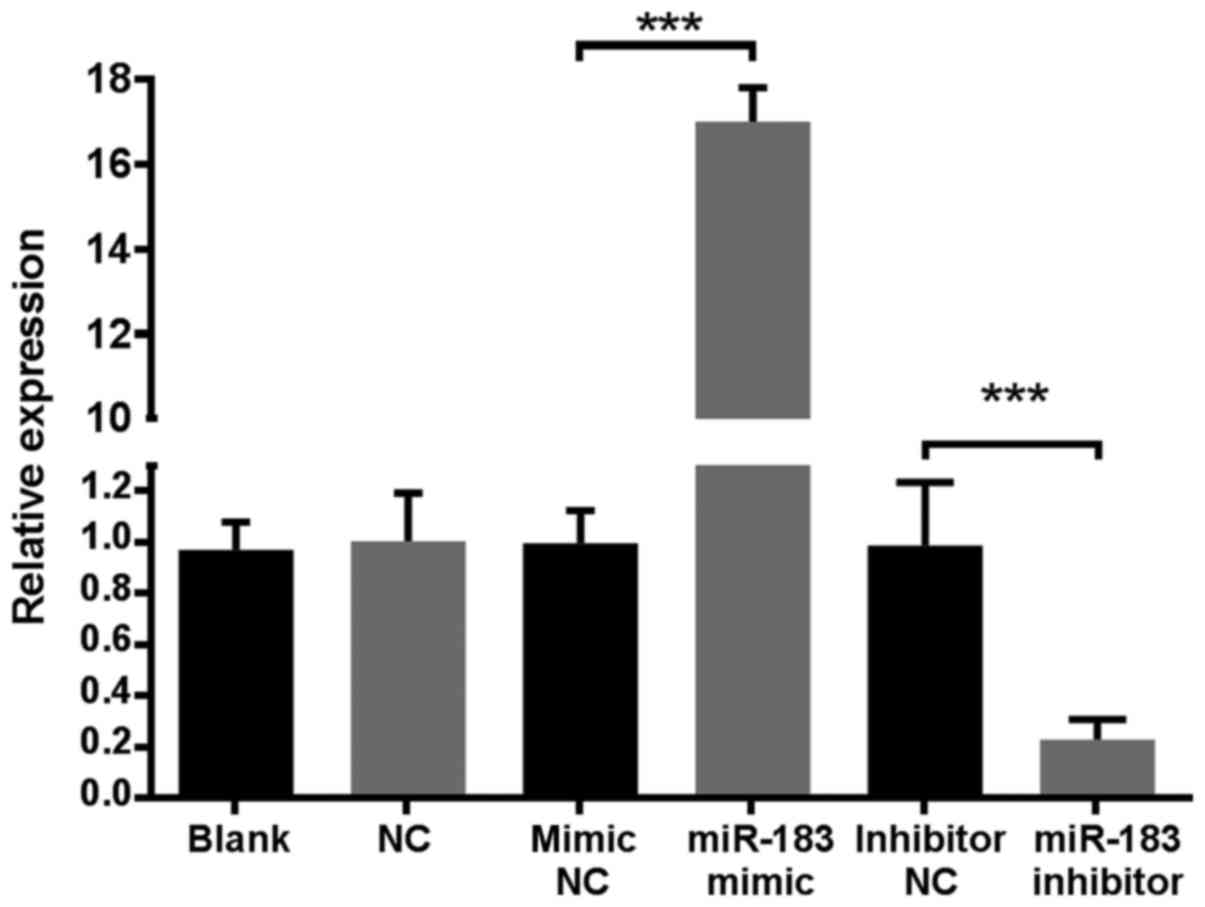
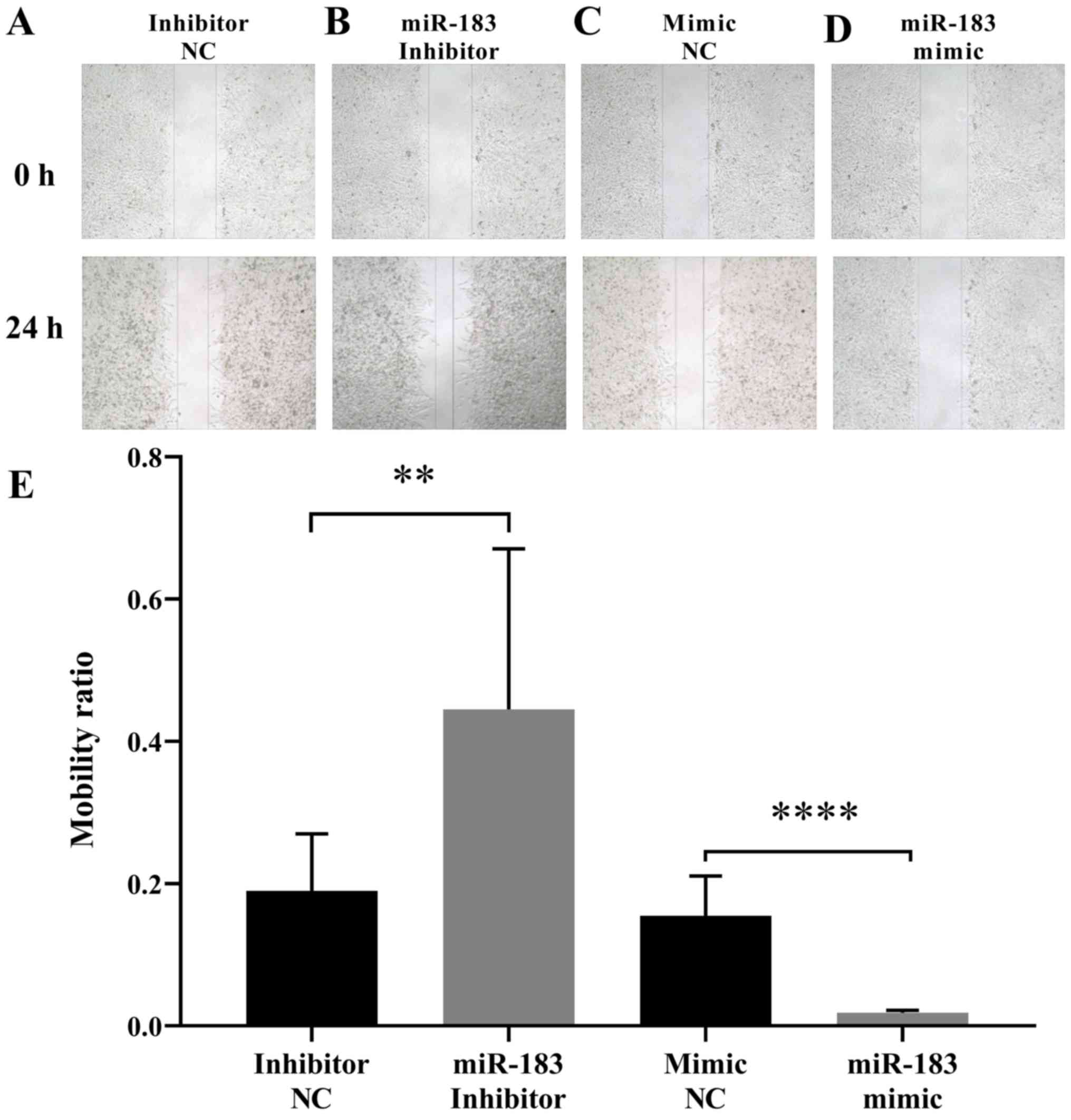
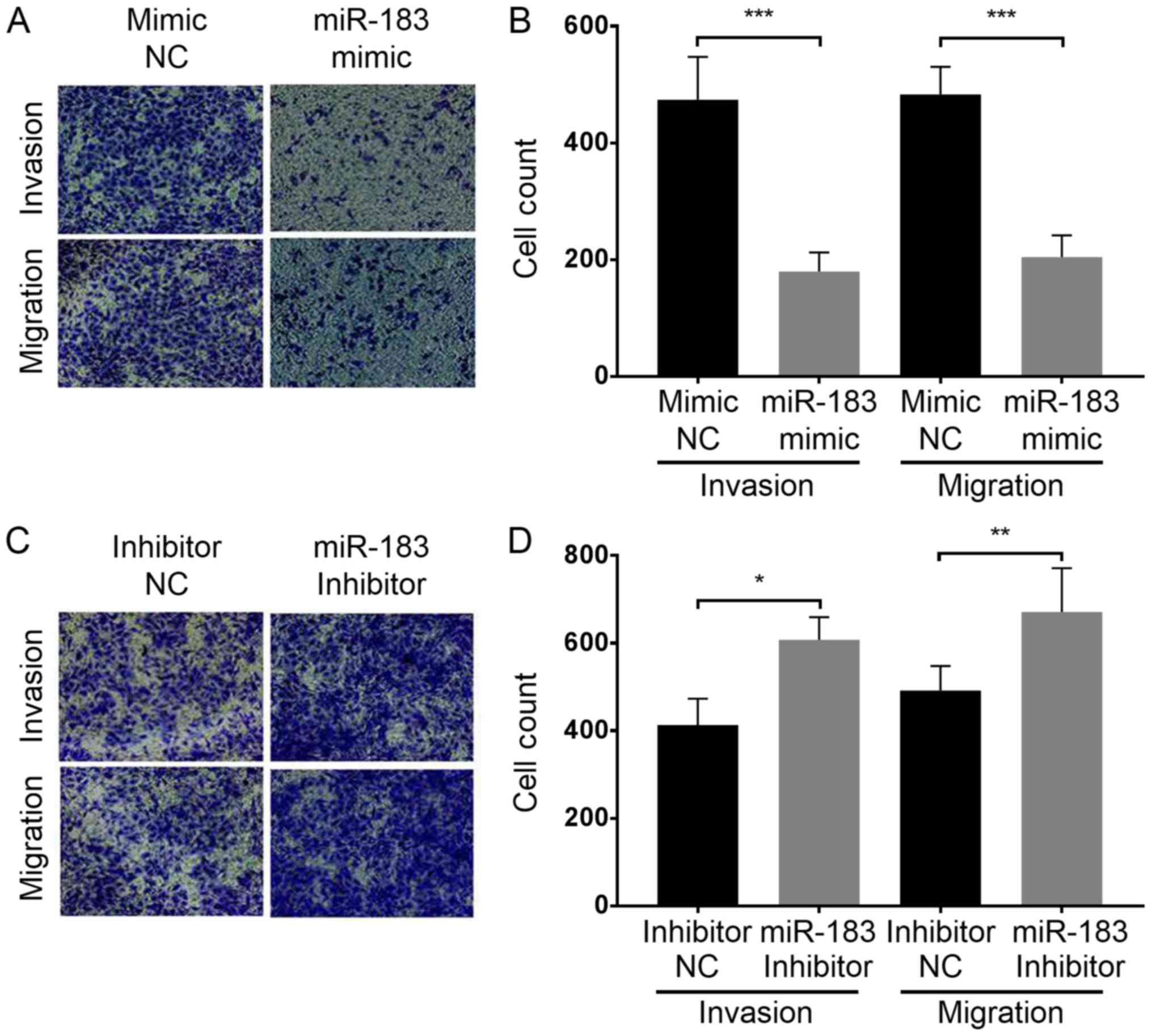
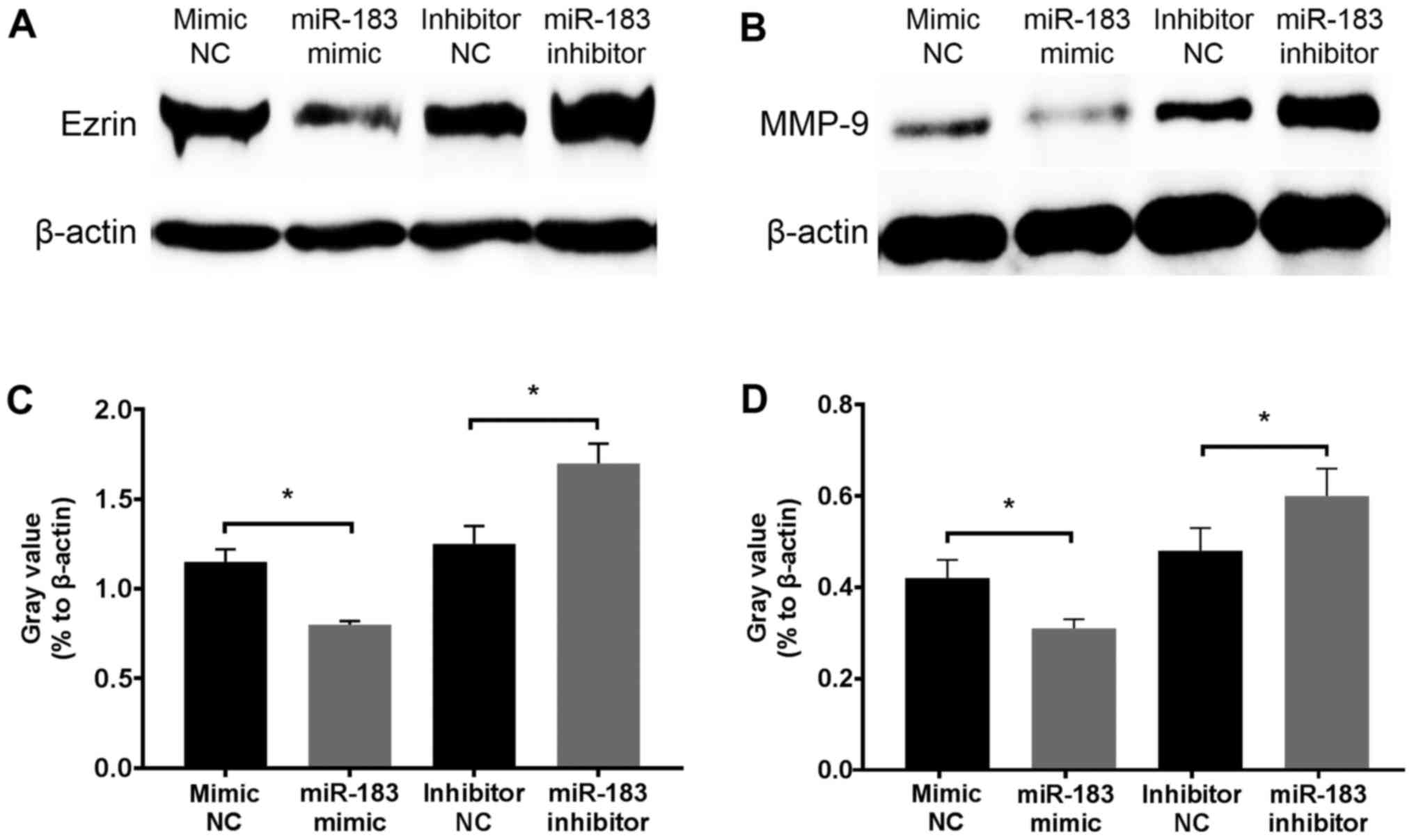
|
1
|
Jemal A, Ward EM, Johnson CJ, Cronin KA,
Ma J, Ryerson B, Mariotto A, Lake AJ, Wilson R, Sherman RL, et al:
Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975-2014,
featuring survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 109:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nikolaou V and Stratigos AJ: Emerging
trends in the epidemiology of melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 170:11–19.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Damsky WE, Theodosakis N and Bosenberg M:
Melanoma metastasis: New concepts and evolving paradigms. Oncogene.
33:2413–2422. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zbytek B, Carlson JA, Granese J, Ross J,
Mihm MC Jr and Slominski A: Current concepts of metastasis in
melanoma. Expert Rev Dermatol. 3:569–585. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nguyen DX, Bos PD and Massagué J:
Metastasis: From dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:274–284. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Hodgson L and Condeelis
J: Directed cell invasion and migration during metastasis. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 24:277–283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Long ZY and Wang TH: Advances of the role
of Ezrin in migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Sheng Li
Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 47:21–26. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu HY, Gu WJ, Wang CZ, Ji XJ and Mu YM:
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and −2 and tissue inhibitor of matrix
metalloproteinase-2 in invasive pituitary adenomas: A systematic
review and meta-analysis of case-control trials. Medicine.
95:e39042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Candido S, Abrams SL, Steelman LS,
Lertpiriyapong K, Fitzgerald TL, Martelli AM, Cocco L, Montalto G,
Cervello M, Polesel J, et al: Roles of NGAL and MMP-9 in the tumor
microenvironment and sensitivity to targeted therapy. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1863:438–448. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pârvănescu V, Georgescu M, Georgescu I,
Șurlin V, Pătraşcu Ș, Picleanu AM and Georgescu E: The role of
matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a prognostic factor in
epithelial and lymphatic neoplasia. Chirurgia. 110:506–510.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li J, Wei K, Yu H, Jin D, Wang G and Yu B:
Prognostic value of Ezrin in various cancers: A systematic review
and updated meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 5:179032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao DH, Zhu J, Wang WB, Dong F, Zhang Q,
Fan HW, Zhang JZ and Wang YM: Correlations of ezrin expression with
pathological characteristics and prognosis of osteosarcoma: A
meta-analysis. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014:8375432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi SD, Fadiel A and Naftolin F: Erratum
to: Ezrin is an essential marker for metastasis of gynecologic
cancer. J Menopausal Med. 22:1882016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Khanna C, Wan X, Bose S, Cassaday R, Olomu
O, Mendoza A, Yeung C, Gorlick R, Hewitt SM and Helman LJ: The
membrane-cytoskeleton linker ezrin is necessary for osteosarcoma
metastasis. Nat Med. 10:182–186. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Korkeila EA, Syrjänen K, Bendardaf R,
Laulajainen M, Carpén O, Pyrhönen S and Sundström J: Preoperative
radiotherapy modulates ezrin expression and its value as a
predictive marker in patients with rectal cancer. Hum Pathol.
42:384–392. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Patara M, Santos EM, de Almeida Coudry R,
Soares FA, Ferreira FO and Rossi BM: Ezrin expression as a
prognostic marker in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res.
17:827–833. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ilmonen S, Vaheri A, Asko-Seljavaara S and
Carpen O: Ezrin in primary cutaneous melanoma. Mod Pathol.
18:503–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bretscher A, Edwards K and Fehon RG: ERM
proteins and merlin: Integrators at the cell cortex. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 3:586–599. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McClatchey AI: Merlin and ERM proteins:
Unappreciated roles in cancer development? Nat Rev Cancer.
3:877–883. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li M, Feng YM and Fang SQ: Overexpression
of ezrin and galectin-3 as predictors of poor prognosis of cervical
cancer. Braz J Med Biol Res. 50:e53562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Horwitz V, Davidson B, Stern D, Trope CG,
Tavor Re'em T and Reich R: Ezrin is associated with disease
progression in ovarian carcinoma. PLoS One. 11:e01625022016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kong J, Di C, Piao J, Sun J, Han L, Chen
L, Yan G and Lin Z: Ezrin contributes to cervical cancer
progression through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Oncotarget. 7:19631–19642. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McRobert EA and Bach LA: Ezrin contributes
to impaired podocyte migration and adhesion caused by advanced
glycation end products. Nephrology. 21:13–20. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Piao J and Liu S, Xu Y, Wang C, Lin Z, Qin
Y and Liu S: Ezrin protein overexpression predicts the poor
prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Exp Mol Pathol.
98:1–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Y, Lin Z, Chen B, Chen S, Jiang Z, Zhou
T, Hou Z and Wang Y: Ezrin/NF-κB activation regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by EGF and promotes
metastasis of colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 92:140–148.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He J, Ma G, Qian J, Zhu Y, Liang M, Yao N,
Ding Q, Chen L, Liu X, Xia T, et al: Interaction between ezrin and
cortactin in promoting epithelial to mesenchymal transition in
breast cancer cells. Med Sci Monit. 23:1583–1596. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lan M, Kojima T, Murata M, Osanai M,
Takano K, Chiba H and Sawada N: Phosphorylation of ezrin enhances
microvillus length via a p38 MAP-kinase pathway in an immortalized
mouse hepatic cell line. Exp Cell Res. 312:111–120. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dang B, Duan X, Wang Z, He W and Chen G: A
therapeutic target of cerebral hemorrhagic stroke: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9. Curr Drug Targets. 18:1358–1366. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Boziki M and Grigoriadis N: An update on
the role of matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of
multiple sclerosis. Med Chem. 14:155–169. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Banday MZ, Sameer AS, Mir AH, Mokhdomi TA,
Chowdri NA and Haq E: Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) −2, −7 and −9
promoter polymorphisms in colorectal cancer in ethnic Kashmiri
population - A case-control study and a mini review. Gene.
589:81–89. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gong L, Wu D, Zou J, Chen J, Chen L, Chen
Y, Ni C and Yuan H: Prognostic impact of serum and tissue MMP-9 in
non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Oncotarget. 7:18458–18468. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yonemori K, Kurahara H, Maemura K and
Natsugoe S: MicroRNA in pancreatic cancer. J Hum Genet. 62:33–40.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xue J, Yang J, Luo M, Cho WC and Liu X:
MicroRNA-targeted therapeutics for lung cancer treatment. Expert
Opin Drug Discov. 12:141–157. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Manasa VG and Kannan S: Impact of microRNA
dynamics on cancer hallmarks: An oral cancer scenario. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283176959202017.doi: 10.1177/1010428317695920. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Latchana N, Ganju A, Howard JH and Carson
WE III: MicroRNA dysregulation in melanoma. Surg Oncol. 25:184–189.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kanekura K, Nishi H, Isaka K and Kuroda M:
MicroRNA and gynecologic cancers. J Obstet Gynaecol Res.
42:612–617. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
D'Angelo B, Benedetti E, Cimini A and
Giordano A: MicroRNAs: A puzzling tool in cancer diagnostics and
therapy. Anticancer Res. 36:5571–5575. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lima CR, Gomes CC and Santos MF: Role of
microRNAs in endocrine cancer metastasis. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
456:62–75. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Moridikia A, Mirzaei H, Sahebkar A and
Salimian J: MicroRNAs: Potential candidates for diagnosis and
treatment of colorectal cancer. J Cell Physiol. 233:901–913. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ma Y, Liang AJ, Fan YP, Huang YR, Zhao XM,
Sun Y and Chen XF: Dysregulation and functional roles of
miR-183-96-182 cluster in cancer cell proliferation, invasion and
metastasis. Oncotarget. 7:42805–42825. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shimono Y, Mukohyama J, Nakamura S and
Minami H: MicroRNA regulation of human breast cancer stem cells. J
Clin Med. 5(pii): E22015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dambal S, Shah M, Mihelich B and Nonn L:
The microRNA-183 cluster: The family that plays together stays
together. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:7173–7188. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wojtas B, Ferraz C, Stokowy T, Hauptmann
S, Lange D, Dralle H, Musholt T, Jarzab B, Paschke R and Eszlinger
M: Differential miRNA expression defines migration and reduced
apoptosis in follicular thyroid carcinomas. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
388:1–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang QH, Sun HM, Zheng RZ, Li YC, Zhang
Q, Cheng P, Tang ZH and Huang F: Meta-analysis of microRNA-183
family expression in human cancer studies comparing cancer tissues
with noncancerous tissues. Gene. 527:26–32. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ruan H, Liang X, Zhao W, Ma L and Zhao Y:
The effects of microRNA-183 promots cell proliferation and invasion
by targeting MMP-9 in endometrial cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
89:812–818. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fan D, Wang Y, Qi P, Chen Y, Xu P, Yang X,
Jin X and Tian X: MicroRNA-183 functions as the tumor suppressor
via inhibiting cellular invasion and metastasis by targeting MMP-9
in cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 141:166–174. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang J, Zuo J, Lei M, Wu S, Zang X and
Zhang C: Ezrin promotes invasion and migration of the MG63
osteosarcoma cell. Chin Med J. 127:1954–1959. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mu Y, Zhang H, Che L and Li K: Clinical
significance of microRNA-183/Ezrin axis in judging the prognosis of
patients with osteosarcoma. Med Oncol. 31:8212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cao LL, Xie JW, Lin Y, Zheng CH, Li P,
Wang JB, Lin JX, Lu J, Chen QY and Huang CM: miR-183 inhibits
invasion of gastric cancer by targeting Ezrin. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:5582–5594. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhu J, Feng Y, Ke Z, Yang Z, Zhou J, Huang
X and Wang L: Down-regulation of miR-183 promotes migration and
invasion of osteosarcoma by targeting Ezrin. Am J Pathol.
180:2440–2451. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhao H, Guo M, Zhao G, Ma Q, Ma B, Qiu X
and Fan Q: miR-183 inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma via
downregulation of the expression of Ezrin in F5M2 cells. Int J Mol
Med. 30:1013–1020. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang G, Mao W and Zheng S: MicroRNA-183
regulates Ezrin expression in lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
582:3663–3668. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hsu YY, Shi GY, Kuo CH, Liu SL, Wu CM, Ma
CY, Lin FY, Yang HY and Wu HL: Thrombomodulin is an
ezrin-interacting protein that controls epithelial morphology and
promotes collective cell migration. FASEB J. 26:3440–3452. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Brambilla D and Fais S: The Janus-faced
role of ezrin in ‘linking’ cells to either normal or metastatic
phenotype. Int J Cancer. 125:2239–2245. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Federici C, Brambilla D, Lozupone F,
Matarrese P, de Milito A, Lugini L, Iessi E, Cecchetti S, Marino M,
Perdicchio M, et al: Pleiotropic function of ezrin in human
metastatic melanomas. Int J Cancer. 124:2804–2812. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kim A, Im M, Yim NH and Ma JY: Reduction
of metastatic and angiogenic potency of malignant cancer by
Eupatorium fortunei via suppression of MMP-9 activity and VEGF
production. Sci Rep. 4:69942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lee KR, Lee JS, Kim YR, Song IG and Hong
EK: Polysaccharide from Inonotus obliquus inhibits migration and
invasion in B16-F10 cells by suppressing MMP-2 and MMP-9 via
downregulation of NF-κB signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 31:2447–2453.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Tang ZY, Liu Y, Liu LX, Ding XY, Zhang H
and Fang LQ: RNAi-mediated MMP-9 silencing inhibits mouse melanoma
cell invasion and migration in vitro and in vivo. Cell Biol Int.
37:849–854. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cheung CC, Lun SW, Chung GT, Chow C, Lo C,
Choy KW and Lo KW: MicroRNA-183 suppresses cancer stem-like cell
properties in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer.
16:4952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Song C, Zhang L, Wang J, Huang Z, Li X, Wu
M, Li S, Tang H and Xie X: High expression of microRNA-183/182/96
cluster as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. Sci Rep.
6:245022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhu C, Deng X, Wu J, Zhang J, Yang H, Fu
S, Zhang Y, Han Y, Zou Y, Chen Z, et al: MicroRNA-183 promotes
migration and invasion of CD133+/CD326+ lung adenocarcinoma
initiating cells via PTPN4 inhibition. Tumour Biol. 37:11289–11297.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Miao F, Zhu J, Chen Y, Tang N, Wang X and
Li X: MicroRNA-183-5p promotes the proliferation, invasion and
metastasis of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol Lett.
11:134–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Xu F, Zhang H, Su Y, Kong J, Yu H and Qian
B: Up-regulation of microRNA-183-3p is a potent prognostic marker
for lung adenocarcinoma of female non-smokers. Clin Transl Oncol.
16:980–985. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhou T, Zhang GJ, Zhou H, Xiao HX and Li
Y: Overexpression of microRNA-183 in human colorectal cancer and
its clinical significance. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:229–233.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Li P, Sheng C, Huang L, Zhang H, Huang L,
Cheng Z and Zhu Q: MiR-183/-96/-182 cluster is up-regulated in most
breast cancers and increases cell proliferation and migration.
Breast Cancer Res. 16:4732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Weeraratne SD, Amani V, Teider N,
Pierre-Francois J, Winter D, Kye MJ, Sengupta S, Archer T, Remke M,
Bai AH, et al: Pleiotropic effects of miR-183~96~182 converge to
regulate cell survival, proliferation and migration in
medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 123:539–552. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Li ZB, Li ZZ, Li L, Chu HT and Jia M:
MiR-21 and miR-183 can simultaneously target SOCS6 and modulate
growth and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:3208–3217. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yang M, Liu R, Li X, Liao J, Pu Y, Pan E,
Yin L and Wang Y: miRNA-183 suppresses apoptosis and promotes
proliferation in esophageal cancer by targeting PDCD4. Mol Cells.
37:873–880. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li C, Deng L, Zhi Q, Meng Q, Qian A, Sang
H, Li X and Xia J: MicroRNA-183 functions as an oncogene by
regulating PDCD4 in gastric cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
16:447–455. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang YY and Feng HM: MEG3 suppresses
human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor cells growth and metastasis
by down-regulation of Mir-183. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:345–356.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Sarver AL, Li L and Subramanian S:
MicroRNA miR-183 functions as an oncogene by targeting the
transcription factor EGR1 and promoting tumor cell migration.
Cancer Res. 70:9570–9580. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yang CL, Zheng XL, Ye K, Ge H, Sun YN, Lu
YF and Fan QX: MicroRNA-183 acts as a tumor suppressor in human
non-small cell lung cancer by down-regulating MTA1. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 46:93–106. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gao P, He M, Zhang C and Geng C:
Integrated analysis of gene expression signatures associated with
colon cancer from three datasets. Gene. 654–695. 2018.
|
|
75
|
Li J, Liang S, Jin H, Xu C, Ma D and Lu X:
Tiam1, negatively regulated by miR-22, miR-183 and miR-31, is
involved in migration, invasion and viability of ovarian cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 27:18352012.PubMed/NCBI
|