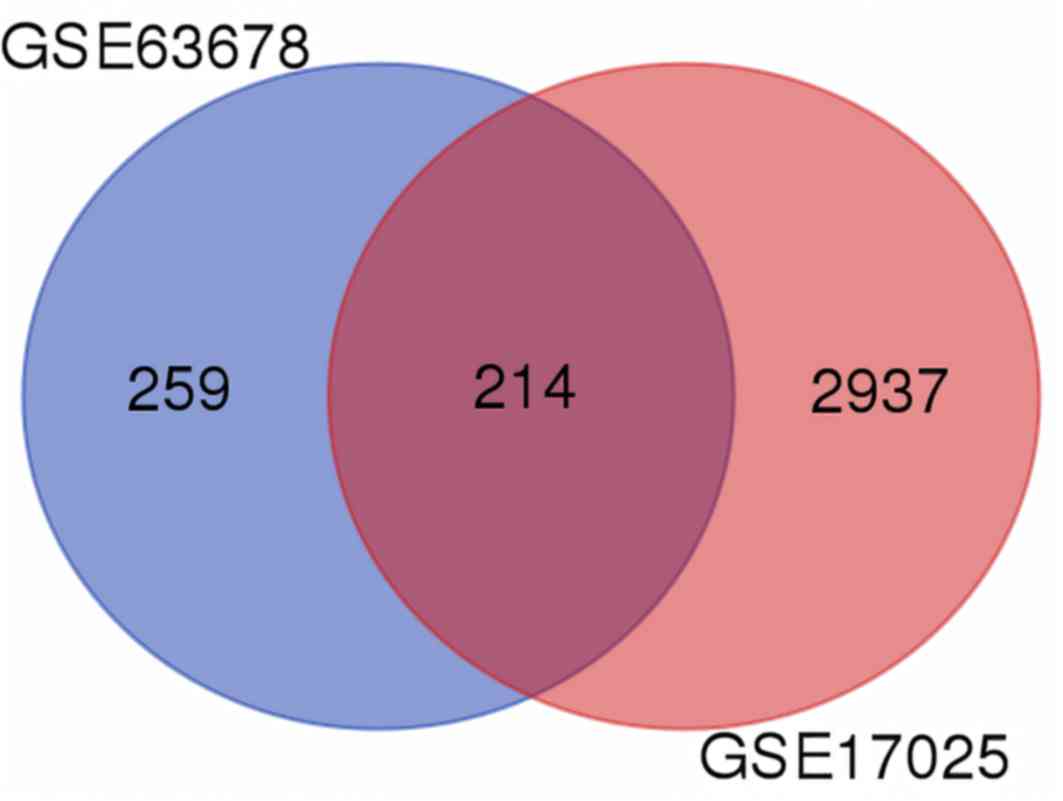
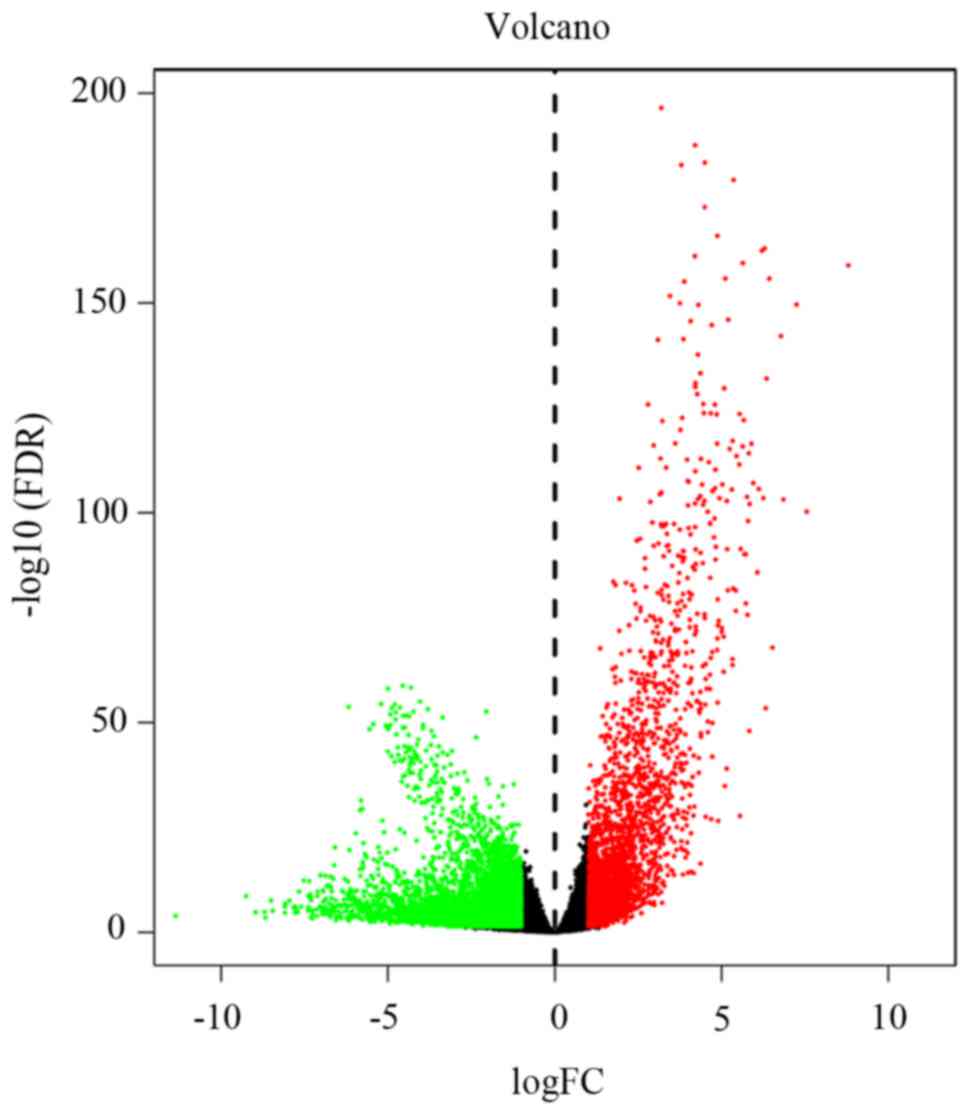
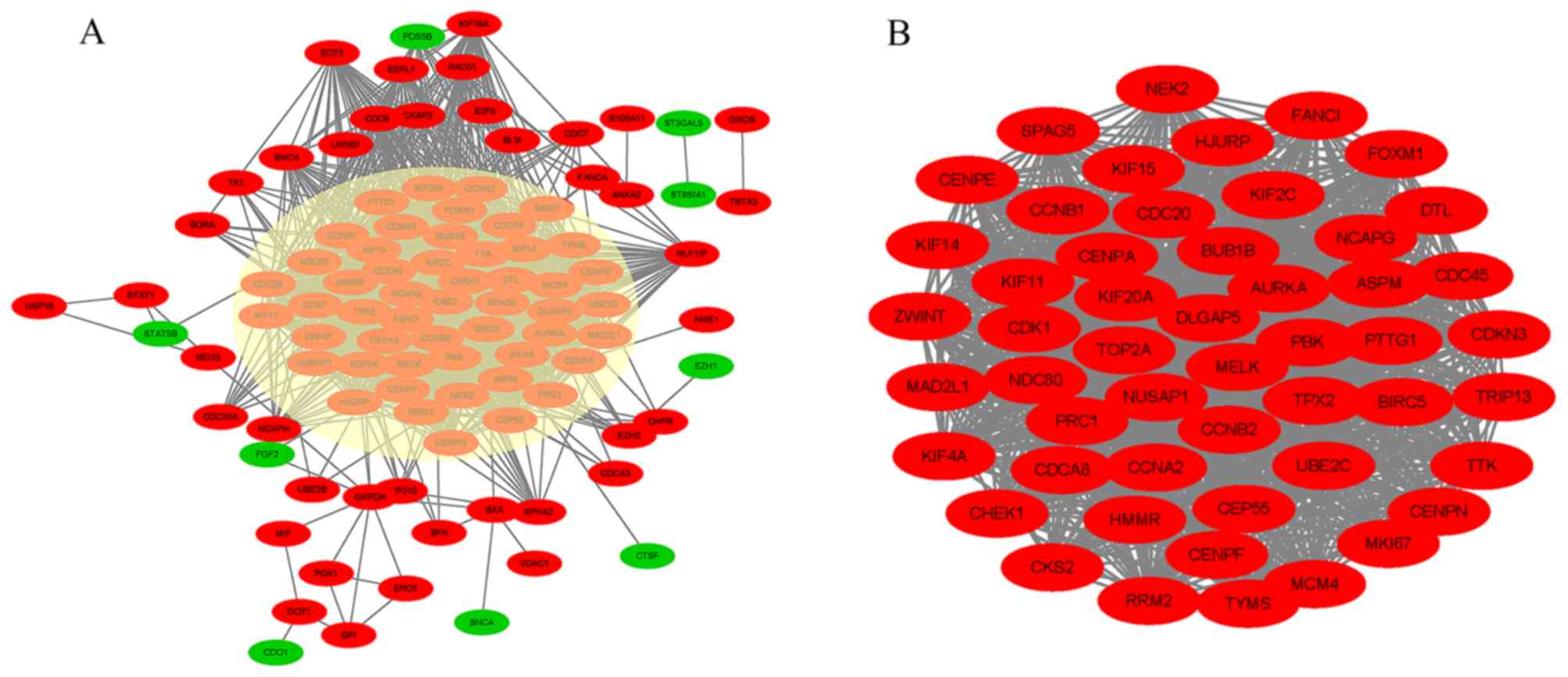
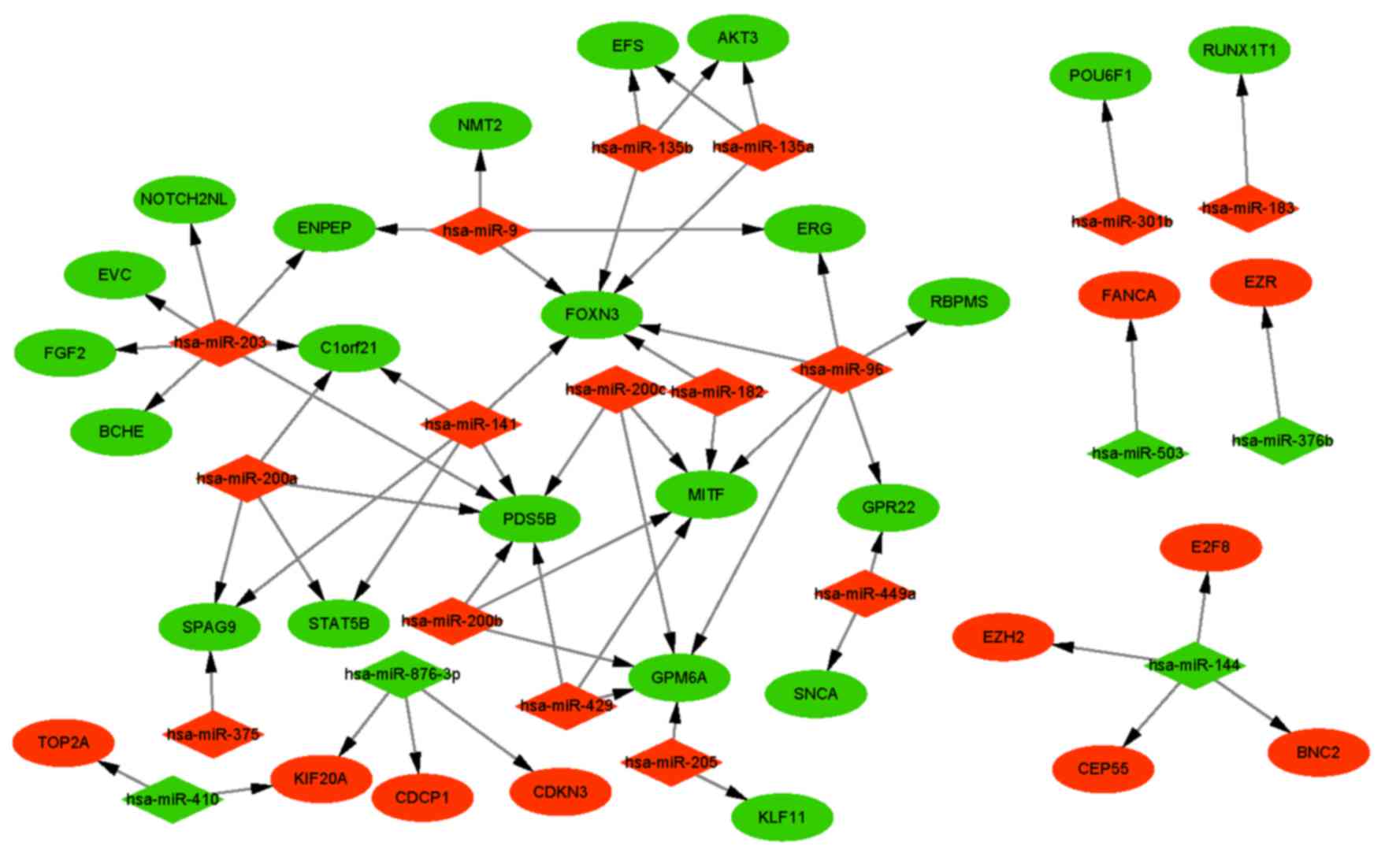
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu
VE, Zhou S, Diaz LA Jr and Kinzler KW: Cancer genome landscapes.
Science. 339:1546–1558. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mehrgou A and Akouchekian M: Therapeutic
impacts of microRNAs in breast cancer by their roles in regulating
processes involved in this disease. J Res Med Sci. 22:1302017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dong P, Konno Y, Watari H, Hosaka M,
Noguchi M and Sakuragi N: The impact of microRNA-mediated PI3K/AKT
signaling on epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness
in endometrial cancer. J Transl Med. 12:2312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ramón LA, Braza-Boïls A, Gilabert J,
Chirivella M, España F, Estellés A and Gilabert-Estellés J:
microRNAs related to angiogenesis are dysregulated in endometrioid
endometrial cancer. Hum Reprod. 27:3036–3045. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Devor EJ, Miecznikowski J, Schickling BM,
Gonzalez-Bosquet J, Lankes HA, Thaker P, Argenta PA, Pearl ML,
Zweizig SL, Mannel RS, et al: Dysregulation of miR-181c expression
influences recurrence of endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma by
modulating NOTCH2 expression: An NRG oncology/gynecologic oncology
group study. Gynecol Oncol. 147:648–653. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Day RS, McDade KK, Chandran UR, Lisovich
A, Conrads TP, Hood BL, Kolli VS, Kirchner D, Litzi T and Maxwell
GL: Identifier mapping performance for integrating transcriptomics
and proteomics experimental results. BMC Bioinformatics.
12:2132011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pappa KI, Polyzos A, Jacob-Hirsch J,
Amariglio N, Vlachos GD, Loutradis D and Anagnou NP: Profiling of
discrete gynecological cancers reveals novel transcriptional
modules and common features shared by other cancer types and
embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 10:e01422292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wilson CL and Miller CJ: Simpleaffy: A
BioConductor package for affymetrix quality control and data
analysis. Bioinformatics. 21:3683–3685. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hardcastle TJ: Generalized empirical
Bayesian methods for discovery of differential data in
high-throughput biology. Bioinformatics. 32:195–202.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:D362–D368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X and Li
T: miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:D105–D110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Anaya J: OncoLnc: Linking TCGA survival
data to mRNAs, miRNAs, and lncRNAs. PeerJ Computer Science.
2:e672016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Suh DS, Park SE, Jin H, Lee K and Bae J:
LRIG2 is a growth suppressor of Hec-1A and Ishikawa endometrial
adenocarcinoma cells by regulating PI3K/AKT- and EGFR-mediated
apoptosis and cell-cycle. Oncogenesis. 7:32018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shyam H, Singh N, Kaushik S, Sharma R and
Balapure AK: Centchroman induces redox-dependent apoptosis and
cell-cycle arrest in human endometrial cancer cells. Apoptosis.
22:570–584. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nosaka K, Iwanaga M, Imaizumi Y, Ishitsuka
K, Ishizawa K, Ishida Y, Amano M, Ishida T, Uike N, Utsunomiya A,
et al: Epidemiological and clinical features of adult T-cell
leukemia-lymphoma in Japan, 2010–2011: A nationwide survey. Cancer
Sci. 108:2478–2486. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsuura E, Nozuma S, Tashiro Y, Kubota R,
Izumo S and Takashima H: HTLV-1 associated myelopathy/tropical
spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP): A comparative study to identify
factors that influence disease progression. J Neurol Sci.
371:112–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee R and Schwartz RA: Human
T-lymphotrophic virus type 1-associated infective dermatitis: A
comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 64:152–160. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kamoi K and Mochizuki M: HTLV-1 uveitis.
Front Microbiol. 3:2702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Strickler HD, Rattray C, Escoffery C,
Manns A, Schiffman MH, Brown C, Cranston B, Hanchard B, Palefsky JM
and Blattner WA: Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I and severe
neoplasia of the cervix in Jamaica. Int J Cancer. 61:23–26. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Imamura N, Inada T, Tagaya Y, Yodoi J and
Kuramoto A: Association between ATL and non-hematopoietic
neoplasms. Hematol Oncol. 11:127–137. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao TM, Bryant MA, Kindt TJ and Simpson
RM: Monoclonally integrated HTLV type 1 in epithelial cancers from
rabbits infected with an HTLV type 1 molecular clone. AIDS Res Hum
Retroviruses. 18:253–258. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma J, Li D, Kong FF, Yang D, Yang H and Ma
XX: miR-302a-5p/367-3p-HMGA2 axis regulates malignant processes
during endometrial cancer development. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Srivastava SK, Ahmad A, Zubair H, Miree O,
Singh S, Rocconi RP, Scalici J and Singh AP: MicroRNAs in
gynecological cancers: Small molecules with big implications.
Cancer Lett. 407:123–138. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chi Y, Jin Q, Liu X, Xu L, He X, Shen Y,
Zhou Q, Zhang J and Jin M: miR-203 inhibits cell proliferation,
invasion, and migration of non-small-cell lung cancer by
downregulating RGS17. Cancer Sci. 108:2366–2372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fernández C, Bellosillo B, Ferraro M,
Seoane A, Sánchez-González B, Pairet S, Pons A, Barranco L, Vela
MC, Gimeno E, et al: MicroRNAs 142-3p, miR-155 and miR-203 are
deregulated in gastric MALT lymphomas compared to chronic
gastritis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 14:75–82. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu SQ, Niu WY, Li YP, Huang HB and Zhan R:
miR-203 inhibits cell growth and regulates G1/S transition by
targeting Bmi-1 in myeloma cells. Mol Med Rep. 14:4795–4801. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xiaohong Z, Lichun F, Na X, Kejian Z,
Xiaolan X and Shaosheng W: MiR-203 promotes the growth and
migration of ovarian cancer cells by enhancing glycolytic pathway.
Tumour Biol. 37:14989–14997. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang YW, Kuo CT, Chen JH, Goodfellow PJ,
Huang TH, Rader JS and Uyar DS: Hypermethylation of miR-203 in
endometrial carcinomas. Gynecol Oncol. 133:340–345. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Benati M, Montagnana M, Danese E, Paviati
E, Giudici S, Franchi M and Lippi G: Evaluation of mir-203
expression levels and DNA promoter methylation status in serum of
patients with endometrial cancer. Clin Lab. 63:1675–1681. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Machackova T, Mlcochova H, Stanik M,
Dolezel J, Fedorko M, Pacik D, Poprach A, Svoboda M and Slaby O:
MiR-429 is linked to metastasis and poor prognosis in renal cell
carcinoma by affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Tumour
Biol. 37:14653–14658. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Peng G, Liao Y and Shen C: miRNA-429
inhibits astrocytoma proliferation and invasion by targeting BMI1.
Pathol Oncol Res. 23:369–376. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu D, Xia P, Diao D, Cheng Y, Zhang H,
Yuan D, Huang C and Dang C: MiRNA-429 suppresses the growth of
gastric cancer cells in vitro. J Biomed Res. 26:389–393. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu L, Li Q, Xu D, Wang Q, An Y, Du Q,
Zhang J, Zhu Y and Miao Y: Hsa-miR-141 downregulates TM4SF1 to
inhibit pancreatic cancer cell invasion and migration. Int J Oncol.
44:459–466. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Menschikowski M, Hagelgans A, Nacke B,
Jandeck C, Sukocheva O and Siegert G: Epigenetic control of
phospholipase A2 receptor expression in mammary cancer cells. BMC
Cancer. 15:9712015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee JW, Park YA, Choi JJ, Lee YY, Kim CJ,
Choi C, Kim TJ, Lee NW, Kim BG and Bae DS: The expression of the
miRNA-200 family in endometrial endometrioid carcinoma. Gynecol
Oncol. 120:56–62. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu Q, Liu M, Zhang J, Xue L, Zhang G, Hu
C, Wang Z, He S, Chen L, Ma K, et al: Overexpression of KLF4
promotes cell senescence through microRNA-203-survivin-p21 pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:60290–60302. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang D, Liu E, Kang J, Yang X and Liu H:
MiR-3613-3p affects cell proliferation and cell cycle in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:93014–93028.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chuwa AH, Sone K, Oda K, Ikeda Y, Fukuda
T, Wada-Hiraike O, Inaba K, Makii C, Takeuchi M, Oki S, et al:
Significance of survivin as a prognostic factor and a therapeutic
target in endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 141:564–569. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li S, Liu X, Liu T, Meng X, Yin X, Fang C,
Huang D, Cao Y, Weng H, Zeng X and Wang X: Identification of
biomarkers correlated with the TNM staging and overall survival of
patients with bladder cancer. Front Physiol. 8:9472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cao R, Wang G, Qian K, Chen L, Qian G, Xie
C, Dan HC, Jiang W, Wu M, Wu CL, et al: Silencing of HJURP induces
dysregulation of cell cycle and ROS metabolism in bladder cancer
cells via PPARγ-SIRT1 feedback loop. J Cancer. 8:2282–2295. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hu B, Wang Q, Wang Y, Chen J, Li P and Han
M: Holliday junction-recognizing protein promotes cell
proliferation and correlates with unfavorable clinical outcome of
hepatocellular carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 10:2601–2607. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|