|
1
|
Patterson-Fortin J and Moliterno AR:
Molecular pathogenesis of myeloproliferative neoplasms: Influence
of age and gender. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 12:424–431. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kwan W and North TE: Netting novel
regulators of hematopoiesis and hematologic malignancies in
zebrafish. Curr Top Dev Biol. 124:125–160. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
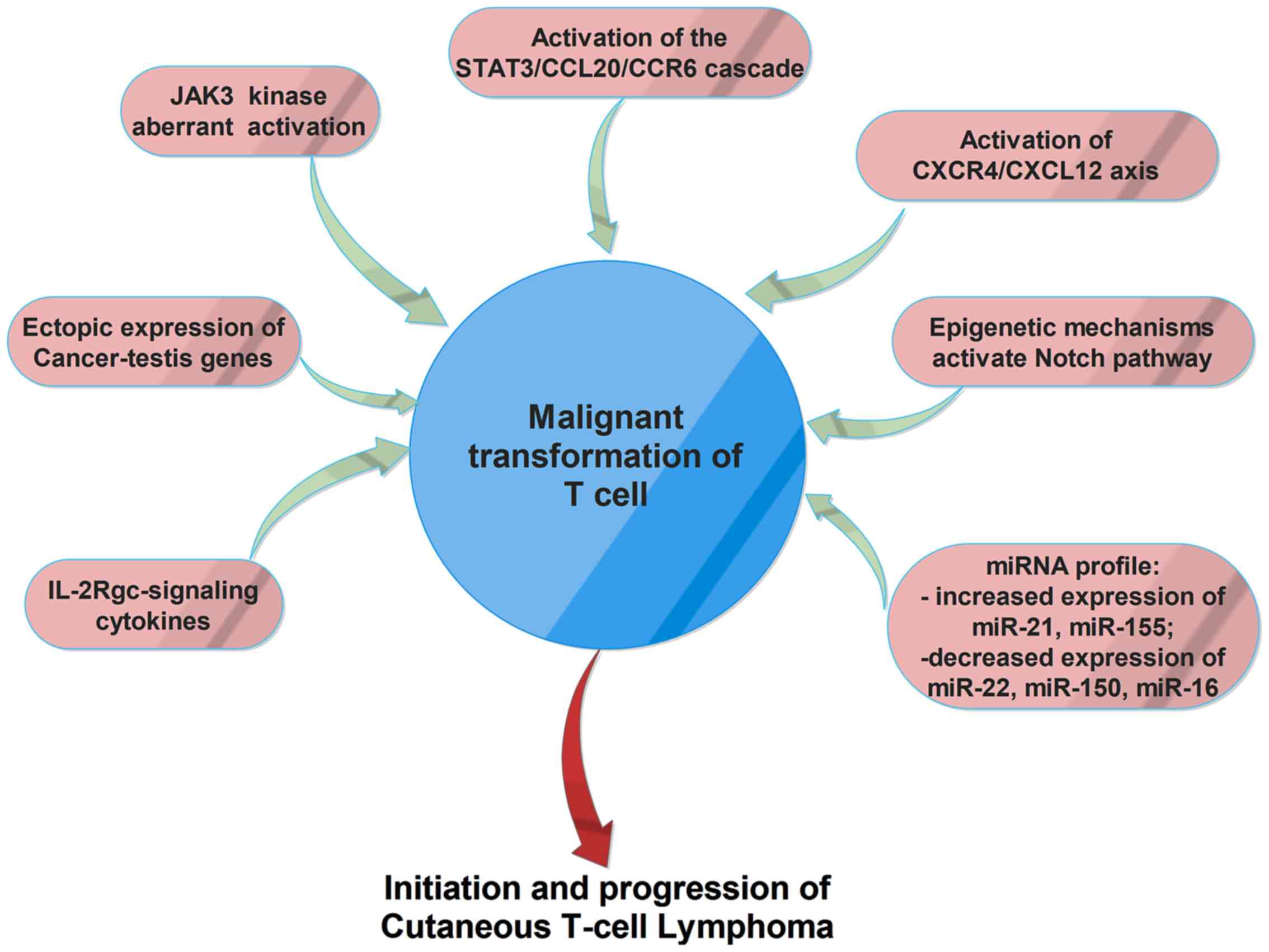
3
|
Deininger MW, Tyner JW and Solary E:
Turning the tide in myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Nat Rev Cancer. 17:425–440. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Swerdlow SH, Harris NL, Campo E, Pileri
SA, Stein H, Jaffe ES and Thiele J: WHO Classification of Tumors of
Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 2. 4th. IARC press; Lyon:
2017
|
|
5
|
Jiang M, Bennani NN and Feldman AL:
Lymphoma classification update: T-cell lymphomas, Hodgkin
lymphomas, and histiocytic/dendritic cell neoplasms. Expert Rev
Hematol. 10:239–249. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, Harris
NL, Stein H, Siebert R, Advani R, Ghielmini M, Salles GA, Zelenetz
AD, et al: The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization
classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 127:2375–2390. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Matutes E: The 2017 WHO update on mature
T- and natural killer (NK) cell neoplasms. Int J Lab Hematol.
40:97–103. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lupu M, Caruntu A, Caruntu C, Papagheorghe
LML, Ilie MA, Voiculescu V, Boda D, Constantin C, Tanase C, Sifaki
M, et al: Neuroendocrine factors: The missing link in non melanoma
skin cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 38:1327–1340. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
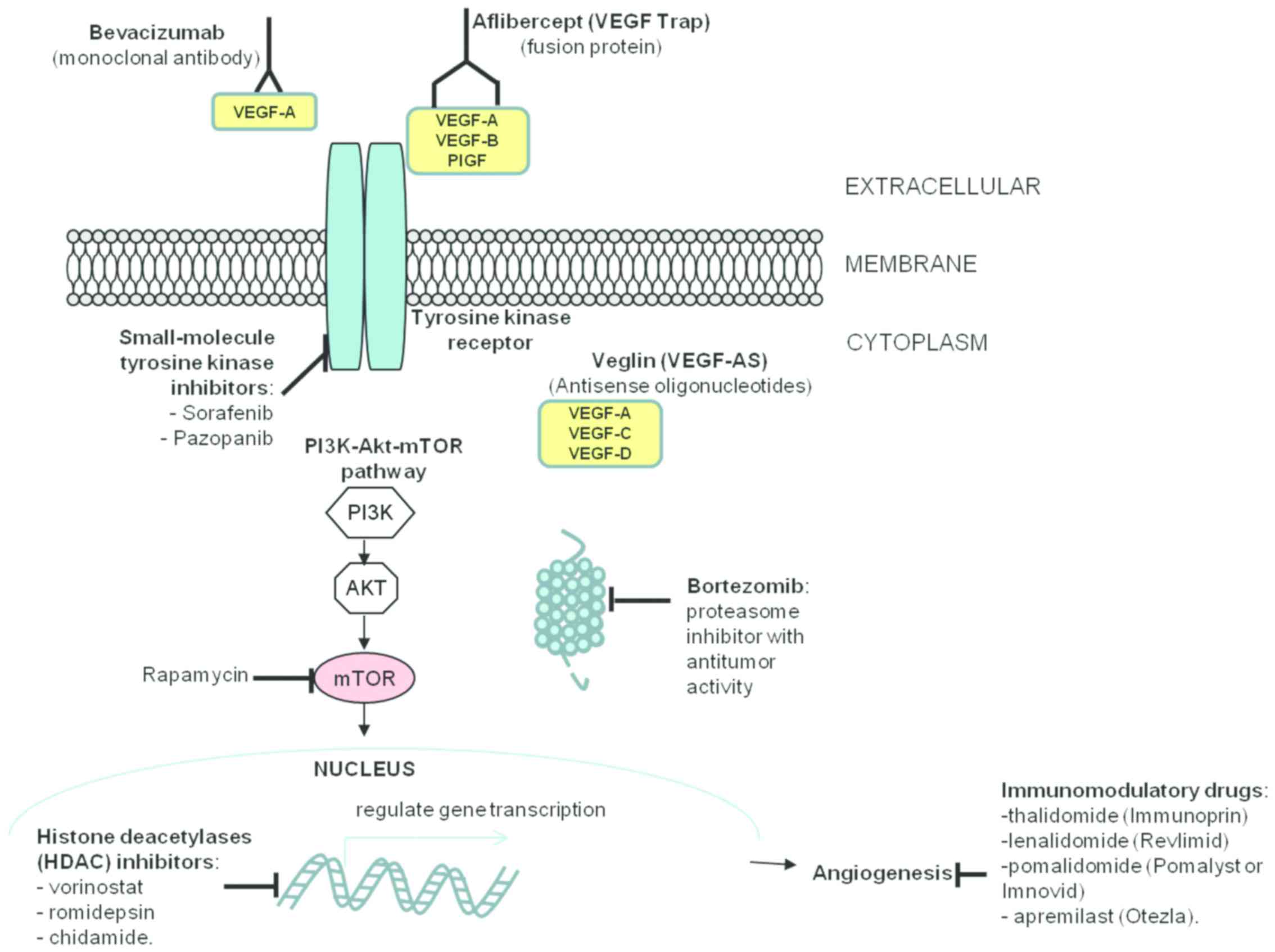
|
Scarisbrick JJ, Hodak E, Bagot M,
Stranzenbach R, Stadler R, Ortiz-Romero PL, Papadavid E, Evison F,
Knobler R, Quaglino P, et al: Blood classification and blood
response criteria in mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome using
flow cytometry: Recommendations from the EORTC cutaneous lymphoma
task force. Eur J Cancer. 93:47–56. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shahrabi S, Rezaeeyan H, Ahmadzadeh A,
Shahjahani M and Saki N: Bone marrow blood vessels: Normal and
neoplastic niche. Oncol Rev. 10:3062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vacca A, Moretti S, Ribatti D, Pellegrino
A, Pimpinelli N, Bianchi B, Bonifazi E, Ria R, Serio G and Dammacco
F: Progression of mycosis fungoides is associated with changes in
angiogenesis and expression of the matrix metalloproteinases 2 and
9. Eur J Cancer. 33:1685–1692. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mazur G, Woźniak Z, Wróbel T, Maj J and
Kuliczkowski K: Increased angiogenesis in cutaneous T-cell
lymphomas. Pathol Oncol Res. 10:34–36. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miyagaki T, Sugaya M, Oka T, Takahashi N,
Kawaguchi M, Suga H, Fujita H, Yoshizaki A, Asano Y and Sato S:
Placental growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor
together regulate tumour progression via increased vasculature in
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Acta Derm Venereol. 97:586–592. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Levine AM, Tulpule A, Quinn DI, Gorospe G
III, Smith DL, Hornor L, Boswell WD, Espina BM, Groshen SG, Masood
R, et al: Phase I study of antisense oligonucleotide against
vascular endothelial growth factor: Decrease in plasma vascular
endothelial growth factor with potential clinical efficacy. J Clin
Oncol. 24:1712–1719. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zain J and O'Connor OA: Targeting histone
deacetylases in the treatment of B- and T-cell malignancies. Invest
New Drugs. 28:S58–S78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Litvinov IV, Netchiporouk E, Cordeiro B,
Zargham H, Pehr K, Gilbert M, Zhou Y, Moreau L, Woetmann A, Ødum N,
et al: Ectopic expression of embryonic stem cell and other
developmental genes in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. OncoImmunology.
3:e9700252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tanase C, Albulescu R, Codrici E, Calenic
B, Popescu ID, Mihai S, Necula L, Cruceru ML and Hinescu ME:
Decreased expression of APAF-1 and increased expression of
cathepsin B in invasive pituitary adenoma. OncoTargets Ther.
8:81–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sibbesen NA, Kopp KL, Litvinov IV, Jønson
L, Willerslev-Olsen A, Fredholm S, Petersen DL, Nastasi C,
Krejsgaard T, Lindahl LM, et al: Jak3, STAT3, and STAT5 inhibit
expression of miR-22, a novel tumor suppressor microRNA, in
cutaneous T-Cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 6:20555–20569. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bagherani N and Smoller BR: An overview of
cutaneous T cell lymphomas. F1000 Res. 5:52016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kabasawa M, Sugaya M, Oka T, Takahashi N,
Kawaguchi M, Suga H, Miyagaki T, Takahashi T, Shibata S, Fujita H,
et al: Decreased interleukin-21 expression in skin and blood in
advanced mycosis fungoides. J Dermatol. 43:819–822. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vieyra-Garcia PA, Wei T, Naym DG, Fredholm
S, Fink-Puches R, Cerroni L, Odum N, O'Malley JT, Gniadecki R and
Wolf P: STAT3/5-dependent IL9 overexpression contributes to
neoplastic cell survival in mycosis fungoides. Clin Cancer Res.
22:3328–3339. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ikeda S, Kitadate A, Ito M, Abe F, Nara M,
Watanabe A, Takahashi N, Miyagaki T, Sugaya M and Tagawa H:
Disruption of CCL20-CCR6 interaction inhibits metastasis of
advanced cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 7:13563–13574.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lauenborg B, Christensen L, Ralfkiaer U,
Kopp KL, Jønson L, Dabelsteen S, Bonefeld CM, Geisler C, Gjerdrum
LM, Zhang Q, et al: Malignant T-cells express lymphotoxin α and
drive endothelial activation in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Oncotarget. 6:15235–15249. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maj J, Jankowska-Konsur AM, Hałoń A,
Woźniak Z, Plomer-Niezgoda E and Reich A: Expression of CXCR4 and
CXCL12 and their correlations to the cell proliferation and
angiogenesis in mycosis fungoides. Postepy Dermatol Alergol.
32:437–442. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gallardo F, Sandoval J, Díaz-Lagares A,
Garcia R, D'Altri T, González J, Alegre V, Servitje O, Crujeiras
AB, Stefánsson ÓA, et al: Notch1 pathway activation results from
the epigenetic abrogation of notch-related microRNAs in mycosis
fungoides. J Invest Dermatol. 135:3144–3152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lindahl LM, Fredholm S, Joseph C, Nielsen
BS, Jønson L, Willerslev-Olsen A, Gluud M, Blümel E, Petersen DL,
Sibbesen N, et al: STAT5 induces miR-21 expression in cutaneous T
cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 7:45730–45744. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Abe F, Kitadate A, Ikeda S, Yamashita J,
Nakanishi H, Takahashi N, Asaka C, Teshima K, Miyagaki T, Sugaya M,
et al: Histone deacetylase inhibitors inhibit metastasis by
restoring a tumor suppressive microRNA-150 in advanced cutaneous
T-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 8:7572–7585. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
da Silva Almeida AC, Abate F, Khiabanian
H, Martinez-Escala E, Guitart J, Tensen CP, Vermeer MH, Rabadan R,
Ferrando A and Palomero T: The mutational landscape of cutaneous
T-cell lymphoma and Sézary syndrome. Nat Genet. 47:1465–1470. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bosseila M, Sayed Sayed K, El-Din Sayed SS
and Abd El Monaem A: Evaluation of angiogenesis in early mycosis
fungoides patients: Dermoscopic and immunohistochemical study.
Dermatology. 231:82–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gratzinger D, Zhao S, Tibshirani RJ, Hsi
ED, Hans CP, Pohlman B, Bast M, Avigdor A, Schiby G, Nagler A, et
al: Prognostic significance of VEGF, VEGF receptors, and
microvessel density in diffuse large B cell lymphoma treated with
anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 88:38–47. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mendt M and Cardier JE: Stromal-derived
factor-1 and its receptor, CXCR4, are constitutively expressed by
mouse liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Implications for the
regulation of hematopoietic cell migration to the liver during
extramedullary hematopoiesis. Stem Cells Dev. 21:2142–2151. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Daggett RN, Kurata M, Abe S, Onishi I,
Miura K, Sawada Y, Tanizawa T and Kitagawa M: Expression dynamics
of CXCL12 and CXCR4 during the progression of mycosis fungoides. Br
J Dermatol. 171:722–731. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Arai F, Hirao A, Ohmura M, Sato H,
Matsuoka S, Takubo K, Ito K, Koh GY and Suda T: Tie2/angiopoietin-1
signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence in the bone
marrow niche. Cell. 118:149–161. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kawaguchi M, Sugaya M, Suga H, Miyagaki T,
Ohmatsu H, Fujita H, Asano Y, Tada Y, Kadono T and Sato S: Serum
levels of angiopoietin-2, but not angiopoietin-1, are elevated in
patients with erythrodermic cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Acta Derm
Venereol. 94:9–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Alshenawy HA: Prognostic significance of
vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblastic growth
factor, and microvessel density and their relation to cell
proliferation in B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Diagn Pathol.
14:321–327. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lauenborg B, Litvinov IV, Zhou Y,
Willerslev-Olsen A, Bonefeld CM, Nastasi C, Fredholm S, Lindahl LM,
Sasseville D, Geisler C, et al: Malignant T-cells activate
endothelial cells via IL-17 F. Blood Cancer J. 7:e5862017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Furudate S, Fujimura T, Kakizaki A,
Kambayashi Y, Asano M, Watabe A and Aiba S: The possible
interaction between periostin expressed by cancer stroma and
tumor-associated macrophages in developing mycosis fungoides. Exp
Dermatol. 25:107–112. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tuzova M, Richmond J, Wolpowitz D,
Curiel-Lewandrowski C, Chaney K, Kupper T and Cruikshank W:
CCR4+ T-cell recruitment to the skin in mycosis
fungoides: Potential contributions by thymic stromal lymphopoietin
and interleukin-16. Leuk Lymphoma. 56:440–449. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hashikawa K, Yasumoto S, Nakashima K,
Arakawa F, Kiyasu J, Kimura Y, Saruta H, Nakama T, Yasuda K,
Tashiro K, et al: Microarray analysis of gene expression by
microdissected epidermis and dermis in mycosis fungoides and adult
T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Int J Oncol. 45:1200–1208. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Furudate S, Fujimura T, Kakizaki A, Hidaka
T, Asano M and Aiba S: Tumor-associated M2 macrophages in mycosis
fungoides acquire immunomodulatory function by interferon alpha and
interferon gamma. J Dermatol Sci. 83:182–189. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fujimura T, Kambayashi Y, Fujisawa Y,
Hidaka T and Aiba S: Tumor-associated macrophages: Therapeutic
targets for skin cancer. Front Oncol. 8:32018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Humphrey RL, Karpetsky TP, Neuwelt EA and
Levy CC: Levels of serum ribonuclease as an indicator of renal
insufficiency in patients with leukemia. Cancer Res. 37:2015–2022.
1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Serban M, Cucu C, Mihăilescu E and Micu D:
Value of ribonuclease and guanase activity for the diagnosis of
leukemias. Rev Roum Med Intern. 11:319–324. 1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Biomarkers Definitions Working G;
Biomarkers Definitions Working Group, : Biomarkers and surrogate
endpoints: Preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin
Pharmacol Ther. 69:89–95. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pistol-Tanase C, Raducan E, Dima SO,
Albulescu L, Alina I, Marius P, Cruceru LM, Codorean E, Neagu TM
and Popescu I: Assessment of soluble angiogenic markers in
pancreatic cancer. Biomarkers Med. 2:447–455. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
FDA-NIH Biomarker Working Group, : BEST
(Biomarkers, EndpointS, and other Tools) Resource (Internet).
Silver Spring; MA, USA: 2016
|
|
47
|
Caruntu C, Boda D, Dumitrascu G,
Constantin C and Neagu M: Proteomics focusing on immune markers in
psoriatic arthritis. Biomarkers Med. 9:513–528. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Neagu M, Caruntu C, Constantin C, Boda D,
Zurac S, Spandidos DA and Tsatsakis AM: Chemically induced skin
carcinogenesis: Updates in experimental models. (Review) Oncol Rep.
35:2516–2528. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Mihai S, Codrici E, Popescu ID, Enciu AM,
Rusu E, Zilisteanu D, Albulescu R, Anton G and Tanase C: Proteomic
biomarkers panel: New insights in chronic kidney disease. Dis
Markers. 2016:31852322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Matei C, Tampa M, Caruntu C, Ion RM,
Georgescu SR, Dumitrascu GR, Constantin C and Neagu M: Protein
microarray for complex apoptosis monitoring of dysplastic oral
keratinocytes in experimental photodynamic therapy. Biol Res.
47:332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tanase CP, Albulescu R and Neagu M:
Application of 3D hydrogel microarrays in molecular diagnostics:
Advantages and limitations. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 11:461–464. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Caruntu C: Catecholamines increase in
vitro proliferation of murine B16F10 melanoma cells. Acta
Endocrinol (Bucur). 10:545–558. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Boda D: Cellomics as integrative omics for
cancer. Curr Proteomics. 10:237–245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zurac S, Neagu M, Constantin C, Cioplea M,
Nedelcu R, Bastian A, Popp C, Nichita L, Andrei R, Tebeica T, et
al: Variations in the expression of TIMP1, TIMP2 and TIMP3 in
cutaneous melanoma with regression and their possible function as
prognostic predictors. Oncol Lett. 11:3354–3360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ion A, Popa IM, Papagheorghe LM, Lisievici
C, Lupu M, Voiculescu V, Caruntu C and Boda D: Proteomic approaches
to biomarker discovery in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Dis Markers.
2016:96024722016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Igreja C, Courinha M, Cachaço AS, Pereira
T, Cabeçadas J, Da Silva MG and Dias S: Characterization and
clinical relevance of circulating and biopsy-derived endothelial
progenitor cells in lymphoma patients. Haematologica. 92:469–477.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Schadendorf D, Matharoo-Ball B, Rees R,
Ugurel S and Utikal J: Prognostic biomarkers of cutaneous
malignancies - serological, immunohistochemical and proteomic
approaches. Curr Cancer Ther Rev. 4:96–104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Hassel JC, Meier R, Joller-Jemelka H, Burg
G and Dummer R: Serological immunomarkers in cutaneous T-cell
lymphoma. Dermatology. 209:296–300. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Moshkovskii SA, Sokolova EE, Brattseva EV,
Karpova MA, Pyatnitskiy MA, Kubanova AA and Archakov AI: Proteome
and cytokine serum profiling to diagnose a mycosis fungoides.
Proteomics Clin Appl. 5:432–439. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Popescu I, Raducan E, Dinischiotu A and
Tanase C: Applications of SELDI-TOF technology in cancer biomarkers
discovery. Rom Biotechnol Lett. 15:5654–5667. 2010.
|
|
61
|
Wilcox RA: Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: 2017
update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J
Hematol. 92:1085–1102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Van Arnam JS, Lim MS and Elenitoba-Johnson
KSJ: Novel insights into the pathogenesis of T-cell lymphomas.
Blood. 131:2320–2330. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kataoka K, Nagata Y, Kitanaka A, Shiraishi
Y, Shimamura T, Yasunaga J, Totoki Y, Chiba K, Sato-Otsubo A, Nagae
G, et al: Integrated molecular analysis of adult T cell
leukemia/lymphoma. Nat Genet. 47:1304–1315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W,
Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S,
Holmgren E, et al: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2335–2342. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J,
Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R and Johnson DH:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Miller KD: E2100: A phase III trial of
paclitaxel versus paclitaxel/bevacizumab for metastatic breast
cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 3:421–422. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lockhart AC, Rothenberg ML, Dupont J,
Cooper W, Chevalier P, Sternas L, Buzenet G, Koehler E, Sosman JA,
Schwartz LH, et al: Phase I study of intravenous vascular
endothelial growth factor trap, aflibercept, in patients with
advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 28:207–214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
D'Amato RJ, Loughnan MS, Flynn E and
Folkman J: Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 91:4082–4085. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Bagot M, Hasan B, Whittaker S,
Beylot-Barry M, Knobler R, Shah E, Marreaud S, Morris S, Dalle S,
Servitje O, et al: A phase III study of lenalidomide maintenance
after debulking therapy in patients with advanced cutaneous T-cell
lymphoma; EORTC 21081 (NCT01098656): Results and lessons learned
for future trial designs. Eur J Dermatol. 27:286–294.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Neagu M, Constantin C and Zurac S: Immune
parameters in the prognosis and therapy monitoring of cutaneous
melanoma patients: Experience, role, and limitations. BioMed Res
Int. 2013:1079402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ferrara N and Kerbel RS: Angiogenesis as a
therapeutic target. Nature. 438:967–974. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Shaked Y, Ciarrocchi A, Franco M, Lee CR,
Man S, Cheung AM, Hicklin DJ, Chaplin D, Foster FS, Benezra R, et
al: Therapy-induced acute recruitment of circulating endothelial
progenitor cells to tumors. Science. 313:1785–1787. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Mayerhofer M, Valent P, Sperr WR, Griffin
JD and Sillaber C: BCR/ABL induces expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor and its transcriptional activator,
hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha, through a pathway involving
phosphoinositide 3-kinase and the mammalian target of rapamycin.
Blood. 100:3767–3775. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Guba M, von Breitenbuch P, Steinbauer M,
Koehl G, Flegel S, Hornung M, Bruns CJ, Zuelke C, Farkas S,
Anthuber M, et al: Rapamycin inhibits primary and metastatic tumor
growth by antiangiogenesis: Involvement of vascular endothelial
growth factor. Nat Med. 8:128–135. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kremer M, Sliva K, Klemke CD and Schnierle
BS: Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cells are sensitive to rapamycin. Exp
Dermatol. 19:800–805. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Marzec M, Liu X, Wysocka M, Rook AH, Odum
N and Wasik MA: Simultaneous inhibition of mTOR-containing complex
1 (mTORC1) and MNK induces apoptosis of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
(CTCL) cells. PLoS One. 6:e248492011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Piekarz RL, Robey R, Sandor V, Bakke S,
Wilson WH, Dahmoush L, Kingma DM, Turner ML, Altemus R and Bates
SE: Inhibitor of histone deacetylation, depsipeptide, in the
treatment of peripheral and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: A case
report. Blood. 98:2865–2868. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hideshima T, Richardson P, Chauhan D,
Palombella VJ, Elliott PJ, Adams J and Anderson KC: The proteasome
inhibitor PS-341 inhibits growth, induces apoptosis, and overcomes
drug resistance in human multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res.
61:3071–3076. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Shah JJ and Orlowski RZ: Proteasome
inhibitors in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Leukemia.
23:1964–1979. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Jain S, Zain J and O'Connor O: Novel
therapeutic agents for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol.
5:242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Buac D, Shen M, Schmitt S, Kona FR,
Deshmukh R, Zhang Z, Neslund-Dudas C, Mitra B and Dou QP: From
bortezomib to other inhibitors of the proteasome and beyond. Curr
Pharm Des. 19:4025–4038. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Orlowski RZ and Kuhn DJ: Proteasome
inhibitors in cancer therapy: lessons from the first decade. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:1649–1657. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Kozuch PS, Rocha-Lima CM, Dragovich T,
Hochster H, O'Neil BH, Atiq OT, Pipas JM, Ryan DP and Lenz HJ:
Bortezomib with or without irinotecan in relapsed or refractory
colorectal cancer: Results from a randomized phase II study. J Clin
Oncol. 26:2320–2326. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Morris MJ, Kelly WK, Slovin S, Ryan C,
Eicher C, Heller G and Scher HI: A phase II trial of bortezomib and
prednisone for castration resistant metastatic prostate cancer. J
Urol. 178:2378–2383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Schmid P, Kühnhardt D, Kiewe P,
Lehenbauer-Dehm S, Schippinger W, Greil R, Lange W, Preiss J,
Niederle N, Brossart P, et al: A phase I/II study of bortezomib and
capecitabine in patients with metastatic breast cancer previously
treated with taxanes and/or anthracyclines. Ann Oncol. 19:871–876.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Heider U, Rademacher J, Lamottke B, Mieth
M, Moebs M, von Metzler I, Assaf C and Sezer O: Synergistic
interaction of the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA with the
proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Eur J
Haematol. 82:440–449. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Kang HJ, Kim JS, Park SK,
Kim HJ, Lee J, Ryoo BY, Ko YH, Huh J, et al: Consortium for
improving survival of lymphoma (CISL) investigators: Bortezomib in
combination with CHOP as first-line treatment for patients with
stage III/IV peripheral T-cell lymphomas: A multicentre,
single-arm, phase 2 trial. Eur J Cancer. 48:3223–3231. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Zinzani PL, Musuraca G, Tani M, Stefoni V,
Marchi E, Fina M, Pellegrini C, Alinari L, Derenzini E, de Vivo A,
et al: Phase II trial of proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in
patients with relapsed or refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J
Clin Oncol. 25:4293–4297. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|