339. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Robbins MJ, Michalovich D, Hill J, Calver
AR, Medhurst AD, Gloger I, Sims M, Middlemiss DN and Pangalos MN:
Molecular cloning and characterization of two novel retinoic
acid-inducible orphan G-protein-coupled receptors (GPRC5B and
GPRC5C). Genomics. 67:8–18. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nagahata T, Sato T, Tomura A, Onda M,
Nishikawa K and Emi M: Identification of RAI3 as a therapeutic
target for breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 12:65–73. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou H and Rigoutsos I: The emerging roles
of GPRC5A in diseases. Oncoscience. 1:765–776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tao Q, Fujimoto J, Men T, Ye X, Deng J,
Lacroix L, Clifford JL, Mao L, Van Pelt CS, Lee JJ, et al:
Identification of the retinoic acid-inducible Gprc5a as a new lung
tumor suppressor gene. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:1668–1682. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fujimoto J, Kadara H, Men T, van Pelt C,
Lotan D and Lotan R: Comparative functional genomics analysis of
NNK tobacco-carcinogen induced lung adenocarcinoma development in
Gprc5a-knockout mice. PLoS One. 5:e118472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Barta P, Van Pelt C, Men T, Dickey BF,
Lotan R and Moghaddam SJ: Enhancement of lung tumorigenesis in a
Gprc5a Knockout mouse by chronic extrinsic airway inflammation. Mol
Cancer. 11:42012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhong S, Yin H, Liao Y, Yao F, Li Q, Zhang
J, Jiao H, Zhao Y, Xu D, Liu S, et al: Lung tumor suppressor GPRC5A
binds EGFR and restrains its effector signaling. Cancer Res.
75:1801–1814. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Detterbeck FC, Boffa DJ and Tanoue LT: The
new lung cancer staging system. Chest. 136:260–271. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Y, Deng J, Fujimoto J, Kadara H, Men
T, Lotan D and Lotan R: Gprc5a deletion enhances the transformed
phenotype in normal and malignant lung epithelial cells by
eliciting persistent Stat3 signaling induced by autocrine leukemia
inhibitory factor. Cancer Res. 70:8917–8926. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kadara H, Fujimoto J, Men T, Ye X, Lotan
D, Lee JS and Lotan R: A Gprc5a tumor suppressor loss of expression
signature is conserved, prevalent, and associated with survival in
human lung adenocarcinomas. Neoplasia. 12:499–505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fujimoto J, Kadara H, Garcia MM, Kabbout
M, Behrens C, Liu DD, Lee JJ, Solis LM, Kim ES, Kalhor N, et al:
G-protein coupled receptor family C, group 5, member A (GPRC5A)
expression is decreased in the adjacent field and normal bronchial
epithelia of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
and non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 7:1747–1754. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jorissen H, Bektas N, Dahl E, Hartmann A,
ten Haaf A, Di Fiore S, Kiefer H, Thess A, Barth S and Klockenbring
T: Production and characterisation of monoclonal antibodies against
RAI3 and its expression in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer.
9:2002009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng L, Yang S, Yang Y, Zhang W, Xiao H,
Gao H, Deng X and Zhang Q: Global gene expression and functional
network analysis of gastric cancer identify extended pathway maps
and GPRC5A as a potential biomarker. Cancer Lett. 326:105–113.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tao Q, Cheng Y, Clifford J and Lotan R:
Characterization of the murine orphan G-protein-coupled receptor
gene Rai3 and its regulation by retinoic acid. Genomics.
83:270–280. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ye X and Lotan R: Potential
misinterpretation of data on differential gene expression in normal
and malignant cells in vitro. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic.
7:322–326. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ye X, Tao Q, Wang Y, Cheng Y and Lotan R:
Mechanisms underlying the induction of the putative human tumor
suppressor GPRC5A by retinoic acid. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:951–962.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|