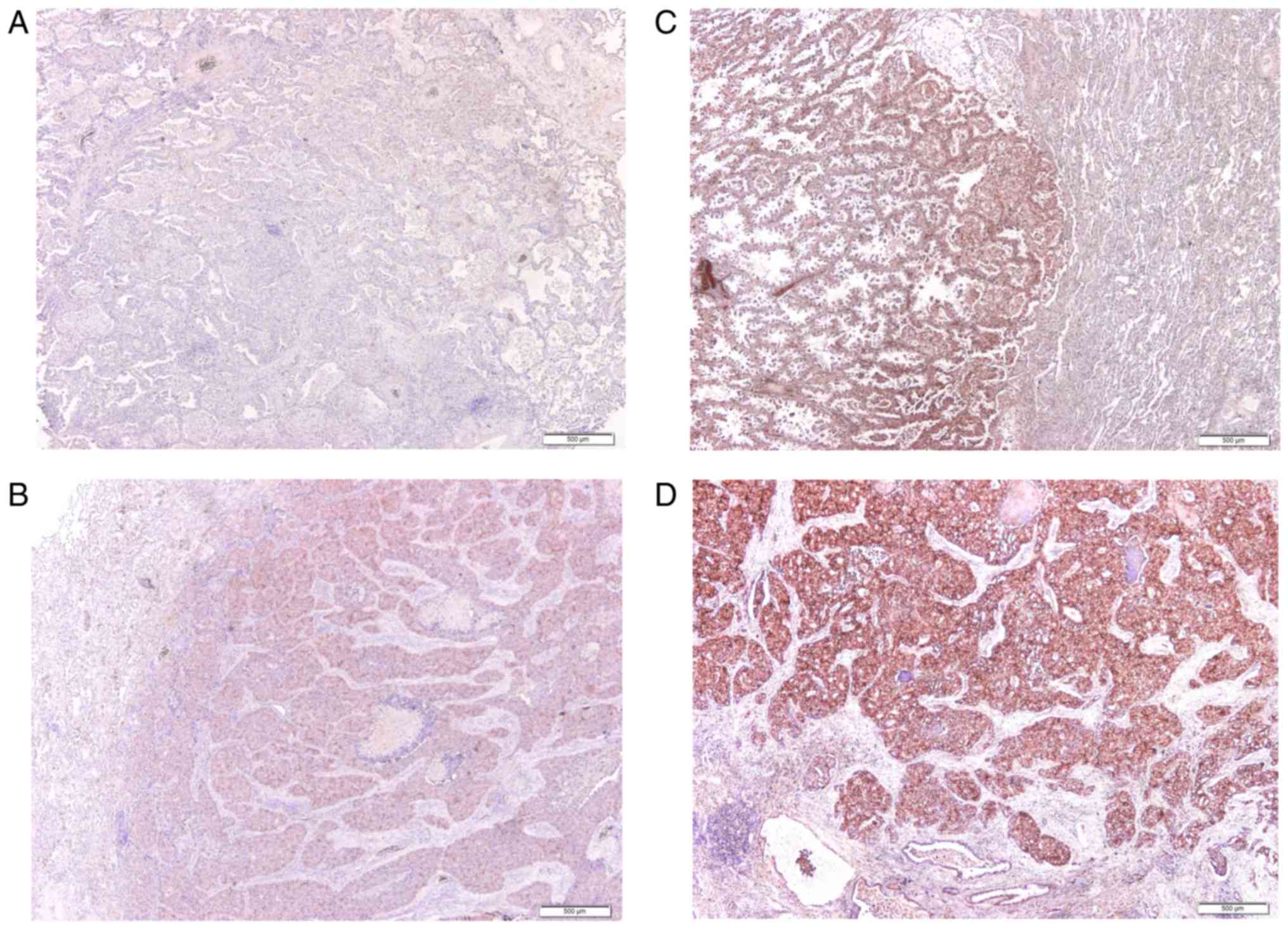
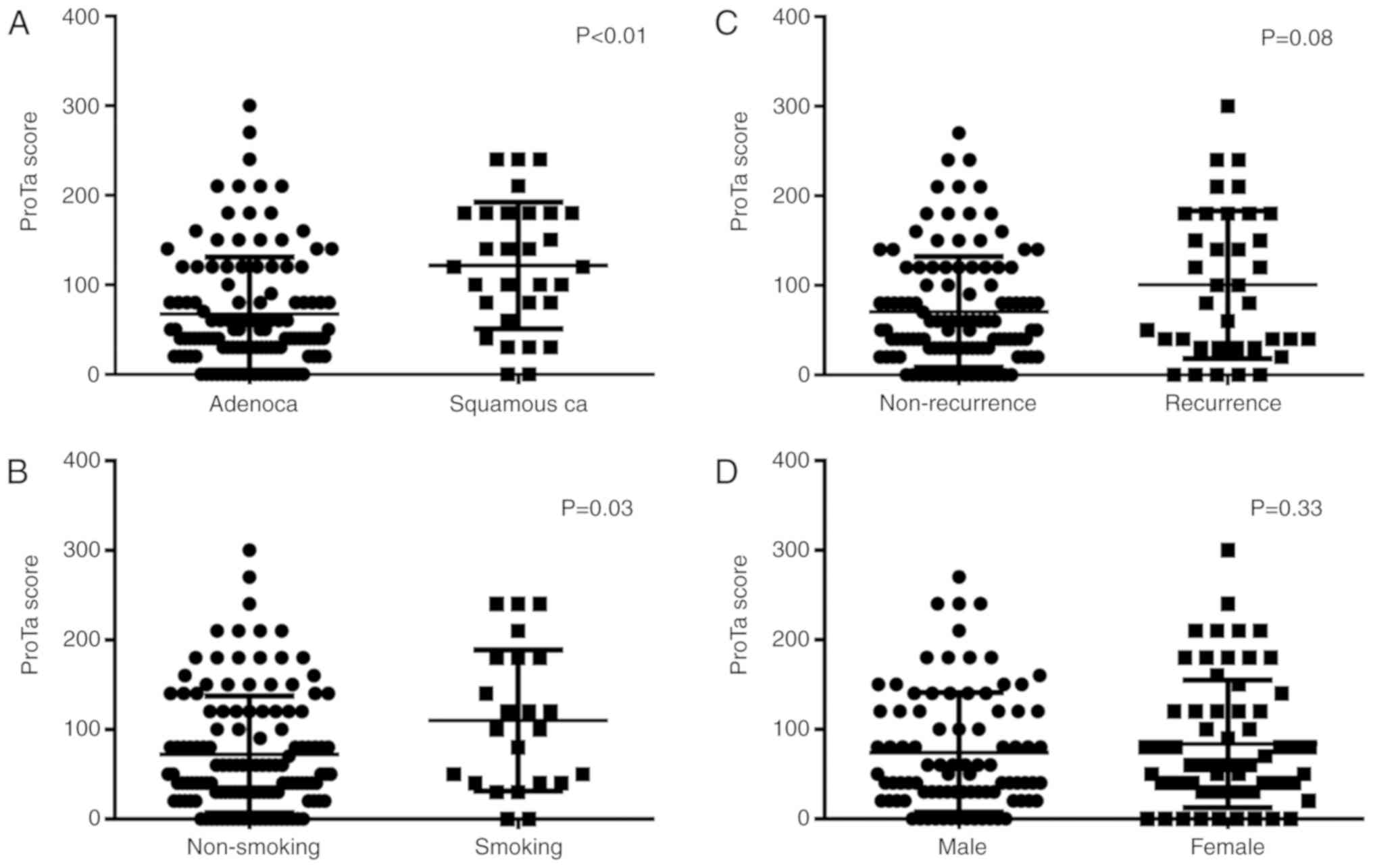
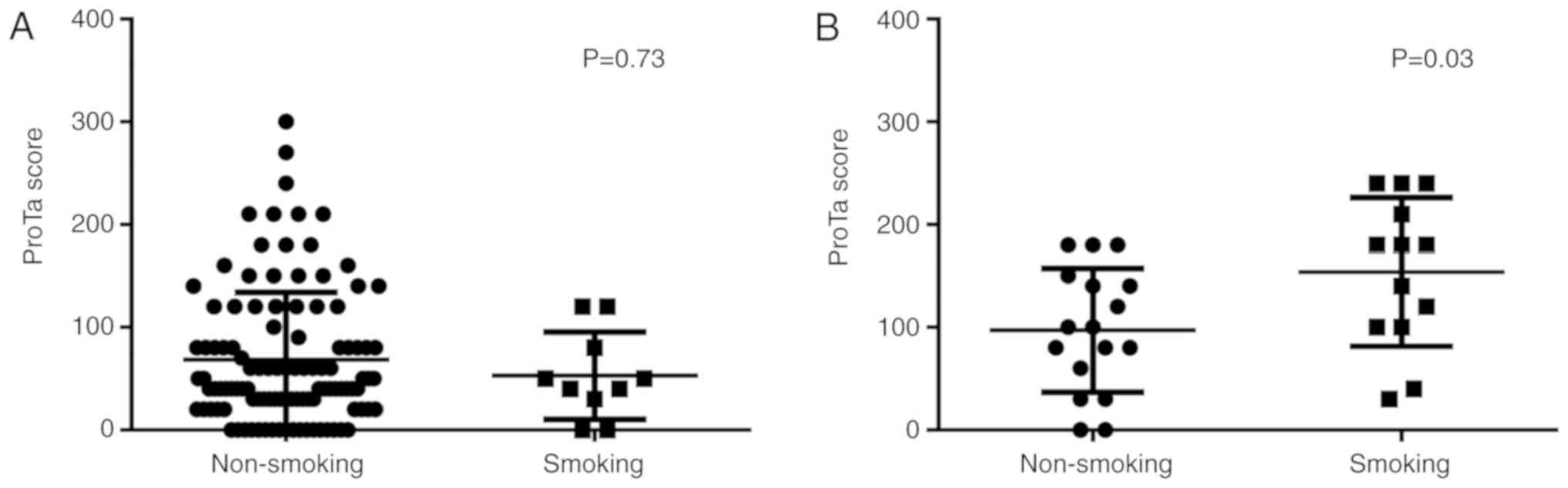
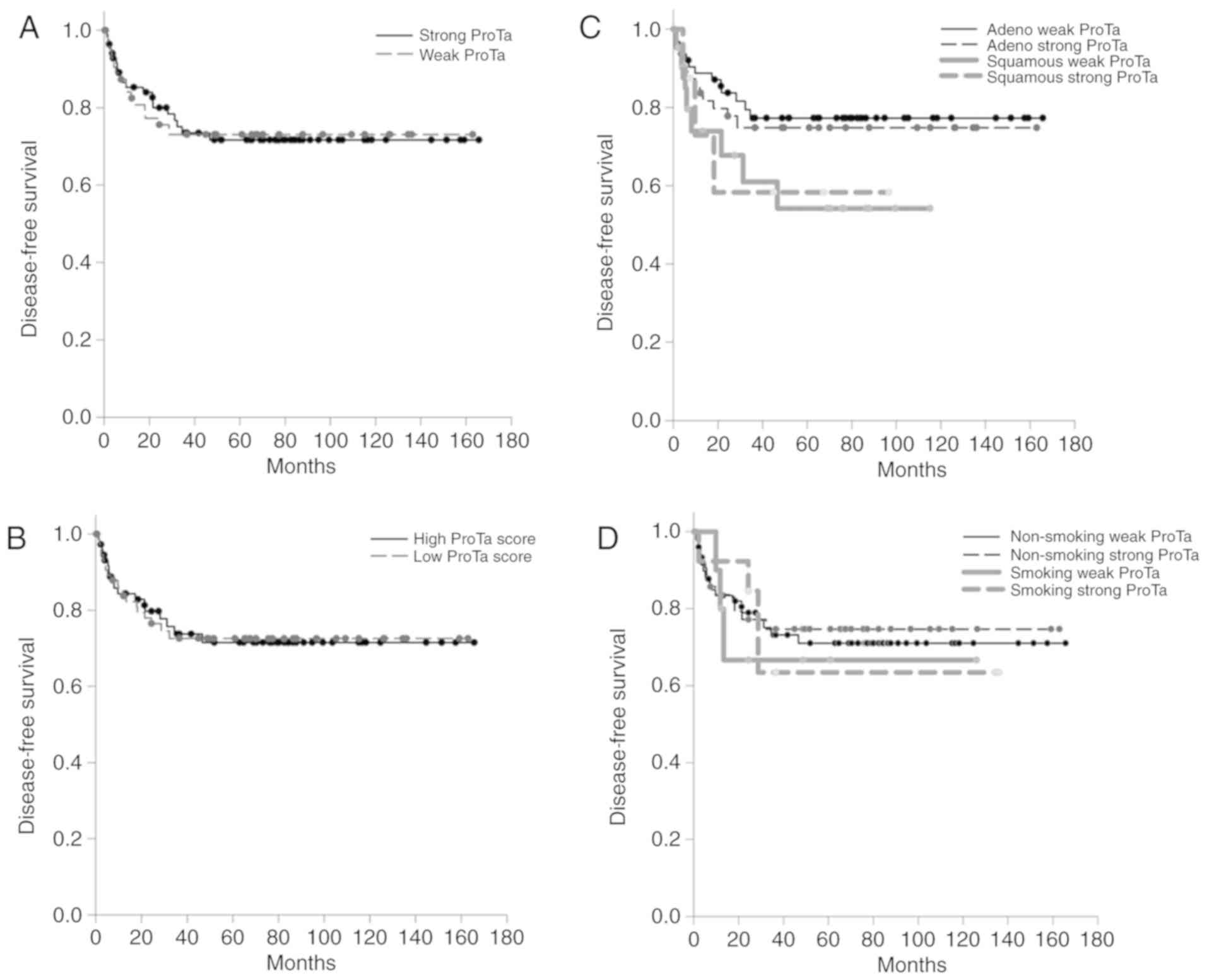
|
1
|
Haritos AA, Goodall GJ and Horecker BL:
Prothymosin alpha: Isolation and properties of the major
immunoreactive form of thymosin alpha 1 in rat thymus. Proc Natl
Acad Sci U S A. 81:1008–1011. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smith MR, al-Katib A, Mohammad R,
Silverman A, Szabo P, Khilnani S, Kohler W, Nath R and Mutchnick
MG: Prothymosin alpha gene expression correlates with
proliferation, not differentiation, of HL-60 cells. Blood.
82:1127–1132. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jiang X, Kim HE, Shu H, Zhao Y, Zhang H,
Kofron J, Donnelly J, Burns D, Ng SC, Rosenberg S and Wang X:
Distinctive roles of PHAP proteins and prothymosin-alpha in a death
regulatory pathway. Science. 299:223–226. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pai CW and Chen YH: Transgenic expression
of prothymosin alpha on zebrafish epidermal cells promotes
proliferation and attenuates UVB-induced apoptosis. Transgenic Res.
19:655–665. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Letsas KP and Frangou-Lazaridis M: Surfing
on prothymosin alpha proliferation and anti-apoptotic properties.
Neoplasma. 53:92–96. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mori M, Barnard GF, Staniunas RJ, Jessup
JM, Steele GD Jr and Chen LB: Prothymosin-alpha mRNA expression
correlates with that of c-myc in human colon cancer. Oncogene.
8:2821–2826. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jou YC, Tung CL, Tsai YS, Shen CH, Syue-Yi
C, Shiau AL, Tsai HT, Wu CL and Tzai TS: Prognostic relevance of
prothymosin-alpha expression in human upper urinary tract
transitional cell carcinoma. Urology. 74:951–957. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tripathi SC, Matta A, Kaur J, Grigull J,
Chauhan SS, Thakar A, Shukla NK, Duggal R, Choudhary AR, Dattagupta
S, et al: Overexpression of prothymosin alpha predicts poor disease
outcome in head and neck cancer. PLoS One. 6:e192132011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ha SY, Song DH, Hwang SH, Cho SY and Park
CK: Expression of prothymosin alpha predicts early recurrence and
poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat
Dis Int. 14:171–177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang M, Cui F, Lu S, Lu H, Jiang T, Chen
J, Zhang X, Jin Y, Peng Z and Tang H: Increased expression of
prothymosin-α, independently or combined with TP53, correlates with
poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4867–4876. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sasaki H, Fujii Y, Masaoka A, Yamakawa Y,
Fukai I, Kiriyama M, Saito Y and Matsui H: Elevated plasma
thymosin-alpha1 levels in lung cancer patients. Eur J Cardiothorac
Surg. 12:885–891. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moody TW, Leyton J, Zia F, Tuthill C,
Badamchian M and Goldstein AL: Thymosinalpha1 is chemopreventive
for lung adenoma formation in A/J mice. Cancer Lett. 155:121–127.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sasaki H, Nonaka M, Fujii Y, Yamakawa Y,
Fukai I, Kiriyama M and Sasaki M: Expression of the prothymosin-a
gene as a prognostic factor in lung cancer. Surg Today. 31:936–938.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Su BH, Tseng YL, Shieh GS, Chen YC, Shiang
YC, Wu P, Li KJ, Yen TH, Shiau AL and Wu CL: Prothymosin α
overexpression contributes to the development of pulmonary
emphysema. Nat Commun. 4:19062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sukhacheva EA, Evstafieva AG, Fateeva TV,
Shakulov VR, Efimova NA, Karapetian RN, Rubtsov YP and Vartapetian
AB: Sensing prothymosin alpha origin, mutations and conformation
with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 266:185–196. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsai YS, Jou YC, Lee GF, Chen YC, Shiau
AL, Tsai HT, Wu CL and Tzai TS: Aberrant prothymosin-alpha
expression in human bladder cancer. Urology. 73:188–192. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz AG,
Balch CM, Haller DG and Morrow M: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 6th.
Springer Publ. Corp.; New York, NY: pp. 165–178. 2002
|
|
18
|
Pesch B, Kendzia B, Gustavsson P, Jöckel
KH, Johnen G, Pohlabeln H, Olsson A, Ahrens W, Gross IM, Brüske I,
et al: Cigarette smoking and lung cancer-Relative risk estimates
for the major histological types from a pooled analysis of
case-control studies. Int J Cancer. 131:1210–1219. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ralhan R, Desouza LV, Matta A, Tripathi
SC, Ghanny S, Datta Gupta S, Bahadur S and Siu KW: Discovery and
verification of head-and-neck cancer biomarkers by differential
protein expression analysis using iTRAQ labeling, multidimensional
liquid chromatography, and tandem mass spectrometry. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 7:1162–1173. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Magdalena C, Dominguez F, Loidi L and
Puente JL: Tumour prothymosin alpha content, a potential prognostic
marker for primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 82:584–590. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu CG, Habib NA, Mitry RR, Reitsma PH, van
Deventer SJ and Chamuleau RA: Overexpression of hepatic prothymosin
alpha, a novel marker for human hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 76:1199–1204. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leys CM, Nomura S, LaFleur BJ, Ferrone S,
Kaminishi M, Montgomery E and Goldenring JR: Expression and
prognostic significance of prothymosin-alpha and ERp57 in human
gastric cancer. Surgery. 141:41–50. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Suzuki S, Takahashi S, Takahashi S,
Takeshita K, Hikosaka A, Wakita T, Nishiyama N, Fujita T, Okamura T
and Shirai T: Expression of prothymosin alpha is correlated with
development and progression in human prostate cancers. Prostate.
66:463–469. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Su BH, Tseng YL, Shieh GS, Chen YC, Wu P,
Shiau AL and Wu CL: Over-expression of prothymosin-α antagonizes
TGFβ signalling to promote the development of emphysema. J Pathol.
238:412–422. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chauhan SS, Kaur J, Kumar M, Matta A,
Srivastava G, Alyass A, Assi J, Leong I, MacMillan C, Witterick I,
et al: Prediction of recurrence-free survival using a protein
expression-based risk classifier for head and neck cancer.
Oncogenesis. 4:e1472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gou LT, Tong AP, Yan F, Yuan Z, He F, Wang
W, Zhou Y, Chen LJ, Tang MH and Yang JL: Altered protein-expressing
profile in hPNAS4-induced apoptosis in A549 human lung
adenocarcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 108:1211–1219. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|