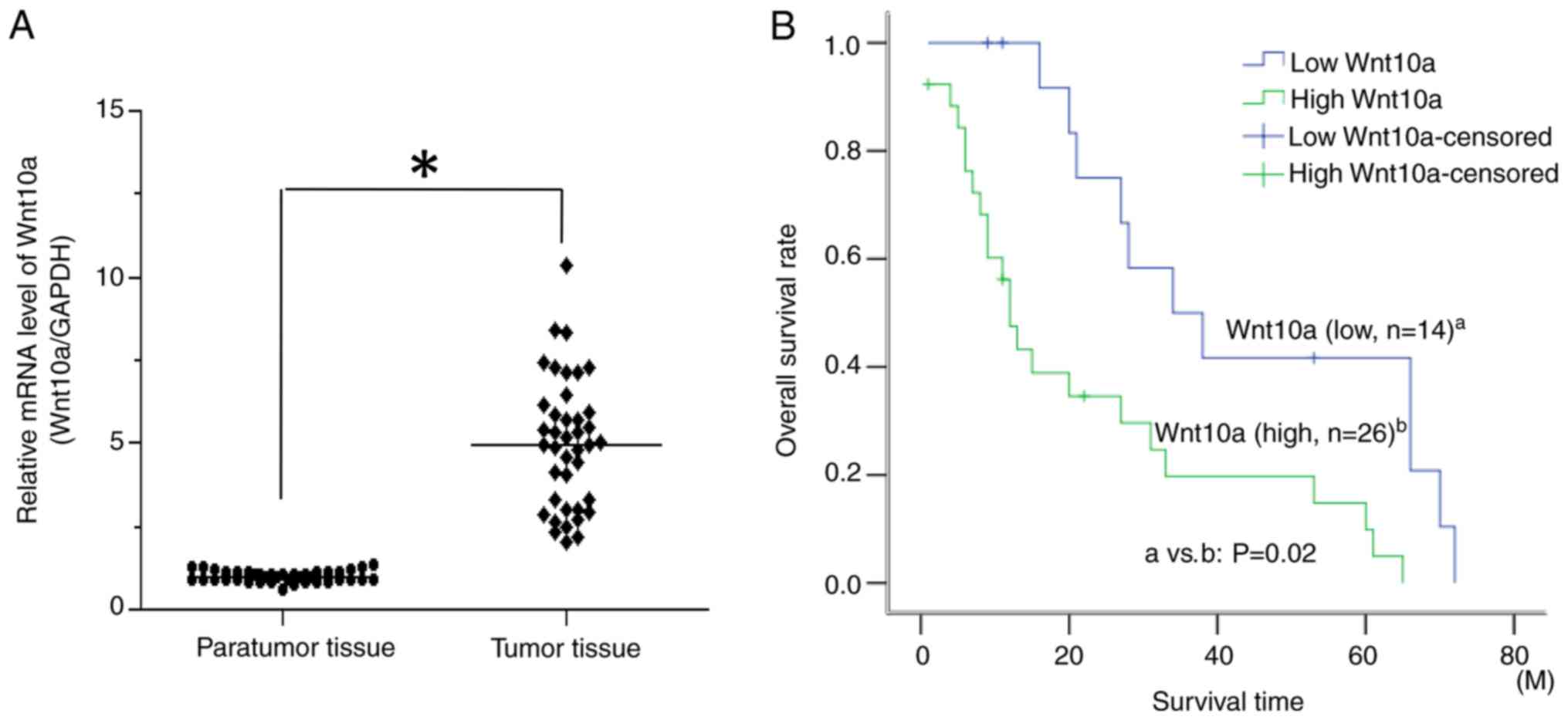
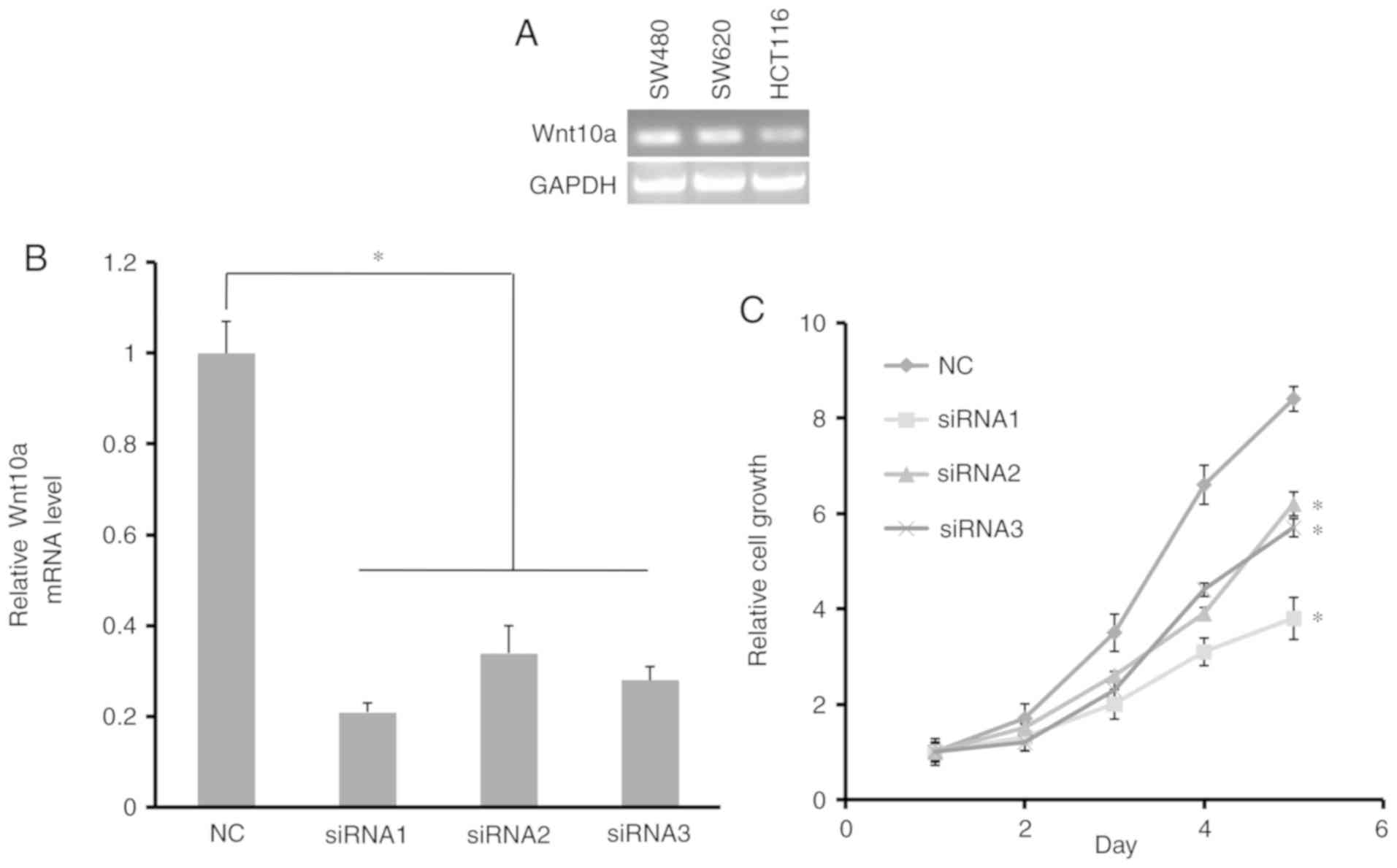
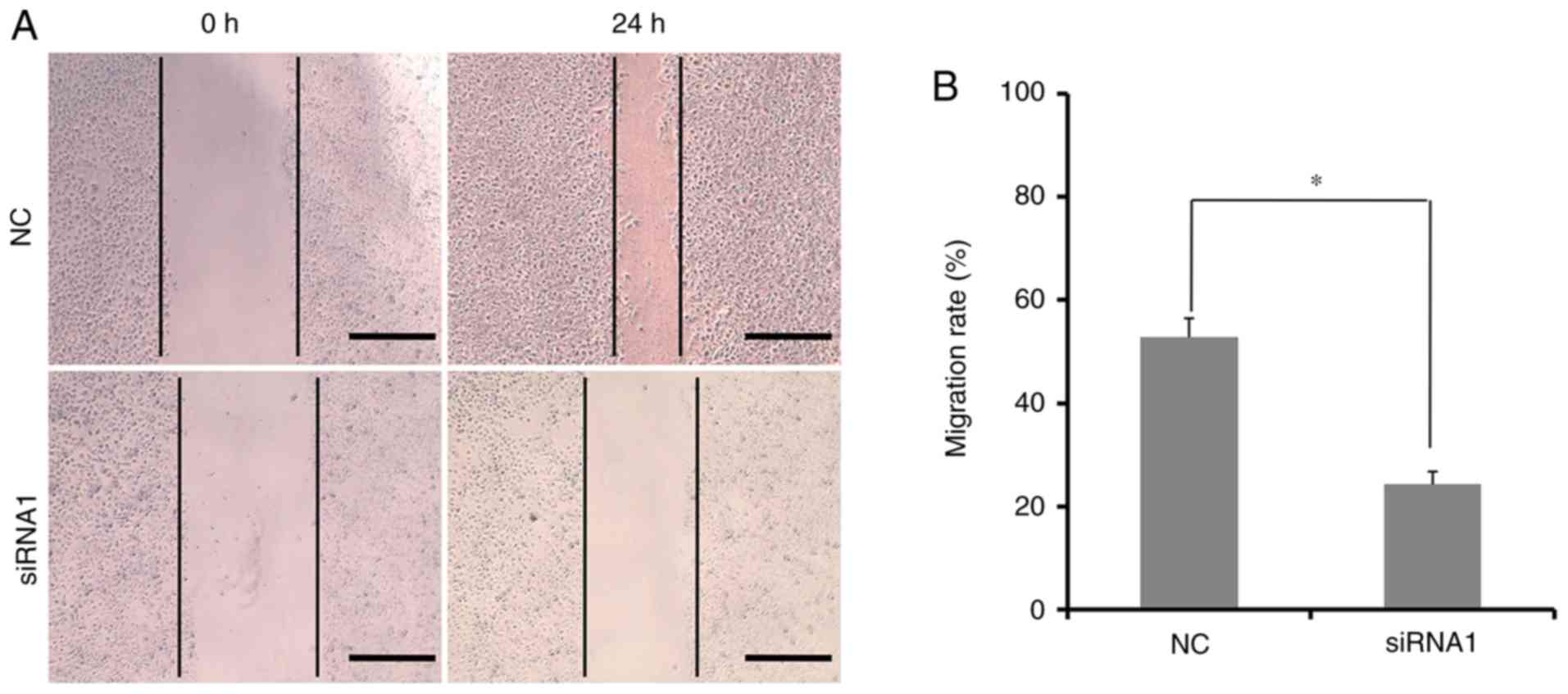
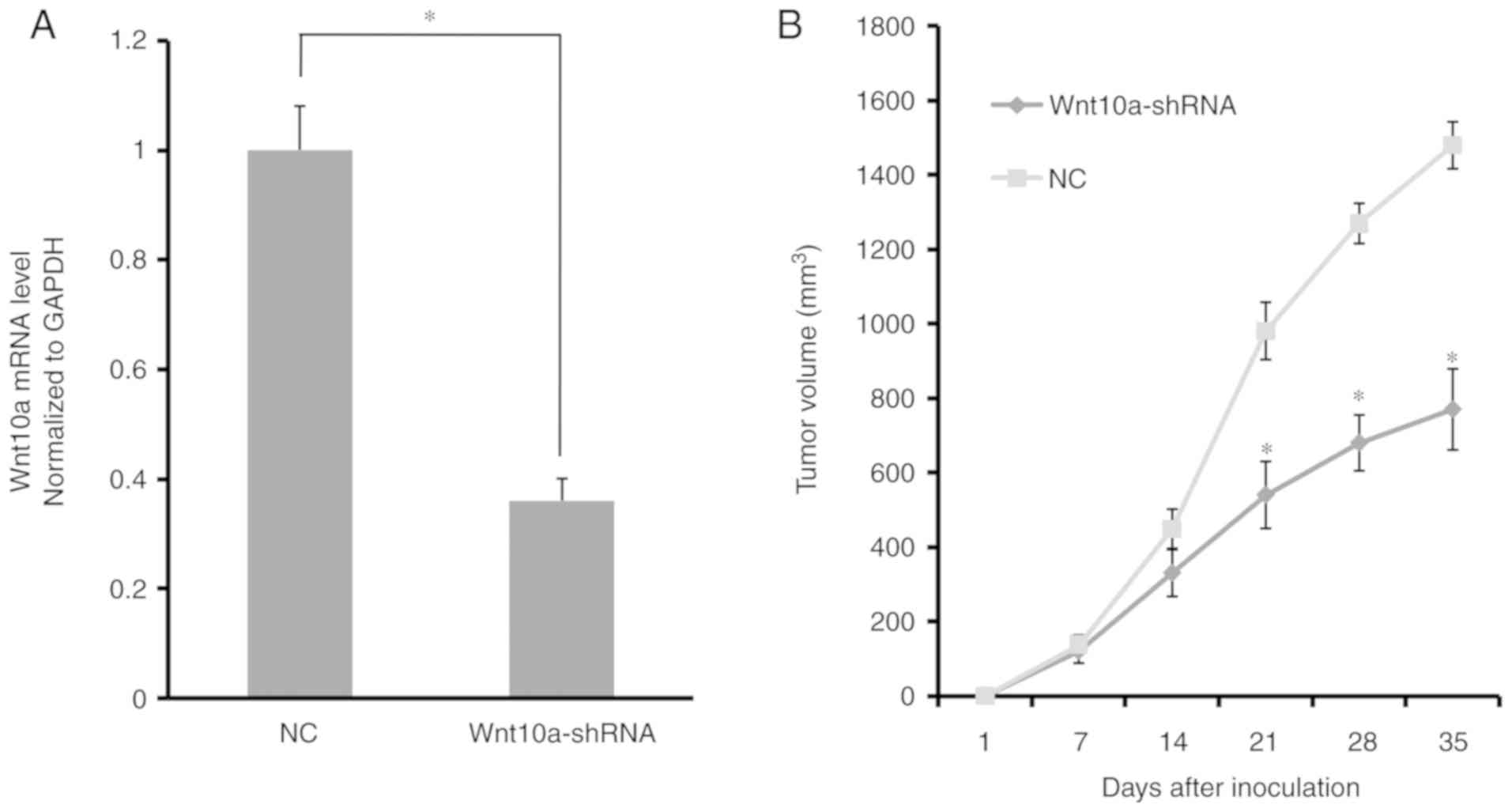
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ,
Meester RGS, Barzi A and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics,
2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:177–193. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pabla B, Bissonnette M and Konda VJ: Colon
cancer and the epidermal growth factor receptor: Current treatment
paradigms, the importance of diet and the role of chemoprevention.
World J Clin Oncol. 6:133–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Millan M, Merino S, Caro A, Feliu F,
Escuder J and Francesch T: Treatment of colorectal cancer in the
elderly. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 7:204–220. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Applegate CC and Lane MA: Role of
retinoids in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. 7:184–203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yan Y and Grothey A: Molecular profiling
in the treatment of colorectal cancer: Focus on regorafenib. Onco
Targets Ther. 8:2949–2957. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Woo IS and Jung YH: Metronomic
chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett.
400:319–324. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barranha R, Costa JL, Carneiro F and
Machado JC: Genetic Heterogeneity in colorectal cancer and its
clinical implications. Acta Med Port. 28:370–375. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sherwood V: WNT signaling: An emerging
mediator of cancer cell metabolism? Mol Cell Biol. 35:2–10. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hashimoto T, Yamashita S, Yoshida H,
Taniguchi H, Ushijima T, Yamada T, Saito Y, Ochiai A, Sekine S and
Hiraoka N: WNT pathway gene mutations are associated with the
presence of dysplasia in colorectal sessile serrated
adenoma/polyps. Am J Surg Pathol. 41:1188–1197. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Men XM, Deng B, Tao X, Qi KK and Xu ZW:
Wnt gene expression in adult porcine longissimus dorsi and its
association with muscle fiber type, energy metabolism, and meat
quality. J Integr Agr. 16:144–150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Clevers H: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nusse R and Clevers H: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling, disease and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell.
169:985–999. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mccracken KW, Aihara E, Martin B, Crawford
CM, Broda T, Treguier J, Zhang X, Shannon JM, Montrose MH and Wells
JM: Wnt/β-catenin promotes gastric fundus specification in mice and
humans. Nature. 541:182–187. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arend RC, Londoño-Joshi AI, Straughn JM Jr
and Buchsbaum DJ: The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: A
review. Gynecol Oncol. 131:772–779. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stanczak A, Stec R, Bodnar L, Olszewski W,
Cichowicz M, Kozlowski W, Szczylik C, Pietrucha T, Wieczorek M and
Lamparska-Przybysz M: Prognostic significance of Wnt-1, β-catenin
and E-cadherin expression in advanced colorectal carcinoma. Pathol
Oncol Res. 17:955–963. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoshioka S, King ML, Ran S, Okuda H,
MacLean JA II, McAsey ME, Sugino N, Brard L, Watabe K and Hayashi
K: WNT7A regulates tumor growth and progression in ovarian cancer
through the WNT/β-catenin pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 10:469–482.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bakker ER, Das AM, Helvensteijn W, Franken
PF, Swagemakers S, van der Valk MA, ten Hagen TL, Kuipers EJ, van
Veelen W and Smits R: Wnt5a promotes human colon cancer cell
migration and invasion but does not augment intestinal
tumorigenesis in Apc1638N mice. Carcinogenesis. 34:2629–2638. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Galbraith RL, Poole EM, Duggan D, Muehling
J, Hsu L, Makar K, Xiao L, Potter JD and Ulrich CM: Polymorphisms
in WNT6 and WNT10A and colorectal adenoma risk. Nutr Cancer.
63:558–564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hsu RJ, Ho JY, Cha TL, Yu DS, Wu CL, Huang
WP, Chu P, Chen YH, Chen JT and Yu CP: WNT10A plays an oncogenic
role in renal cell carcinoma by activating WNT/beta-catenin
pathway. PLoS One. 7:e476492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kirikoshi H, Inoue S, Sekihara H and Katoh
M: Expression of WNT10A in human cancer. Int J Oncol. 19:997–1001.
2011.
|
|
21
|
Kirikoshi H, Sekihara H and Katoh M:
WNT10A and WNT6, clustered in human chromosome 2q35 region with
head-to-tail manner, are strongly coexpressed in SW480 cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 283:798–805. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cunninghan D, Atkin W, Lenz HJ, Lynch HT,
Minsky B, Nordlinger B and Starling N: Colorectal cancer. Lancet.
375:1030–1047. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg R: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
März L and Piso P: Treatment of peritoneal
metastases from colorectal cancer. Gastroenterol Rep. 3:298–302.
2015.
|
|
26
|
Hrckulak D, Kolar M, Strnad H and Korinek
V: TCF/LEF transcription factors: An update from the internet
resources. Cancer (Basel). 8(pii): E702016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yu JS and Cui W: Proliferation, survival
and metabolism: The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in pluripotency
and cell fate determination. Development. 143:3050–3060. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kimmelman AC and White E: Autophagy and
tumor metabolism. Cell Metab. 25:1037–1043. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zoncu R, Efeyan A and Sabatini DM: mTOR:
From growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:21–35. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bahrami A, Hasanzadeh M, Hassanian SM,
ShahidSales S, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Ferns GA and Avan A: The
potential value of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway for
assessing prognosis in cervical cancer and as a target for therapy.
J Cell Biochem. 118:4163–4169. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yoshida N, Kinugasa T, Ohshima K, Yuge K,
Ohchi T, Fujino S, Shiraiwa S, Katagiri M and Akagi Y: Analysis of
Wnt and b-catenin expression in advanced colorectal cancer.
Anticancer Res. 35:4403–4410. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang X and Hao J: Development of
anticancer agents targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Am J
Cancer Res. 5:2344–2360. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tran FH and Zheng JJ: Modulating the wnt
signaling pathway with small molecules. Protein Sci. 26:650–661.
2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|