Introduction
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), the most common
malignancy of the head and neck, accounts for 2% of cancer-related
mortalities worldwide, with a steadily increasing incidence
(1). Despite advances in treatment
strategies, which have included a combination of surgery,
radiotherapy and chemotherapy, the survival rates of patients with
OSCC remain at <50% (2). The
deregulated proliferation and apoptosis of cancer cells have been
reported to serve a critical role in the initiation and progression
of OSCC (3). Therefore, an improved
understanding of the molecular basis underlying this malignancy
could facilitate the development of an effective therapeutic
strategy.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs/miRs), a type of non-coding RNA,
are capable of binding the 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) of the
target mRNA and repressing gene expression by either enhancing mRNA
degradation or suppressing mRNA translation (4). Due to their ability to modulate gene
expression, miRNAs have been reported to participate in a wide
range of cellular processes, including cell proliferation,
senescence, apoptosis and migration (5). Accumulating evidence has demonstrated
that the deregulation of miRNAs mediates the development of
numerous malignancies, including cancer of the breast, gastric
system, prostate and large intestine, through the modulation of
tumor cell viability, angiogenesis and metastasis (6). In human OSCC, miRNAs can serve either an
oncogenic or tumor-suppressing role during tumorigenesis. For
example, certain miRNAs, including miR-21, miR-222 and miR-448,
were discovered to be overexpressed in OSCC and function as
oncogenes (7–9). By contrast, other miRNAs, including
miR-9, miR-99a and miR-491-5p, were found to be downregulated in
OSCC and exhibit tumor-suppressive behavior (10–13).
miR-342-3p serves a critical role in numerous
physiological and pathological processes. miR-342-3p negatively
regulates cell viability by repressing the anti-apoptotic gene
network in human and mouse macrophages (14). Furthermore, it was identified as a
powerful enhancer of adipogenesis by targeting C-terminal-binding
protein 2 (CtBP2), leading to the release of the key adipogenic
regulator CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein α from CtBP2 binding
(15). In addition, miR-342-3p serves
a role in the osteogenic differentiation of umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells (16).
Recently, evidence suggested that miR-342-3p is abnormally
expressed in tissues of various types of cancer and participates in
tumorigenesis. Gao et al (17)
reported that miR-342-3p exhibited decreased expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma and that it may be used as an independent
predictor for poor prognoses. In non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC), miR-342-3p demonstrated decreased expression and was shown
to serve an inhibitory role in cell proliferation by targeting
anterior gradient protein 2 (18).
miR-342-3p was also reported to be downregulated in cervical cancer
tissue and repressed cell proliferation by targeting forkhead box
protein M1, a well-established oncogenic factor (19). Although these studies demonstrate the
important role of miR-342-3p in cancer progression, its expression
in OSCC tissues and its function in OSCC progression remain
unclear.
In the present study, the expression of miR-342-3p
were detected OSCC cells and tissues using reverse
transcription-quantitative PCR. The effect of miR-342-3p
overexpression or silencing on the proliferation of OSCC cells was
explored using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), colony formation assay
and 5-Bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU)-incorporation assay. Finally,
luciferase assays, western blot analysis and rescue experiments
were performed to investigate whether LIM and SH3 protein 1 (LASP1)
was the functional mediator of miR-342-3p.
Materials and methods
Cell lines and reagents
Human OSCC lines, including OC3, SCC-4, Tca8113,
SCC-9 and OEC-M1, and human normal oral keratinocytes (hNOKs) were
obtained from the State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Sichuan
University (Sichuan, China) and the State Key Laboratory of
Oncology in South China, Sun Yat-Sen University (Guangdong, China),
respectively. The primary antibody to LASP1 was purchased from
Sigma-Aldrich (SAB2101318); Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany) and
α-tubulin antibody (sc-398103) was obtained from Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Inc. (Dallas, TX, USA).
Cell culture
Human OSCC lines, including OC3, SCC-4, Tca8113,
SCC-9 and OEC-M1, and human normal oral keratinocytes (hNOKs) were
cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) (Invitrogen;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with
10% FBS (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), 10 mM HEPES, 1 mM
sodium pyruvate, 2 mM glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 mg/ml
streptomycin at 37°C in a humidified incubator with 5%
CO2. The cells were passaged every 2 or 3 days. The
cells at passage 10–15 were used in this study.
Tissue samples
The present study was approved by the Ethics
Committee of The Third Affiliated Hospital, Inner Mongolia Medical
University (Inner Mongolia, China). In total, 30 paired OSCC tumor
tissues and the adjacent non-cancerous specimens were collected
from patients undergoing surgical resection at The Third Affiliated
Hospital, Inner Mongolia Medical University. No patient had
received any therapy, including radiotherapy or chemotherapy, prior
to surgery. Patients provided written informed consent prior to
study initiation. All tissue samples were frozen in liquid nitrogen
once the diagnosis had been confirmed by tissue pathology.
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
(RT-qPCR)
miRNA was extracted from human tissue samples and
cultured cells using the mirVana miRNA Isolation kit (Ambion;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), following the manufacturer's
protocol. Expression of miR-342-3p was detected on a CFX96 Touch™
Real-Time PCR Detection system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.,
Hercules, CA, USA) using the PrimeScript miRNA RT-PCR kit (Takara
Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Dalian, China), according to the
manufacturer's protocols, and U6 was used to normalize miRNA
levels. The thermocycling conditions of quantitative PCR were as
follows: 94°C for 45 sec, 59°C for 45 sec and 72°C for 60 sec, for
35 cycles and 72°C for 10 min. The sequences of the primers used
were as follows: miR-342-3p forward, 5′-TCCTCGCTCTCACACAGAAATC-3′
and reverse, 5′-TATGGTTGTTCACGACTCCTTCAC-3′; and U6 forward,
5′-ATTGGAACGATACAGAGAAGATT-3′ and reverse,
5′-GGAACGCTTCACGAATTTG-3′.
Total RNA was isolated from cells using TRIzol
(Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and
reverse-transcribed into cDNA using the PrimeScript RT reagent kit
(Takara Biotechnology Co.) with the following temperature protocol;
25°C for 5 min, followed by 42°C for 60 min and 70°C for 5 min. The
RT-qPCR was performed on a CFX96 Touch™ Real-Time PCR Detection
system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) using the Power SYBR Green
Master mix (Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and
GAPDH was used to normalize mRNA levels. The relative expression
levels of miRNA and mRNA were calculated using 2−ΔΔCq
method (20). The primer sequences
were as follows: LASP1 forward, 5′-GGTGCGGCAAGATCGTGTA-3′ and
reverse, 5′-GGTCTCGCAATGGAA-3′; and GAPDH forward,
5′-ACAACTTTGGTATCGTGGAAGG-3′ and reverse,
5′-GCCATCACGCCACAGTTTC-3′.
Transient transfection of miR-342-3p
mimics or inhibitors
Given that Tca8113 and SCC-9 cell lines express an
intermediate level of miR-342-3p compared with other OSCC cell
lines (OC3, SCC-4 and OEC-M1), they were selected for subsequent
gain-of-function and loss-of-function experiments. miR-342-3p
mimics (100 nmol/l) or antagomiR-342-3p (100 nmol/l) (Guangzhou
RiboBio Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China) were transfected into Tca8113
or SCC-9 cells with Lipofectamine® RNAiMAX Transfection
Reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), following the
manufacturer's protocols, and used for subsequent experiments at 24
or 48 h post-transfection. miR-342-3p mimic sense sequence was,
5′UCUCACACAGAAAUCGCACCCGU-3′; The antagomir sequence was,
5′ACGGGTGCGATTTCTGTGTGAGA-3′.
Cell proliferation assays
The cells were seeded in 96-well plates at 3,000
cells/well. After 72 h of culture in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS
at 37°C, cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting kit-8
(CCK-8) (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, Inc., Kumamoto, Japan)
following the manufacturer's protocols. Assays were performed in
triplicate and the results are presented as the mean ± standard
deviation (SD).
Colony formation assay
To evaluate the colony formation ability of tumor
cells, the cells were seeded at 2,000 cells/well in a 6-well plate.
Cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS at 37°C for 2
weeks and then fixed with fixed with pure methanol for 15 min at
room temperature. Subsequent to being stained with 0.5% crystal
violet solution for 20 min, the colonies were counted using ImageJ
software version 2.0.0 (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda,
MD, USA). Assays were performed in triplicate and the results are
presented as the mean ± SD.
5-Bromo-2-deoxyuridine
(BrdU)-incorporation assay
A total of 5×104 Tca8113 or SCC-9 cells
were incubated with 10 µM BrdU for 30 min at 37°C in a humidified
incubator with 5% CO2. Following a wash with PBS, the
cells were rinsed thoroughly and incubated with 6 M HCl in PBS at
room temperature for 30 min. Subsequent to two washes with 0.1 M
borate buffer and a wash with PBS containing 0.1% bovine serum
albumin (BSA, Sigma-Aldrich, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany), the
cells were incubated with 10 µg/ml anti-BrdU fluorescein (BD
Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) for 1 h at room temperature in the
dark, followed by flow cytometry analysis in the FACSCanto™ II cell
analyzer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). Data were analyzed
using FlowJo v.10 software (FlowJo LLC, Ashland, OR, USA).
Luciferase reporter assay
Both TargetScan (www.targetscan.org) and miRanda (http://diana.imis.athena-innovation.gr/DianaTools/index.php)
predicted LASP1 as a potential target gene of miR-342-3p with
binding site located at 3′UTR of LASP1. Therefore, a duel
luciferase reporter assay was used to examine whether miR-342-3p
binds to the 3′UTR of LASP1 mRNA. First, the plasmid with LASP1
3′UTR oligonucleotide fragment was constructed and inserted in
(pGL3-LASP1-WT). Then, we mutated miR-342-3p binding sequences at
LASP1 3′UTR (pGL3-LASP1-M) from 5′-…GUGUGAG…-3′ to 5′-…CACACUC…-3′.
The effectiveness of constructs was verified by sequencing. Tca8113
or SCC-9 cells were seeded into 24-well plates (5×104
cell/well). The following day, 5 ng pRL-TK vector (an internal
control) and 50 ng pGL3 luciferase reporter plasmid (Promega
Corporation, Madison, WI, USA) carrying the wild-type (WT) or
mutant LASP1 3′-UTR were co-transfected into Tca8113 or SCC-9 cells
along with miR-342-3p mimics or antagomiR-342-3p using the
Lipofectamine 2000 transfection reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.). At 48 h post-transfection, the cells were
harvested for luciferase activity measurement using the
Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay system (Promega Corporation,
Madison, WI, USA) following the manufacturer's protocol. The
Renilla luciferase activity was used as an internal control and the
firefly luciferase activity was calculated as the mean ± SD after
being normalized by Renilla luciferase activity.
Western blotting
The cells were lysed using RIPA buffer (Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology, Shanghai, China) containing a protease
inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany).
After 40 min, the cells were centrifuged for 20 min at 4°C at
12,000 × g speed, and then the supernatant was carefully removed to
obtain the total protein. The protein concentration was measured
using the Pierce BCA Protein Assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.) following the manufacturer's protocols. The detailed protocol
has been described previously (21).
Equal amounts of protein per lane (50 µg) were separated by 10%
SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Merck
KGaA). Subsequent to being blocked with 5% non-fat milk in
tris-buffered saline/Tween-20 (TBST) for 1 h at room temperature,
the membranes were incubated with the aforementioned primary
antibodies (Rabbit anti-LASP1 antibody, 1:500; Mouse anti-α-tubulin
antibody, 1:2,000) at 4°C overnight. Following three washes with
TBST, the membranes were incubated with horseradish
peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (1:2,000, cat. no.
KC-MM-035; Kangcheng Bio-tech, Shanghai, China) and horseradish
peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:2,000, cat. no.:
KC-RB-035; Kangcheng) for 1 h at room temperature and washed again
3 times in TBST. The immunocomplexes were detected using by an ECL™
Western Blotting Detection Reagents (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL,
USA).
Plasmid and siRNA transfection
The Gateway Technology (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) was used in this study to clone LASP1 gene into a
pcDNA3.1 plasmid (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
pcDNA3.1-LASP1 were transfected into the cells with Lipofectamine
RNAiMAX Transfection Reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.). The siRNA oligos targeting Lasp1
(5′-CUUAUCCAGACAGUUCACCdTdT-3′;) and the negative control siRNA
(siCtrl) (5′-AGAGAUGUAGUCGCUCGCUdTdT-3′;) were synthesized by
Zoonbio Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Nanjing, China). A total of 20 nM
siRNA oligos were transfected into the cells with Lipofectamine
RNAiMAX Transfection Reagent. After 12 h of transfection, the cells
underwent subsequent experimentation.
Statistical analysis
Each experiment was performed in triplicate. The
data are presented as the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was
performed using the SPSS v17.0 software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL,
USA). The unpaired Student's t-test was used for comparing the
statistical significance between 2 groups. The statistical
differences for comparing >2 groups were analyzed using the
one-way analysis of variance followed by Dunnett's post hoc test.
Pearson's correlation analysis was performed to examine the
correlation between the miR-342-3p and LASP1 levels in clinical
specimens. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference.
Results
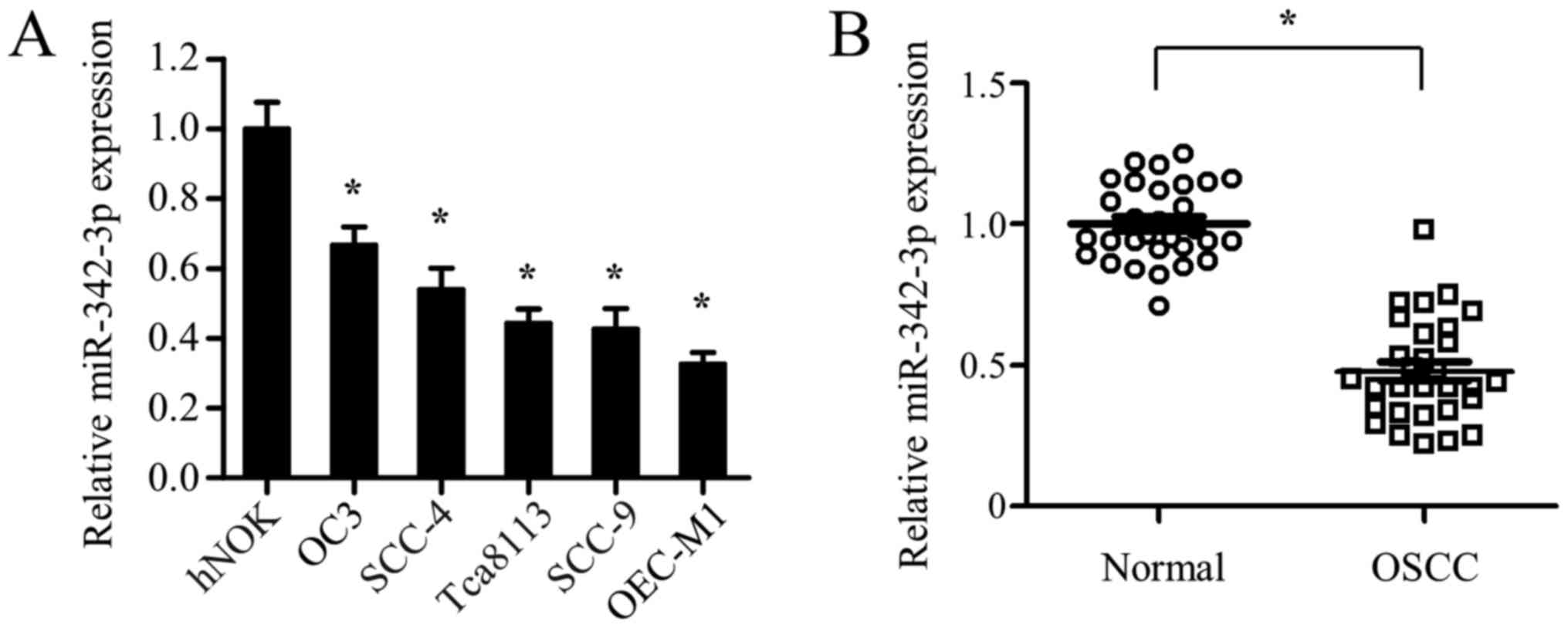
OSCC cells and tissues exhibit reduced
miR-342-3p expression
To explore the role of miR-342-3p in OSCC, the
expression profile of miR-342-3p in hNOKs and 5 oral squamous cell
carcinoma cell lines (OC3, SCC-4, Tca8113, SCC-9 and OEC-M1) was
examined first. Compared with that in hNOK cells, miR-342-3p
expression was significantly decreased in all 5 OSCC cell lines
(Fig. 1A). The expression levels of
miR-342-3p in 30 pairs of OSCC tumor tissues and adjacent
non-tumorous tissues were analyzed next. Consistent with the
results from the cell lines, miR-342-3p expression was
significantly decreased in OSCC tumor tissues compared with that in
the adjacent non-cancerous specimens (Fig. 1B). Together, the present data
demonstrated that miR-342-3p expression was significantly
downregulated in OSCC cells and tissues, suggesting that miR-342-3p
may serve a role in the development of OSCC. Given that Tca8113 and
SCC-9 cell lines express an intermediate level of miR-342-3p
compared with other OSCC cell lines (OC3, SCC-4 and OEC-M1)
(Fig. 1A), they were selected for
subsequent gain-of-function and loss-of-function experiments.
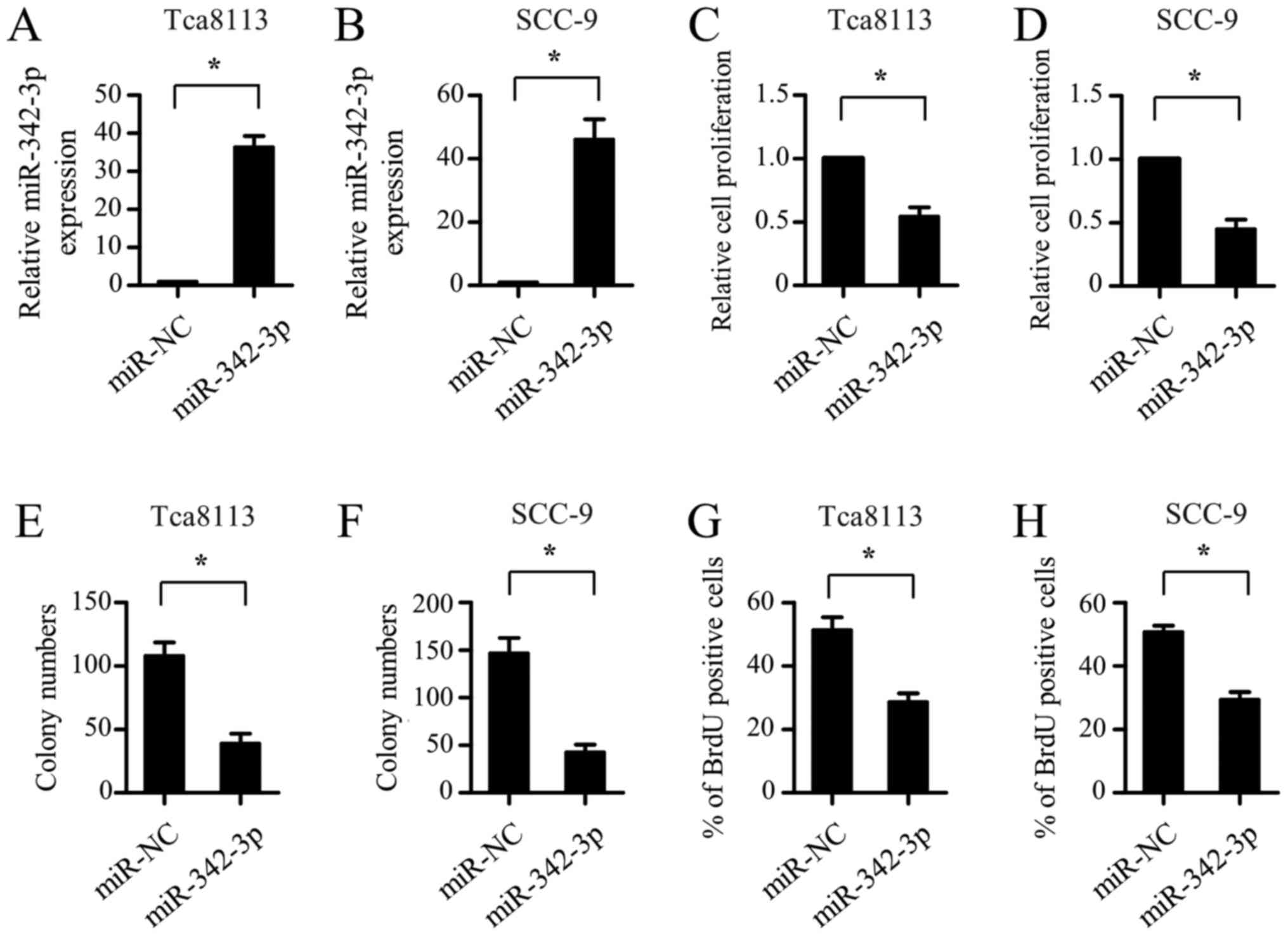
Upregulation of miR-342-3p inhibits
the proliferation of OSCC cells
The reduced expression of miR-342-3p in OSCC samples
suggested that it may function as a tumor suppressor. To
investigate the role of miR-342-3p, miR mimics were transfected
into the Tca8113 and SCC-9 cells. As shown in Fig. 2A and B, the expression of miR-342-3p
in the Tca8113 and SCC-9 cells was significantly increased
following transfection with an miR-342-3p-mimic. CCK-8 assay
results showed that ectopic expression of miR-342-3p significantly
inhibited the proliferation of the Tca8113 and SCC-9 cells
(Fig. 2C and D). In addition,
miR-342-3p overexpression resulted in a marked decrease in the
clonogenic potential of the Tca8113 and SCC-9 cells (Fig. 2E and F). In accordance with the
results from the CCK-8 assay, the BrdU-incorporation assay revealed
the suppression of OSCC cell proliferation by miR-342-3p mimic
transfection (Fig. 2G and H). Taken
together, these findings suggest that miR-342-3p inhibits the
proliferation of OSCC cells.
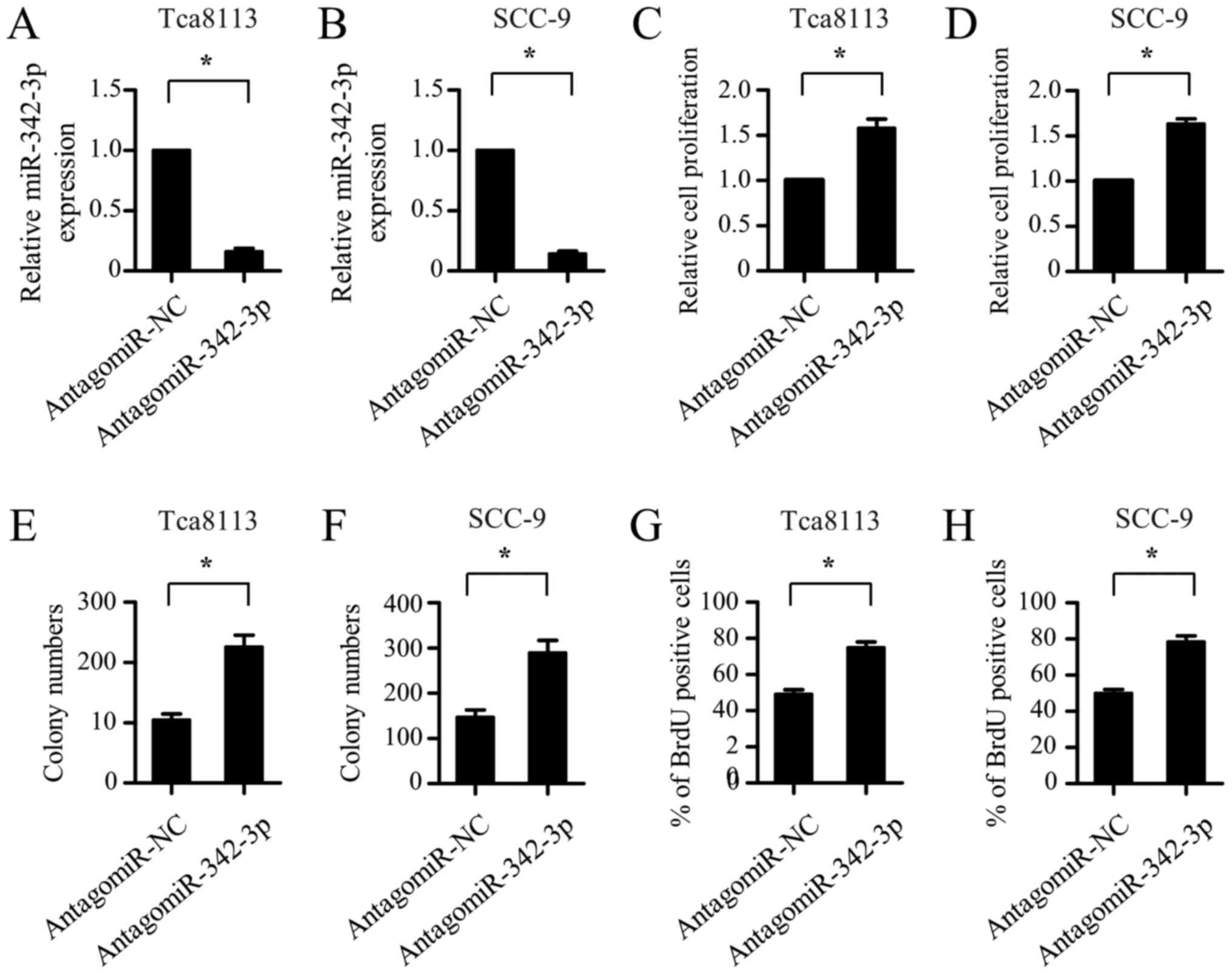
Inhibition of miR-342-3p promotes the
proliferation of OSCC cells
To confirm the suppressive role of miR-342-3p in the
proliferation of OSCC cells, the effect of miR-342-3p inhibition on
OSCC cell proliferation was explored. AntagomiR-342-3p was
transfected into the Tca8113 and SCC-9 cells to silence the
expression of endogenous miR-342-3p. As shown in Fig. 3A and B, endogenous miR-342-3p
expression was significantly downregulated in the Tca8113 and SCC-9
cells following antagomiR-342-3p transfection. CCK-8 assays
revealed that the inhibition of miR-342-3p markedly promoted the
proliferation of the Tca8113 and SCC-9 cells (Fig. 3C and D). Furthermore, the
colony-forming ability of the Tca8113 and SCC-9 cells was notably
enhanced by antagomiR-342-3p transfection (Fig. 3E and F). The BrdU-incorporation assay
further demonstrated that the Tca8113 and SCC-9 cells transfected
with antagomiR-342-3p exhibited a marked increase in cell
proliferation ability compared with the cells transfected with
antagomiR negative control (Fig. 3G and
H). Overall, these results indicate that the inhibition of
miR-342-3p promotes the proliferation of OSCC cells.
miR-342-3p directly targets LASP1 in
OSCC cells
Notably, LASP1, an oncogene implicated in the
initiation and progression of OSCC (22), was found to possess the putative
binding sites for miR-342-3p in its 3′-UTR (Fig. 4A). To determine the direct binding
between miR-342-3p and the 3′-UTR of LASP1, the WT LASP1 3′-UTR and
a 3′-UTR with mutations in the predicted miR-342-3p binding site
were cloned into a luciferase reporter plasmid. Luciferase reporter
assays showed that miR-342-3p overexpression significantly
suppressed the luciferase activity in the Tca8113 and SCC-9 cells
transfected with the WT 3′-UTR plasmid, whereas the enforced
expression miR-342-3p had little effect on the luciferase activity
in the cells transfected with plasmid carrying the mutant binding
site (Fig. 4B). Additionally,
miR-342-3p inhibition notably promoted the luciferase activity in
the Tca8113 and SCC-9 cells with the plasmid carrying the WT
3′-UTR, whereas the enhanced effect was substantially reverted when
the miR-342-3p binding sites on the plasmid were mutated,
suggesting that LASP1 is a direct target of miR-342-3p (Fig. 4C). Moreover, RT-qPCR and western blot
analysis revealed that miR-342-3p overexpression significantly
decreased the mRNA and protein expression of LASP1 in the Tca8113
and SCC-9 cells, while the inhibition of endogenous miR-342-3p
markedly increased LASP1 expression at the mRNA and protein levels
(Fig. 4D-G). Taken together, these
data indicate that miR-342-3p negatively regulates the expression
of LASP1 through directly targeting its 3′-UTR. The correlation
between miR-342-3p and LASP1 levels in clinical specimens was also
explored. A total of 10 pairs of tumor tissues and the adjacent
non-cancerous specimens from the same patients were collected, and
the expression of miR-342-3p and LASP1 mRNA was tested. As
demonstrated in Fig. 4H, when the
relative expression levels (OSCC/normal) of LASP1 were plotted
against those of miR-342-3p for each patient, a significant inverse
correlation was revealed (P<0.0053; R=−0.8011). These data
suggest that miR-342-3p downregulation is associated with the
increase in LASP1 in OSCC tumor tissues.
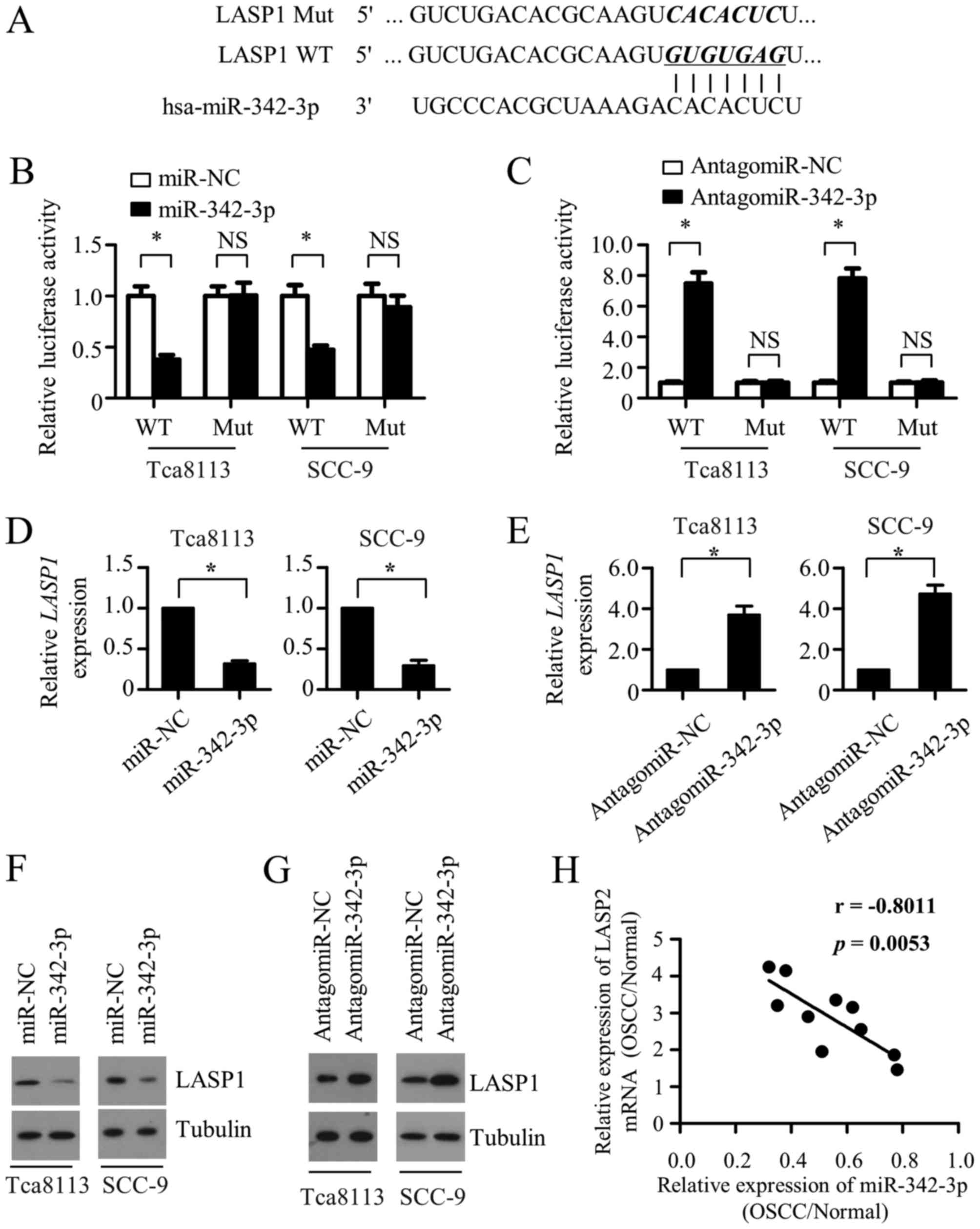 | Figure 4.miR-342-3p directly targets LASP1 in
OSCC cells. (A) Predicted miR-342-3p target sequence in the 3′-UTR
of LASP1 mRNA, and the WT and mutated versions used in the
luciferase reporter plasmids. Luciferase activity data (shown as
the mean ± SD of triplicate measurements) of (B) Tca8113 and SCC-9
cells transfected with WT or mutant LASP1 3′-UTR luciferase
reporter plasmid along with miR-NC or miR-342-3p, and (C) Tca8113
and SCC-9 cells co-transfected with antagomiR-NC or
antagomiR-342-3p and WT or mutant LASP1 3′-UTR luciferase reporter
vectors. Quantitative PCR was performed to detect the expression of
LASP1 mRNA in Tca8113 and SCC-9 cells transfected with (D) miR-NC
or miR-342-3p or (E) antagomiR-NC or antagomiR-342-3p. Expression
of LASP1 mRNA was normalized to GAPDH. Results are shown as the
mean ± SD of triplicate measurements. (F) Western blotting was used
to measure the expression of LASP1 protein in Tca8113 and SCC-9
cells transfected with (F) miR-NC or miR-342-3p or (G) antagomiR-NC
or antagomiR-342-3p. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. (H) A
statistically significant inverse correlation between miR-342-3p
expression and LASP1 mRNA in OSCC vs. normal tissues from the same
patient was observed following Pearson's correlation analysis
(R=−0.8011; P=0.0053). *P<0.05. miR, microRNA; LASP1, LIM and
SH3 protein 1; OSCC, oral squamous cell carcinoma; 3′-UTR, 3′
untranslated region; WT, wild-type; NC, negative control; SD,
standard deviation; NS, not significant. |
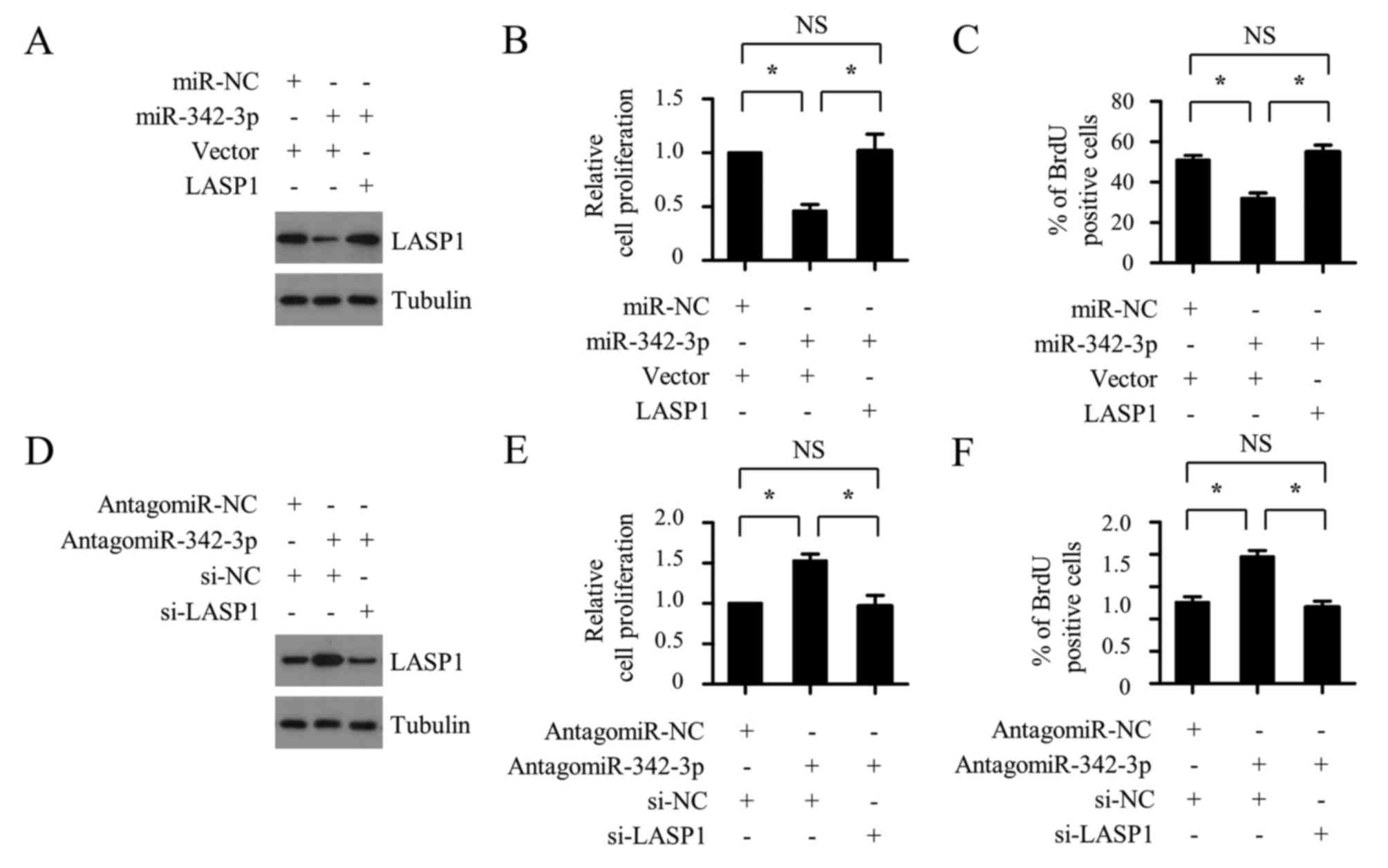
miR-342-3p suppresses the
proliferation of OSCC cells by inhibiting LASP1
To investigate whether miR-342-3p suppresses the
cell proliferation of OSCC cells by targeting LASP1, the
3′-UTR-deleted LASP1 plasmid was co-transfected with miR-342-3p
mimic into SCC-9 cells, and the cell proliferation ability was
determined using CCK-8 and BrdU-incorporation assays. As shown in
Fig. 5A-C, the miR-342-3p mimic
transfection resulted in decreased cell proliferation of OSCC
cells, whereas this inhibitory effect was completely reversed by
LASP1 plasmid transfection. Furthermore, LASP1 silencing with
siLASP1 markedly abrogated the SCC-9 cell proliferation increase
that was caused by miR-342-3p inhibition (Fig. 5D-F). These results support the
hypothesis that miR-342-3p targets LASP1 to inhibit the
proliferation of OSCC cells.
Discussion
Increasing evidence demonstrates that miRNA
deregulation serves a key role in carcinogenesis. Therefore, miRNAs
have been investigated extensively to identify novel diagnostic and
prognostic cancer biomarkers, and to aid the development of
effective therapeutic targets. In OSCC, various miRNAs are
abnormally expressed and participate in cancer initiation and
progression (23). For example,
miR-155 was reported to exhibit a significant upregulation in OSCC
tissues compared within their matched normal samples (24). Moreover, miR-155 promotes OSCC
development by downregulating tumor suppressor protein cell
division cycle 73 (25). By contrast,
miR-9 shows decreased expression in OSCC tissues and serves a
tumor-suppressor role by impairing the expression of miR-99a and
inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling (10).
Previous studies have reported the involvement of
miR-342-3p in different malignancies, including hepatocellular
carcinoma, cervical cancer and lung cancer (17–19,26–28).
However, the role of miR-342-3p in OSCC remains unknown. The
present study demonstrated that miR-342-3p exhibited decreased
expression in OSCC tissues when compared with that in adjacent
non-tumorous tissues, suggesting that miR-342-3p may serve a
tumor-suppressing role. Further experiments confirmed the
inhibitory role of miR-342-3p in the proliferation of OSCC cells,
as assessed by the CCK-8, colony formation and BrdU-incorporation
assays. Collectively, these tests indicate that miR-342-3p acts as
a tumor suppressor in OSCC, which is consistent with its role in a
number of tumors. Previous studies also revealed the crucial role
of miR-342-3p in tumor metastasis (18,19);
however, whether it affects the cell migration of OSCC cells
requires further investigation. It has been reported that miR-9,
99a and 491-5p are downregulated in OSCC and exhibit
tumor-suppressive activities (10–13). The
downregulation level of miR-342-3p was compared with those of
miR-9, 99a and 491-5p in OSCC tissues relative to normal tissues
and it was found to be analogous.
LASP1, a member of the LIM proteins, was initially
identified from a cDNA library of human breast cancer tissues
(29). LASP1 is ubiquitously
expressed in all normal tissues and participates in a wide spectrum
of cellular processes (30). A
growing number of studies suggest that LASP1 is overexpressed in
numerous malignant tumors and is correlated with poor clinical
prognoses for patients with different cancer types, including
ovarian, breast, bladder, NSCLC and colorectal cancer (31–35). LASP1
was reported to exhibit increased expression in patients with OSCC
and was significantly correlated with the primary tumor size
(22). Further study demonstrated
that LASP1 promotes OSCC cell proliferation through accelerating
cell-cycle progression (22).
However, the mechanism underlying LASP1 regulation remains to be
investigated. A growing body of evidence has revealed the critical
role of miRNAs in controlling LASP1 expression in an increasing
number of cancer types. For example, miR-203a-3p suppressed cell
proliferation and migration by directly targeting LASP1 in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma (36), and
miR-203 was reported to inhibit tumor proliferation by repressing
LASP1 expression in NSCLC (34). In
the present study, LASP1 was identified as a potential target gene
of miR-342-3p through bioinformatic prediction analysis. A
luciferase reporter assay revealed that miR-342-3p inhibited the
expression of LASP1 by directly binding to its 3′-UTR. RT-qPCR and
western blot analysis confirmed the suppressive role of miR-342-3p
in LASP1 expression. Furthermore, the present results demonstrated
that LASP1 overexpression effectively reversed the suppressive
effect of miR-342-3p on OSCC cell proliferation, validating the
functional significance of LASP1 in mediating the tumor suppressor
role of miR-342-3p. Although these studies demonstrate that
miR-342-3p inhibits OSCC cell proliferation by directly targeting
LASP1, the correlation between miR-342-3p and LASP1 expression in
clinical OSCC tissues remains to be investigated.
In summary, the present study demonstrated that
miR-342-3p functions as a tumor suppressor through downregulation
of LASP1 expression in OSCC. Novel insights into molecular
mechanisms regulating OSCC progression have been provided, as well
as a promising molecular target for the development of a novel,
more efficacious therapeutic approach for the treatment of patients
with OSCC.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Research
Program of Science and Technology of Baotou (grant no.
wsjj2011037).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
BC coordinated and designed the project, designed
the experiments and edited the manuscript. XS, YJ, MY and YZ
performed the experiments. XS and YJ analyzed the data and wrote
the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Ethics
Committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital, Inner Mongolia Medical
University (Baotou, Inner Mongolia, China). All participants
provided written informed consent.
Patient consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was
obtained from the patient.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
miR-342-3p
|
microRNA-342-3p
|
|
LASP1
|
LIM and SH3 protein 1
|
|
OSCC
|
oral squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
3′-UTR
|
3′-untranslated region
|
References
|
1
|
Scully C and Bagan J: Oral squamous cell
carcinoma: Overview of current understanding of aetiopathogenesis
and clinical implications. Oral Dis. 15:388–399. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ishida K, Tomita H, Nakashima T, Hirata A,
Tanaka T, Shibata T and Hara A: Current mouse models of oral
squamous cell carcinoma: Genetic and chemically induced models.
Oral Oncol. 73:16–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gharat SA, Momin M and Bhavsar C: Oral
squamous cell carcinoma: Current treatment strategies and
nanotechnology-based approaches for prevention and therapy. Crit
Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 33:363–400. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rupaimoole R, Calin GA, Lopez-Berestein G
and Sood AK: miRNA deregulation in cancer cells and the tumor
microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 6:235–246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ling H, Fabbri M and Calin GA: MicroRNAs
and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug
development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 12:847–865. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Reis PP, Tomenson M, Cervigne NK, Machado
J, Jurisica I, Pintilie M, Sukhai MA, Perez-Ordonez B, Grénman R,
Gilbert RW, et al: Programmed cell death 4 loss increases tumor
cell invasion and is regulated by miR-21 in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 9:2382010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang F, Zhao W, Zhou L, Zhang L, Liu Z
and Yu D: miR-222 regulates the cell biological behavior of oral
squamous cell carcinoma by targeting PUMA. Oncol Rep. 31:1255–1262.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shen L, Liu L, Ge L, Xie L, Liu S, Sang L,
Zhan T and Li H: miR-448 downregulates MPPED2 to promote cancer
proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 12:2747–2752. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu T, Liu K, Wu Y, Fan J, Chen J, Li C,
Yang Q and Wang Z: MicroRNA-9 inhibits the proliferation of oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells by suppressing expression of CXCR4
via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncogene. 33:5017–5027.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan B, Fu Q, Lai L, Tao X, Fei Y, Shen J,
Chen Z and Wang Q: Downregulation of microRNA 99a in oral squamous
cell carcinomas contributes to the growth and survival of oral
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 6:675–681. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yen YC, Shiah SG, Chu HC, Hsu YM, Hsiao
JR, Chang JY, Hung WC, Liao CT, Cheng AJ, Lu YC and Chen YW:
Reciprocal regulation of microRNA-99a and insulin-like growth
factor I receptor signaling in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.
Mol Cancer. 13:62014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang WC, Chan SH, Jang TH, Chang JW, Ko
YC, Yen TC, Chiang SL, Chiang WF, Shieh TY, Liao CT, et al:
miRNA-491-5p and GIT1 serve as modulators and biomarkers for oral
squamous cell carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res.
74:751–764. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Czimmerer Z, Varga T, Kiss M, Vázquez CO,
Doan-Xuan QM, Rückerl D, Tattikota SG, Yan X, Nagy ZS, Daniel B, et
al: The IL-4/STAT6 signaling axis establishes a conserved microRNA
signature in human and mouse macrophages regulating cell survival
via miR-342-3p. Genome Med. 8:632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang L, Xu L, Xu M, Liu G, Xing J, Sun C
and Ding H: Obesity-associated MiR-342-3p promotes adipogenesis of
mesenchymal stem cells by suppressing CtBP2 and releasing C/EBPα
from CtBP2 binding. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:2285–2298. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang M, Qing Y, Shi Q, Cao Y and Song K:
miR-342-3p elevates osteogenic differentiation of umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells via inhibiting Sufu in vitro. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 491:571–577. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao Y, Zhang SG, Wang ZH and Liao JC:
Down-regulation of miR-342-3p in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues
and its prognostic significance. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:2098–2102. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xue X, Fei X, Hou W, Zhang Y, Liu L and Hu
R: miR-342-3p suppresses cell proliferation and migration by
targeting AGR2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett.
412:170–178. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li XR, Chu HJ, Lv T, Wang L, Kong SF and
Dai SZ: miR-342-3p suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion
by targeting FOXM1 in human cervical cancer. FEBS Lett.
588:3298–3307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roberts KP, Ensrud KM and Hamilton DW: A
comparative analysis of expression and processing of the rat
epididymal fluid and sperm-bound forms of proteins D and E. Biol
Reprod. 67:525–533. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shimizu F, Shiiba M, Ogawara K, Kimura R,
Minakawa Y, Baba T, Yokota S, Nakashima D, Higo M, Kasamatsu A, et
al: Overexpression of LIM and SH3 Protein 1 leading to accelerated
G2/M phase transition contributes to enhanced tumourigenesis in
oral cancer. PLoS One. 8:e831872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Min A, Zhu C, Peng S, Rajthala S, Costea
DE and Sapkota D: MicroRNAs as important players and biomarkers in
oral carcinogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2015:1869042015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi LJ, Zhang CY, Zhou ZT, Ma JY, Liu Y,
Bao ZX and Jiang WW: MicroRNA-155 in oral squamous cell carcinoma:
Overexpression, localization, and prognostic potential. Head Neck.
37:970–976. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rather MI, Nagashri MN, Swamy SS, Gopinath
KS and Kumar A: Oncogenic microRNA-155 down-regulates tumor
suppressor CDC73 and promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma cell
proliferation: Implications for cancer therapeutics. J Biol Chem.
288:608–618. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao L and Zhang Y: miR-342-3p affects
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation via regulating NF-κB
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 457:370–377. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie X, Liu H, Wang M, Ding F, Xiao H, Hu
F, Hu R and Mei J: miR-342-3p targets RAP2B to suppress
proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Tumour Biol. 36:5031–5038. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tai MC, Kajino T, Nakatochi M, Arima C,
Shimada Y, Suzuki M, Miyoshi H, Yatabe Y, Yanagisawa K and
Takahashi T: miR-342-3p regulates MYC transcriptional activity via
direct repression of E2F1 in human lung cancer. Carcinogenesis.
36:1464–1473. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tomasetto C, Moog-Lutz C, Régnier CH,
Schreiber V, Basset P and Rio MC: Lasp-1 (MLN 50) defines a new LIM
protein subfamily characterized by the association of LIM and SH3
domains. FEBS Lett. 373:245–249. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Orth MF, Cazes A, Butt E and Grunewald TG:
An update on the LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 (LASP1): A versatile
structural, signaling, and biomarker protein. Oncotarget. 6:26–42.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Grunewald TG, Kammerer U, Winkler C,
Schindler D, Sickmann A, Honig A and Butt E: Overexpression of
LASP-1 mediates migration and proliferation of human ovarian cancer
cells and influences zyxin localisation. Br J Cancer. 96:296–305.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Grunewald TG, Kammerer U, Schulze E,
Schindler D, Honig A, Zimmer M and Butt E: Silencing of LASP-1
influences zyxin localization, inhibits proliferation and reduces
migration in breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 312:974–982. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Kawakami K,
Tatarano S, Uchida Y, Kawahara K, Nishiyama K, Seki N and Nakagawa
M: Functional role of LASP1 in cell viability and its regulation by
microRNAs in bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 30:434–443. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zheng J, Wang F, Lu S and Wang X: LASP-1,
regulated by miR-203, promotes tumor proliferation and
aggressiveness in human non-small cell lung cancer. Exp Mol Pathol.
100:116–124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao L, Wang H, Liu C, Liu Y, Wang X, Wang
S, Sun X, Li J, Deng Y, Jiang Y and Ding Y: Promotion of colorectal
cancer growth and metastasis by the LIM and SH3 domain protein 1.
Gut. 59:1226–1235. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang N, Jiang X, Chen Z, Song X, Wu L,
Zong D, Song D, Yin L, Wang D, Chen C, et al: MiR-203a-3p
suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis through inhibiting
LASP1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
36:1382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|