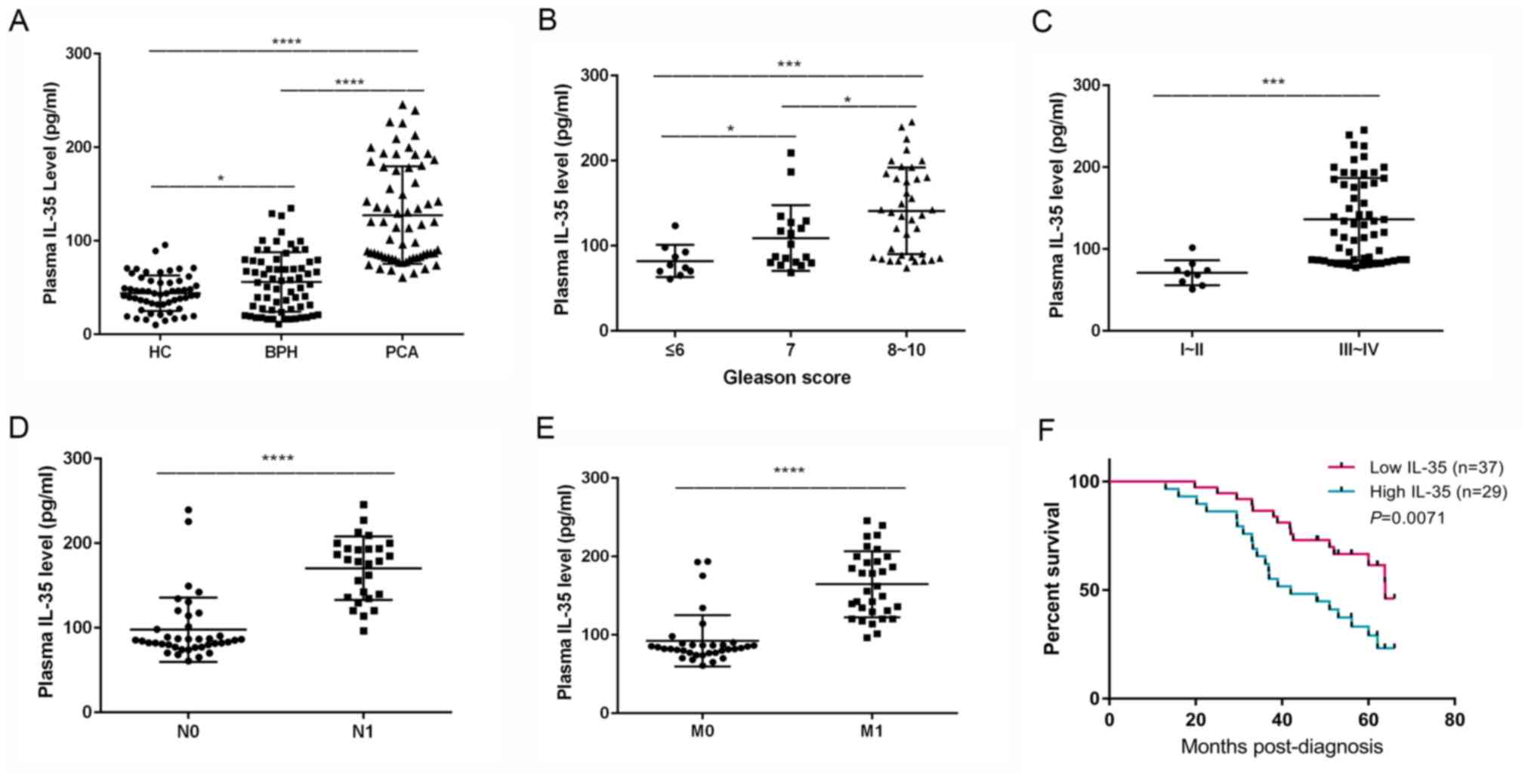
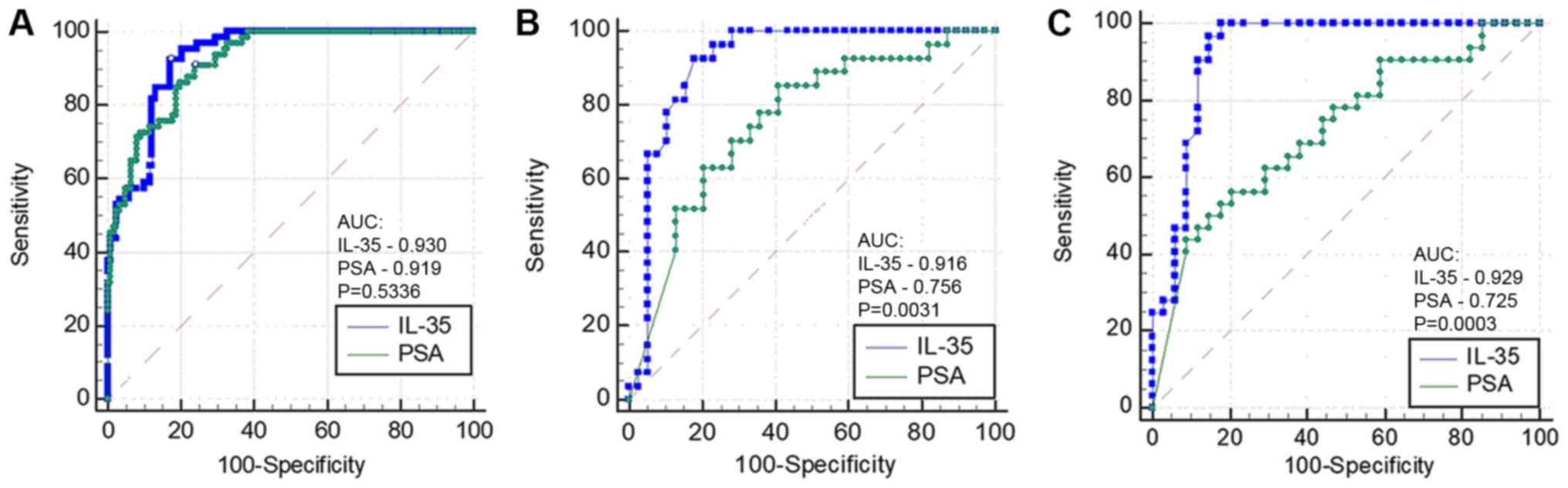
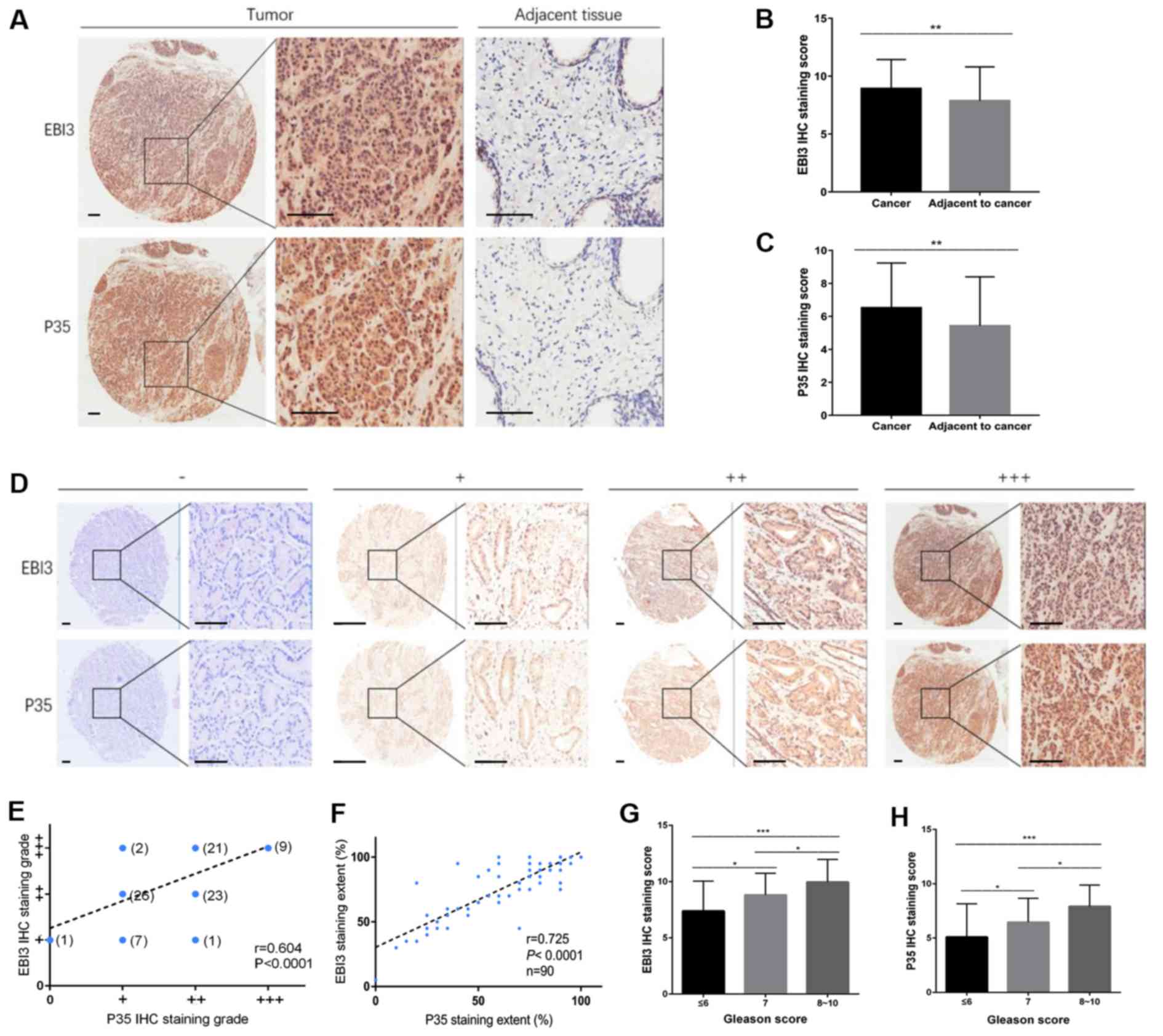
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lilja H, Ulmert D and Vickers AJ:
Prostate-specific antigen and prostate cancer: Prediction,
detection and monitoring. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:268–278. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shariat SF, Semjonow A, Lilja H, Savage C,
Vickers AJ and Bjartell A: Tumor markers in prostate cancer I:
Blood-based markers. Acta Oncol. 50 (Suppl 1):S61–S75. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hwang JE, Joung JY, Shin SP, Choi MK, Kim
JE, Kim YH, Park WS, Lee SJ and Lee KH: Ad5/35E1aPSESE4: A novel
approach to marking circulating prostate tumor cells with a
replication competent adenovirus controlled by PSA/PSMA
transcription regulatory elements. Cancer Lett. 372:57–64. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cooperberg MR, Broering JM and Carroll PR:
Time trends and local variation in primary treatment of localized
prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:1117–1123. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Collison LW, Chaturvedi V, Henderson AL,
Giacomin PR, Guy C, Bankoti J, Finkelstein D, Forbes K, Workman CJ,
Brown SA, et al: IL-35-mediated induction of a potent regulatory T
cell population. Nat Immunol. 11:1093–1101. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeng JC, Zhang Z, Li TY, Liang YF, Wang
HM, Bao JJ, Zhang JA, Wang WD, Xiang WY, Kong B, et al: Assessing
the role of IL-35 in colorectal cancer progression and prognosis.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 6:1806–1816. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jin P, Ren H, Sun W, Xin W, Zhang H and
Hao J: Circulating IL-35 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
patients. Hum Immunol. 75:29–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jin L, Xu X, Ye B, Pan M, Shi Z and Hu Y:
Elevated serum interleukin-35 levels correlate with poor prognosis
in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:18861–18866. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu W, Jiang H, Li Yi and Yan MX: IL-35
expression is increased in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and in
the peripheral blood of patients. Oncol Lett. 13:3303–3308. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Z, Liu JQ, Liu Z, Shen R, Zhang G, Xu
J, Basu S, Feng Y and Bai X: Tumor-derived IL-35 promotes tumor
growth by enhancing myeloid cell accumulation and angiogenesis. J
Immunol. 190:2415–2423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nicholl MB, Ledgewood CL, Chen XH, Bai Q,
Qin CL, Cook KM, Herrick EJ, DiazArias A, Moore BJ and Fang YJ:
IL-35 promotes pancreas cancer growth through enhancement of
proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis: Evidence for a role as
an autocrine growth factor. Cytokine. 70:126–133. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao Z, Chen X, Hao SN, Jia R, Wang N,
Chen S, Li M, Wang C and Mao H: Increased interleukin-35 expression
in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes correlates with poor prognosis in
patients with breast cancer. Cytokine. 89:76–81. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tao Q, Pan Y, Wang Y, Wang H, Xiong S, Li
Q, Wang J, Tao L, Wang Z, Wu F, et al: Regulatory T cells derived
IL-35 promotes the growth of adult acute myeloid leukemia blasts.
Int J Cancer. 137:2384–2393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gu X, Tian T, Zhang B, Liu Y, Yuan C, Shao
LJ, Guo Y and Fan K: Elevated plasma interleukin-35 levels predict
poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour
Biol. 36:2651–2656. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fu YP, Yi Y, Cai XY, Sun J, Ni XC, He HW,
Wang JX, Lu ZF, Huang JL, Cao Y, et al: Overexpression of
interleukin-35 associates with hepatocellular carcinoma
aggressiveness and recurrence after curative resection. Br J
Cancer. 114:767–776. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fan YG, Zhai JM, Wang W, Feng B, Yao GL,
An YH and Zeng Chao: IL-35 over-expression is associated with
genesis of gastric cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:2845–2849.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Buyyounouski MK, Choyke PL, McKenney JK,
Sartor O, Sandler HM, Amin MB, Kattan MW and Lin DW: Prostate
cancer-major changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer
eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:245–253.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Epstein JI, Egevad L, Amin MB, Delahunt B,
Srigley JR and Humphrey PA; Grading Committee, : The 2014
International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus
Conference on Gleason Grading of prostatic carcinoma: Definition of
grading patterns and proposal for a new grading system. Am J Surg
Pathol. 40:244–252. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Whiteside TL: The tumor microenvironment
and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene. 27:5904–5912.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Salomon BL, Leclerc M, Tosello J, Ronin E,
Piaggio E and Cohen JL: Tumor necrosis factor α and regulatory T
cells in oncoimmunology. Front Immunol. 9:4442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vivekanandhan S and Mukhopadhyay D:
Genetic status of KRAS influences transforming growth factor-beta
(TGF-β) signaling: An insight into Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) mediated
tumorigenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 54:72–79. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang S, Liu Q, Liao Q, Wu Q, Sun B, Yang
Z, Hu X, Tan M and Li L: Interleukin-6/signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 promotes prostate cancer resistance to
androgen deprivation therapy via regulating pituitary tumor
transforming gene 1 expression. Cancer Sci. 109:678–687. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Seyerl M, Kirchberger S, Majdic O, Seipelt
J, Jindra C, Schrauf C and Stöckl J: Human rhinoviruses induce
IL-35-producing Treg via induction of B7-H1 (CD274) and sialo
adhesin (CD169) on DC. Eur J Immunol. 40:321–329. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou C, Zhang J, Chen Y, Wang H and Hou J:
Interleukin-35 as a predictor of prostate cancer in patients
undergoing initial prostate biopsy. Onco Targets Ther.
10:3485–3491. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chatrabnous N, Ghaderi A, Ariafar A,
Razeghinia M S, Nemati M and Jafarzadeh A: Serum concentration of
interleukin-35 and its association with tumor stages and FOXP3 gene
polymorphism in patients with prostate cancer. Cytokine.
113:221–227. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Sun H, Wu H, Tan QD and Xiang K:
Interleukin 35 is an independent prognostic factor and a
therapeutic target for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Contemp Oncol
(Pozn). 2:120–124. 2015.
|
|
28
|
Huang C, Li N, Li Z, Chang A, Chen Y, Zhao
T, Li Y, Wang X, Zhang W, Wang Z, et al: Tumour-derived Interleukin
35 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell extravasation and
metastasis by inducing ICAM1 expression. Nat Commun. 8:140352017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang C, Li Z, Li N, Li Y, Chang A, Zhao
T, Wang X, Wang H, Gao S, Yang S, et al: Interleukin 35 expression
correlates with microvessel density in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma, recruits monocytes, and promotes growth and
angiogenesis of Xenograft tumors in mice. Gastroenterology.
154:675–688. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Turnis ME, Sawant DV, Szymczak-Workman AL,
Andrews LP, Delgoffe GM, Yano H, Beres AJ, Vogel P, Workman CJ and
Vignali DA: Interleukin-35 limits anti-tumor immunity. Immunity.
44:316–329. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang K, Liu J and Li J: IL-35-producing B
cells in gastric cancer patients. Medicine (Baltimore).
97:e07102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Trinchieri G, Pflanz S and Kastelein RA:
The IL-12 family of heterodimeric cytokines: New players in the
regulation of T cell responses. Immunity. 19:641–644. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sun L, He C, Nair L, Yeung J and Egwuagu
CE: Interleukin 12 (IL-12) family cytokines: Role in immune
pathogenesis and treatment of CNS autoimmune disease. Cytokine.
75:249–255. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Collison LW, Delgoffe GM, Guy CS, Vignali
KM, Chaturvedi V, Fairweather D, Satoskar AR, Garcia KC, Hunter CA,
Drake CG, et al: The composition and signaling of the IL-35
receptor are unconventional. Nat Immunol. 13:290–299. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang RX, Yu CR, Dambuza IM, Mahdi RM,
Dolinska MB, Sergeev YV, Wingfeld PT, Kim SH and Egwuagu CE:
Interleukin-35 induces regulatory B cells that suppress autoimmune
disease. Nat Med. 20:633–641. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma YH, Chen L, Xie G, Zhou Y, Yue C, Yuan
X, Zheng Y, Wang W, Deng L and Shen L: Elevated level of
Interleukin-35 in colorectal cancer induces conversion of T cells
into iTr35 by activating STAT1/STAT3. Oncotarget. 7:73003–73015.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|