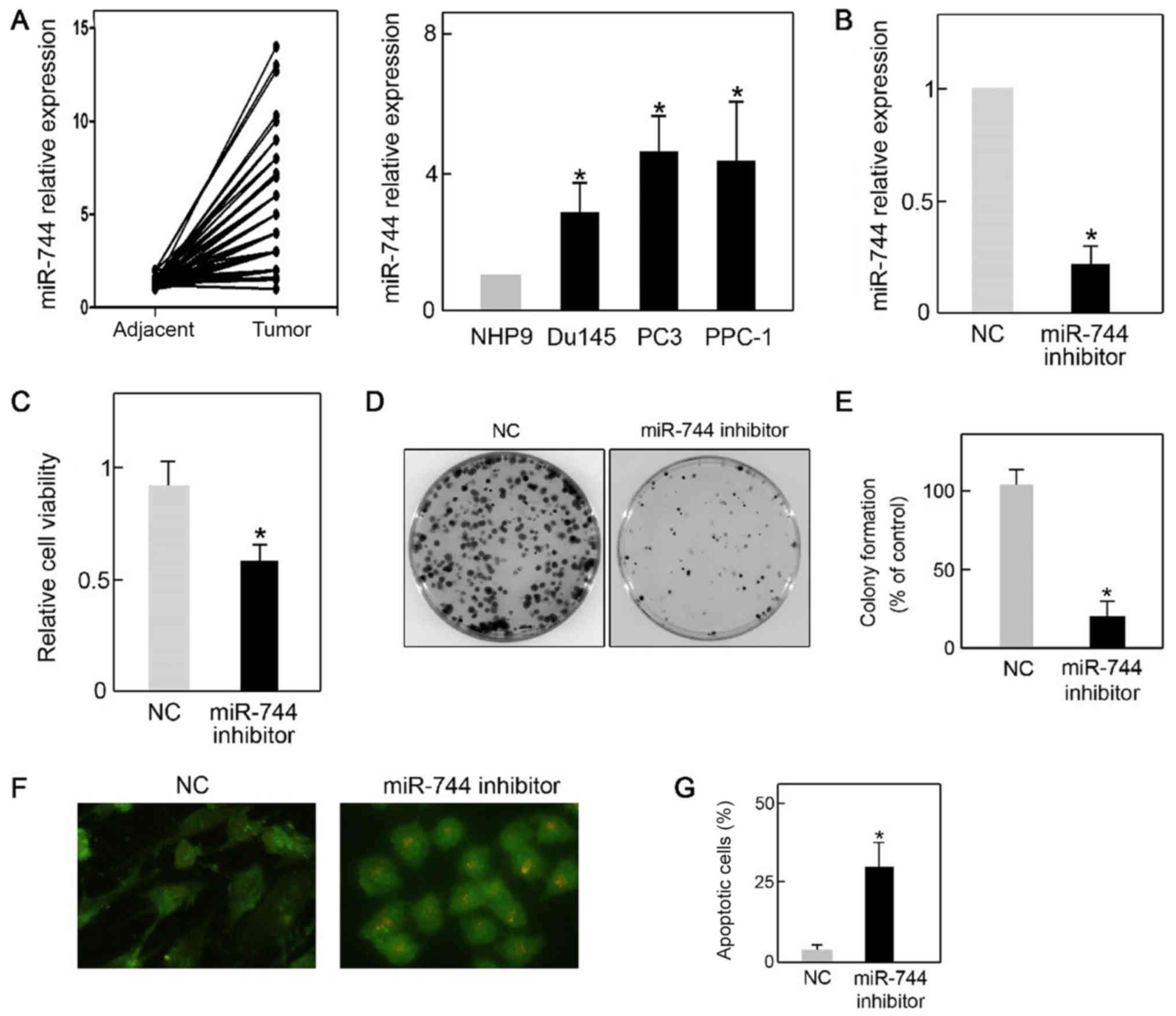
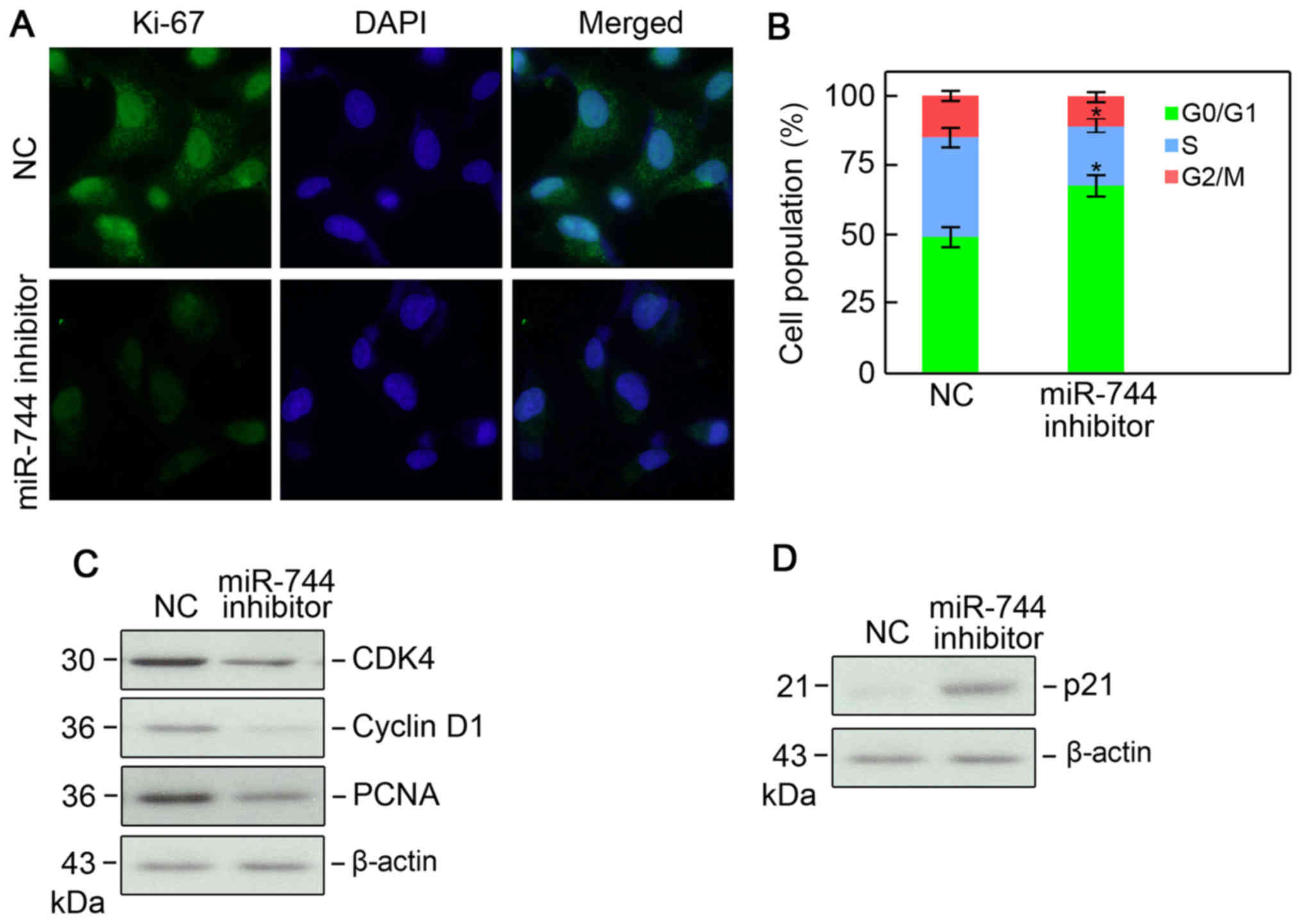
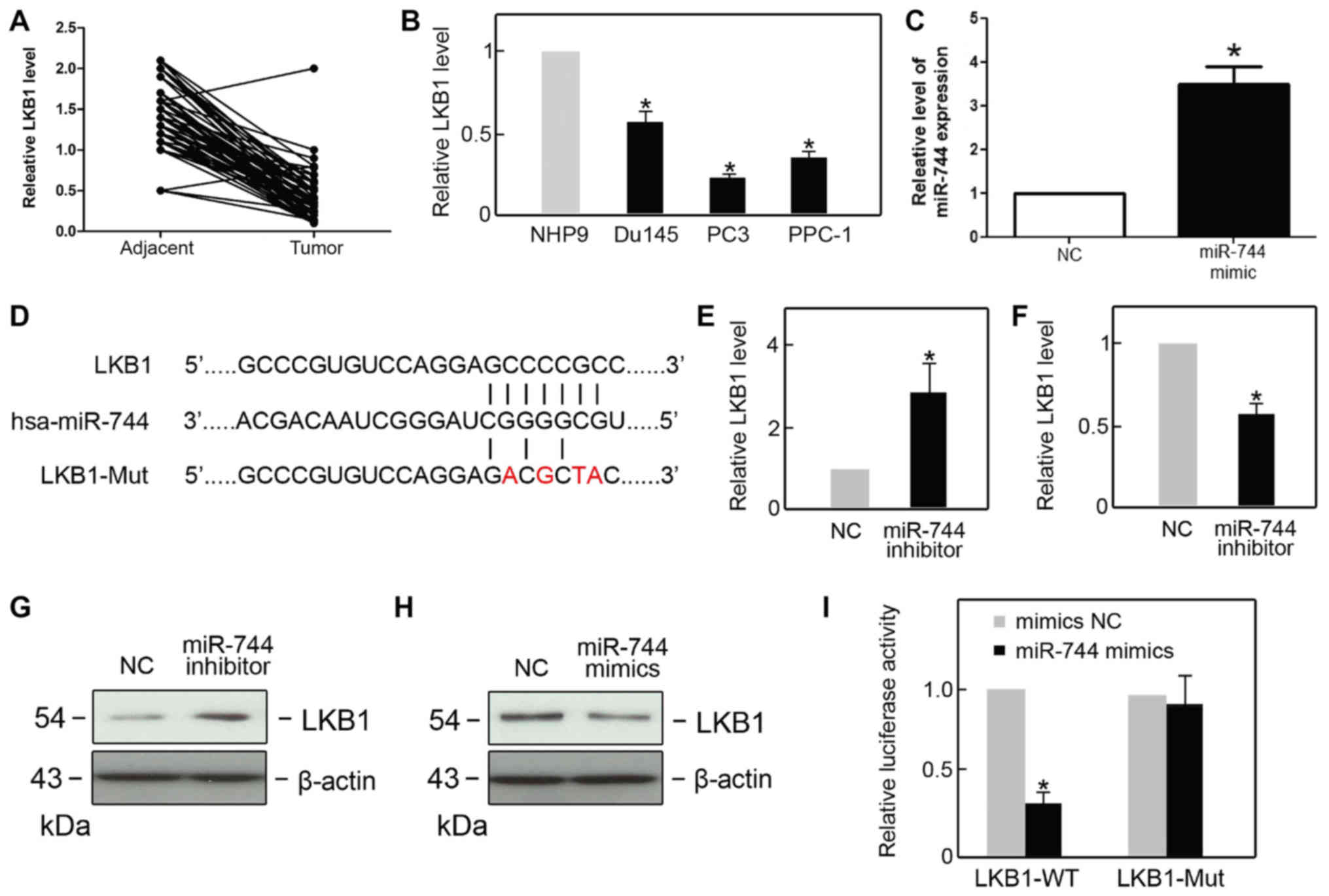
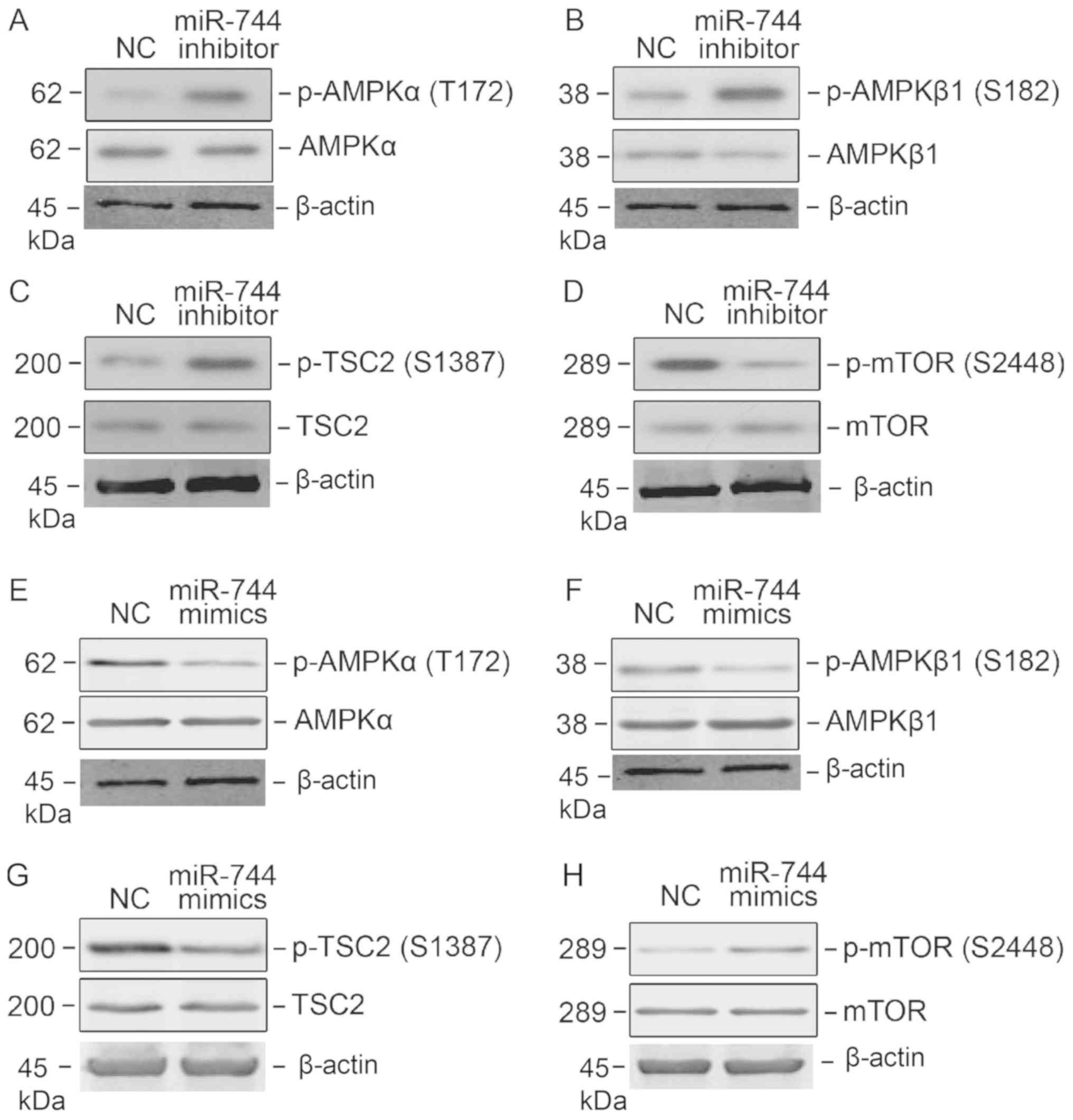
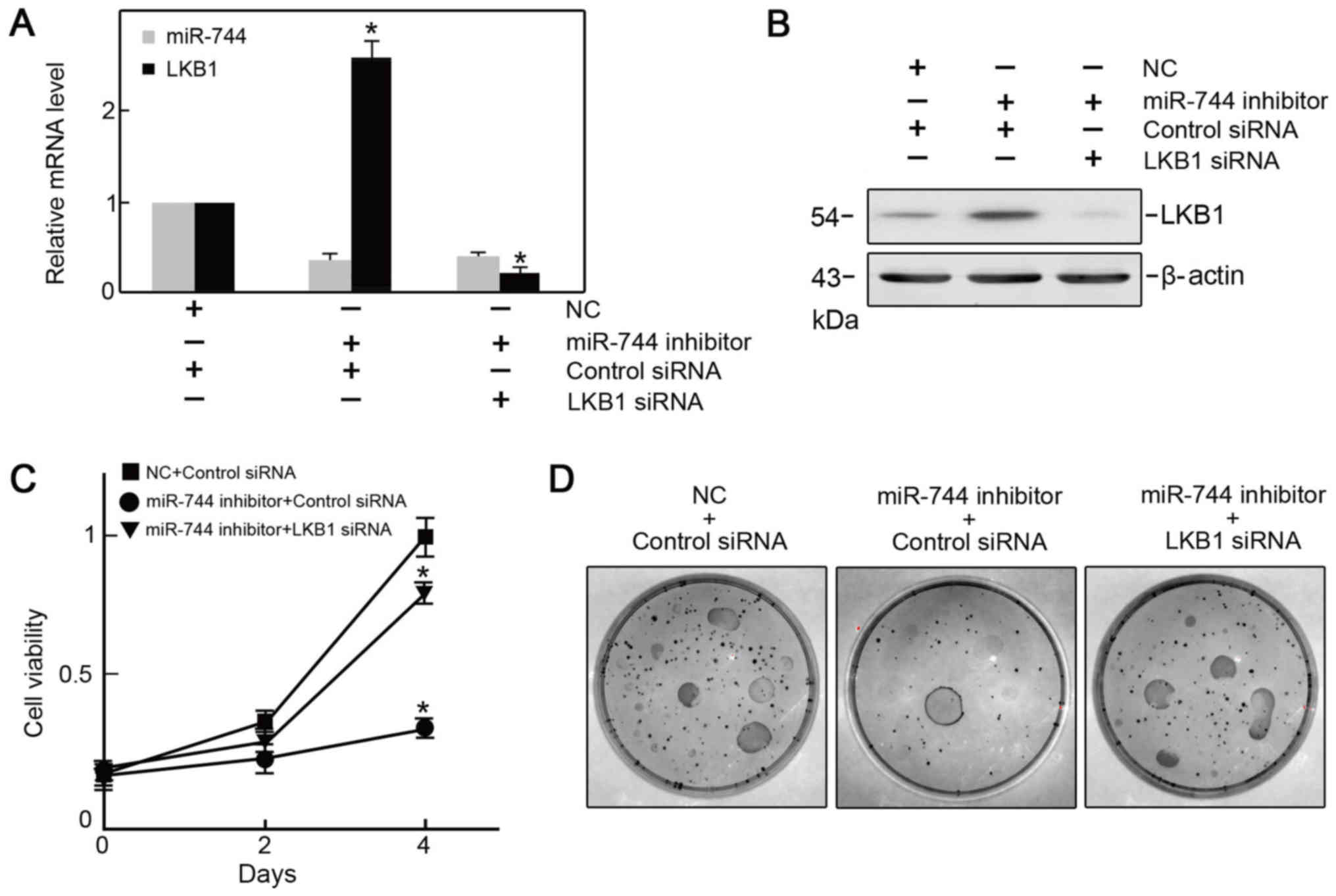
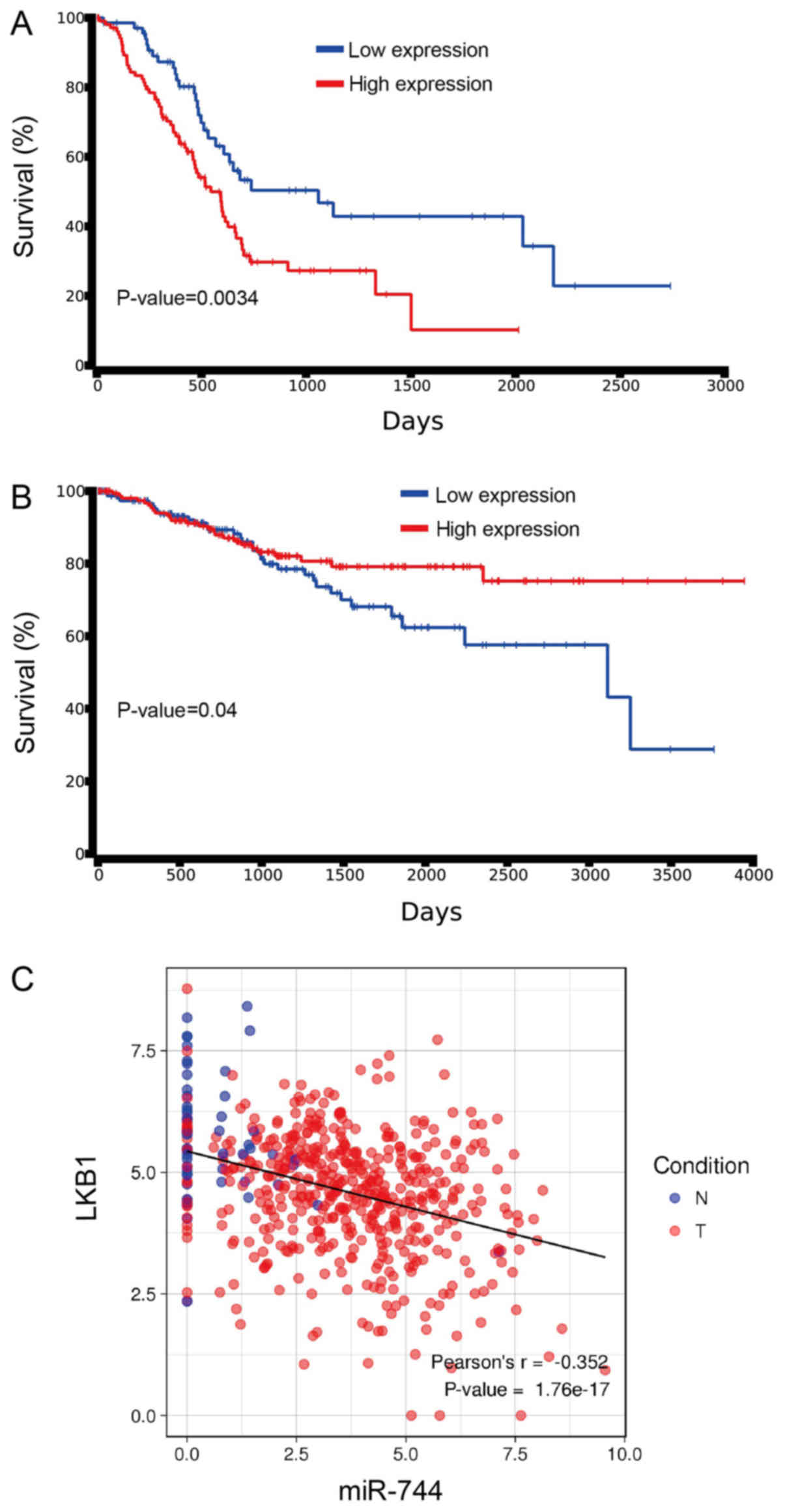
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S and He J:
Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2011. Chin J Cancer
Res. 27:2–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pound CR, Partin AW, Eisenberger MA, Chan
DW, Pearson JD and Walsh PC: Natural history of progression after
PSA elevation following radical prostatectomy. JAMA. 281:1591–1597.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xie H, Li C, Dang Q, Chang LS and Li L:
Infiltrating mast cells increase prostate cancer chemotherapy and
radiotherapy resistances via modulation of p38/p53/p21 and ATM
signals. Oncotarget. 7:1341–1353. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sutherland SI, Pe Benito R, Henshall SM,
Horvath LG and Kench JG: Expression of phosphorylated-mTOR during
the development of prostate cancer. Prostate. 74:1231–1239. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Galardi S, Mercatelli N, Farace MG and
Ciafrè SA: NF-kB and c-Jun induce the expression of the oncogenic
miR-221 and miR-222 in prostate carcinoma and glioblastoma cells.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:3892–3902. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
David R: Small RNAs: miRNA machinery
disposal. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:4–5. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xiao R, Li C and Chai B: miRNA-144
suppresses proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells
through GSPT1. Biomed Pharmacother. 74:138–144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xue J, Chi Y, Chen Y, Huang S, Ye X, Niu
J, Wang W, Pfeffer LM, Shao ZM, Wu ZH and Wu J: MiRNA-621
sensitizes breast cancer to chemotherapy by suppressing FBXO11 and
enhancing p53 activity. Oncogene. 35:448–458. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lewis H, Lance R, Troyer D, Beydoun H,
Hadley M, Orians J, Benzine T, Madric K, Semmes OJ, Drake R, et al:
miR-888 is an expressed prostatic secretions-derived microRNA that
promotes prostate cell growth and migration. Cell Cycle.
13:227–239. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jin M, Zhang T, Liu C, Badeaux MA, Liu B,
Liu R, Jeter C, Chen X, Vlassov AV and Tang DG: miRNA-128
suppresses prostate cancer by inhibiting BMI-1 to inhibit
tumor-initiating cells. Cancer Res. 74:4183–4195. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xuan H, Xue W, Pan J, Sha J, Dong B and
Huang Y: Downregulation of miR-221, −30d and −15a contributes to
pathogenesis of prostate cancer by targeting Bmi-1. Biochemistry
(Mosc). 80:276–283. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singh PK, Preus L, Hu Q, Yan L, Long MD,
Morrison CD, Nesline M, Johnson CS, Koochekpour S, Kohli M, et al:
Serum microRNA expression patterns that predict early treatment
failure in prostate cancer patients. Oncotarget. 5:824–840. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miyamae M, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D,
Kawaguchi T, Hirajima S, Okajima W, Ohashi T, Imamura T, Konishi H,
Shiozaki A, et al: Plasma microRNA profiles: Identification of
miR-744 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in
pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 113:1467–1476. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Song MY, Pan KF, Su HJ, Zhang L, Ma JL, Li
JY, Yuasa Y, Kang D, Kim YS and You WC: Identification of serum
microRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for early detection of
gastric cancer. PLoS One. 7:e336082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fang Y, Zhu X, Wang J, Li N, Li D, Sakib
N, Sha Z and Song W: MiR-744 functions as a proto-oncogene in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and metastasis via
transcriptional control of ARHGAP5. Oncotarget. 6:13164–13175.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou W, Li Y, Gou S, Xiong J, Wu H, Wang
C, Yan H and Liu T: MiR-744 increases tumorigenicity of pancreatic
cancer by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget.
6:37557–37569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin F, Lei S, Ma J, Shi L, Mao D and Zhang
S, Huang J, Liu X, Ding D, Zhang Y and Zhang S: Inhibitory effect
of jianpi-jiedu prescription-contained serum on colorectal cancer
SW48 cell proliferation by mTOR-P53-P21 signalling pathway. Zhong
Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 41:1128–1136. 2016.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jackson BL, Grabowska A and Ratan HL:
MicroRNA in prostate cancer: Functional importance and potential as
circulating biomarkers. BMC Cancer. 14:9302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song C, Chen H, Wang T, Zhang W, Ru G and
Lang J: Expression profile analysis of microRNAs in prostate cancer
by next-generation sequencing. Prostate. 75:500–516. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Josson S, Gururajan M, Hu P, Shao C, Chu
GY, Zhau HE, Liu C, Lao K, Lu CL, Lu YT, et al: miR-409-3p/-5p
promotes tumorigenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and
bone metastasis of human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:4636–4646. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wei P, Qiao B, Li Q, Han X, Zhang H, Huo Q
and Sun J: microRNA-340 suppresses tumorigenic potential of
prostate cancer cells by targeting high-mobility group
nucleosome-binding domain 5. DNA Cell Biol. 35:33–43. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ji H, Li Y, Jiang F, Wang X, Zhang J, Shen
J and Yang X: Inhibition of transforming growth factor beta/SMAD
signal by MiR-155 is involved in arsenic trioxide-induced
anti-angiogenesis in prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 105:1541–1549.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guan H, Liu C, Fang F, Huang Y, Tao T,
Ling Z, You Z, Han X, Chen S, Xu B and Chen M: MicroRNA-744
promotes prostate cancer progression through aberrantly activating
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget. 8:14693–14707. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pencheva N and Tavazoie SF: Control of
metastatic progression by microRNA regulatory networks. Nat Cell
Biol. 15:546–554. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang X, Han X, Tang Y, Wu Y, Qu B and
Shen N: miR-744 enhances type I interferon signaling pathway by
targeting PTP1B in primary human renal mesangial cells. Sci Rep.
5:129872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zeng H, Qu J, Jin N, Xu J, Lin C, Chen Y,
Yang X, He X, Tang S, Lan X, et al: Feedback activation of leukemia
inhibitory factor receptor limits response to histone deacetylase
inhibitors in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 30:459–473. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vislovukh A, Kratassiouk G, Porto E,
Gralievska N, Beldiman C, Pinna G, El'skaya A, Harel-Bellan A,
Negrutskii B and Groisman I: Proto-oncogenic isoform A2 of
eukaryotic translation elongation factor eEF1 is a target of
miR-663 and miR-744. Br J Cancer. 108:2304–2311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hezel AF and Bardeesy N: LKB1; linking
cell structure and tumor suppression. Oncogene. 27:6908–6919. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Blagih J, Krawczyk CM and Jones RG: LKB1
and AMPK: Central regulators of lymphocyte metabolism and function.
Immunol Rev. 249:59–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shaw RJ, Kosmatka M, Bardeesy N, Hurley
RL, Witters LA, DePinho RA and Cantley LC: The tumor suppressor
LKB1 kinase directly activates AMP-activated kinase and regulates
apoptosis in response to energy stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:3329–3335. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Agarwal S, Bell CM, Rothbart SB and Moran
RG: AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) control of mTORC1 is p53-
and TSC2-independent in pemetrexed-treated carcinoma cells. J Biol
Chem. 290:27473–27486. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jozwiak J, Jozwiak S, Grzela T and
Lazarczyk M: Positive and negative regulation of TSC2 activity and
its effects on downstream effectors of the mTOR pathway.
Neuromolecular Med. 7:287–296. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen MB, Zhang Y, Wei MX, Shen W, Wu XY,
Yao C and Lu PH: Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
mediates plumbagin-induced apoptosis and growth inhibition in
cultured human colon cancer cells. Cell Signal. 25:1993–2002. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|