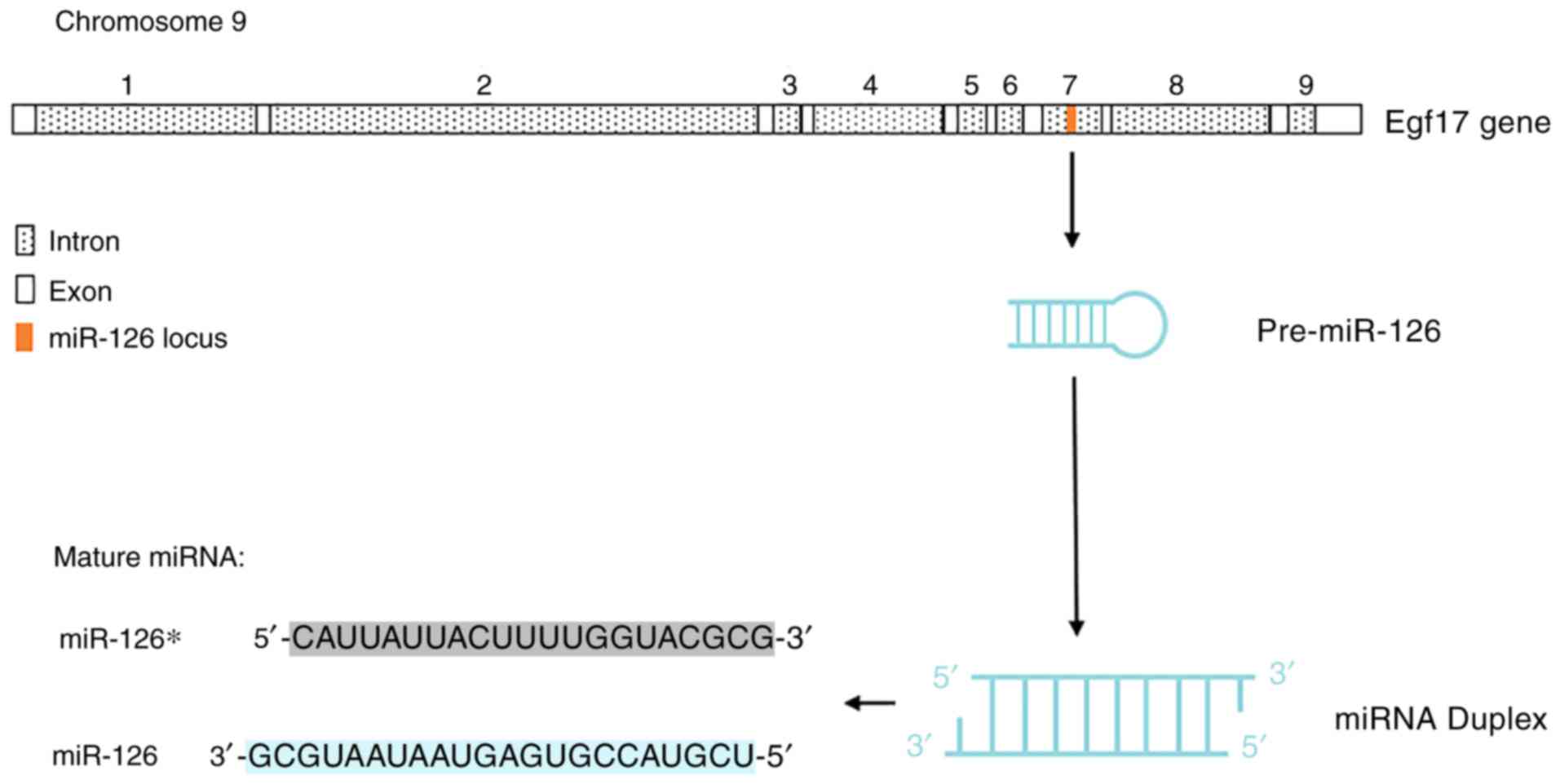
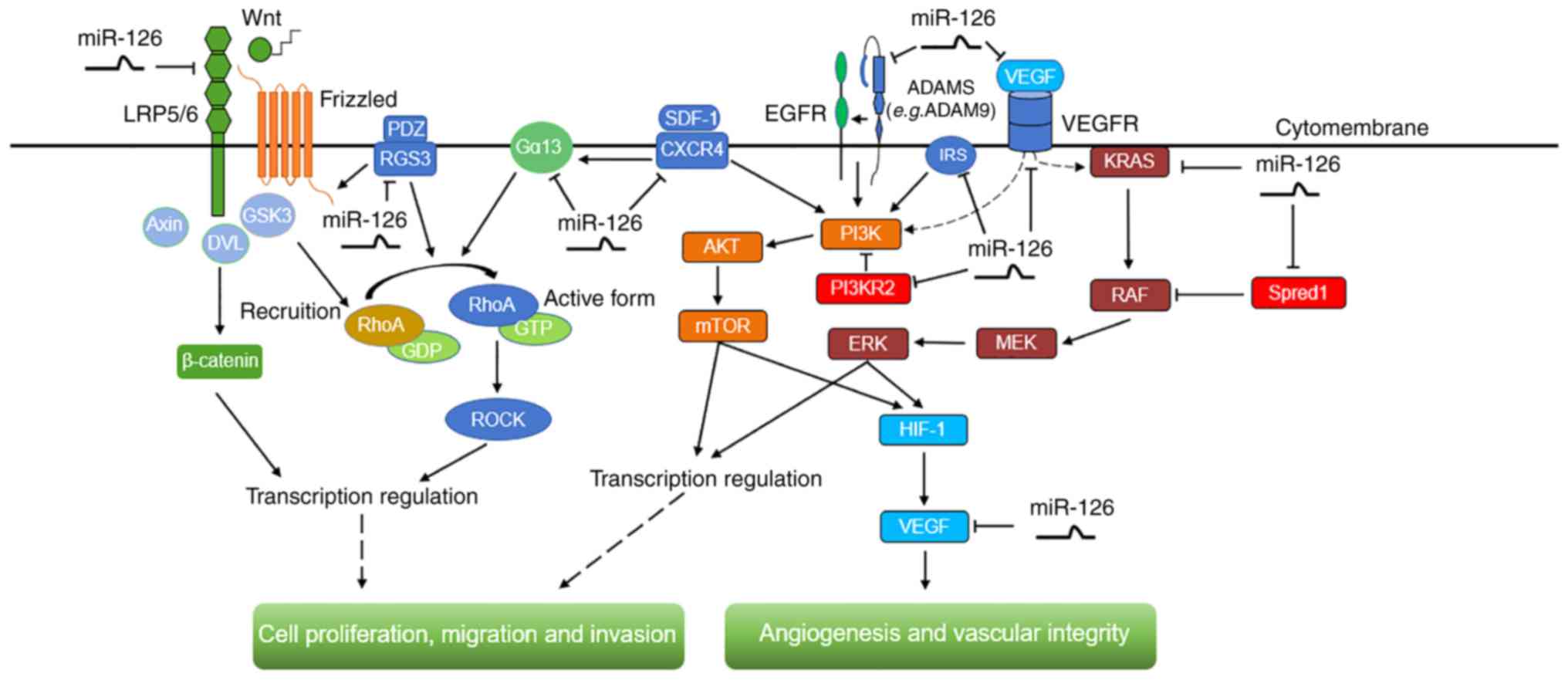
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang L, Huang J, Yang N, Greshock J,
Megraw MS, Giannakakis A, Liang S, Naylor TL, Barchetti A, Ward MR,
et al: MicroRNAs exhibit high frequency genomic alterations in
human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:9136–9141. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Di Leva G, Garofalo M and Croce CM:
MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 9:287–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moretti F, Thermann R and Hentze MW:
Mechanism of translational regulation by miR-2 from sites in the 5′
untranslated region or the open reading frame. RNA. 16:2493–2502.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Z, Li Z, Li Y and Zang A: MicroRNA
and signaling pathways in gastric cancer. Cancer Gene Ther.
21:305–316. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fish JE, Santoro MM, Morton SU, Yu S, Yeh
RF, Wythe JD, Ivey KN, Bruneau BG, Stainier DY and Srivastava D:
miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev
Cell. 15:272–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang S, Aurora AB, Johnson BA, Qi X,
McAnally J, Hill JA, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R and Olson EN: The
endothelial-specific microRNA miR-126 governs vascular integrity
and angiogenesis. Dev Cell. 15:261–271. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meister J and Schmidt MHH: miR-126 and
miR-126* New players in cancer. ScientificWorldJournal.
10:2090–2100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Soncin F, Mattot V, Lionneton F, Spruyt N,
Lepretre F, Begue A and Stehelin D: VE-statin, an endothelial
repressor of smooth muscle cell migration. EMBO J. 22:5700–5711.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Parker LH, Schmidt M, Jin SW, Gray AM,
Beis D, Pham T, Frantz G, Palmieri S, Hillan K, Stainier DY, et al:
The endothelial-cell-derived secreted factor Egfl7 regulates
vascular tube formation. Nature. 428:754–758. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Campagnolo L, Leahy A, Chitnis S,
Koschnick S, Fitch MJ, Fallon JT, Loskutoff D, Taubman MB and
Stuhlmann H: EGFL7 is a chemoattractant for endothelial cells and
is up-regulated in angiogenesis and arterial injury. Am J Pathol.
167:275–284. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Morgenbesser SD, Dufault MR, Martin TB,
Lim E, Callahan M, Weber W, Winter SF, McLaren RP, Richards B, Cook
BP, et al: Characterization of EGFL7 expression and function in
tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 65 Suppl
9:S11032005.
|
|
16
|
Hu MH, Ma CY, Wang XM, Ye CD, Zhang GX,
Chen L and Wang JG: MicroRNA-126 inhibits tumor proliferation and
angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by down-regulating EGFL7
expression. Oncotarget. 7:66922–66934. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harris TA, Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M, Mendell
JT and Lowenstein CJ: MicroRNA-126 regulates endothelial expression
of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:1516–1521. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang ST, Wang F, Shao M, Wang Y and Zhu
HQ: MicroRNA-126 suppresses inflammation in endothelial cells under
hyperglycemic condition by targeting HMGB1. Vascul Pharmacol.
88:48–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feng R, Chen X, Yu Y, Su L, Yu B, Li J,
Cai Q, Yan M, Liu B and Zhu Z: miR-126 functions as a tumour
suppressor in human gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 298:50–63. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ebrahimi F, Gopalan V, Smith RA and Lam
AK: miR-126 in human cancers: Clinical roles and current
perspectives. Exp Mol Pathol. 96:98–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A,
Iovino N, Aravin A, Pfeffer S, Rice A, Kamphorst AO, Landthaler M,
et al: A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA
library sequencing. Cell. 129:1401–1414. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A,
Meyer J, Lendeckel W and Tuschl T: Identification of
tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr Biol. 12:735–739. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu Y, Correa AM, Hoque A, Guan B, Ye F,
Huang J, Swisher SG, Wu TT, Ajani JA and Xu XC: Prognostic
significance of differentially expressed miRNAs in esophageal
cancer. Int J Cancer. 128:132–143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu SG, Qin XG, Zhao BS, Qi B, Yao WJ,
Wang TY, Li HC and Wu XN: Differential expression of miRNAs in
esophageal cancer tissue. Oncol Lett. 5:1639–1642. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu R, Gu J, Jiang P, Zheng Y, Liu X,
Jiang X, Huang E, Xiong S, Xu F, Liu G, et al: DNMT1-microRNA126
epigenetic circuit contributes to esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma growth via ADAM9-EGFR-AKT signaling. Clin Cancer Res.
21:854–863. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li H, Meng F, Ma J, Yu Y, Hua X, Qin J and
Li Y: Insulin receptor substrate-1 and Golgi phosphoprotein 3 are
downstream targets of miR-126 in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 32:1225–1233. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nie ZC, Weng WH, Li J, Xu YT and Li Z:
Down-regulation of miR-126 in esophageal carcinoma tissues and its
inhibition effect on proliferation and migration of esophageal
carcinoma cell line EC109. Tumor. 35:55–64. 2015.
|
|
29
|
Nie ZC, Weng WH, Shang YS, Long Y, Li J,
Xu YT and Li Z: MicroRNA-126 is down-regulated in human esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma and inhibits the proliferation and
migration in EC109 cell via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:4745–4754. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kong R, Ma Y, Feng J, Li S, Zhang W, Jiang
J, Zhang J, Qiao Z, Yang X and Zhou B: The crucial role of miR-126
on suppressing progression of esophageal cancer by targeting
VEGF-A. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 21:32016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li X, Wang F and Qi Y: miR-126 inhibits
the invasion of gastric cancer cell in part by targeting Crk. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:2031–2037. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yue S, Shi H, Han J, Zhang T, Zhu W and
Zhang D: Prognostic value of microRNA-126 and CRK expression in
gastric cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 9:6127–6135. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Otsubo T, Akiyama Y, Hashimoto Y, Shimada
S, Goto K and Yuasa Y: MicroRNA-126 inhibits SOX2 expression and
contributes to gastric carcinogenesis. PLoS One. 6:e166172011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang J, Chen X, Li P, Su L, Yu B, Cai Q,
Li J, Yu Y, Liu B and Zhu Z: CRKL promotes cell proliferation in
gastric cancer and is negatively regulated by miR-126. Chem Biol
Interact. 206:230–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen H, Li L, Wang S, Lei Y, Ge Q, Lv N,
Zhou X and Chen C: Reduced miR-126 expression facilitates
angiogenesis of gastric cancer through its regulation on VEGF-A.
Oncotarget. 5:11873–11885. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu LY, Wang W, Zhao LY, Guo B, Yang J,
Zhao XG, Hou N, Ni L, Wang AY, Song TS, et al: Mir-126 inhibits
growth of SGC-7901 cells by synergistically targeting the oncogenes
PI3KR2 and Crk, and the tumor suppressor PLK2. Int J Oncol.
45:1257–1265. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang J, Chen X, Su L, Li P, Cai Q, Liu B,
Wu W and Zhu Z: MicroRNA-126 inhibits cell proliferation in gastric
cancer by targeting LAT-1. Biomed Pharmacother. 72:66–73. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang Z, Wang R, Zhang T and Dong X:
MicroRNA-126 regulates migration and invasion of gastric cancer by
targeting CADM1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:8869–8880.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang P, Li Z, Liu H, Zhou D, Fu A and
Zhang E: MicroRNA-126 increases chemosensitivity in drug-resistant
gastric cancer cells by targeting EZH2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
479:91–96. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang J, Zhou Y, Fei X, Chen X, Yan J, Liu
B and Zhu Z: ADAM9 functions as a promoter of gastric cancer growth
which is negatively and post-transcriptionally regulated by
miR-126. Oncol Rep. 37:2033–2040. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang J, Zhou Y, Fei X, Chen X and Zhu Z:
Regulator of G-protein signaling 3 targeted by miR-126 correlates
with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients. Anticancer Drugs.
28:161–169. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Banerjee N, Kim H, Talcott S and
Mertens-Talcott S: Pomegranate polyphenolics suppressed
azoxymethane-induced colorectal aberrant crypt foci and
inflammation: Possible role of miR-126/VCAM-1 and
miR-126/PI3K/AKT/mTOR. Carcinogenesis. 34:2814–2822. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Guo C, Sah JF, Beard L, Willson JK,
Markowitz SD and Guda K: The noncoding RNA, miR-126, suppresses the
growth of neoplastic cells by targeting phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase signaling and is frequently lost in colon cancers. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 47:939–946. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hansen TF, Andersen CL, Nielsen BS,
Spindler KL, Sørensen FB, Lindebjerg J, Brandslund I and Jakobsen
A: Elevated microRNA-126 is associated with high vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 2 expression levels and high
microvessel density in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 2:1101–1106.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang Y, Wang X, Xu B, Wang B, Wang Z,
Liang Y, Zhou J, Hu J and Jiang B: Epigenetic silencing of miR-126
contributes to tumor invasion and angiogenesis in colorectal
cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:1976–1984. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yuan W, Guo YQ, Li XY, Deng MZ, Shen ZH,
Bo CB, Dai YF, Huang MY, Yang ZY, Quan YS, et al: MicroRNA-126
inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting
the chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 and Ras homolog gene family,
member A, signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 7:60230–60244. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu Y, Zhou Y, Feng X, An P, Quan X, Wang
H, Ye S, Yu C, He Y and Luo H: MicroRNA-126 functions as a tumor
suppressor in colorectal cancer cells by targeting CXCR4 via the
AKT and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 44:203–210. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li N, Tang A, Huang S, Li Z, Li X, Shen S,
Ma J and Wang X: miR-126 suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation
and invasion via inhibiting RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Mol Cell
Biochem. 380:107–119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhou Y, Feng X, Liu YL, Ye SC, Wang H, Tan
WK, Tian T, Qiu YM and Luo HS: Down-regulation of miR-126 is
associated with colorectal cancer cells proliferation, migration
and invasion by targeting IRS-1 via the AKT and ERK1/2 signaling
pathways. PLoS One. 8:e812032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li N, Li X, Huang S, Shen S and Wang X:
miR-126 inhibits colon cancer proliferation and invasion through
targeting IRS1, SLC7A5 and TOM1 gene. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi
Xue Ban. 38:809–817. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Du C, Lv Z, Cao L, Ding C, Gyabaah OA, Xie
H, Zhou L, Wu J and Zheng S: miR-126-3p suppresses tumor metastasis
and angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting LRP6 and
PIK3R2. J Transl Med. 12:2592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao C, Li Y, Zhang M, Yang Y and Chang L:
miR-126 inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells partially by targeting Sox2. Hum
Cell. 28:91–99. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ji JS, Xu M, Song JJ, Zhao ZW, Chen MJ,
Chen WQ, Tu JF and Yang XM: Inhibition of microRNA-126 promotes the
expression of Spred1 to inhibit angiogenesis in hepatocellular
carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization: In vivo
study. Onco Targets Ther. 9:4357–4367. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gong C, Fang J, Li G, Liu HH and Liu ZS:
Effects of microRNA-126 on cell proliferation, apoptosis and tumor
angiogenesis via the down-regulating ERK signaling pathway by
targeting EGFL7 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:52527–52542. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Xiang LY, Ou HH, Liu XC, Chen ZJ, Li XH,
Huang Y and Yang DH: Loss of tumor suppressor miR-126 contributes
to the development of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular
carcinoma metastasis through the upregulation of ADAM9. Tumor Biol.
39:10104283177091282017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Hamada S, Satoh K, Fujibuchi W, Hirota M,
Kanno A, Unno J, Masamune A, Kikuta K, Kume K and Shimosegawa T:
miR-126 acts as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer cells via
the regulation of ADAM9. Mol Cancer Res. 10:3–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jiao LR, Frampton AE, Jacob J, Pellegrino
L, Krell J, Giamas G, Tsim N, Vlavianos P, Cohen P, Ahmad R, et al:
MicroRNAs targeting oncogenes are down-regulated in pancreatic
malignant transformation from benign tumors. PLoS One.
7:e320682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Feng SD, Mao Z, Liu C, Nie YS, Sun B, Guo
M and Su C: Simultaneous overexpression of miR-126 and miR-34a
induces a superior antitumor efficacy in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Onco Targets Ther. 10:5591–5604. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Pagano F, De Marinis E, Grignani F and
Nervi C: Epigenetic role of miRNAs in normal and leukemic
hematopoiesis. Epigenomics. 5:539–552. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yan J, Dang Y, Liu S, Zhang Y and Zhang G:
LncRNA HOTAIR promotes cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer by
targeting miR-126 to activate the PI3K/AKT/MRP1 genes. Tumor Biol.
37:16345–16355. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Wang XY, Wu MH, Liu F, Li Y, Li N, Li GY
and Shen SR: Differential miRNA expression and their target genes
between NGX6-positive and negative colon cancer cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 345:283–290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang JH, Chen XT, Wen ZS, Zheng M, Deng
JM, Wang MZ, Lin HX, Chen K, Li J, Yun JP, et al: High expression
of GOLPH3 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma correlates with
poor prognosis. PLoS One. 7:e456222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Shi CS, Huang NN and Kehrl JH: Regulator
of G-protein signaling 3 isoform 1 (PDZ-RGS3) enhances canonical
Wnt signaling and promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition. J
Biol Chem. 287:33480–33487. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Singh SK, Chen NM, Hessmann E, Siveke J,
Lahmann M, Singh G, Voelker N, Vogt S, Esposito I, Schmidt A, et
al: Antithetical NFATc1-Sox2 and p53-miR200 signaling networks
govern pancreatic cancer cell plasticity. EMBO J. 34:517–530. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liu H, Wang S and Huang C: VEGFA+936C/T
and −634G/C polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk: A meta-analysis.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:1979–1983. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Crawford M, Brawner E, Batte K, Yu L,
Hunter MG, Otterson GA, Nuovo G, Marsh CB and Nana-Sinkam SP:
MicroRNA-126 inhibits invasion in non-small cell lung carcinoma
cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 373:607–612. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Xiong Y, Kotian S, Zeiger MA, Zhang L and
Kebebew E: miR-126-3p inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth and
metastasis, and is associated with aggressive thyroid cancer. PLoS
One. 10:e01304962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shi B, Sepp-Lorenzino L, Prisco M, Linsley
P, deAngelis T and Baserga R: Micro RNA 145 targets the insulin
receptor substrate-1 and inhibits the growth of colon cancer cells.
J Biol Chem. 282:32582–32590. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hara T, Jones MF, Subramanian M, Li XL, Ou
O, Zhu Y, Yang Y, Wakefield LM, Hussain SP, Gaedcke J, et al:
Selective targeting of KRAS-mutant cells by miR-126 through
repression of multiple genes essential for the survival of
KRAS-mutant cells. Oncotarget. 5:7635–7650. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Otsubo T, Akiyama Y, Yanagihara K and
Yuasa Y: SOX2 is frequently downregulated in gastric cancers and
inhibits cell growth through cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Br J
Cancer. 98:824–831. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Osaki M, Oshimura M and Ito H: PI3K-Akt
pathway: Its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Okumura E, Fukuhara T, Yoshida H, Hanada
Si S, Kozutsumi R, Mori M, Tachibana K and Kishimoto T: Akt
inhibits Myt1 in the signalling pathway that leads to meiotic
G2/M-phase transition. Nat Cell Biol. 4:111–116. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xu WH, Zhang JB, Dang Z, Li X, Zhou T, Liu
J, Wang DS, Song WJ and Dou KF: Long non-coding RNA URHC regulates
cell proliferation and apoptosis via ZAK through the ERK/MAPK
signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci.
10:664–676. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wang SC, Lin JK, Wang HS, Yang SH, Li AF
and Chang SC: Nuclear expression of CXCR4 is associated with
advanced colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 25:1185–1191.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Li Z, Li N, Wu M, Li X, Luo Z and Wang X:
Expression of miR-126 suppresses migration and invasion of colon
cancer cells by targeting CXCR4. Mol Cell Biochem. 381:233–242.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wolfe A, Thomas A, Edwards G, Jaseja R,
Guo GL and Apte U: Increased activation of the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in spontaneous hepatocellular carcinoma observed in
farnesoid X receptor knockout mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
338:12–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Huang J, Xiao D, Li G, Ma J, Chen P, Yuan
W, Hou F, Ge J, Zhong M, Tang Y, et al: EphA2 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 33:2737–2747. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yanaka Y, Muramatsu T, Uetake H, Kozaki K
and Inazawa J: miR-544a induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
through the activation of WNT signaling pathway in gastric cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 36:1363–1371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Germano G, Allavena P and Mantovani A:
Cytokines as a key component of cancer-related inflammation.
Cytokine. 43:374–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ma J, Liu J, Wang Z, Gu X, Fan Y, Zhang W,
Xu L, Zhang J and Cai D: NF-kappaB-dependent microRNA-425
upregulation promotes gastric cancer cell growth by targeting PTEN
upon IL-1β induction. Mol Cancer. 13:402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Sun Z, Meng C, Wang S, Zhou N, Guan M, Bai
C, Lu S, Han Q and Zhao RC: MicroRNA-1246 enhances migration and
invasion through CADM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer.
14:6162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang JL, Hu Y, Kong X, Wang ZH, Chen HY,
Xu J and Fang JY: Candidate microRNA biomarkers in human gastric
cancer: A systematic review and validation study. PLoS One.
8:e736832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Barshack I, Meiri E, Rosenwald S, Lebanony
D, Bronfeld M, Aviel-Ronen S, Rosenblatt K, Polak-Charcon S,
Leizerman I, Ezagouri M, et al: Differential diagnosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma from metastatic tumors in the liver using
microRNA expression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:1355–1362. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Fidler IJ: The pathogenesis of cancer
metastasis: The ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:453–458. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Hansen TF, Sørensen FB, Lindebjerg J and
Jakobsen A: The predictive value of microRNA-126 in relation to
first line treatment with capecitabine and oxaliplatin in patients
with metastatic colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 12:832012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Ding J, Wu K and
Fan D: Survival prediction of gastric cancer by a seven-microRNA
signature. Gut. 59:579–585. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Budhu A, Jia HL, Forgues M, Liu CG,
Goldstein D, Lam A, Zanetti KA, Ye QH, Qin LX, Croce CM, et al:
Identification of metastasis-related microRNAs in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 47:897–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Feng R, Sah BK, Beeharry MK, Yuan F, Su L,
Jin X, Yan M, Liu B, Li C and Zhu Z: Dysregulation of miR-126/Crk
protein axis predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients.
Cancer Biomark. 21:335–343. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Yin J, Bai Z, Song J, Yang Y, Wang J, Han
W, Zhang J, Meng H, Ma X, Yang Y, et al: Differential expression of
serum miR-126, miR-141 and miR-21 as novel biomarkers for early
detection of liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Chin J Cancer
Res. 26:95–103. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Li H, Zhang H, Lu G, Li Q, Gu J, Song Y,
Gao S and Ding Y: Mechanism analysis of colorectal cancer according
to the microRNA expression profile. Oncol Lett. 12:2329–2336. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Imamura T, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Miyamae
M, Okajima W, Ohashi T, Kiuchi J, Nishibeppu K, Konishi H, Shiozaki
A, et al: Depleted tumor suppressor miR-107 in plasma relates to
tumor progression and is a novel therapeutic target in pancreatic
cancer. Sci Rep. 7:57082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Ghosh A, Ghosh A, Datta S, Dasgupta D, Das
S, Ray S, Gupta S, Datta S, Chowdhury A, Chatterjee R, et al:
Hepatic miR-126 is a potential plasma biomarker for detection of
hepatitis B virus infected hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
138:2732–2744. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhou W, Yang W, Ma J, Zhang H, Li Z, Zhang
L, Liu J, Han Z, Wang H and Hong L: Role of miR-483 in digestive
tract cancers: From basic research to clinical value. J Cancer.
9:407–414. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Wu XM, Shao XQ, Meng XX, Zhang XN, Zhu L,
Liu SX, Lin J and Xiao HS: Genome-wide analysis of microRNA and
mRNA expression signatures in hydroxycamptothecin-resistant gastric
cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:259–269. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Borel F, Konstantinova P and Jansen PL:
Diagnostic and therapeutic potential of miRNA signatures in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 56:1371–1383.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Liang G, Zhu Y, Jing A, Wang J, Hu F, Feng
W, Xiao Z and Chen B: Cationic microRNA-delivering nanocarriers for
efficient treatment of colon carcinoma in xenograft model. Gene
Ther. 23:829–838. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Zhang Y, Wang Z and Gemeinhart RA:
Progress in microRNA delivery. J Control Release. 172:962–974.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Li XM, Wang AM, Zhang J and Yi H:
Down-regulation of miR-126 expression in colorectal cancer and its
clinical significance. Med Oncol. 28:1054–1057. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|