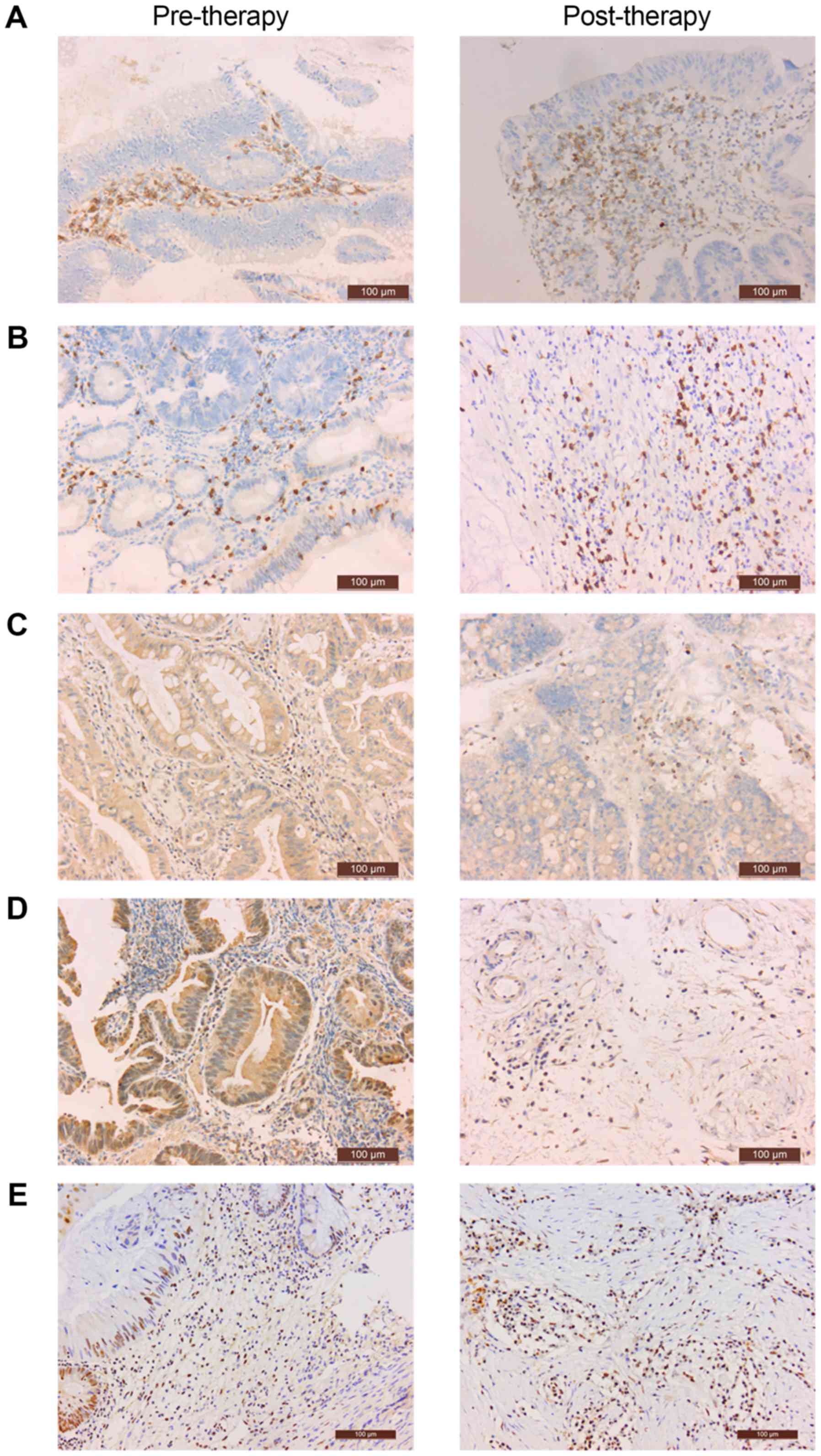
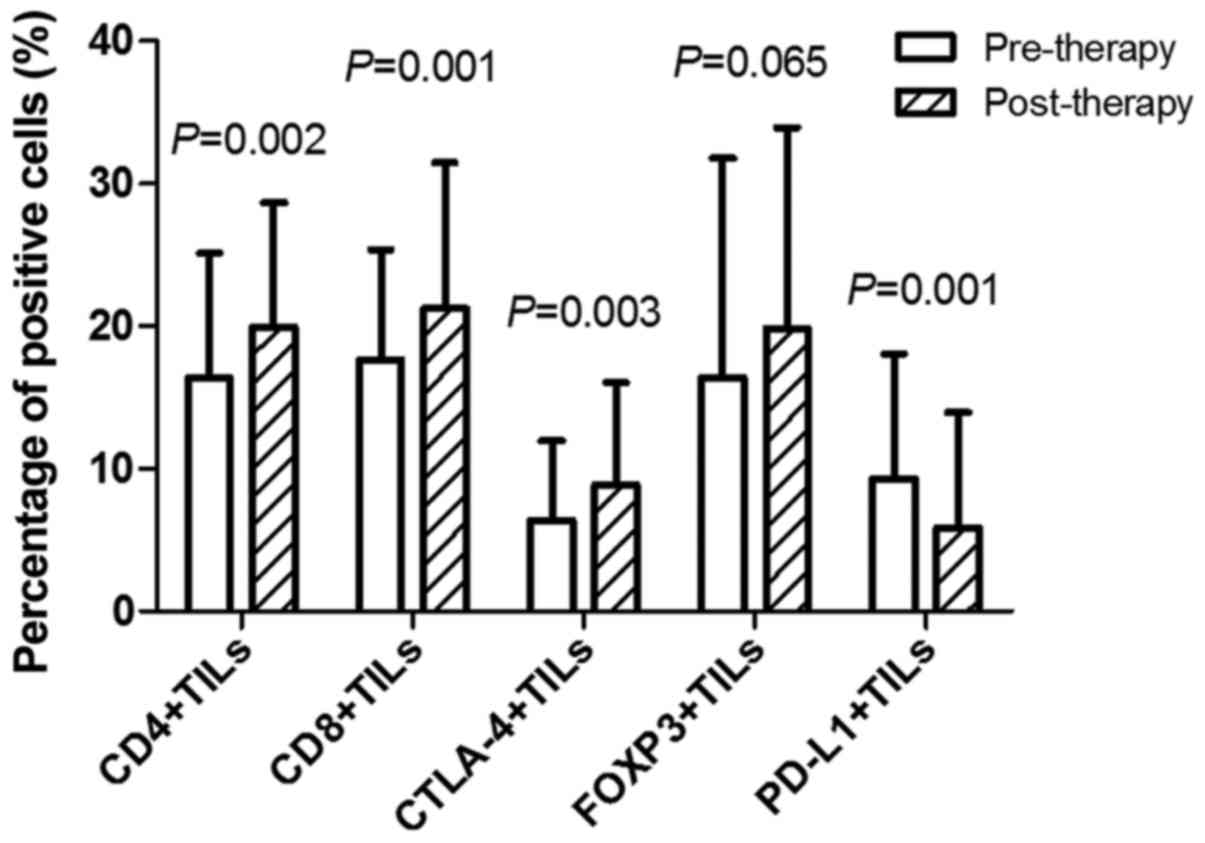
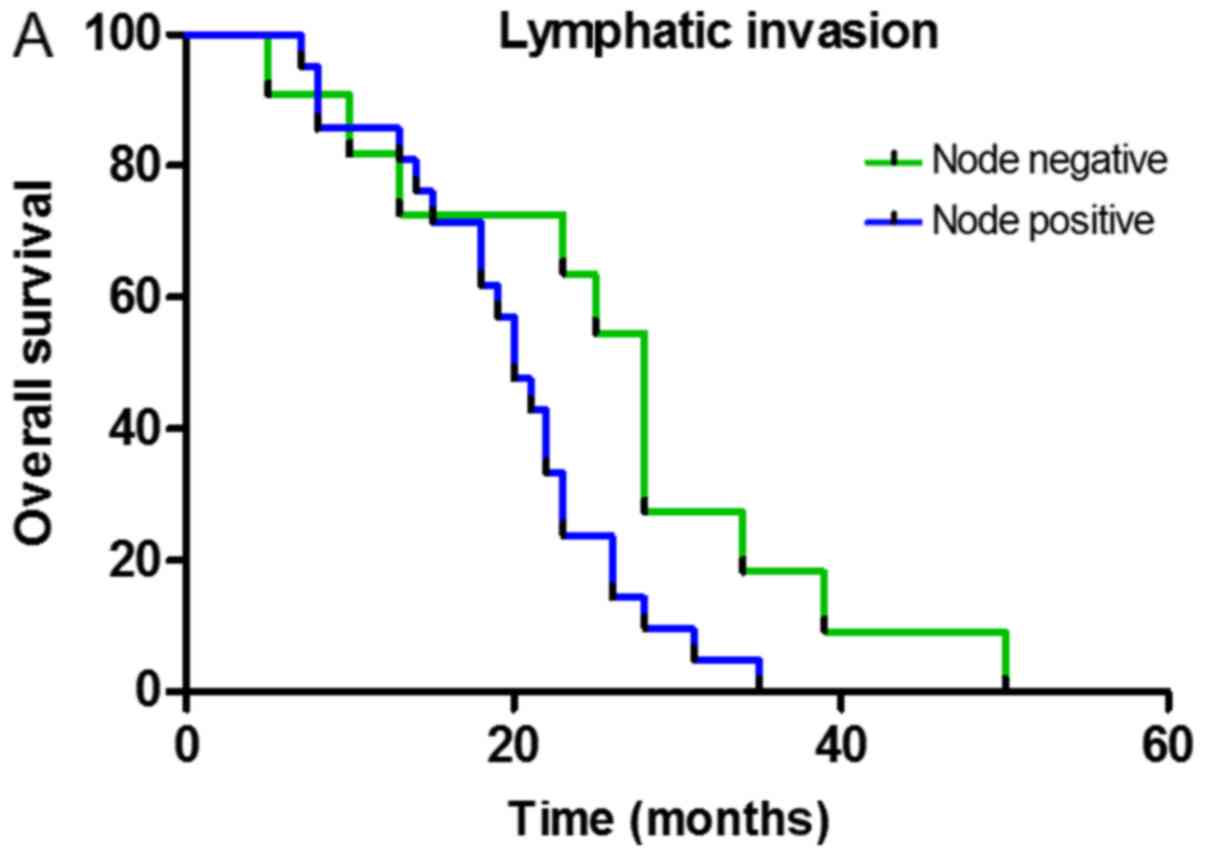
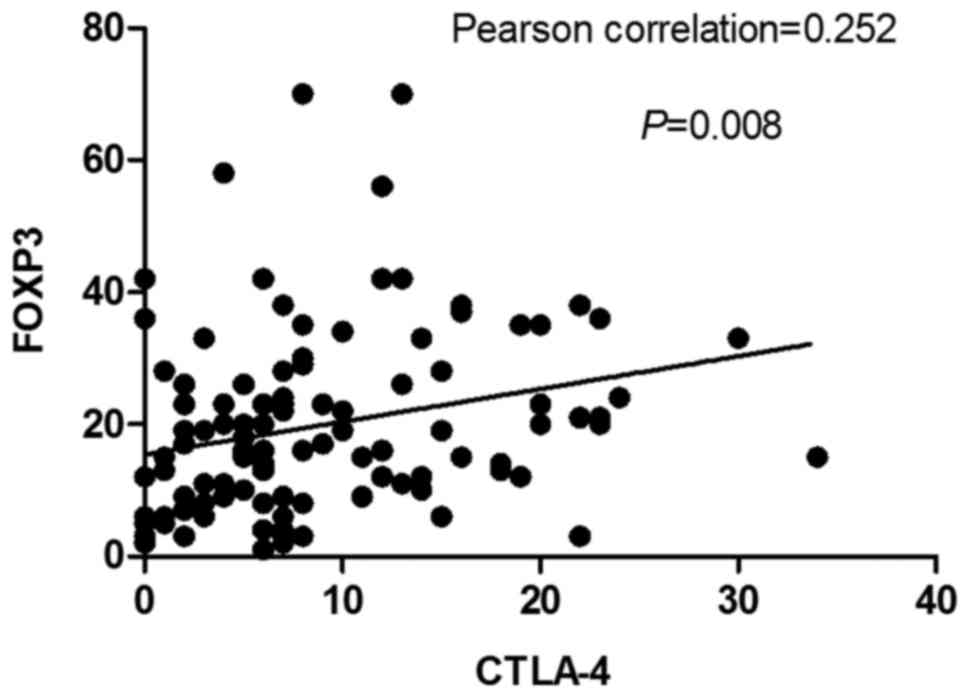
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paget S: The distribution of secondary
growths in cancer of the breast. 1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
8:98–101. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Albini A, Magnani E and Noonan DM: The
tumor microenvironment: Biology of a complex cellular and tissue
society. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 54:244–248. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kumamoto Y, Mattei LM, Sellers S, Payne GW
and Iwasaki A: CD4+ T cells support cytotoxic T lymphocyte priming
by controlling lymph node input. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:8749–8754. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hori S, Nomura T and Sakaguchi S: Control
of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3.
Science. 299:1057–1061. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Grossman WJ, Verbsky JW, Barchet W,
Colonna M, Atkinson JP and Ley TJ: Human T regulatory cells can use
the perforin pathway to cause autologous target cell death.
Immunity. 21:589–601. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Paust S, Lu L, McCarty N and Cantor H:
Engagement of B7 on effector T cells by regulatory T cells prevents
autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:10398–10403. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
von Boehmer H: Mechanisms of suppression
by suppressor T cells. Nat Immunol. 6:338–344. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chaudhary B, Khaled YS, Ammori BJ and
Elkord E: Neuropilin 1: Function and therapeutic potential in
cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 63:81–99. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bloch O, Crane CA, Kaur R, Safaee M,
Rutkowski MJ and Parsa AT: Gliomas promote immunosuppression
through induction of B7-H1 expression in tumor-associated
macrophages. Clin Cancer Res. 19:3165–3175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu B, Chen L, Liu L, Zhu Y, Wu C, Jiang J
and Zhang X: T-cell-mediated tumor immune surveillance and
expression of B7 co-inhibitory molecules in cancers of the upper
gastrointestinal tract. Immunol Res. 50:269–275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brunner MC, Chambers CA, Chan FK, Hanke J,
Winoto A and Allison JP: CTLA-4-Mediated inhibition of early events
of T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 162:5813–5820. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salvi S, Fontana V, Boccardo S, Merlo DF,
Margallo E, Laurent S, Morabito A, Rijavec E, Dal Bello MG, Mora M,
et al: Evaluation of CTLA-4 expression and relevance as a novel
prognostic factor in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 61:1463–1472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Karabon L, Markiewicz M, Kosmaczewska A,
Partyka A, Pawlak-Adamska E, Tomkiewicz A, Ciszak L, Jagoda K,
Dzierzak-Mietla M, Kyrcz-Krzemien S and Frydecka I: Pretransplant
donor and recipient CTLA-4 mRNA and protein levels as a prognostic
marker for aGvHD in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell
transplantation. Immunol Lett. 165:52–59. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zou W and Chen L: Inhibitory B7-family
molecules in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol.
8:467–477. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe
AH: PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 26:677–704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sabatier R, Finetti P, Mamessier E,
Adelaide J, Chaffanet M, Ali HR, Viens P, Caldas C, Birnbaum D and
Bertucci F: Prognostic and predictive value of PDL1 expression in
breast cancer. Oncotarget. 6:5449–5464. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shen JK, Cote GM, Choy E, Yang P, Harmon
D, Schwab J, Nielsen GP, Chebib I, Ferrone S, Wang X, et al:
Programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in osteosarcoma. Cancer
Immunol Res. 2:690–698. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Curiel TJ, Wei S, Dong H, Alvarez X, Cheng
P, Mottram P, Krzysiek R, Knutson KL, Daniel B, Zimmermann MC, et
al: Blockade of B7-H1 improves myeloid dendritic cell-mediated
antitumor immunity. Nat Med. 9:562–567. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang L, Gajewski TF and Kline J:
PD-1/PD-L1 interactions inhibit antitumor immune responses in a
murine acute myeloid leukemia model. Blood. 114:1545–1552. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dworak O, Keilholz L and Hoffmann A:
Pathological features of rectal cancer after preoperative
radiochemotherapy. Int J Colorectal Dis. 12:19–23. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kalbasi A, June CH, Haas N and Vapiwala N:
Radiation and immunotherapy: A synergistic combination. J Clin
Invest. 123:2756–2763. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yasuda K, Nirei T, Sunami E, Nagawa H and
Kitayama J: Density of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T lymphocytes in biopsy
samples can be a predictor of pathological response to
chemoradiotherapy (CRT) for rectal cancer. Radiat Oncol. 6:492011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Garcia-Martinez E, Gil GL, Benito AC,
González-Billalabeitia E, Conesa MA, García García T, García-Garre
E, Vicente V and de la Peña Ayala F: Tumor-infiltrating immune cell
profiles and their change after neoadjuvant chemotherapy predict
response and prognosis of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
16:4882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang J and Guo Z: Immune escape of tumor.
Chin J Cancer Biother. 4:315–317. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Rettig L, Seidenberg S, Parvanova I,
Samaras P, Curioni A, Knuth A and Pascolo S: Gemcitabine depletes
regulatory T-cells in human and mice and enhances triggering of
vaccine-specific cytotoxic T-cells. Int J Cancer. 129:832–838.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maeda K, Hazama S, Tokuno K, Kan S, Maeda
Y, Watanabe Y, Kamei R, Shindo Y, Maeda N, Yoshimura K, et al:
Impact of chemotherapy for colorectal cancer on regulatory T-cells
and tumor immunity. Anticancer Res. 31:4569–4574. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Van der Most RG, Currie AJ, Mahendran S,
Prosser A, Darabi A, Robinson BW, Nowak AK and Lake RA: Tumor
eradication after cyclophosphamide depends on concurrent depletion
of regulatory T cells: A role for cycling TNFR2-expressing
effector-suppressor T cells in limiting effective chemotherapy.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 58:1219–1228. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Frey DM, Droeser RA, Viehl CT, Zlobec I,
Lugli A, Zingg U, Oertli D, Kettelhack C, Terracciano L and
Tornillo L: High frequency of tumor-infiltrating FOXP3(+)
regulatory T cells predicts improved survival in mismatch
repair-proficient colorectal cancer patients. Int J Cancer.
126:2635–2643. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin YC, Mahalingam J, Chiang JM, Su PJ,
Chu YY, Lai HY, Fang JH, Huang CT, Chiu CT and Lin CY: Activated
but not resting regulatory T cells accumulated in tumor
microenvironment and correlated with tumor progression in patients
with colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 132:1341–1350. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Llosa NJ, Cruise M, Tam A, Wicks EC,
Hechenbleikner EM, Taube JM, Blosser RL, Fan H, Wang H, Luber BS,
et al: The vigorous immune microenvironment of microsatellite
instable colon cancer is balanced by multiple counter-inhibitory
checkpoints. Cancer Discov. 5:43–51. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saigusa S, Toiyama Y, Tanaka K, Inoue Y,
Mori K, Ide S, Imaoka H, Kawamura M, Mohri Y and Kusunoki M:
Implication of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in tumor
recurrence and prognosis in rectal cancer with neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy. Int J Clin Oncol. 21:946–952. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Butte MJ, Keir ME, Phamduy TB, Sharpe AH
and Freeman GJ: Programmed death-1 ligand 1 interacts specifically
with the B7-1 costimulatory molecule to inhibit T cell responses.
Immunity. 27:111–122. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tamura H, Dong H, Zhu G, Sica GL, Flies
DB, Tamada K and Chen L: B7-H1 costimulation preferentially
enhances CD28-independent T-helper cell function. Blood.
97:1809–1816. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Parsa AT, Waldron JS, Panner A, Crane CA,
Parney IF, Barry JJ, Cachola KE, Murray JC, Tihan T, Jensen MC, et
al: Loss of tumor suppressor PTEN function increases B7-H1
expression and immunoresistance in glioma. Nat Med. 13:84–88. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Walker LS: Treg and CTLA-4: Two
intertwining pathways to immune tolerance. J Autoimmun. 45:49–57.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Birebent B, Lorho R, Lechartier H, de
Guibert S, Alizadeh M, Vu N, Beauplet A, Robillard N and Semana G:
Suppressive properties of human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells are
dependent on CTLA-4 expression. Eur J Immunol. 34:3485–3496. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu C, Li W and Yao Y: Regulating mechanism
of regulatory T cells in immunoregulatory responses. Int J Pathol
Clin Med. 28:199–204. 2008.
|
|
40
|
Postow MA, Callahan MK, Barker CA, Yamada
Y, Yuan J, Kitano S, Mu Z, Rasalan T, Adamow M, Ritter E, et al:
Immunologic correlates of the abscopal effect in a patient with
melanoma. N Engl J Med. 366:925–931. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qu Y, Zhang B, Liu S, Zhang A, Wu T and
Zhao Y: 2-Gy whole-body irradiation significantly alters the
balance of CD4+ CD25- T effector cells and CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ T
regulatory cells in mice. Cell Mol Immunol. 7:419–427. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Billiard F, Buard V, Benderitter M and
Linard C: Abdominal γ-radiation induces an accumulation of
function-impaired regulatory T cells in the small intestine. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 80:869–876. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mizukami Y, Kono K, Kawaguchi Y, Akaike H,
Kamimura K, Sugai H and Fujii H: Localisation pattern of Foxp3+
regulatory T cells is associated with clinical behaviour in gastric
cancer. Br J Cancer. 98:148–153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Matsutani S, Shibutani M, Maeda K,
Nagahara H, Fukuoka T, Nakao S, Hirakawa K and Ohira M:
Significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes before and after
neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 109:966–979.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|