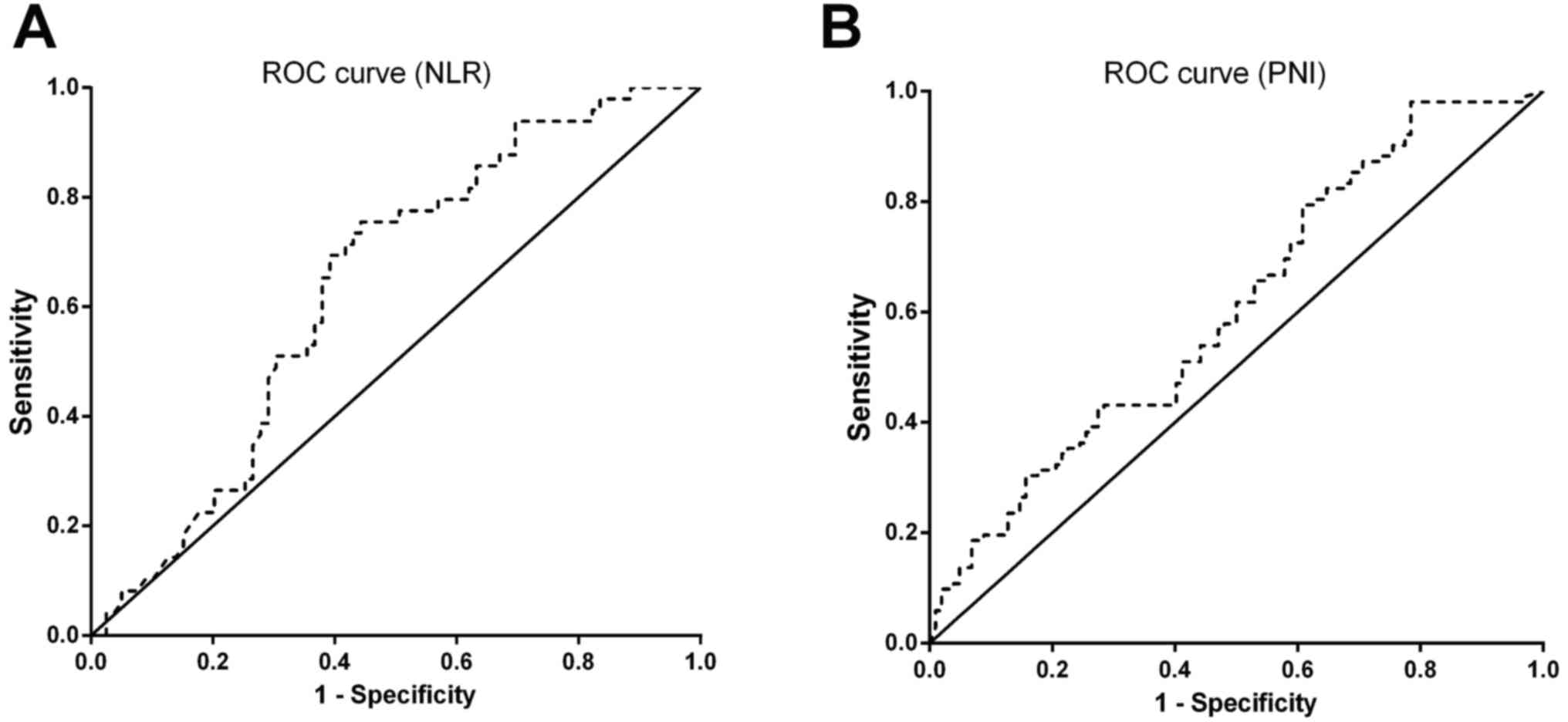
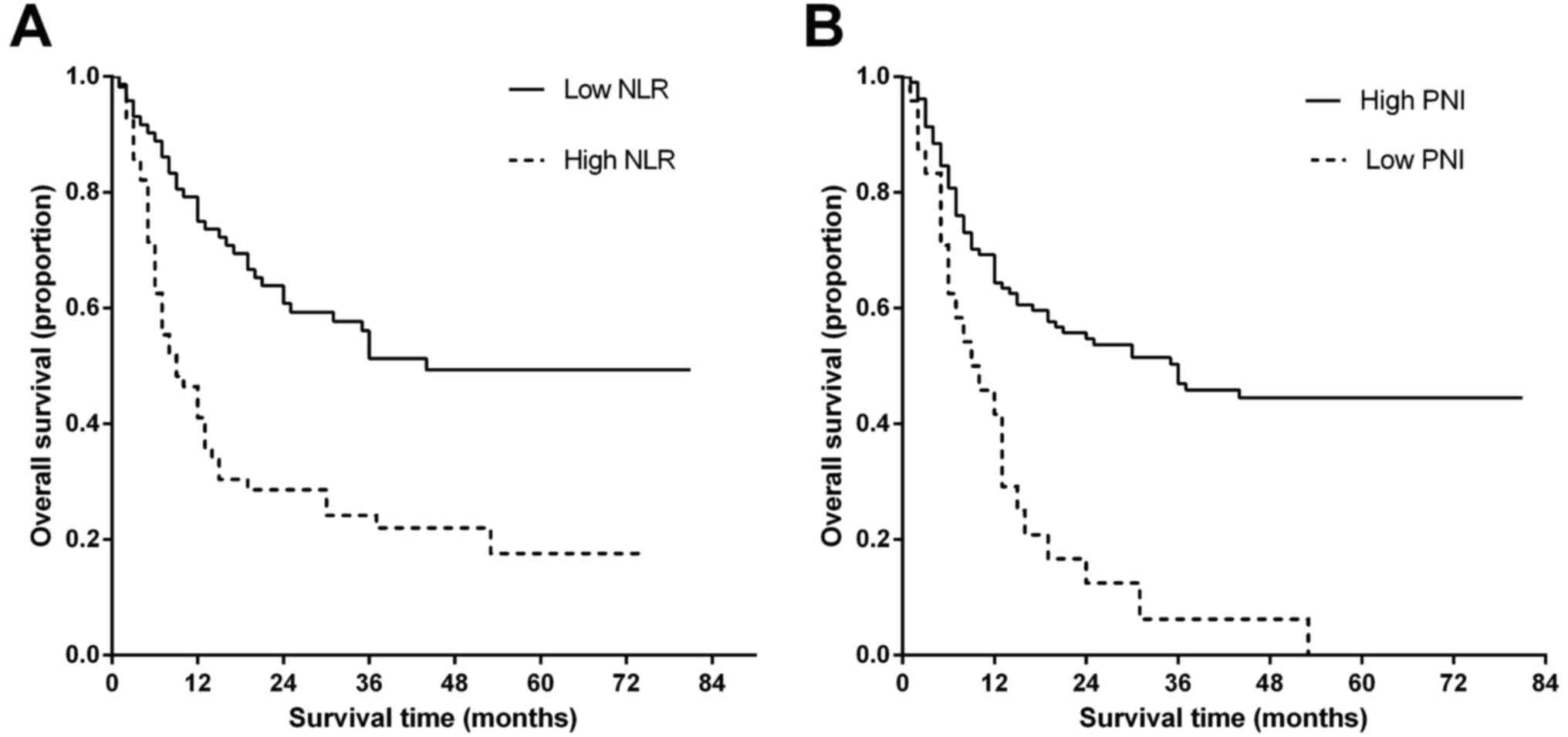
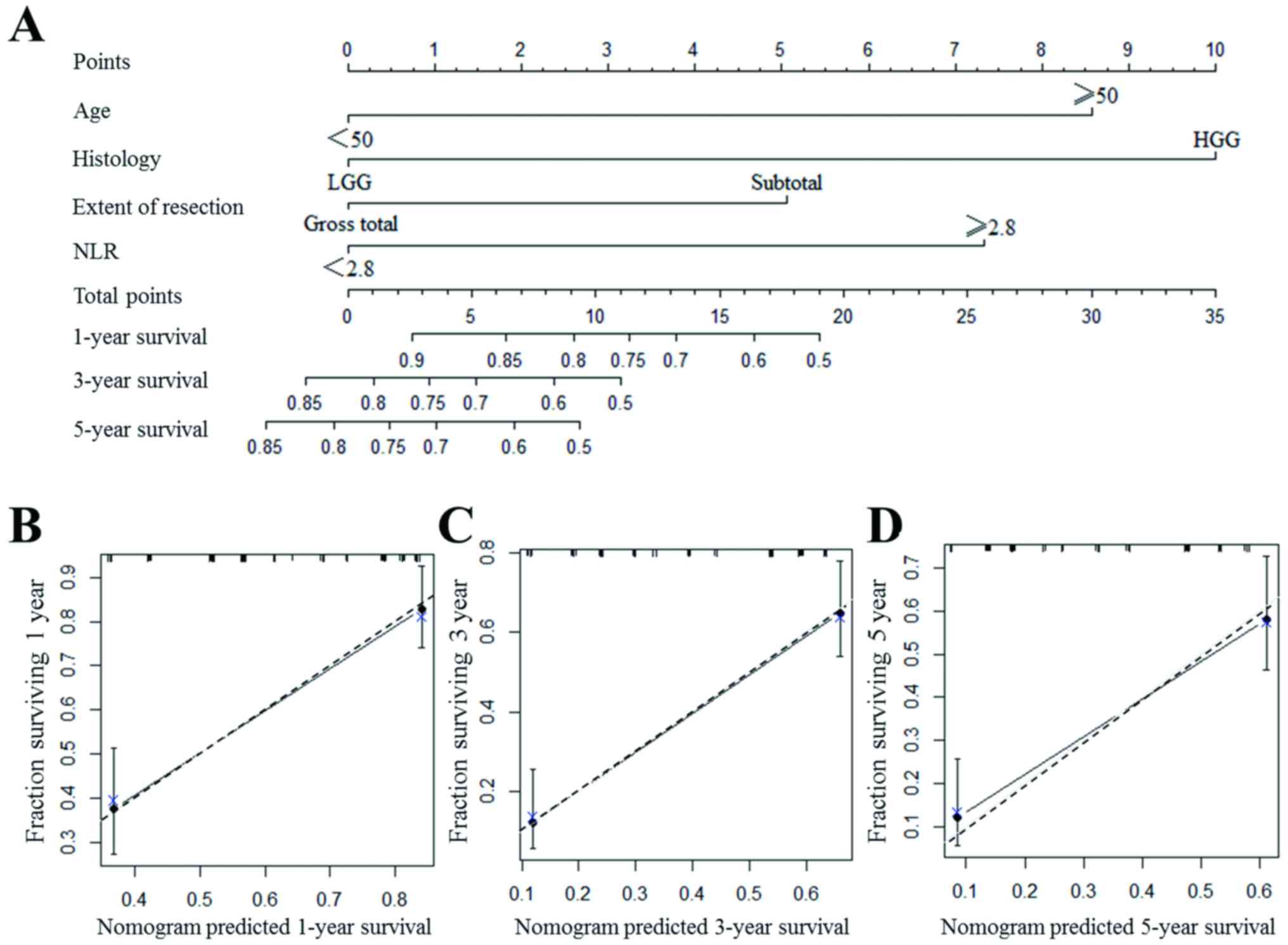
|
1
|
Ostrom QT, Bauchet L, Davis FG, Deltour I,
Fisher JL, Langer CE, Pekmezci M, Schwartzbaum JA, Turner MC, Walsh
KM, et al: The epidemiology of glioma in adults: A ‘state of the
science’ review. Neuro Oncol. 16:896–913. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gorlia T, van den Bent MJ, Hegi ME,
Mirimanoff RO, Weller M, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Belanger K,
Brandes AA, Allgeier A, et al: Nomograms for predicting survival of
patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: Prognostic factor
analysis of EORTC and NCIC trial 26981-22981/CE. 3. Lancet Oncol.
9:29–38. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liang TH, Kuo SH, Wang CW, Chen WY, Hsu
CY, Lai SF, Tseng HM, You SL, Chen CM and Tseng WY: Adverse
prognosis and distinct progression patterns after concurrent
chemoradiotherapy for glioblastoma with synchronous subventricular
zone and corpus callosum invasion. Radiother Oncol. 118:16–23.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gabay C and Kushner I: Acute-phase
proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J
Med. 340:448–454. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Templeton AJ, Ace O, McNamara MG,
Al-Mubarak M, Vera-Badillo FE, Hermanns T, Seruga B, Ocaña A,
Tannock IF and Amir E: Prognostic role of platelet to lymphocyte
ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Cancer Epidemiol Prevention Biomarkers Prev. 23:1204–1212. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Guthrie GJ, Charles KA, Roxburgh CS,
Horgan PG, McMillan DC and Clarke SJ: The systemic
inflammation-based neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio: Experience in
patients with cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 88:218–230. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang HB, Xing M, Ma LN, Feng LX and Yu Z:
Prognostic significance of
neutrophil-lymphocyteratio/platelet-lymphocyteratioin lung cancers:
A meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 7:76769–76778. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kijima T, Arigami T, Uchikado Y, Uenosono
Y, Kita Y, Owaki T, Mori S, Kurahara H, Kijima Y, Okumura H, et al:
Combined fibrinogen and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic
marker of advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci.
108:193–199. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Suzuki R, Takagi T, Hikichi T, Konno N,
Sugimoto M, Watanabe KO, Nakamura J, Waragai Y, Kikuchi H, Takasumi
M, et al: Derived neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio predicts gemcitabine
therapy outcome in unresectable pancreatic cancer. Oncol Lett.
11:3441–3445. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang Y, Gao P, Chen X, Song Y, Shi J, Zhao
J, Sun J, Xu Y and Wang Z: Prognostic significance of preoperative
prognostic nutritional index in colorectal cancer: Results from a
retrospective cohort study and a meta-analysis. Oncotarget.
7:58543–58552. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang Z, Zhang B, Hou L, Xie Y and Cao X:
Pre-operative prognostic nutritional index predicts the outcomes
for triple-negative breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 35:12165–12171.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Yang T, Xu G, Liu H, Ren C, Xie W
and Wang M: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 promotes tumor proliferation
and induces radio resistance in glioblastoma. Transl Oncol.
9:548–556. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Onodera T, Goseki N and Kosaki G:
Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of
malnourished cancer patients. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi.
85:1001–1005. 1984.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Harrell FE Jr, Lee KL and Mark DB:
Multivariable prognostic models: Issues in developing models,
evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing
errors. Stat Med. 15:361–387. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Crusz SM and Balkwill FR: Inflammation and
cancer: Advances and new agents. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 12:584–596.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bambury RM, Teo MY, Power DG, Yusuf A,
Murray S, Battley JE, Drake C, O'Dea P, Bermingham N, Keohane C, et
al: The association of pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio
with overall survival in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. J
Neurooncol. 114:149–154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Auezova R, Ryskeldiev N, Doskaliyev A,
Kuanyshev Y, Zhetpisbaev B, Aldiyarova N, Ivanova N, Akshulakov S
and Auezova L: Association of preoperative levels of selected blood
inflammatory markers with prognosis in gliomas. OncoTargets Ther.
9:6111–6117. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Denkert C, Loibl S, Noske A, Roller M,
Müller BM, Komor M, Budczies J, Darb-Esfahani S, Kronenwett R,
Hanusch C, et al: Tumor-associated lymphocytes as an independent
predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 28:105–113. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jablonska J, Leschner S, Westphal K,
Lienenklaus S and Weiss S: Neutrophils responsive to endogenous
IFN-beta regulate tumor angiogenesis and growth in a mouse tumor
model. J Clin Invest. 120:1151–1164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lord BI, Bronchud MH, Owens S, Chang J,
Howell A, Souza L and Dexter TM: The kinetics of human
granulopoiesis following treatment with granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
86:9499–9503. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Buzby GP, Mullen JL, Matthews DC, Hobbs CL
and Rosato EF: Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal
surgery. Am J Surg. 139:160–167. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma W, Zhang P, Qi J, Gu L, Zang M, Yao H,
Shi X, Wang C and Jiang Y: Prognostic value of platelet to
lymphocyte ratio in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Sci
Rep. 6:353782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lo HC, Tsao LY, Hsu WY, Chen HN, Yu WK and
Chi CY: Relation of cord serum levels of growth hormone,
insulin-like growth factors, insulin-like growth factor binding
proteins, leptin, and interleukin-6 with birth weight, birth
length, and head circumference in term and preterm neonates.
Nutrition. 18:604–608. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ and
DeMatteo RP: Nomograms in oncology: More than meets the eye. Lancet
Oncol. 16:e173–e180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|