|
1
|
Tomasetti C, Li L and Vogelstein B: Stem
cell divisions, somatic mutations, cancer etiology, and cancer
prevention. Science. 355:1330–1334. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Veite-Schmahl MJ, Joesten WC and Kennedy
MA: HMGA1 expression levels are elevated in pancreatic
intraepithelial neoplasia cells in the Ptf1a-Cre; LSL-KrasG12D
transgenic mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer.
117:639–647. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Akhurst RJ and Derynck R: TGF-beta
signaling in cancer-a double-edged sword. Trends Cell Biol.
11:S44–S51. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ and Balmain A:
TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat
Genet. 29:117–129. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hezel AF, Deshpande V, Zimmerman SM,
Contino G, Alagesan B, O'Dell MR, Rivera LB, Harper J, Lonning S,
Brekken RA and Bardeesy N: TGF-β and αvβ6 integrin act in a common
pathway to suppress pancreatic cancer progression. Cancer Res.
72:4840–4845. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yuan JH, Yang F, Wang F, Ma JZ, Guo YJ,
Tao QF, Liu F, Pan W, Wang TT, Zhou CC, et al: A long noncoding RNA
activated by TGF-β promotes the invasion-metastasis cascade in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 25:666–681. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou Q, Chung AC, Huang XR, Dong Y, Yu X
and Lan HY: Identification of novel long noncoding RNAs associated
with TGF-β/Smad3-mediated renal inflammation and fibrosis by RNA
sequencing. Am J Pathol. 184:409–417. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li L, Zhang GQ, Chen H, Zhao ZJ, Chen HZ,
Liu H, Wang G, Jia YH, Pan SH and Kong R: Plasma and tumor levels
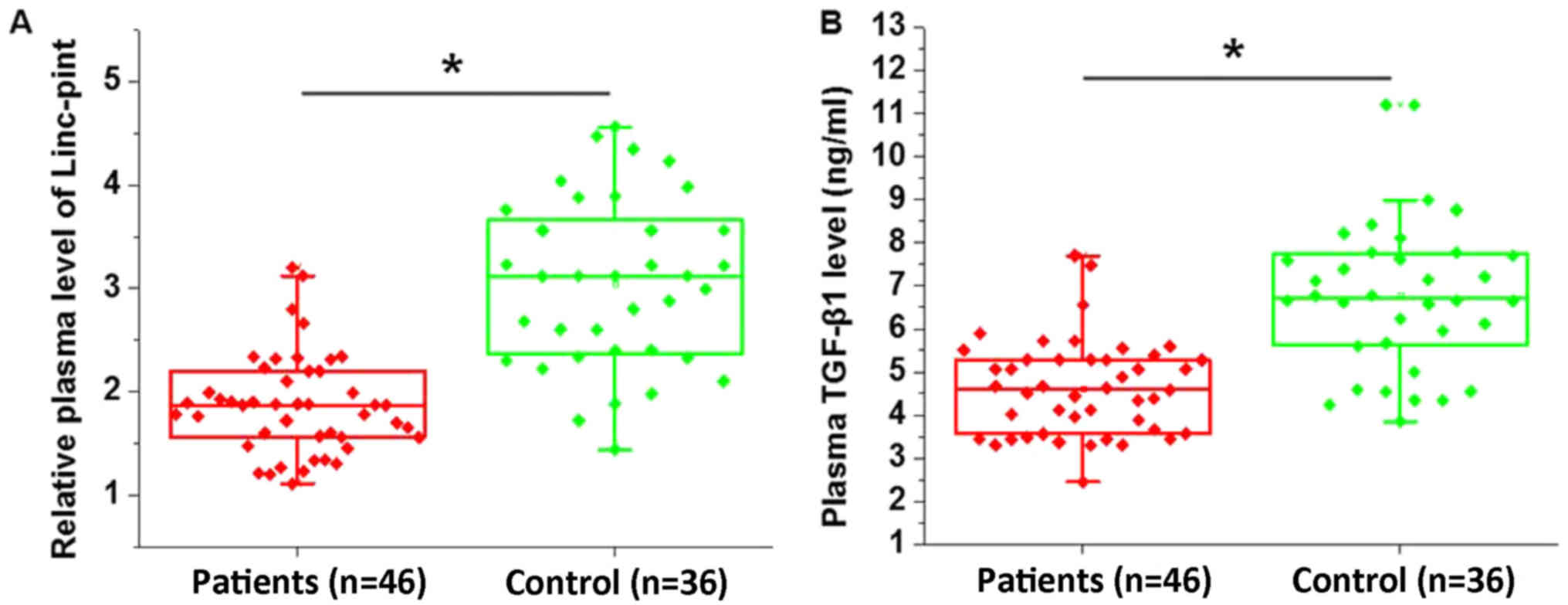
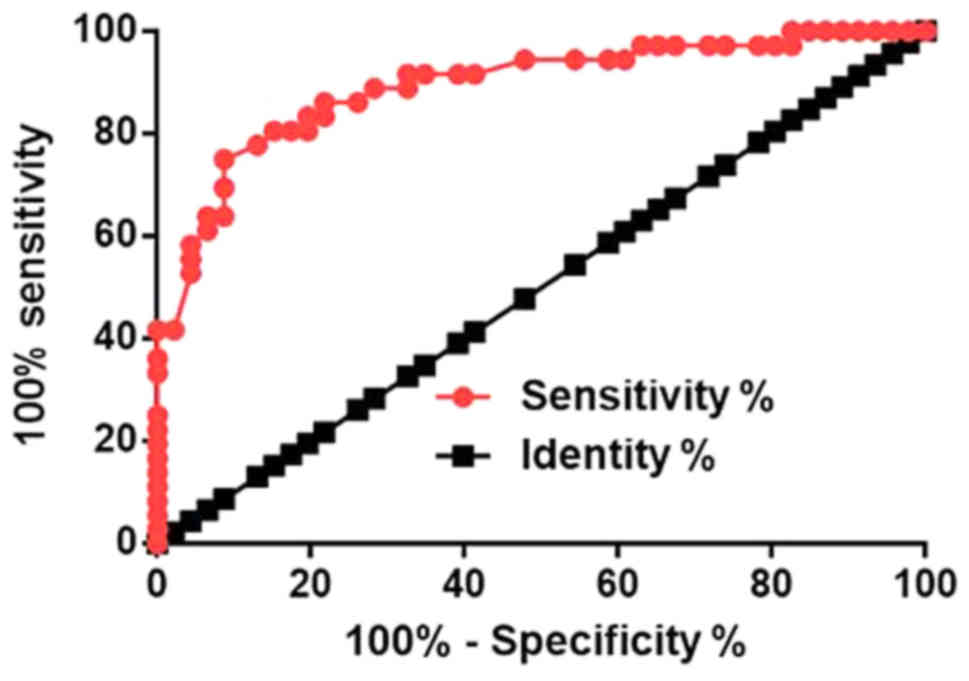
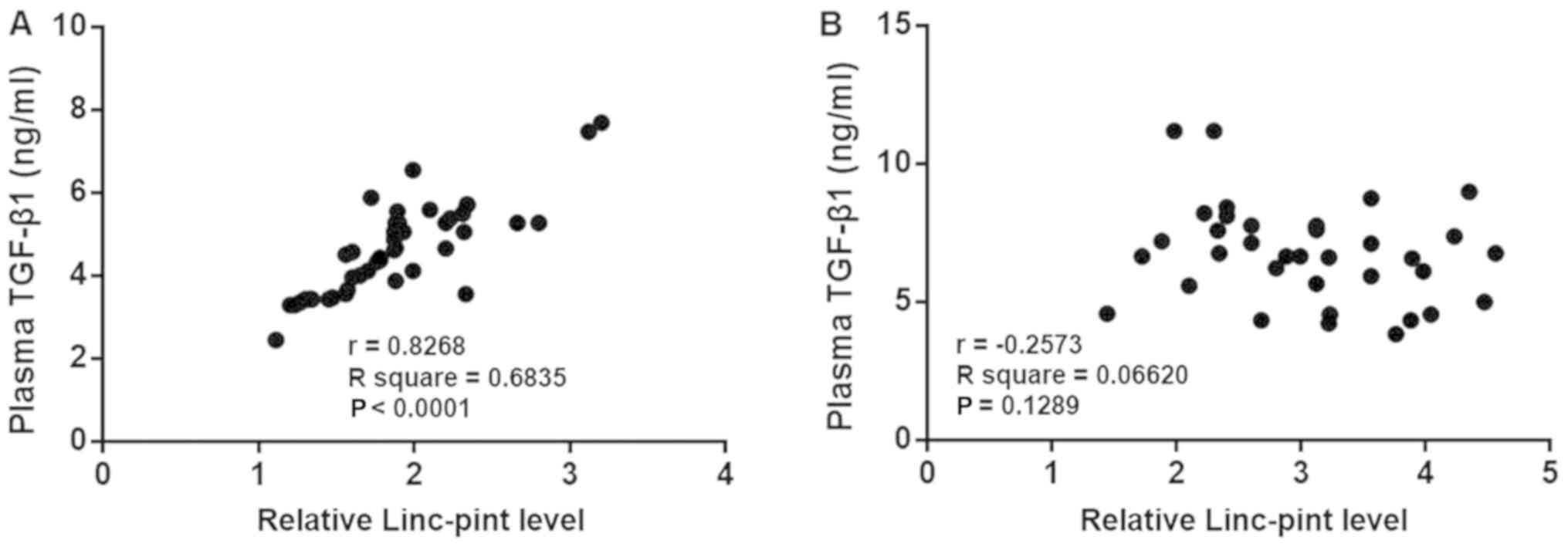
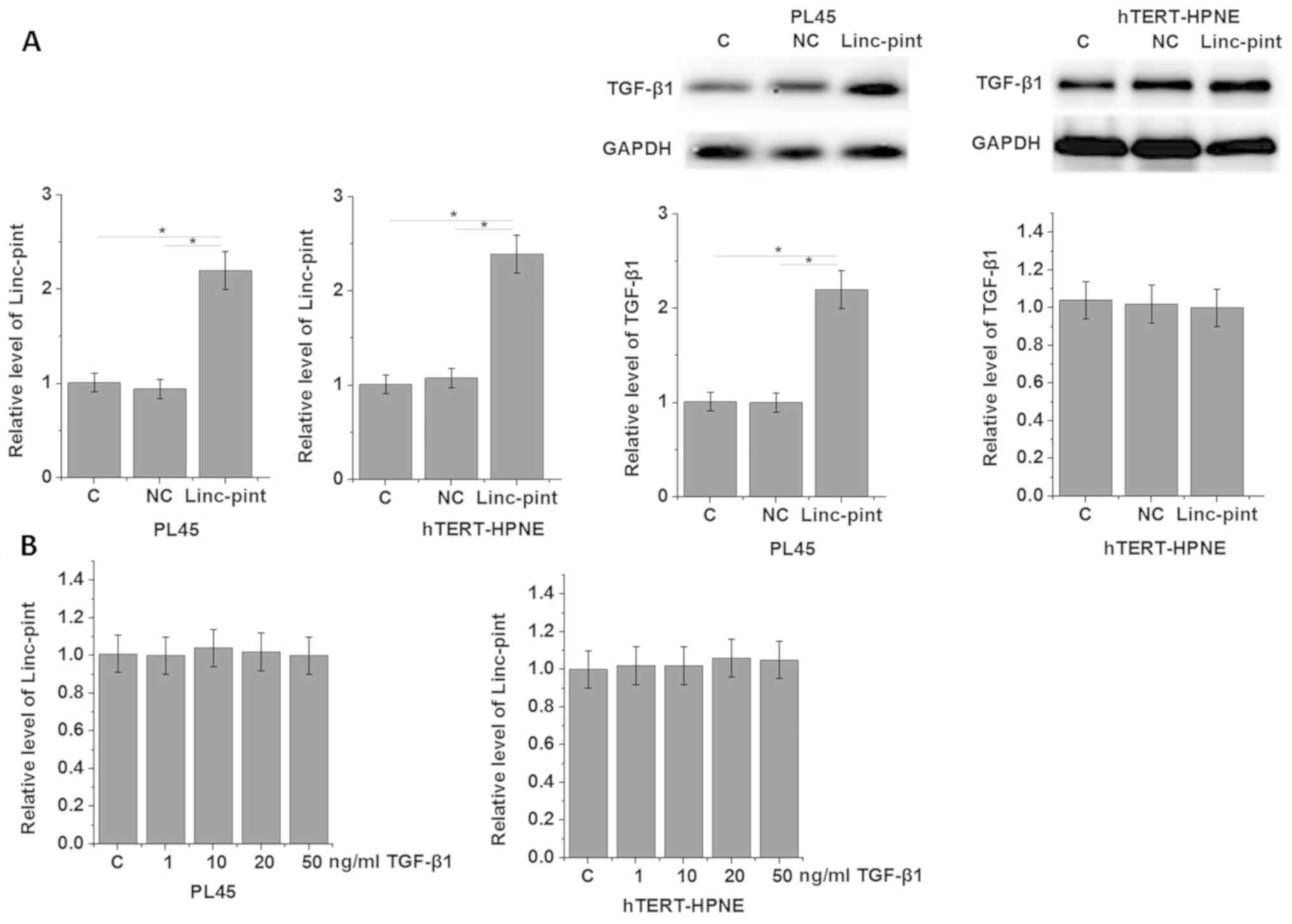
of Linc-pint are diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for
pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 7:71773–71781. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marín-Béjar O, Mas AM, González J,
Martinez D, Athie A, Morales X, Galduroz M, Raimondi I, Grossi E,
Guo S, et al: The human lncRNA LINC-PINT inhibits tumor cell
invasion through a highly conserved sequence element. Genome Biol.
18:2022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Garitano-Trojaola A, San José-Enériz E,
Ezponda T, Unfried JP, Carrasco-León A, Razquin N, Barriocanal M,
Vilas-Zornoza A, Sangro B, Segura V, et al: Deregulation of
linc-PINT in acute lymphoblastic leukemia is implicated in abnormal
proliferation of leukemic cells. Oncotarget. 9:12842–12852. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chun YS, Pawlik TM and Vauthey JN: 8th
Edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Pancreas and
hepatobiliary cancers. Ann Surg Oncol. 25:845–847. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Seoane J and Gomis RR: TGF-β family
signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 9(pii): a0222772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen W, Tao GQ, Zhang Y, Cai B, Sun J and
Tian ZQ: TGF-β in pancreatic cancer initiation and progression: Two
sides of the same coin. Cell Biosci. 7:392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang X, Feng W, Zhang J, Ge L, Zhang Y,
Jiang X, Peng W, Wang D, Gong A and Xu M: Long non-coding RNA PVT1
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the TGF-β/Smad
pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 40:1093–1102.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xing W, Gao W, Mao G, Zhang J, Lv X, Wang
G and Yan J: Long non-coding RNAs in aging organs and tissues. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 44 (Suppl):S30–S37. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen J, Chen Y, Gu L, Li X, Gao Y, Lyu X,
Chen L, Luo G, Wang L, Xie Y, et al: LncRNAs act as prognostic and
diagnostic biomarkers in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 7:74325–74336. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ijiri N, Panariti A, Mogas A, Nair P,
Hamid Q, Martin J and Baglole C: Lncrna Neat1 promotes Il-8
expression in fibroblasts derived from COPD patients and in
response to cigarette smoking. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
195:A76762017.https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/abs/10.1164/ajrccm-conference.2017.195.1_MeetingAbstracts.A7676
|
|
20
|
Gao M, Li H, Lv X, Zhou B and Yin Z:
Association between four polymorphisms in lncRNA and risk of lung
cancer in a Chinese never-smoking female population. DNA Cell Biol.
37:651–658. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu V, Singh P, Rahimy E, Zheng H, Kuo SZ,
Kim E, Wang-Rodriguez J and Ongkeko WM: RNA-seq analysis identifies
key long non-coding RNAs connected to the pathogenesis of
alcohol-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol
Lett. 12:2846–2853. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morikawa M, Derynck R and Miyazono K:
TGF-β and the TGF-β family: Context-dependent roles in cell and
tissue physiology. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 8:a0218732016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|