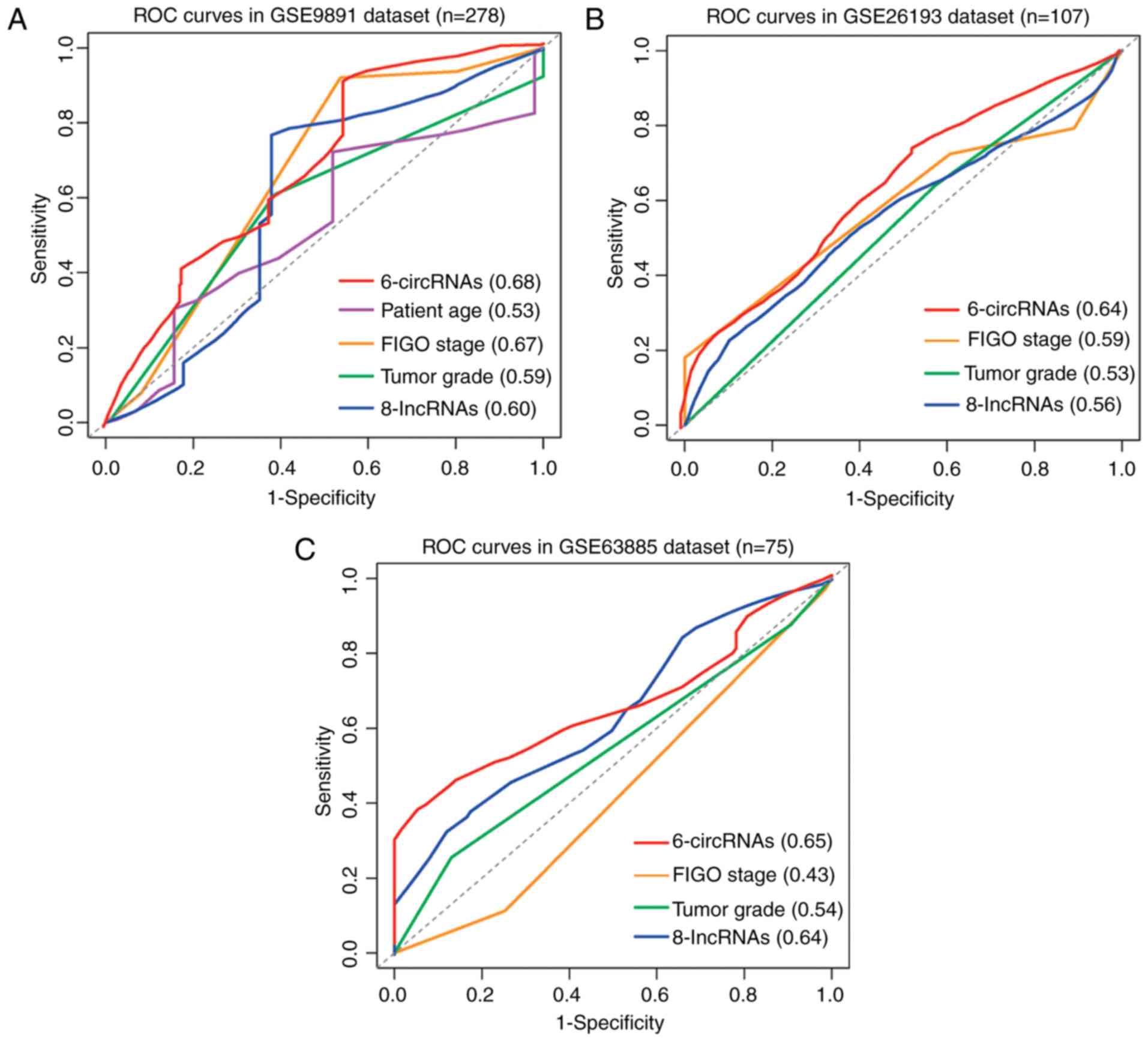
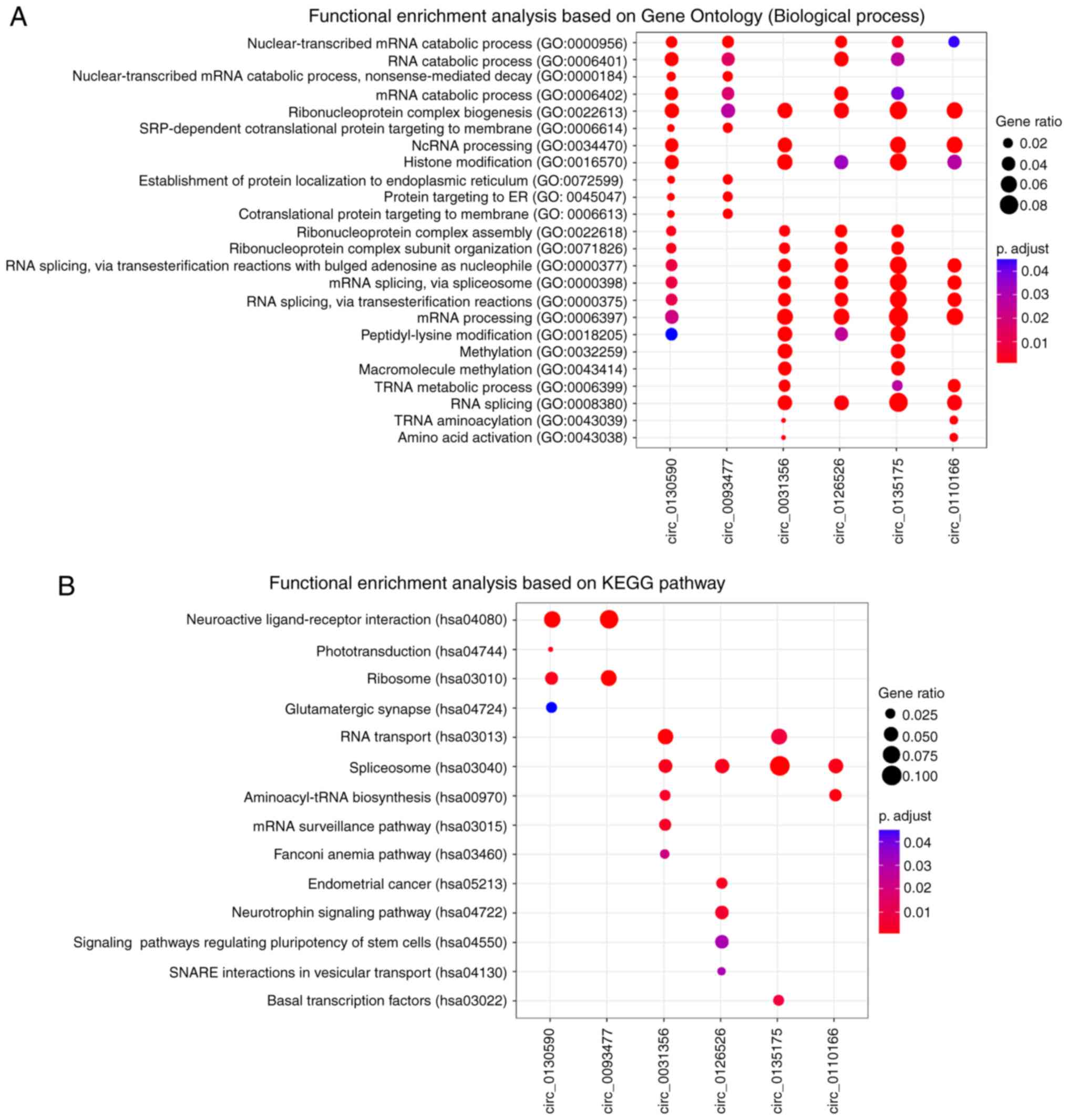
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rustin G, van der Burg M, Griffin C, Qian
W and Swart AM: Early versus delayed treatment of relapsed ovarian
cancer. Lancet. 377:380–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bowtell DD: The genesis and evolution of
high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:803–808. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li C, Bonazzoli E, Bellone S, Choi J, Dong
W, Menderes G, Altwerger G, Han C, Manzano A, Bianchi A, et al:
Mutational landscape of primary, metastatic, and recurrent ovarian
cancer reveals c-MYC gains as potential target for BET inhibitors.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:619–624. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kumar L, Shamsuzzam A, Haque R, Baghel T
and Nazir A: Circular RNAs: The emerging class of non-coding RNAs
and their potential role in human neurodegenerative diseases. Mol
Neurobiol. 54:7224–7234. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen LL: The biogenesis and emerging roles
of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:205–211. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shang Q, Yang Z, Jia R and Ge S: The novel
roles of circRNAs in human cancer. Mol Cancer. 18:62019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chekulaeva M and Rajewsky N: Roles of long
noncoding RNAs and circular RNAs in translation. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. a0326802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wilusz JE and Sharp PA: Molecular biology.
A circuitous route to noncoding RNA. Science. 340:440–441. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hansen TB, Kjems J and Damgaard CK:
Circular RNA and miR-7 in cancer. Cancer Res. 73:5609–5612. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Y, Zheng Q, Bao C, Li S, Guo W, Zhao J,
Chen D, Gu J, He X and Huang S: Circular RNA is enriched and stable
in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res.
25:981–984. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng Q, Bao C, Guo W, Li S, Chen J, Chen
B, Luo Y, Lyu D, Li Y, Shi G, et al: Circular RNA profiling reveals
an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging
multiple miRNAs. Nat Commun. 7:112152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Du Z, Fei T, Verhaak RG, Su Z, Zhang Y,
Brown M, Chen Y and Liu XS: Integrative genomic analyses reveal
clinically relevant long noncoding RNAs in human cancer. Nat Struct
Mol Biol. 20:908–913. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Glazar P, Papavasileiou P and Rajewsky N:
circBase: A database for circular RNAs. RNA. 20:1666–1670. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang H and Wong WH: SeqMap: Mapping
massive amount of oligonucleotides to the genome. Bioinformatics.
24:2395–2396. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ishwaran H and Kogalur UB: Consistency of
random survival forests. Stat Probab Lett. 80:1056–1064. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhan X, Dong C, Liu G, Li Y and Liu L:
Panel of seven long noncoding RNA as a candidate prognostic
biomarker for ovarian cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 10:2805–2813.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou M, Sun Y, Sun Y, Xu W, Zhang Z, Zhao
H, Zhong Z and Sun J: Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA expression
profiles reveals a novel lncRNA signature to discriminate
nonequivalent outcomes in patients with ovarian cancer. Oncotarget.
7:32433–32448. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li ZC, Huang MH, Zhong WQ, Liu ZQ, Xie Y,
Dai Z and Zou XY: Identification of drug-target interaction from
interactome network with ‘guilt-by-association’ principle and
topology features. Bioinformatics. 32:1057–1064. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wilkerson MD and Hayes DN:
ConsensusClusterPlus: A class discovery tool with confidence
assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics. 26:1572–1573. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Panagopoulou M, Karaglani M,
Balgkouranidou I, Biziota E, Koukaki T, Karamitrousis E, Nena E,
Tsamardinos I, Kolios G, Lianidou E, et al: Circulating cell-free
DNA in breast cancer: Size profiling, levels, and methylation
patterns lead to prognostic and predictive classifiers. Oncogene.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Varkaris A, Katsiampoura A, Davis JS, Shah
N, Lam M, Frias RL, Ivan C, Shimizu M, Morris J, Menter D, et al:
Circulating inflammation signature predicts overall survival and
relapse-free survival in metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer;
2019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Huelsmann E, Zighelboim I, Ahmed A and
Dewdney S: The role of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the management
of patients with advanced stage ovarian cancer: Survey results from
members of the society of gynecologic oncologists, a 5-year
follow-up. Gynecol Oncol Rep. 20:47–50. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|