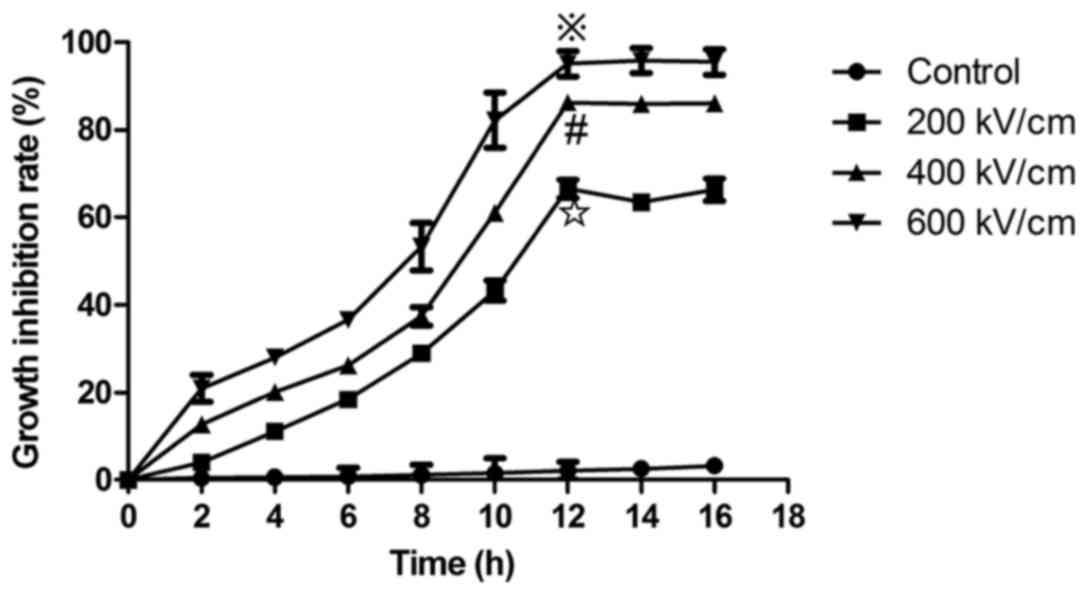
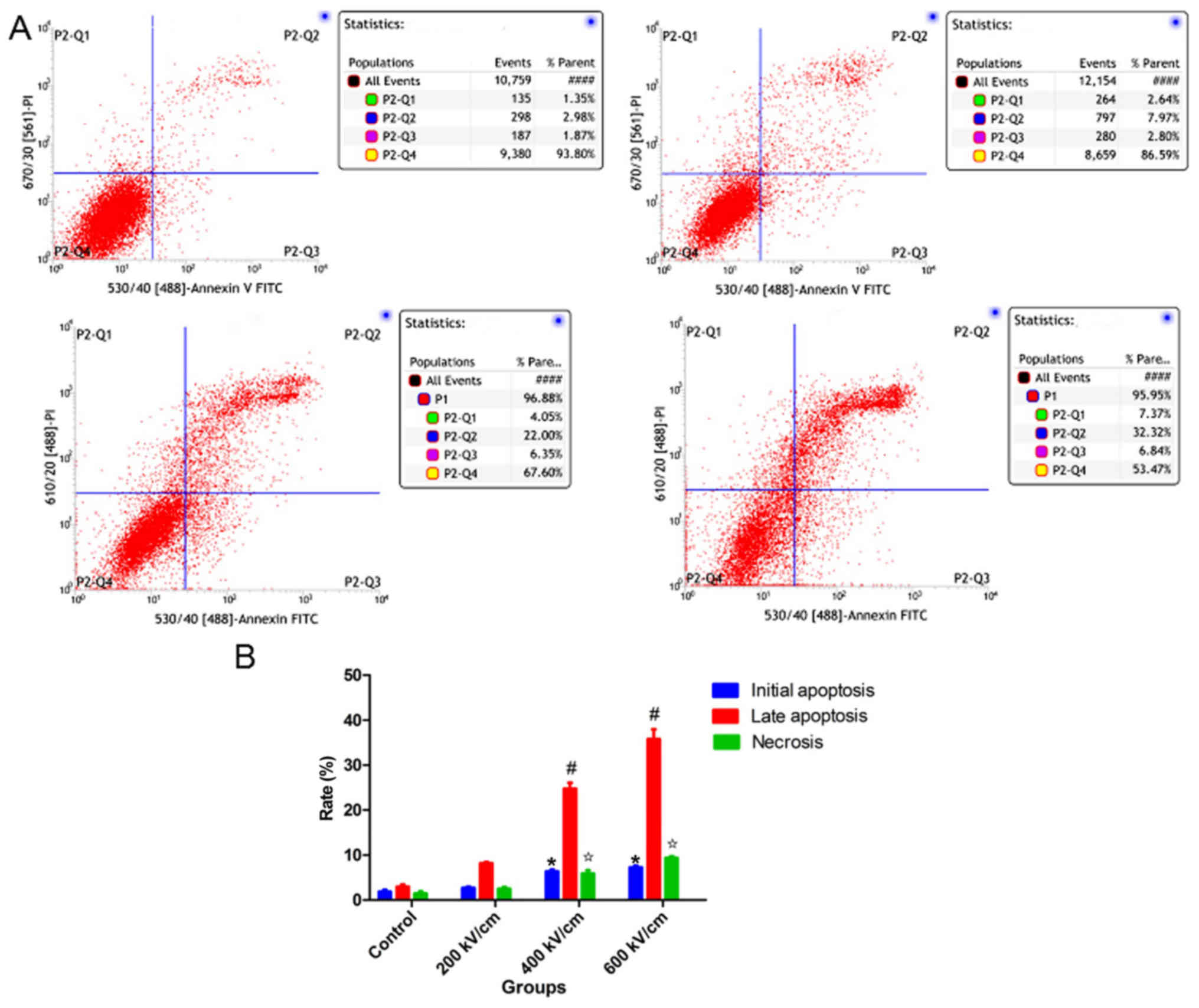
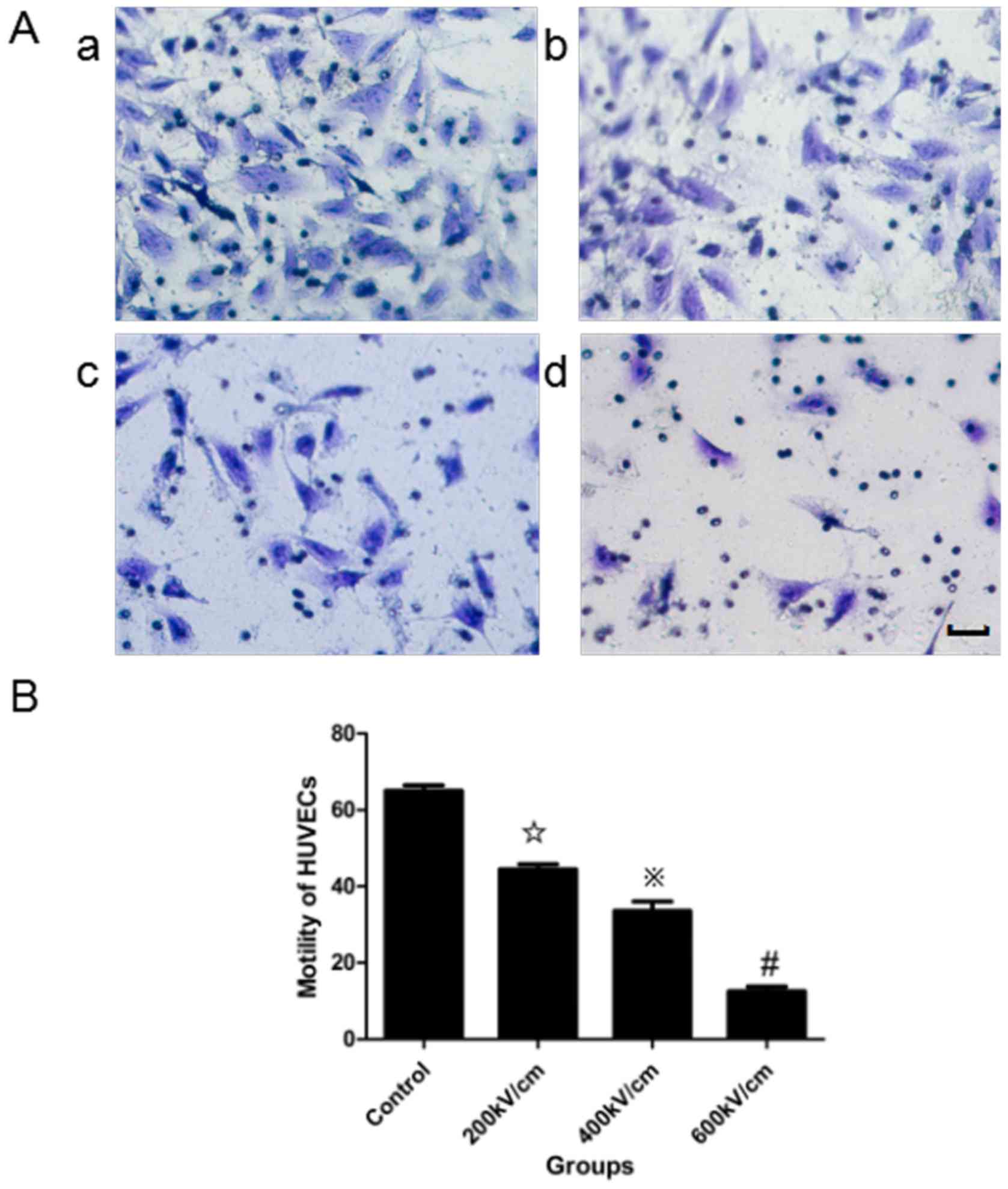
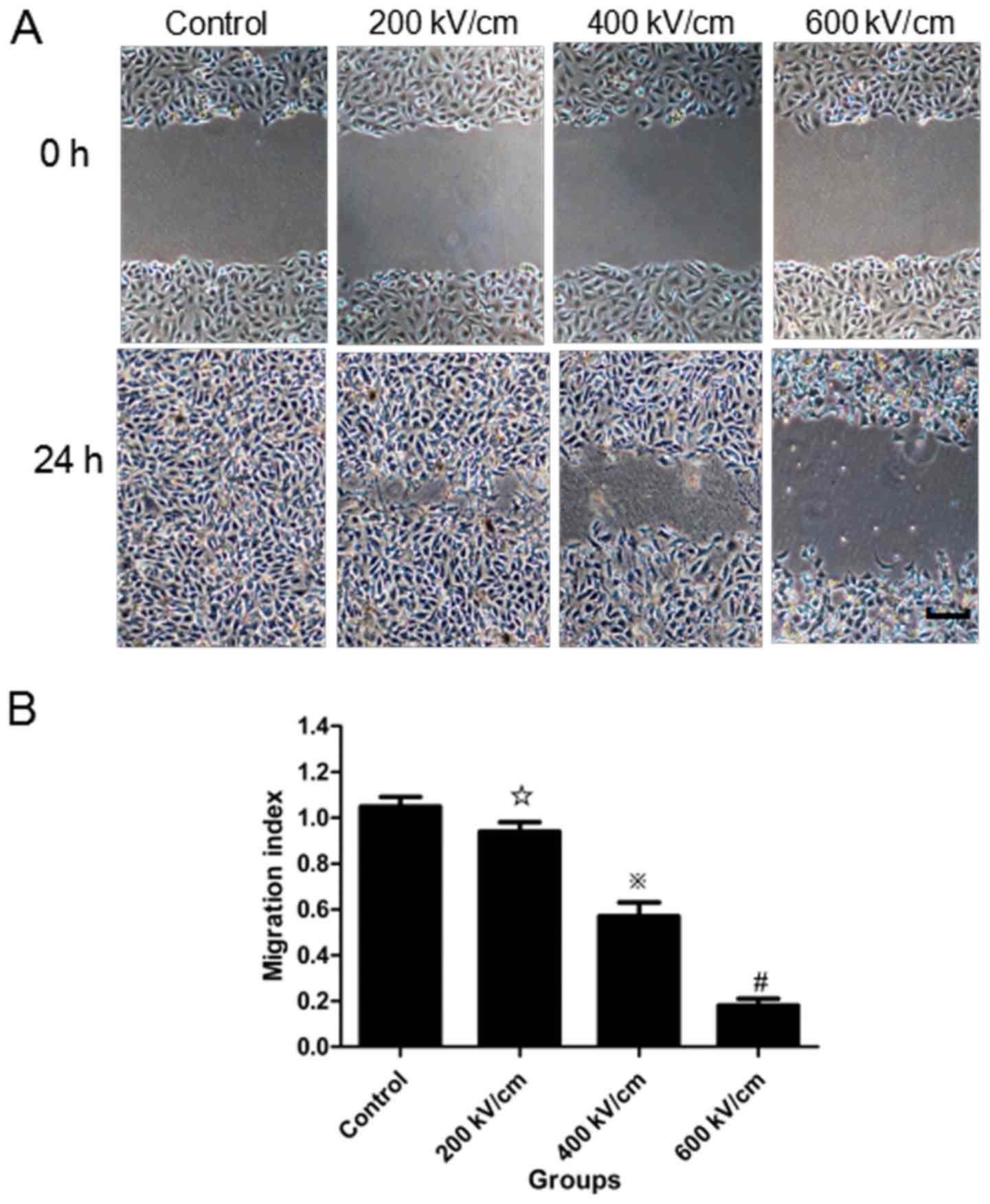
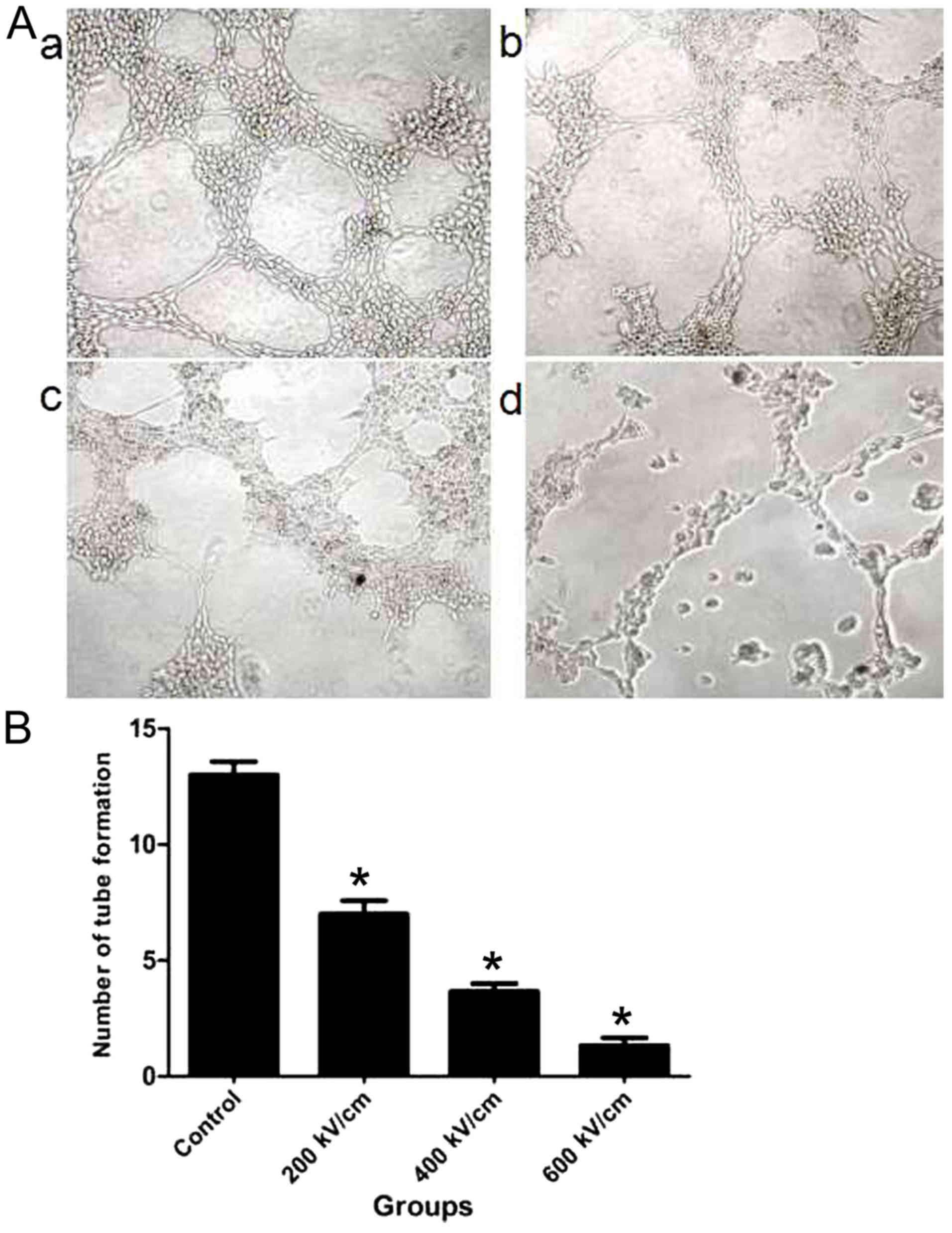
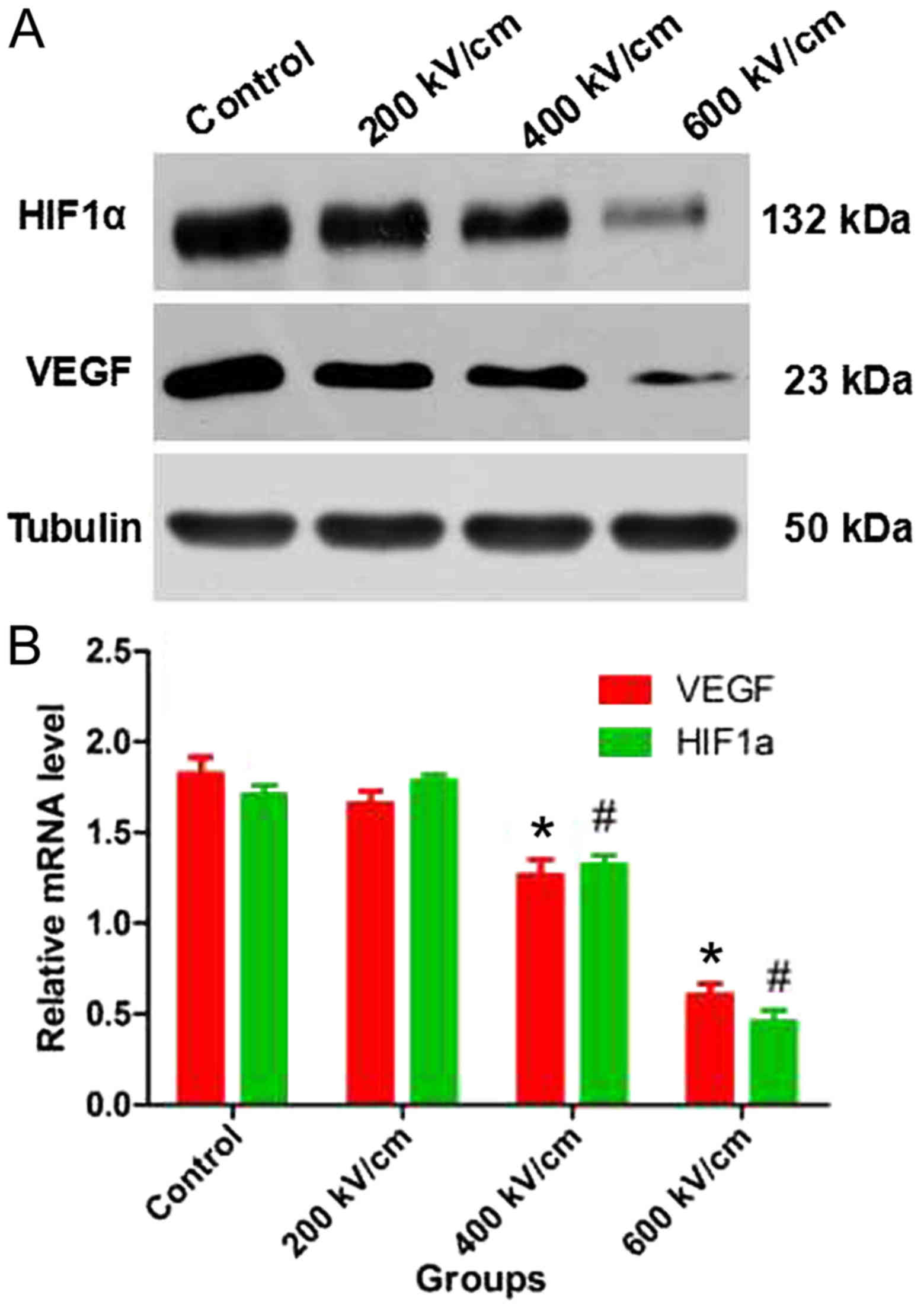
|
1
|
Landt S, Wehling M, Heidecke H, Jeschke S,
Korlach S, Stöblen F, Schmid P, Blohmer JU, Lichtenegger W, Sehouli
J and Kümmel S: Prognostic significance of angiogenic factors in
uterine cervical cancer. Anticancer Res. 31:2589–2595.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Monk BJ, Willmott LJ and Sumner DA:
Anti-angiogenesis agents in metastatic or recurrent cervical
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 116:181–186. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Monk BJ and Herzog TJ: The evolution of
cost-effective screening and prevention of cervical carcinoma:
Implications of the 2006 consensus guidelines and human
papillomavirus vaccination. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 197:337–339. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ackermann M, Carvajal IM, Morse BA, Moreta
M, O'Neil S, Kossodo S, Peterson JD, Delventhal V, Marsh HN,
Furfine ES and Konerding MA: Adnectin CT-322 inhibits tumor growth
and affects microvascular architecture and function in Colo205
tumor xenografts. Int J Oncol. 38:71–80. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Verheul HM and Pinedo HM: Possible
molecular mechanisms involved in the toxicity of angiogenesis
inhibition. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:475–485. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma J and Waxman DJ: Combination of
antiangiogenesis with chemotherapy for more effective cancer
treatment. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3670–3684. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seol HJ, Ulak R, Ki KD and Lee JM:
Cytotoxic and targeted systemic therapy in advanced and recurrent
cervical cancer: Experience from clinical trials. Tohoku J Exp Med.
232:269–276. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baum CE, Stone AP and Tyo JS:
Ultra-wideband, short-pulse electromagnetics. 8th. New York:
Springer; 2007, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wu L, Yao C, Xiong Z, Zhang R, Wang Z, Wu
Y, Qin Q and Hua Y: The effects of a picosecond pulsed electric
field on angiogenesis in the cervical cancer xenograft models.
Gynecol Oncol. 141:175–181. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arnaoutova I, George J, Kleinman HK and
Benton G: The endothelial cell tube formation assay on basement
membrane turns 20: State of the science and the art. Angiogenesis.
12:267–274. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hua YY, Wang XS, Zhang Y, Yao CG, Zhang XM
and Xiong ZA: Intense picosecond pulsed electric fields induce
apoptosis through a mitochondrial-mediated pathway in HeLa cells.
Mol Med Rep. 5:981–987. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Folkman J: The role of angiogenesis in
tumor growth. Semin Cancer Biol. 3:65–71. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eskander RN and Tewari KS: Targeting
angiogenesis in advanced cervical cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol.
6:280–292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kerbel RS: Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J
Med. 358:2039–2049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Erös de Bethlenfalva-Hora C, Mertens JC,
Piguet AC, Kettenbach J, Schmitt J, Terracciano L, Weimann R,
Dufour JF and Geier A: Radiofrequency ablation suppresses distant
tumour growth in a novel rat model of multifocal hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Sci (Lond). 126:243–252. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Groblewska M, Siewko M, Mroczko B and
Szmitkowski M: The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and
their inhibitors (TIMPs) in the development of esophageal cancer.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 50:12–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ribatti D: Genetic and epigenetic
mechanisms in the early development of the vascular system. J Anat.
208:139–152. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Denekamp J, Hill SA and Hobson B: Vascular
occlusion and tumour cell death. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol.
19:271–275. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hajitou A, Grignet C, Devy L, Berndt S,
Blacher S, Deroanne CF, Bajou K, Fong T, Chiang Y, Foidart JM and
Noël A: The antitumoral effect of endostatin and angiostatin is
associated with a down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth
factor expression in tumor cells. FASEB J. 16:1802–1804. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kaur B, Khwaja FW, Severson EA, Matheny
SL, Brat DJ and Van Meir EG: Hypoxia and the
hypoxia-inducible-factor pathway in glioma growth and angiogenesis.
Neuro Oncol. 7:134–153. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chaplin DJ and Horsman MR: The influence
of tumour temperature on ischemia-induced cell death: Potential
implications for the evaluation of vascular mediated therapies.
Radiother Oncol. 30:59–65. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Noguera R, Fredlund E, Piqueras M, Pietras
A, Beckman S, Navarro S and Påhlman S: HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha
are differentially regulated in vivo in neuroblastoma: High
HIF-1alpha correlates negatively to advanced clinical stage and
tumor vascularization. Clin Cancer Res. 15:7130–7136. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brown JM and Wilson WR: Exploiting tumour
hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:437–447. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vaupel P and Mayer A: Hypoxia in tumors:
Pathogenesis-related classification, characterization of hypoxia
subtypes, and associated biological and clinical implications. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 812:19–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|