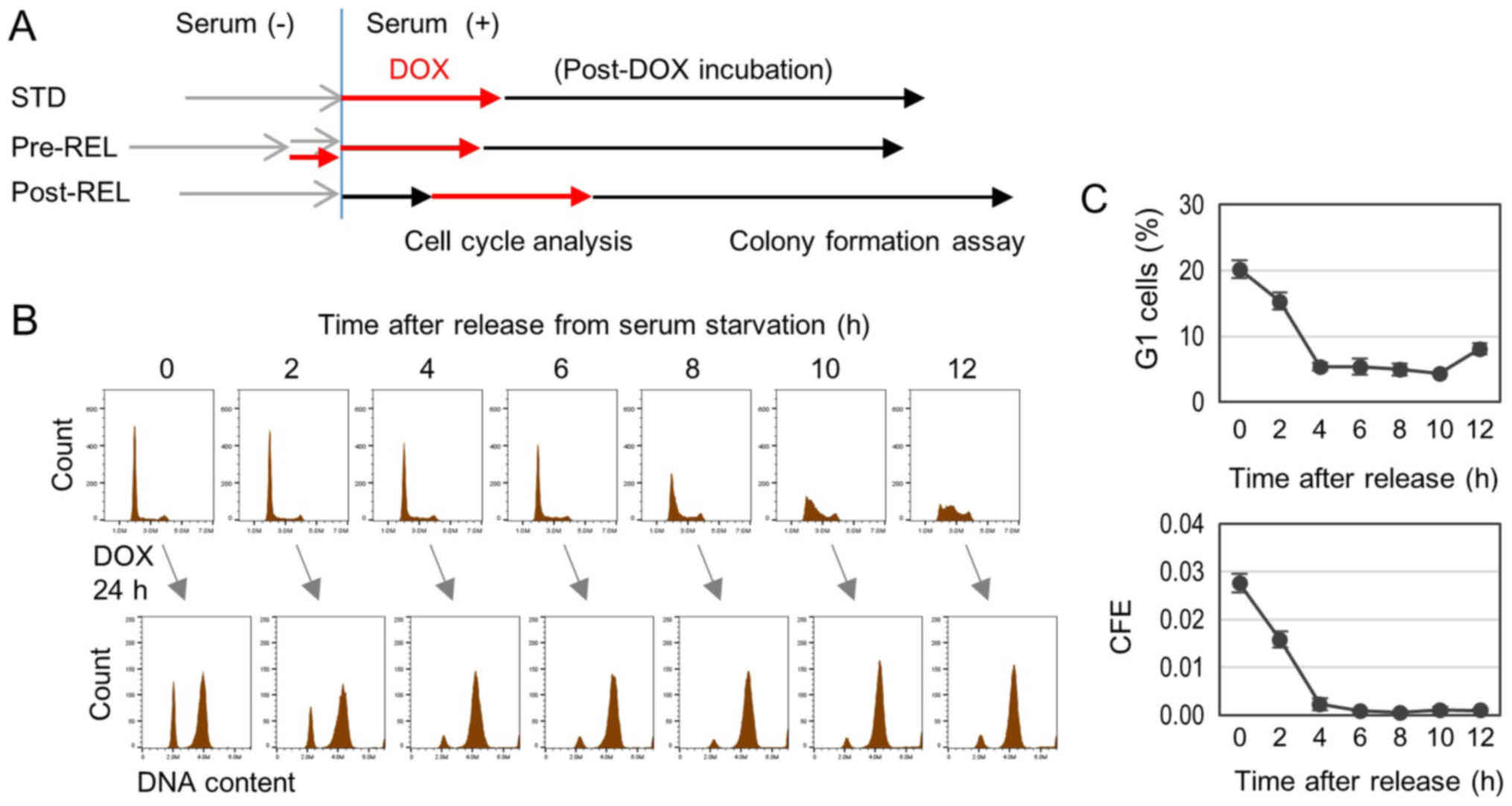
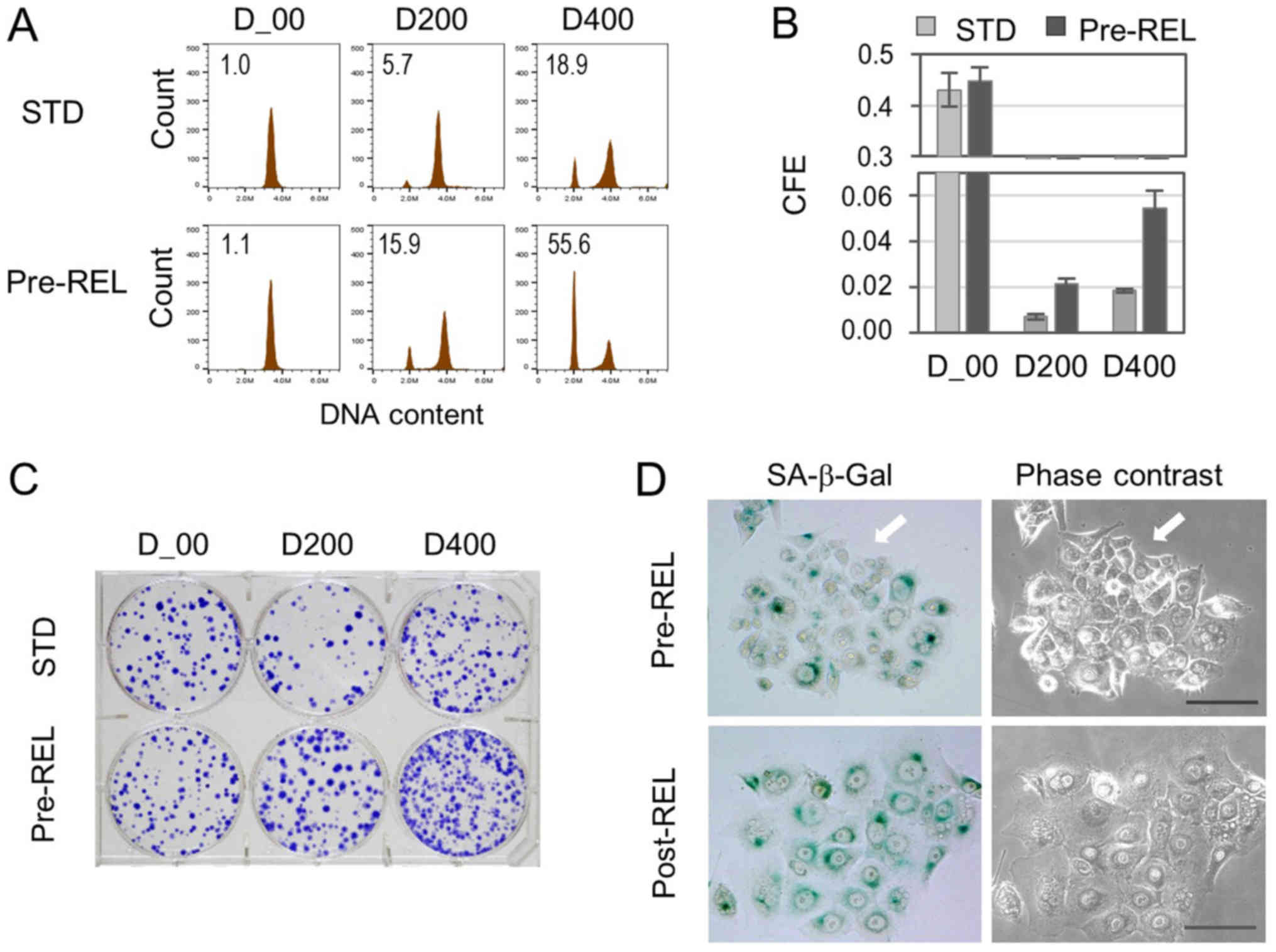
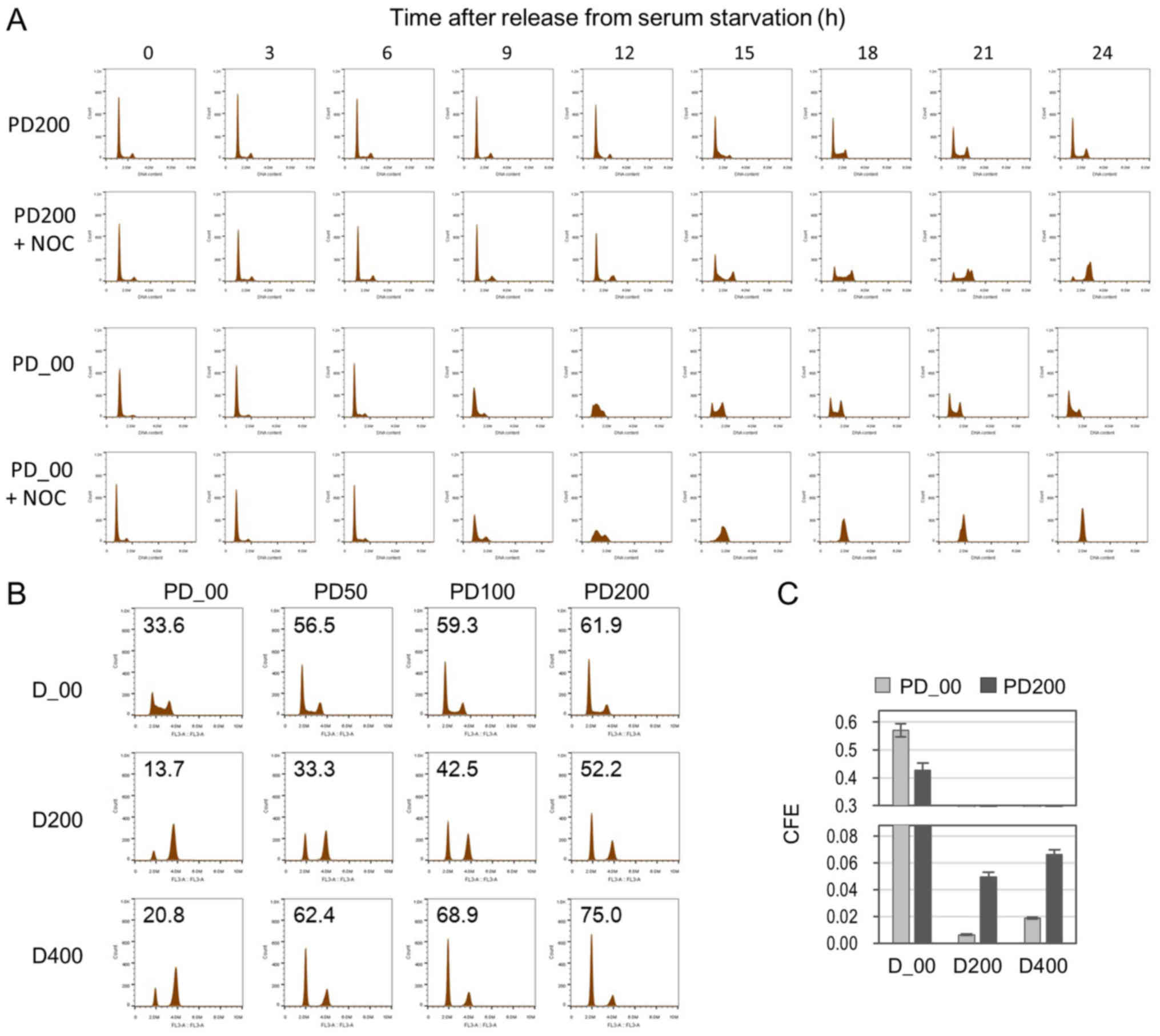
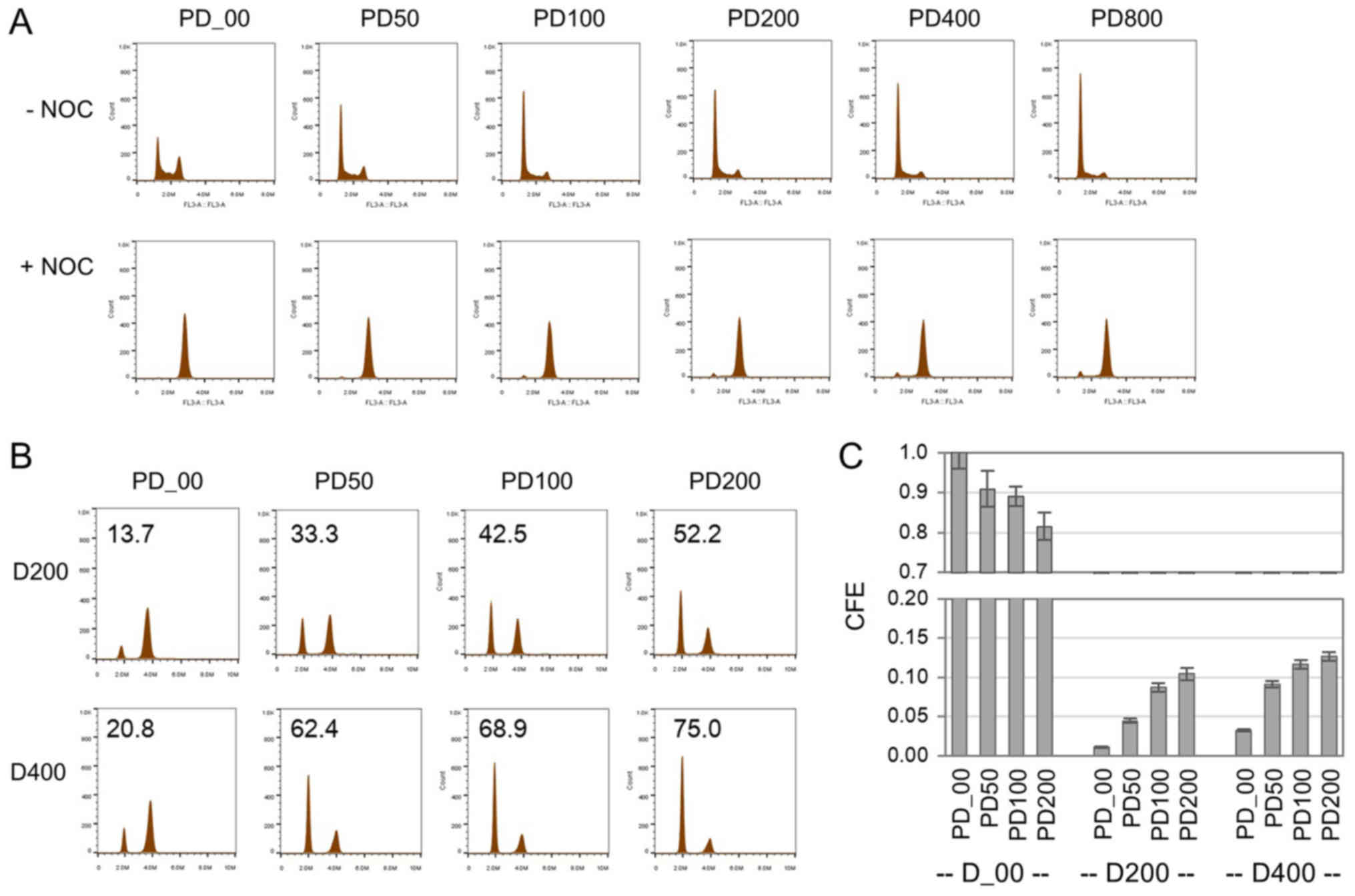
|
1
|
Campisi J: Senescent cells, tumor
suppression, and organismal aging: Good citizens, bad neighbors.
Cell. 120:513–522. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Collado M and Serrano M: The power and the
promise of oncogene-induced senescence markers. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:472–476. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Di Mitri D and Alimonti A:
Non-cell-autonomous regulation of cellular senescence in cancer.
Trends Cell Biol. 26:215–226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang X, Tsao SW, Wong YC and Cheung AL:
Induction of senescent-like growth arrest as a new target in
anticancer treatment. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 3:153–159. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tchkonia T, Zhu Y, van Deursen J, Campisi
J and Kirkland JL: Cellular senescence and the senescent secretory
phenotype: Therapeutic opportunities. J Clin Invest. 123:966–972.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ewald JA, Desotelle JA, Wilding G and
Jarrard DF: Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 102:1536–1546. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Petrova NV, Velichko AK, Razin SV and
Kantidze OL: Small molecule compounds that induce cellular
senescence. Aging Cell. 15:999–1017. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Elmore LW, Rehder CW, Di X, McChesney PA,
Jackson-Cook CK, Gewirtz DA and Holt SE: Adriamycin-induced
senescence in breast tumor cells involves functional p53 and
telomere dysfunction. J Biol Chem. 277:35509–35515. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sliwinska MA, Mosieniak G, Wolanin K,
Babik A, Piwocka K, Magalska A, Szczepanowska J, Fronk J and Sikora
E: Induction of senescence with doxorubicin leads to increased
genomic instability of HCT116 cells. Mech Ageing Dev. 130:24–32.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Su D, Zhu S, Han X, Feng Y, Huang H, Ren
G, Pan L, Zhang Y, Lu J and Huang B: BMP4-Smad signaling pathway
mediates adriamycin-induced premature senescence in lung cancer
cells. J Biol Chem. 284:12153–12164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hamilton E and Infante JR: Targeting
CDK4/6 in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 45:129–138. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu H, Yu S, Liu Q, Yuan X, Mani S, Pestell
RG and Wu K: Recent advances of highly selective CDK4/6 inhibitors
in breast cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 10:972017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: CDK inhibitors:
Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes
Dev. 13:1501–1512. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Malumbres M, Ortega S and Barbacid M:
Genetic analysis of mammalian cyclin-dependent kinases and their
inhibitors. Biol Chem. 381:827–838. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fry DW, Harvey PJ, Keller PR, Elliott WL,
Meade M, Trachet E, Albassam M, Zheng X, Leopold WR, Pryer NK, et
al: Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD
0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor
xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:1427–1438. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Toogood PL, Harvey PJ, Repine JT, Sheehan
DJ, VanderWel SN, Zhou H, Keller PR, McNamara DJ, Sherry D, Zhu T,
et al: Discovery of a potent and selective inhibitor of
cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6. J Med Chem. 48:2388–2406. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guha M: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors
move into Phase III. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11:892–894. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kovatcheva M, Liu DD, Dickson MA, Klein
ME, O'Connor R, Wilder FO, Socci ND, Tap WD, Schwartz GK, Singer S,
et al: MDM2 turnover and expression of ATRX determine the choice
between quiescence and senescence in response to CDK4 inhibition.
Oncotarget. 6:8226–8243. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ziemke EK, Dosch JS, Maust JD, Shettigar
A, Sen A, Welling TH, Hardiman KM and Sebolt-Leopold JS:
Sensitivity of KRAS-mutant colorectal cancers to combination
therapy that cotargets MEK and CDK4/6. Clin Cancer Res. 22:405–414.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chang BD, Xuan Y, Broude EV, Zhu H, Schott
B, Fang J and Roninson IB: Role of p53 and p21waf1/cip1 in
senescence-like terminal proliferation arrest induced in human
tumor cells by chemotherapeutic drugs. Oncogene. 18:4808–4818.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ben-Porath I and Weinberg RA: The signals
and pathways activating cellular senescence. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 37:961–976. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, Acosta M, Scott
G, Roskelley C, Medrano EE, Linskens M, Rubelj I and Pereira-Smith
O: A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and
in aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:9363–9367. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Trzepacz C, Lowy AM, Kordich JJ and Groden
J: Phosphorylation of the tumor suppressor adenomatous polyposis
coli (APC) by the cyclin-dependent kinase p34. J Biol Chem.
272:21681–21684. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mizuno H, Nakanishi Y, Ishii N, Sarai A
and Kitada K: A signature-based method for indexing cell cycle
phase distribution from microarray profiles. BMC Genomics.
10:1372009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zieve GW, Turnbull D, Mullins JM and
McIntosh JR: Production of large numbers of mitotic mammalian cells
by use of the reversible microtubule inhibitor nocodazole.
Nocodazole accumulated mitotic cells. Exp Cell Res. 126:397–405.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Long BH and Fairchild CR: Paclitaxel
inhibits progression of mitotic cells to G1 phase by interference
with spindle formation without affecting other microtubule
functions during anaphase and telephase. Cancer Res. 54:4355–4361.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Erol A: Deciphering the intricate
regulatory mechanisms for the cellular choice between cell repair,
apoptosis or senescence in response to damaging signals. Cell
Signal. 23:1076–1081. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Roos WP, Thomas AD and Kaina B: DNA damage
and the balance between survival and death in cancer biology. Nat
Rev Cancer. 16:20–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen X, Lowe M, Herliczek T, Hall MJ,
Danes C, Lawrence DA and Keyomarsi K: Protection of normal
proliferating cells against chemotherapy by staurosporine-mediated,
selective, and reversible G(1) arrest. J Natl Cancer Inst.
92:1999–2008. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Blagosklonny MV and Pardee AB: Exploiting
cancer cell cycling for selective protection of normal cells.
Cancer Res. 61:4301–4305. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|