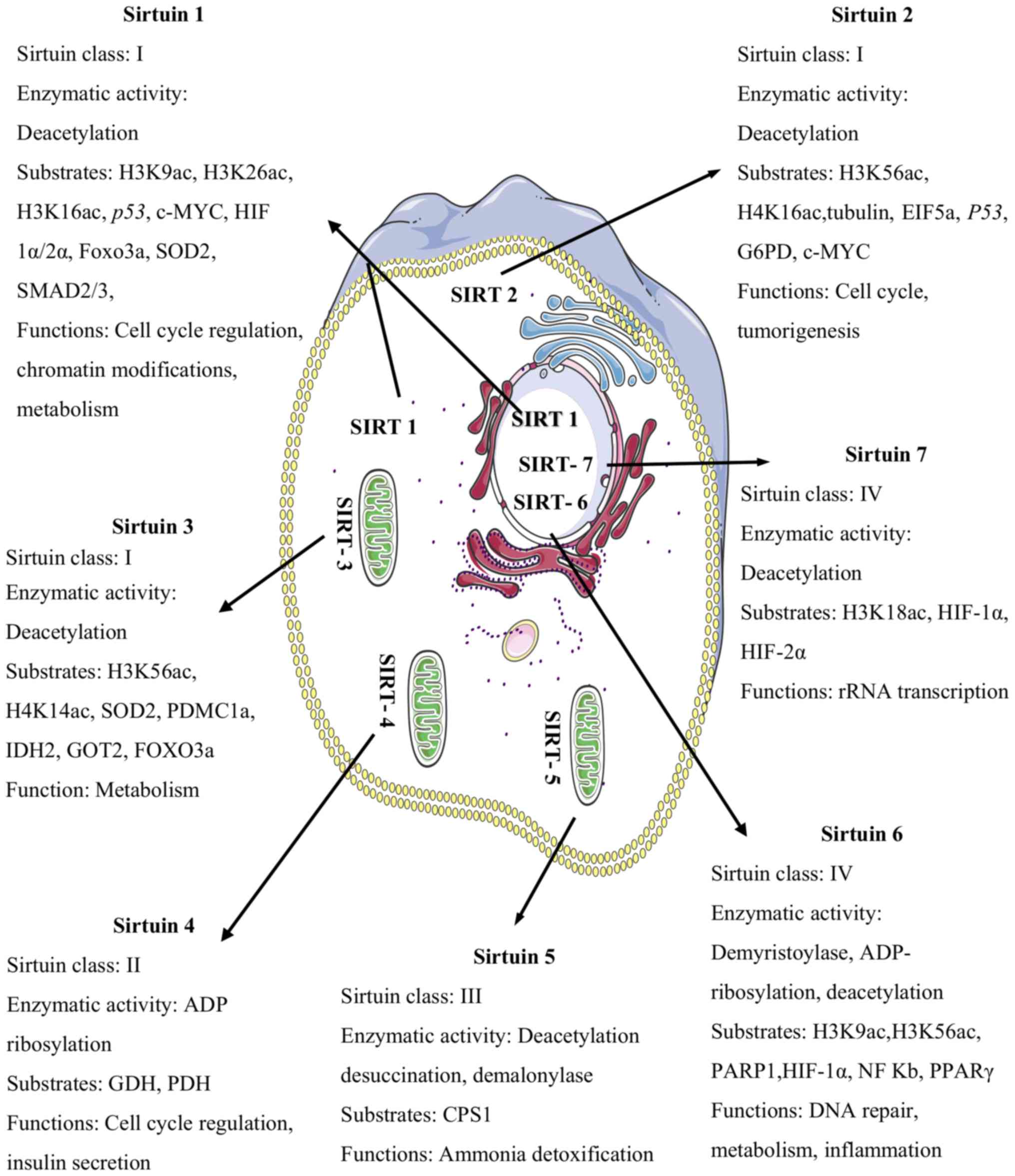
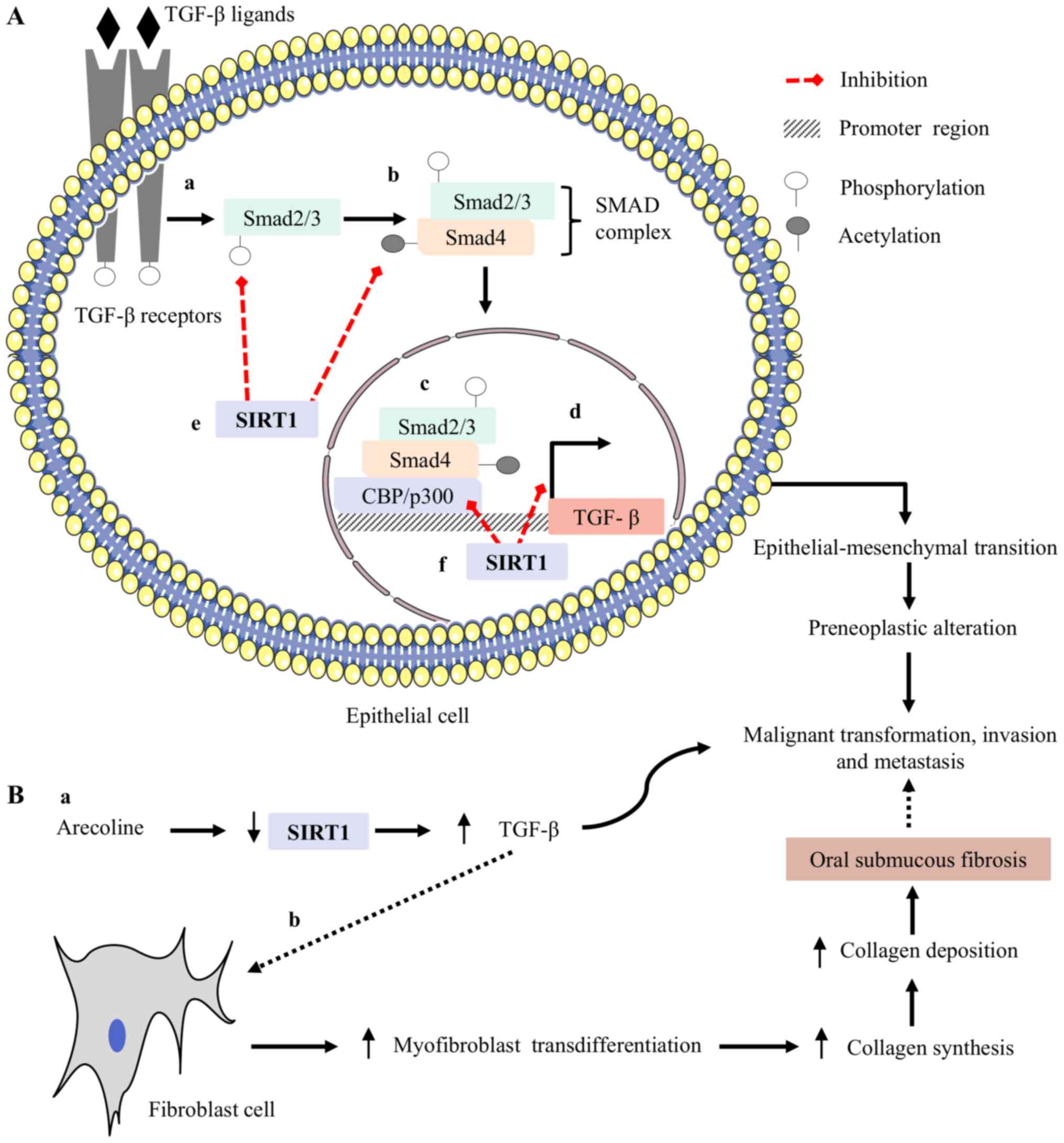
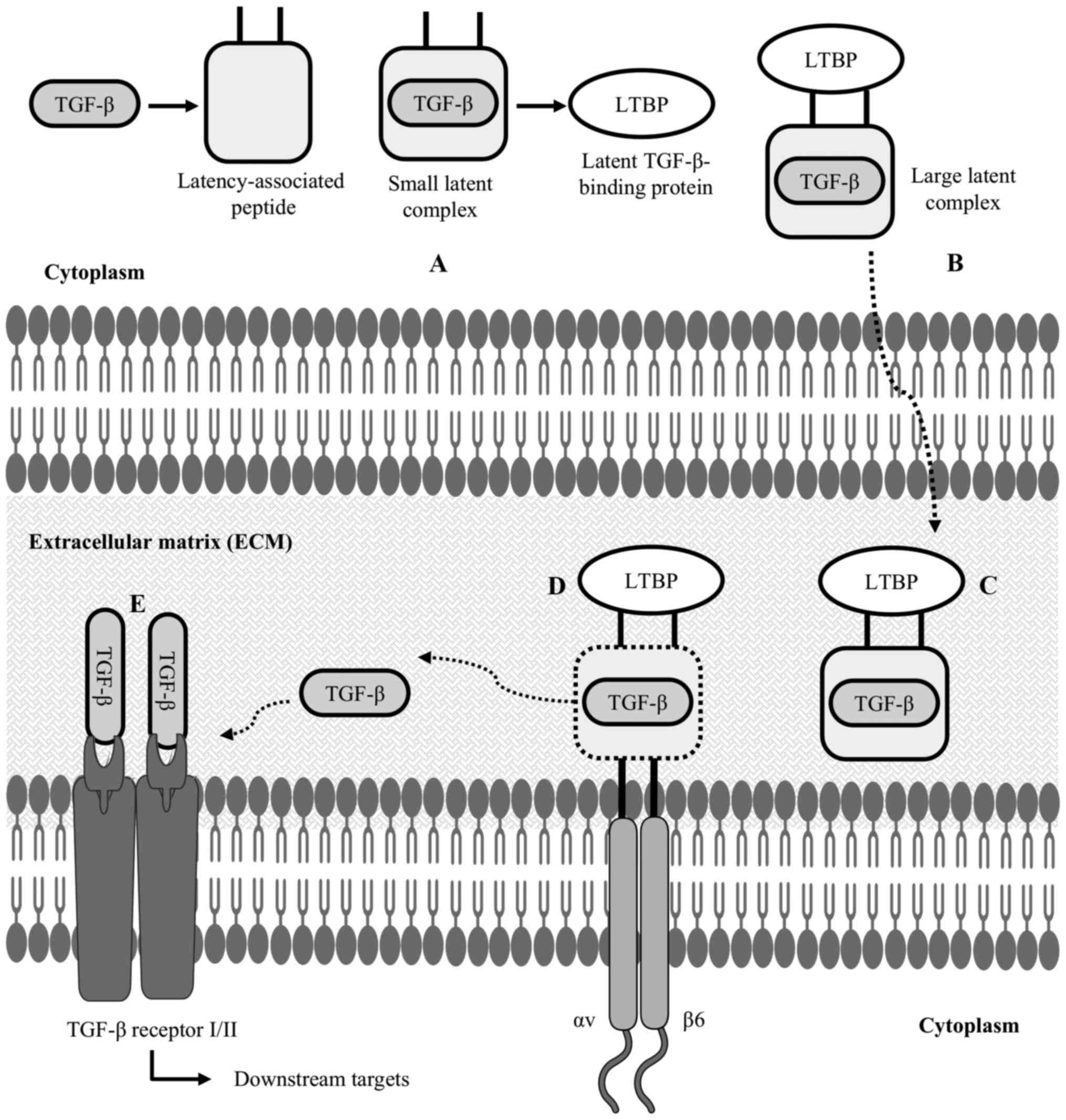
|
1
|
Carafa V, Rotili D, Forgione M, Cuomo F,
Serretiello E, Hailu GS, Jarho E, Lahtela-Kakkonen M, Mai A and
Altucci L: Sirtuin functions and modulation: From chemistry to the
clinic. Clin Epigenetics. 8:612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Deng CX: SIRT1, is it a tumor promoter or
tumor suppressor? Int J Biol Sci. 5:147–152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bosch-Presegué L and Vaquero A: The dual
role of sirtuins in cancer. Genes Cancer. 2:648–662. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang RH, Sengupta K, Li C, Kim HS, Cao L,
Xiao C, Kim S, Xu X, Zheng Y, Chilton B, et al: Impaired DNA damage
response, genome instability, and tumorigenesis in SIRT1 mutant
mice. Cancer Cell. 14:312–323. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen IC, Chiang WF, Huang HH, Chen PF,
Shen YY and Chiang HC: Role of SIRT1 in regulation of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell
carcinoma metastasis. Mol Cancer. 13:2542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kang YY, Sun FL, Zhang Y and Wang Z: SIRT1
acts as a potential tumor suppressor in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. J Chin Med Assoc. 81:416–422. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Murofushi T, Tsuda H, Mikami Y, Yamaguchi
Y and Suzuki N: CAY10591, a SIRT1 activator, suppresses cell
growth, invasion, and migration in gingival epithelial carcinoma
cells. J Oral Sci. 59:415–423. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiong P, Li YX, Tang YT and Chen HG:
Proteomic analyses of Sirt1-mediated cisplatin resistance in OSCC
cell line. Protein J. 30:499–508. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Warnakulasuriya S: Global epidemiology of
oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 45:309–316. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of
Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Betel-quid and areca-nut chewing and
some areca-nut-derived nitrosamines. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog
Risks Hum. 85:1–334. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peters AH, O'Carroll D, Scherthan H,
Mechtler K, Sauer S, Schöfer C, Weipoltshammer K, Pagani M, Lachner
M, Kohlmaier A, et al: Loss of the Suv39h histone
methyltransferases impairs mammalian heterochromatin and genome
stability. Cell. 107:323–337. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vaquero A, Scher M, Lee D,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Reinberg D: Human SirT1 interacts
with histone H1 and promotes formation of facultative
heterochromatin. Mol Cell. 16:93–105. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vaquero A, Scher M, Erdjument-Bromage H,
Tempst P, Serrano L and Reinberg D: SIRT1 regulates the histone
methyl-transferase SUV39H1 during heterochromatin formation.
Nature. 450:440–444. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Palacios JA, Herranz D, De Bonis ML,
Velasco S, Serrano M and Blasco MA: SIRT1 contributes to telomere
maintenance and augments global homologous recombination. J Cell
Biol. 191:1299–1313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuan Z, Zhang X, Sengupta N, Lane WS and
Seto E: SIRT1 regulates the function of the Nijmegen breakage
syndrome protein. Mol Cell. 27:149–162. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jeong J, Juhn K, Lee H, Kim SH, Min BH,
Lee KM, Cho MH, Park GH and Lee KH: SIRT1 promotes DNA repair
activity and deacetylation of Ku70. Exp Mol Med. 39:8–13. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sawada M, Sun W, Hayes P, Leskov K,
Boothman DA and Matsuyama S: Ku70 suppresses the apoptotic
translocation of Bax to mitochondria. Nat Cell Biol. 5:320–329.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF, Chua
KF, Greer PL, Lin Y, Tran H, Ross SE, Mostoslavsky R, Cohen HY, et
al: Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by
the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science. 303:2011–2015. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kobayashi Y, Furukawa-Hibi Y, Chen C,
Horio Y, Isobe K, Ikeda K and Motoyama N: SIRT1 is a critical
regulator of FOXO-mediated transcription in response to oxidative
stress. Int J Mol Med. 16:237–243. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Motta MC, Divecha N, Lemieux M, Kamel C,
Chen D, Gu W, Bultsma Y, McBurney M and Guarente L: Mammalian SIRT1
represses forkhead transcription factors. Cell. 116:551–563. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chua KF, Mostoslavsky R, Lombard DB, Pang
WW, Saito S, Franco S, Kaushal D, Cheng HL, Fischer MR, Stokes N,
et al: Mammalian SIRT1 limits replicative life span in response to
chronic genotoxic stress. Cell Metab. 2:67–76. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yi J and Luo J: SIRT1 and p53, effect on
cancer, senescence and beyond. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1804:1684–1689. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Peng L, Yuan Z, Ling H, Fukasawa K,
Robertson K, Olashaw N, Koomen J, Chen J, Lane WS and Seto E: SIRT1
deacetylates the DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) protein and alters
its activities. Mol Cell Biol. 31:4720–4734. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Glozak MA, Sengupta N, Zhang X and Seto E:
Acetylation and deacetylation of non-histone proteins. Gene.
363:15–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Glozak MA and Seto E: Histone deacetylases
and cancer. Oncogene. 26:5420–5432. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huffman DM, Grizzle WE, Bamman MM, Kim JS,
Eltoum IA, Elgavish A and Nagy TR: SIRT1 is significantly elevated
in mouse and human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:6612–6618. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen HC, Jeng YM, Yuan RH, Hsu HC and Chen
YL: SIRT1 promotes tumorigenesis and resistance to chemotherapy in
hepatocellular carcinoma and its expression predicts poor
prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:2011–2019. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hao C, Zhu PX, Yang X, Han ZP, Jiang JH,
Zong C, Zhang XG, Liu WT, Zhao QD, Fan TT, et al: Overexpression of
SIRT1 promotes metastasis through an epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 14:9782014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen X, Sun K, Jiao S, Cai N, Zhao X, Zou
H, Xie Y, Wang Z, Zhong M and Wei L: High levels of SIRT1
expression enhance tumorigenesis and associate with a poor
prognosis of colorectal carcinoma patients. Sci Rep. 4:74812014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao G, Qin Q, Zhang J, Liu Y, Deng S, Liu
L, Wang B, Tian K and Wang C: Hypermethylation of HIC1 promoter and
aberrant expression of HIC1/SIRT1 might contribute to the
carcinogenesis of pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 20 Suppl
3:S301–S311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stunkel W, Peh BK, Tan YC, Nayagam VM,
Wang X, Salto-Tellez M, Ni B, Entzeroth M and Wood J: Function of
the SIRT1 protein deacetylase in cancer. Biotechnol J. 2:1360–1368.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ford J, Jiang M and Milner J:
Cancer-specific functions of SIRT1 enable human epithelial cancer
cell growth and survival. Cancer Res. 65:10457–10463. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
He Z, Yi J, Jin L, Pan B, Chen L and Song
H: Overexpression of Sirtuin-1 is associated with poor clinical
outcome in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
37:7139–7148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hida Y, Kubo Y, Murao K and Arase S:
Strong expression of a longevity-related protein, SIRT1, in Bowen's
disease. Arch Dermatol Res. 299:103–106. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bradbury CA, Khanim FL, Hayden R, Bunce
CM, White DA, Drayson MT, Craddock C and Turner BM: Histone
deacetylases in acute myeloid leukaemia show a distinctive pattern
of expression that changes selectively in response to deacetylase
inhibitors. Leukemia. 19:1751–1759. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jung W, Hong KD, Jung WY, Lee E, Shin BK,
Kim HK, Kim A and Kim BH: SIRT1 expression is associated with good
prognosis in colorectal cancer. Korean J Pathol. 47:332–339. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jang SH, Min KW, Paik SS and Jang KS: Loss
of SIRT1 histone deacetylase expression associates with tumour
progression in colorectal adenocarcinoma. J Clin Pathol.
65:735–739. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Firestein R, Blander G, Michan S,
Oberdoerffer P, Ogino S, Campbell J, Bhimavarapu A, Luikenhuis S,
de Cabo R, Fuchs C, et al: The SIRT1 deacetylase suppresses
intestinal tumorigenesis and colon cancer growth. PLoS One.
3:e20202008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Voelter-Mahlknecht S and Mahlknecht U: The
sirtuins in the pathogenesis of cancer. Clin Epigenetics. 1:71–83.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Potente M, Ghaeni L, Baldessari D,
Mostoslavsky R, Rossig L, Dequiedt F, Haendeler J, Mione M, Dejana
E, Alt FW, et al: SIRT1 controls endothelial angiogenic functions
during vascular growth. Genes Dev. 21:2644–2658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Byles V, Zhu L, Lovaas JD, Chmilewski LK,
Wang J, Faller DV and Dai Y: SIRT1 induces EMT by cooperating with
EMT transcription factors and enhances prostate cancer cell
migration and metastasis. Oncogene. 31:4619–4629. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Verrecchia F and Mauviel A: Transforming
growth factor-beta and fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol.
13:3056–3062. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ekanayaka RP and Tilakaratne WM: Oral
submucous fibrosis: Review on mechanisms of malignant
transformation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol.
122:192–199. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chang YC, Lin CW, Yu CC, Wang BY, Huang
YH, Hsieh YC, Kuo YL and Chang WW: Resveratrol suppresses
myofibroblast activity of human buccal mucosal fibroblasts through
the epigenetic inhibition of ZEB1 expression. Oncotarget.
7:12137–12149. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Uehara O, Takimoto K, Morikawa T, Harada
F, Takai R, Adhikari BR, Itatsu R, Nakamura T, Yoshida K, Matsuoka
H, et al: Upregulated expression of MMP-9 in gingival epithelial
cells induced by prolonged stimulation with arecoline. Oncol Lett.
14:1186–1192. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chiba I, Muthumala M, Yamazaki Y, Uz Zaman
A, Iizuka T, Amemiya A, Shibata T, Kashiwazaki H, Sugiura C and
Fukuda H: Characteristics of mutations in the p53 gene of oral
squamous-cell carcinomas associated with betel-quid chewing in Sri
Lanka. Int J Cancer. 77:839–842. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wei B, Guo C, Liu S and Sun MZ: Annexin A4
and cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 447:72–78. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Laemmle A, Lechleiter A, Roh V, Schwarz C,
Portmann S, Furer C, Keogh A, Tschan MP, Candinas D, Vorburger SA
and Stroka D: Inhibition of SIRT1 impairs the accumulation and
transcriptional activity of HIF-1α protein under hypoxic
conditions. PLoS One. 7:e334332012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ceccacci E and Minucci S: Inhibition of
histone deacetylases in cancer therapy: Lessons from leukaemia. Br
J Cancer. 114:605–611. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hu J, Jing H and Lin H: Sirtuin inhibitors
as anticancer agents. Future Med Chem. 6:945–966. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jin Y, Cao Q, Chen C, Du X, Jin B and Pan
J: Tenovin-6-mediated inhibition of SIRT1/2 induces apoptosis in
acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells and eliminates ALL
stem/progenitor cells. BMC Cancer. 15:2262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dai W, Zhou J, Jin B and Pan J: Class
III-specific HDAC inhibitor Tenovin-6 induces apoptosis, suppresses
migration and eliminates cancer stem cells in uveal melanoma. Sci
Rep. 6:226222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Eckschlager T, Plch J, Stiborova M and
Hrabeta J: Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int
J Mol Sci. 18(pii): E14142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ota H, Tokunaga E, Chang K, Hikasa M,
Iijima K, Eto M, Kozaki K, Akishita M, Ouchi Y and Kaneki M: Sirt1
inhibitor, Sirtinol, induces senescence-like growth arrest with
attenuated Ras-MAPK signaling in human cancer cells. Oncogene.
25:176–185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bhalla S and Gordon LI: Functional
characterization of NAD dependent de-acetylases SIRT1 and SIRT2 in
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Cancer Biol Ther.
17:300–309. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Süssmuth SD, Haider S, Landwehrmeyer GB,
Farmer R, Frost C, Tripepi G, Andersen CA, Di Bacco M, Lamanna C,
Diodato E, et al: An exploratory double-blind, randomized clinical
trial with selisistat, a SirT1 inhibitor, in patients with
Huntington's disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 79:465–476. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Heltweg B, Gatbonton T, Schuler AD,
Posakony J, Li H, Goehle S, Kollipara R, Depinho RA, Gu Y, Simon JA
and Bedalov A: Antitumor activity of a small-molecule inhibitor of
human silent information regulator 2 enzymes. Cancer Res.
66:4368–4377. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kalle AM, Mallika A, Badiger J, Alinakhi,
Talukdar P and Sachchidanand: Inhibition of SIRT1 by a small
molecule induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 401:13–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lai YH, Lin SY, Wu YS, Chen HW and Chen
JJW: AC-93253 iodide, a novel Src inhibitor, suppresses NSCLC
progression by modulating multiple Src-related signaling pathways.
J Hematol Oncol. 10:1722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Rotili D, Tarantino D, Nebbioso A, Paolini
C, Huidobro C, Lara E, Mellini P, Lenoci A, Pezzi R, Botta G, et
al: Discovery of salermide-related sirtuin inhibitors: Binding mode
studies and antiproliferative effects in cancer cells including
cancer stem cells. J Med Chem. 55:10937–10947. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lara E, Mai A, Calvanese V, Altucci L,
Lopez Nieva P, Martinez Chantar ML, Varela Rey M, Rotili D,
Nebbioso A, Ropero S, et al: Salermide, a Sirtuin inhibitor with a
strong cancer-specific proapoptotic effect. Oncogene. 28:781–791.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Jiang Z, Chen K, Cheng L, Yan B, Qian W,
Cao J, Li J, Wu E, Ma Q and Yang W: Resveratrol and cancer
treatment: Updates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1403:59–69. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chauhan D, Bandi M, Singh AV, Ray A, Raje
N, Richardson P and Anderson KC: Preclinical evaluation of a novel
SIRT1 modulator SRT1720 in multiple myeloma cells. Br J Haematol.
155:588–598. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Tasoulas J, Giaginis C, Patsouris E,
Manolis E and Theocharis S: Histone deacetylase inhibitors in oral
squamous cell carcinoma treatment. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.
24:69–78. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Bruzzese F, Leone A, Rocco M, Carbone C,
Piro G, Caraglia M, Di Gennaro E and Budillon A: HDAC inhibitor
vorinostat enhances the antitumor effect of gefitinib in squamous
cell carcinoma of head and neck by modulating ErbB receptor
expression and reverting EMT. J Cell Physiol. 226:2378–2390. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Suzuki M, Endo M, Shinohara F, Echigo S
and Rikiishi H: Enhancement of cisplatin cytotoxicity by SAHA
involves endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
64:1115–1122. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Eriksson I, Joosten M, Roberg K and
Ollinger K: The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A
reduces lysosomal pH and enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Exp
Cell Res. 319:12–20. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sato T, Suzuki M, Sato Y, Echigo S and
Rikiishi H: Sequence-dependent interaction between cisplatin and
histone deacetylase inhibitors in human oral squamous cell
carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 28:1233–1241. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Shoji M, Ninomiya I, Makino I, Kinoshita
J, Nakamura K, Oyama K, Nakagawara H, Fujita H, Tajima H, Takamura
H, et al: Valproic acid, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, enhances
radiosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 40:2140–2146. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gan CP, Hamid S, Hor SY, Zain RB, Ismail
SM, Wan Mustafa WM, Teo SH, Saunders N and Cheong SC: Valproic
acid: growth inhibition of head and neck cancer by induction of
terminal differentiation and senescence. Head Neck. 34:344–353.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Gong L, Wang WM, Ji Y, Wang Y and Li DW:
Effects of sodium butyrate on proliferation of human oral squamous
carcinoma cell line and expression of p27Kip1. Zhonghua Kou Qiang
Yi Xue Za Zhi. 45:619–622. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lin Z and Fang D: The roles of SIRT1 in
cancer. Genes Cancer. 4:97–104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K and Kauppinen A:
Crosstalk between oxidative stress and SIRT1: Impact on the ageing
process. Int J Mol Sci. 14:3834–3859. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Agarwal SK: Integrins and cadherins as
therapeutic targets in fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 5:1312014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Xue H, Atakilit A, Zhu W, Li X, Ramos DM
and Pytela R: Role of the avb6 integrin in human oral squamous cell
carcinoma growth in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
288:610–618. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Xu M, Yin L, Cai Y, Hu Q, Huang J, Ji Q,
Hu Y, Huang W, Liu F, Shi S and Deng X: Epigenetic regulation of
integrin β6 transcription induced by TGF-β1 in human oral squamous
cell carcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 119:4193–4204. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|