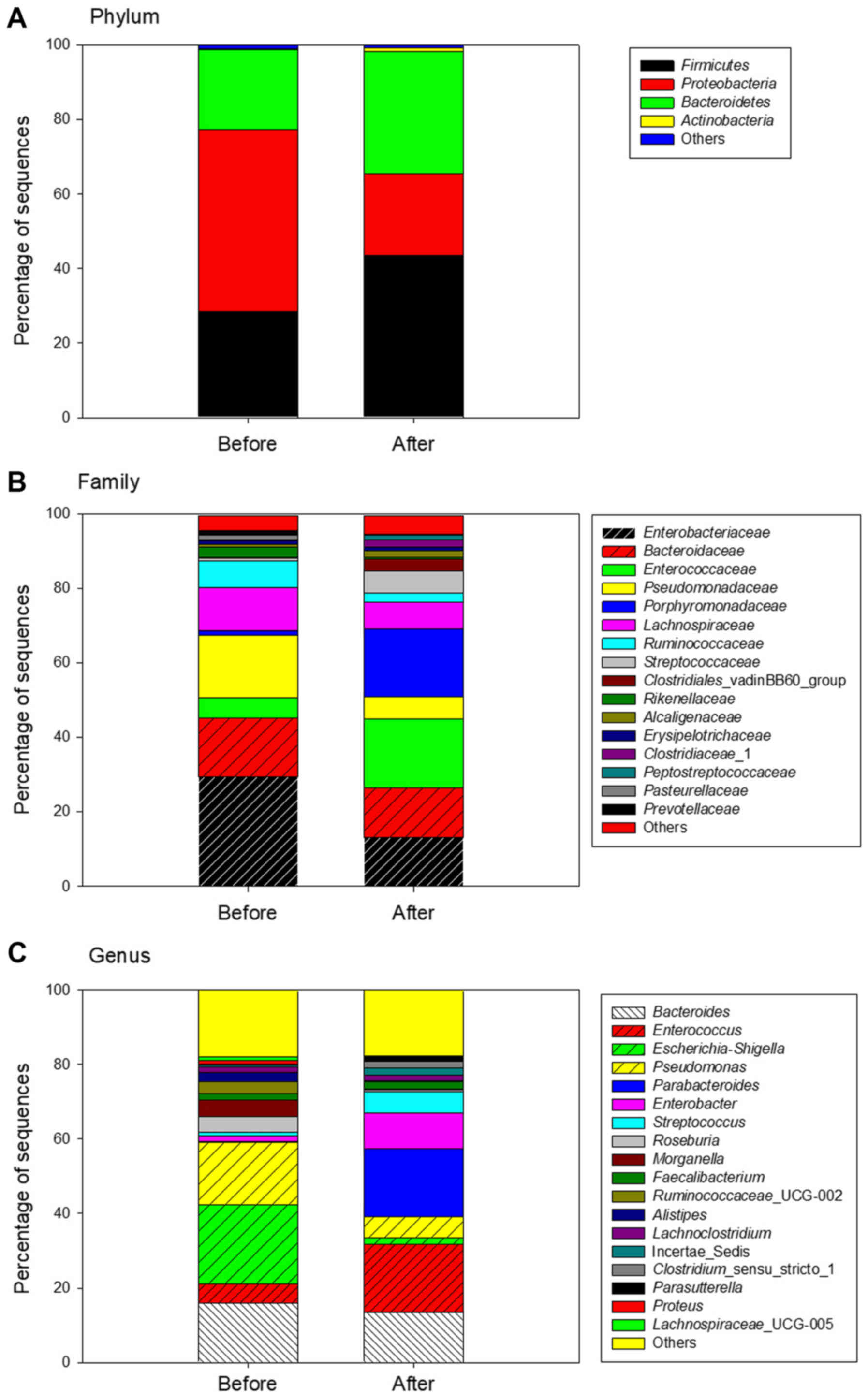
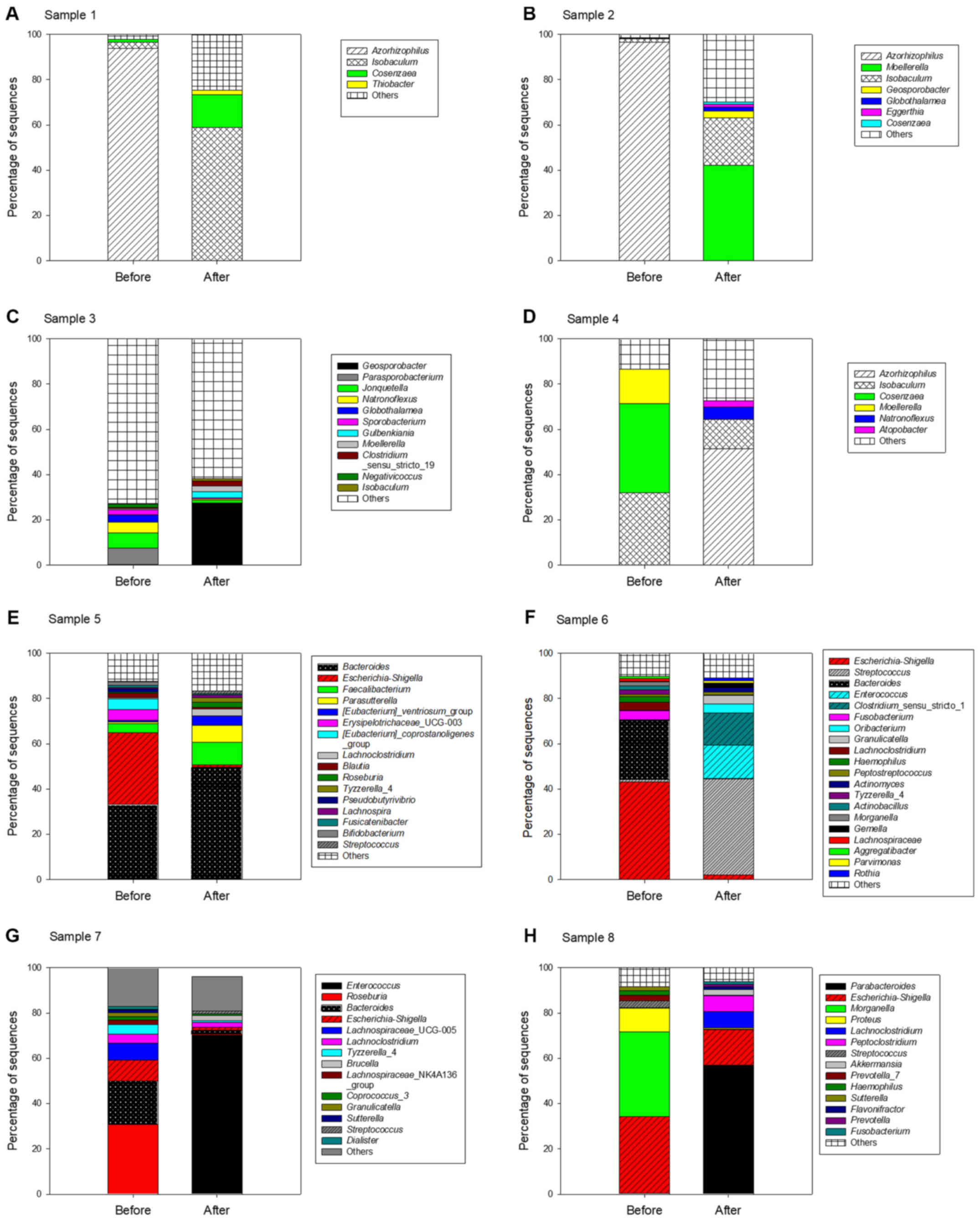
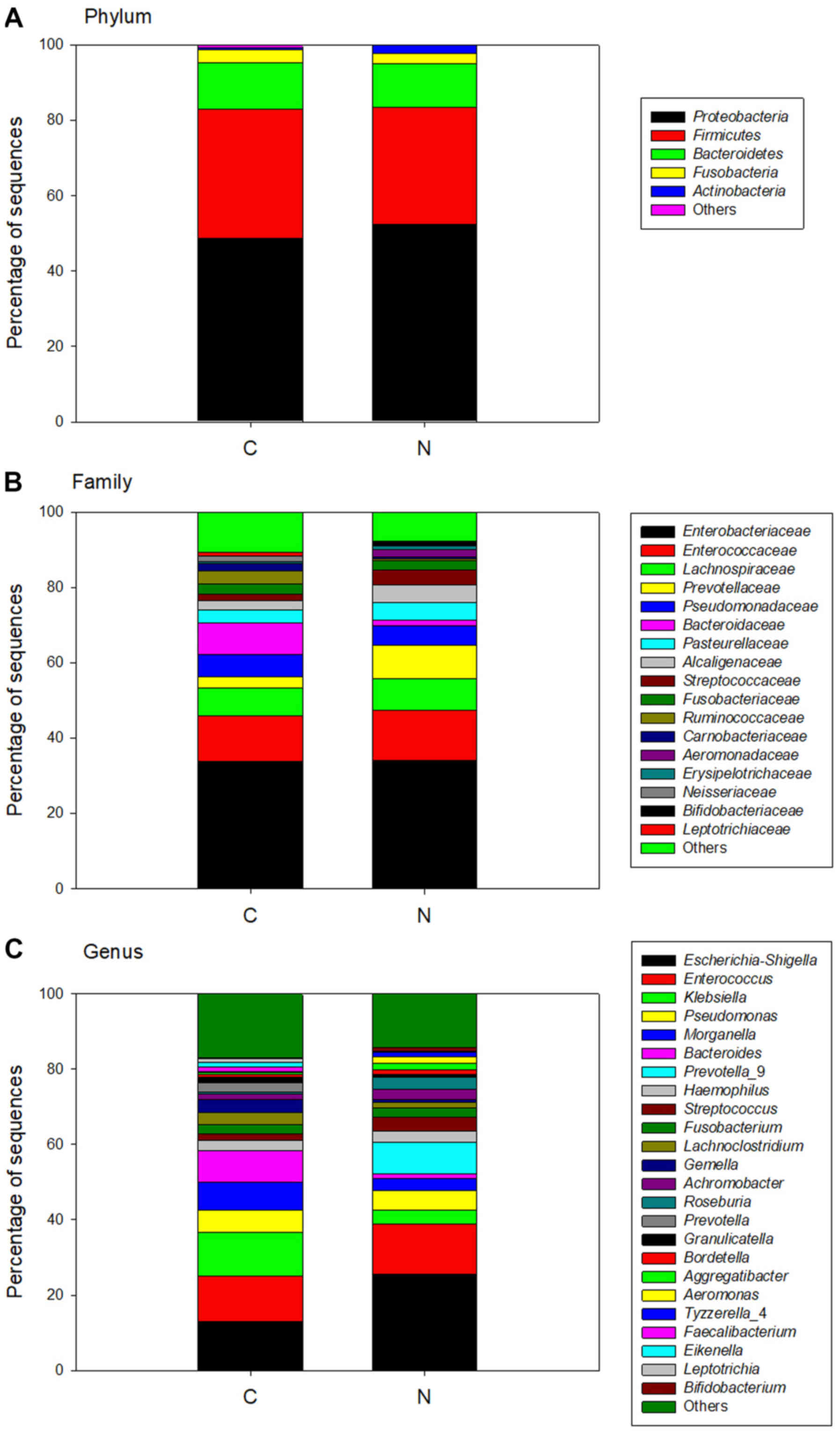
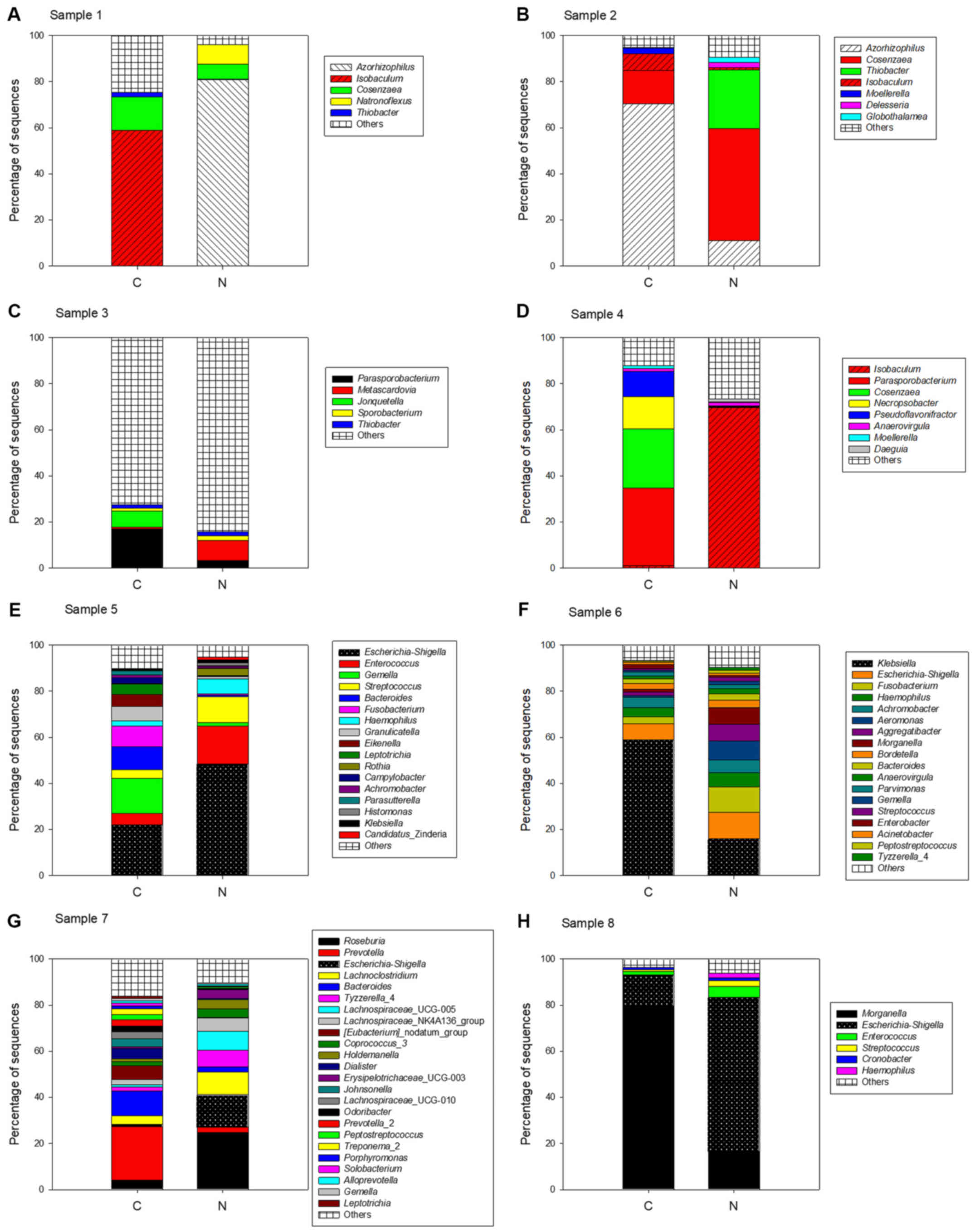
|
1
|
Bäckhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson
DA and Gordon JI: Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine.
Science. 307:1915–1920. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf
KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T, Pons N, Levenez F, Yamada T, et al: A
human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic
sequencing. Nature. 464:59–65. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gao Z, Guo B, Gao R, Zhu Q and Qin H:
Microbiota disbiosis is associated with colorectal cancer. Front
Microbiol. 6:202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sobhani I, Tap J, Roudot-Thoraval F,
Roperch JP, Letulle S, Langella P, Corthier G, Van Nhieu Tran J and
Furet JP: Microbial dysbiosis in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients.
PLoS One. 6:e163932011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Larsen N, Vogensen FK, van den Berg FW,
Nielsen DS, Andreasen AS, Pedersen BK, Al-Soud WA, Sørensen SJ,
Hansen LH and Jakobsen M: Gut microbiota in human adults with type
2 diabetes differs from non-diabetic adults. PLoS One. 5:e90852010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tannock GW: Molecular analysis of the
intestinal microflora in IBD. Mucosal Immunol. 1 Suppl 1:S15–S18.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S and Gordon
JI: Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity.
Nature. 444:1022–1023. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Burt RW: Colon cancer screening.
Gastroenterology. 119:837–853. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Platz EA, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Rimm EB,
Spiegelman D and Giovannucci E: Proportion of colon cancer risk
that might be preventable in a cohort of middle-aged US men. Cancer
Causes Control. 11:579–588. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Watson AJ and Collins PD: Colon cancer: A
civilization disorder. Dig Dis. 29:222–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tilg H, Adolph TE, Gerner RR and Moschen
AR: The intestinal microbiota in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell.
33:954–964. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu S, Rhee KJ, Albesiano E, Rabizadeh S,
Wu X, Yen HR, Huso DL, Brancati FL, Wick E, McAllister F, et al: A
human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation
of T helper type 17 T cell responses. Nat Med. 15:1016–1022. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Castellarin M, Warren RL, Freeman JD,
Dreolini L, Krzywinski M, Strauss J, Barnes R, Watson P,
Allen-Vercoe E, Moore RA and Holt RA: Fusobacterium
nucleatum infection is prevalent in human colorectal carcinoma.
Genome Res. 22:299–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arthur JC, Perezchanona E, Mühlbauer M,
Tomkovich S, Uronis JM, Fan TJ, Campbell BJ, Abujamel T, Dogan B,
Rogers AB, et al: Intestinal inflammation targets cancer-inducing
activity of the microbiota. Science. 338:120–123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sobhani I, Amiot A, Le Baleur Y, Levy M,
Auriault ML, Van Nhieu JT and Delchier JC: Microbial dysbiosis and
colon carcinogenesis: Could colon cancer be considered a
bacteria-related disease? Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 6:215–229.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Isaac A, Kochubiei O and Vizir M:
Colorectal cancer treatment. KhNMU. 2014.
|
|
18
|
Xinli L, Dachang W, Cuili Z and Yi X: Side
effects of antibiotics on the intestinal microflora by PCR-DGGE.
Pak J Pharm Sci. 26:339–343. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmidt TM, Delong EF and Pace NR:
Analysis of a marine picoplankton community by 16S rRNA gene
cloning and sequencing. J Bacteriol. 173:4371–4378. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wuyts J and Peer YVD: The European
ribosomal RNA database. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:D101–D103. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thompson JR, Marcelino LA and Polz MF:
Heteroduplexes in mixed-template amplifications: Formation,
consequence and elimination by ‘reconditioning PCR’. Nucleic Acids
Res. 30:2083–2088. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall
JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH,
Robinson CJ, et al: Introducing mothur: Open-source,
platform-independent, community-supported software for describing
and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol.
75:7537–7541. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM,
Ludwig W, Peplies J and Glöckner FO: SILVA: A comprehensive online
resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence
data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:7188–7196. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chao A: Estimating the population size for
capture-recapture data with unequal catchability. Biometrics.
43:783–791. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chao A, Hwang WH, Chen YC and Kuo CY:
Estimating the number of shared species in two communities.
Statistica Sinica. 10:227–246. 2000.
|
|
26
|
Shannon CE: The mathematical theory of
communication. 1963. MD Comput. 14:306–317. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Simpson EH: Measurement of diversity.
Nature. 163:April 30–1949. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F,
Jeanmougin F and Higgins DG: The CLUSTAL_X windows interface:
Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by
quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:4876–4882. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Saitou N and Nei M: The neighbor-joining
method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol
Biol Evol. 4:406–425. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kumar S, Tamura K and Nei M: MEGA3:
Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis
and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform. 5:150–163. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schwabe RF and Jobin C: The microbiome and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:800–812. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Allen-Vercoe E and Jobin C:
Fusobacterium and enterobacteriaceae: Important
players for CRC? Immunol Lett. 162:54–61. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim J, Artinyan A, Mailey B, Christopher
S, Lee W, McKenzie S, Chen SL, Bhatia S, Pigazzi A and
Garcia-Aguilar J: An interaction of race and ethnicity with
socioeconomic status in rectal cancer outcomes. Ann Surg.
253:647–654. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Day GE, Provost E and Lanier AP: Alaska
native mortality rates and trends. Public Health Rep. 124:54–64.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lanier AP, Day GE, Kelly JJ and Provost E:
Disparities in cancer mortality among Alaska Native people,
1994–2003. Alaska Med. 49:120–125. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yothers G, Sargent DJ, Wolmark N, Goldberg
RM, O'Connell MJ, Benedetti JK, Saltz LB, Dignam JJ and Blackstock
AW; ACCENT Collaborative Group, : Outcomes among black patients
with stage II and III colon cancer receiving chemotherapy: An
analysis of ACCENT adjuvant trials. J Natl Cancer Inst.
103:1498–1506. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hester CM, Jala VR, Langille MG, Umar S,
Greiner KA and Haribabu B: Fecal microbes, short chain fatty acids,
and colorectal cancer across racial/ethnic groups. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:2759–2769. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bruno ME, Rogier EW, Frantz AL, Stefka AT,
Thompson SN and Kaetzel CS: Regulation of the polymeric
immunoglobulin receptor in intestinal epithelial cells by
enterobacteriaceae: Implications for mucosal homeostasis. Immunol
Invest. 39:356–382. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Morgan XC, Tickle TL, Sokol H, Gevers D,
Devaney KL, Ward DV, Reyes JA, Shah SA, LeLeiko N, Snapper SB, et
al: Dysfunction of the intestinal microbiome in inflammatory bowel
disease and treatment. Genome Biol. 13:R792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Stecher B: The roles of inflammation,
nutrient availability and the commensal microbiota in enteric
pathogen infection. Microbiol Spectr. 3:2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mira-Pascual L, Cabrera-Rubio R, Ocon S,
Costales P, Parra A, Suarez A, Moris F, Rodrigo L, Mira A and
Collado MC: Microbial mucosal colonic shifts associated with the
development of colorectal cancer reveal the presence of different
bacterial and archaeal biomarkers. J Gastroenterol. 50:167–179.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Garrett WS, Gallini CA, Yatsunenko T,
Michaud M, DuBois A, Delaney ML, Punit S, Karlsson M, Bry L,
Glickman JN, et al: Enterobacteriaceae act in concert with the gut
microbiota to induce spontaneous and maternally transmitted
colitis. Cell Host Microbe. 8:292–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lupp C, Robertson ML, Wickham ME, Sekirov
I, Champion OL, Gaynor EC and Finlay BB: Host-mediated inflammation
disrupts the intestinal microbiota and promotes the overgrowth of
enterobacteriaceae. Cell Host Microbe. 2:2042007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Holzapfel WH and Wood BJB: The family
enterococcaceae. John Wiley Sons Ltd; 2014
|
|
45
|
Wang T, Cai G, Qiu Y, Fei N, Zhang M, Pang
X, Jia W, Cai S and Zhao L: Structural segregation of gut
microbiota between colorectal cancer patients and healthy
volunteers. ISME J. 6:320–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Balamurugan R, Rajendiran E, George S,
Samuel GV and Ramakrishna BS: Real-time polymerase chain reaction
quantification of specific butyrate-producing bacteria,
Desulfovibrio and Enterococcus faecalis in the feces
of patients with colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
23:1298–1303. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Balish E and Warner T: Enterococcus
faecalis induces inflammatory bowel disease in interleukin-10
knockout mice. Am J Pathol. 160:2253–2257. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sun T, Liu S, Zhou Y, Yao Z, Zhang D, Cao
S, Wei Z, Tan B, Li Y, Lian Z and Wang S: Evolutionary biologic
changes of gut microbiota in an ‘adenoma-carcinoma sequence’ mouse
colorectal cancer model induced by 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine.
Oncotarget. 8:444–457. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kohoutova D, Smajs D, Moravkova P, Cyrany
J, Moravkova M, Forstlova M, Cihak M, Rejchrt S and Bures J:
Escherichia coli strains of phylogenetic group B2 and D and
bacteriocin production are associated with advanced colorectal
neoplasia. BMC Infect Dis. 14:7332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Farkas-Himsley H and Yu H: Purified
colicin as cytotoxic agent of neoplasia: Comparative study with
crude colicin. Cytobios. 42:193–207. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bonnet M, Buc E, Sauvanet P, Darcha C,
Dubois D, Pereira B, Déchelotte P, Bonnet R, Pezet D and
Darfeuille-Michaud A: Colonization of the human gut by E. coli and
colorectal cancer risk. Clin Cancer Res. 20:859–867. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Peterson CT, Vaughn AR, Sharma V, Chopra
D, Mills PJ, Peterson SN and Sivamani RK: Effects of turmeric and
curcumin dietary supplementation on human gut microbiota: A
double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study. J Evid
Based Integr Med. 23:2515690X187907252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Stecher B, Robbiani R, Walker AW,
Westendorf AM, Barthel M, Kremer M, Chaffron S, Macpherson AJ, Buer
J, Parkhill J, et al: Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
exploits inflammation to compete with the intestinal microbiota.
PLos Biol. 5:2177–2189. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gevers D, Kugathasan S, Denson LA,
Vázquez-Baeza Y, Van Treuren W, Ren B, Schwager E, Knights D, Song
SJ, Yassour M, et al: The treatment-naive microbiome in new-onset
Crohn's disease. Cell Host Microbe. 15:382–392. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wu N, Yang X, Zhang R, Li J, Xiao X, Hu Y,
Chen Y, Yang F, Lu N, Wang Z, et al: Dysbiosis signature of fecal
microbiota in colorectal cancer patients. Microb Ecol. 66:462–470.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hendrickx AP, Top J, Bayjanov JR,
Kemperman H, Rogers MR, Paganelli FL, Bonten MJ and Willems RJ:
Antibiotic-driven dysbiosis mediates intraluminal agglutination and
alternative segregation of enterococcus faecium from the
intestinal epithelium. MBio. 6:e01346–e01315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sanchez-Diaz AM, Cuartero C, Rodriguez JD,
Lozano S, Alonso JM, Rodríguez-Domínguez M, Tedim AP, Del Campo R,
López J, Cantón R and Ruiz-Garbajosa P: The rise of
ampicillin-resistant Enterococcus faecium high-risk clones
as a frequent intestinal colonizer in oncohaematological
neutropenic patients on levofloxacin prophylaxis: A risk for
bacteraemia? Clin Microbiol Infect. 22(59): e51–e58. 2016.
|
|
58
|
Becking JH: The family azotobacteraceae.
Springer; New York: 2006
|
|
59
|
Chen L, Zhang YH, Huang T and Cai YD: Gene
expression profiling gut microbiota in different races of humans.
Sci Rep. 6:230752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Collins MD, Hutson RA, Foster G, Falsen E
and Weiss N: Isobaculum melis gen. nov., sp. nov., a
Carnobacterium-like organism isolated from the intestine of a
badger. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 52:207–210. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Aller AI, Castro C, Medina MJ, González
MT, Sevilla P, Morilla MD, Corzo JE and Martín-Mazuelos E:
Isolation of Moellerella wisconsensis from blood culture
from a patient with acute cholecystitis. Clin Microbiol Infect.
15:1193–1194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Stock I, Falsen E and Wiedemann B:
Moellerella wisconsensis: Identification, natural antibiotic
susceptibility and its dependency on the medium applied. Diagn
Microbiol Infect Dis. 45:1–11. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gagnière J, Raisch J, Veziant J, Barnich
N, Bonnet R, Buc E, Bringer MA, Pezet D and Bonnet M: Gut
microbiota imbalance and colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
22:501–518. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Dubrow R, Edberg S, Wikfors E, Callan D,
Troncale F, Vender R, Brand M and Yapp R: Fecal carriage of
Streptococcus bovis and colorectal adenomas.
Gastroenterology. 101:721–725. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Farhadi T, Fakharian A and Ovchinnikov RS:
Virtual screening for potential inhibitors of CTX-M-15 protein of
Klebsiella pneumoniae. Interdiscip Sci. 10:694–703. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Swidsinski A, Khilkin M, Kerjaschki D,
Schreiber S, Ortner M, Weber J and Lochs H: Association between
intraepithelial escherichia coli and colorectal cancer.
Gastroenterology. 115:281–286. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Poulsen ML and Bisgaard ML: MUTYH
associated polyposis (MAP). Curr Genomics. 9:420–435. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Khan AA and Cash P: E. coli and colon
cancer: Is mutY a culprit? Cancer Lett. 341:127–131. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yu T, Guo F, Yu Y, Sun T, Ma D, Han J,
Qian Y, Kryczek I, Sun D, Nagarsheth N, et al: Fusobacterium
nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to colorectal cancer by
modulating autophagy. Cell. 170(548–563): e162017.
|
|
70
|
Bourassa L and Clarridge JE III: Clinical
significance and characterization of streptococcus tigurinus
isolates in an adult population. J Clin Microbiol. 53:3574–3579.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Kim B, Huh HJ, Chung DR, Kim WS, Ki CS and
Lee NY: The first case of concurrent infective endocarditis and
spondylitis caused by streptococcus tigurinus. Ann Lab Med.
35:654–656. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Michelena A, Bonavila C, Zubeltzu B and
Goenaga MA: Endocarditis due to Streptococcus tigurinus:
Presentation of a case and a review of the literature. Enferm
Infecc Microbiol Clín. 33:575–576. 2015.(In Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Skowron MA, Zebrowska J, Wegrzyn G and
Skowron PM: MmoSTI restriction endonuclease, isolated from
Morganella morganii infecting a tropical moth, Actias
selene, cleaving 5′-|CCNGG-3′ sequences. J Appl Genetics.
57:143–149. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Murphy K, Ryan C, Dempsey EM, O'Toole PW,
Ross RP, Stanton C and Ryan CA: Neonatal sulfhemoglobinemia and
hemolytic anemia associated with intestinal morganella
morganii. Pediatrics. 136:1641–1645. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Shahbazi E, Mollasalehi H and
Minai-Tehrani D: Development and evaluation of an improved
quantitative loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for
rapid detection of morganella morganii. Talanta. 191:54–58.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Koh GY, Kane A, Lee K, Xu Q, Wu X, Roper
J, Mason JB and Crott JW: Parabacteroides distasonis
attenuates toll-like receptor 4 signaling and Akt activation and
blocks colon tumor formation in high-fat diet-fed
azoxymethane-treated mice. Int J Cancer. April 26–2018.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Dziarski R, Park SY, Kashyap DR, Dowd SE
and Gupta D: Pglyrp-regulated gut microflora prevotella
falsenii, parabacteroides distasonis and bacteroides
eggerthii enhance and alistipes finegoldii attenuates
colitis in mice. PLos One. 11:e01461622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Davis-Richardson AG, Ardissone AN, Dias R,
Simell V, Leonard MT, Kemppainen KM, Drew JC, Schatz D, Atkinson
MA, Kolaczkowski B, et al: Bacteroides dorei dominates gut
microbiome prior to autoimmunity in Finnish children at high risk
for type 1 diabetes. Front Microbiol. 5:6782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ignacio A, Fernandes MR, Avila-Campos MJ
and Nakano V: Enterotoxigenic and non-enterotoxigenic
bacteroides fragilis from fecal microbiota of children. Braz
J Microbiol. 46:1141–1145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|