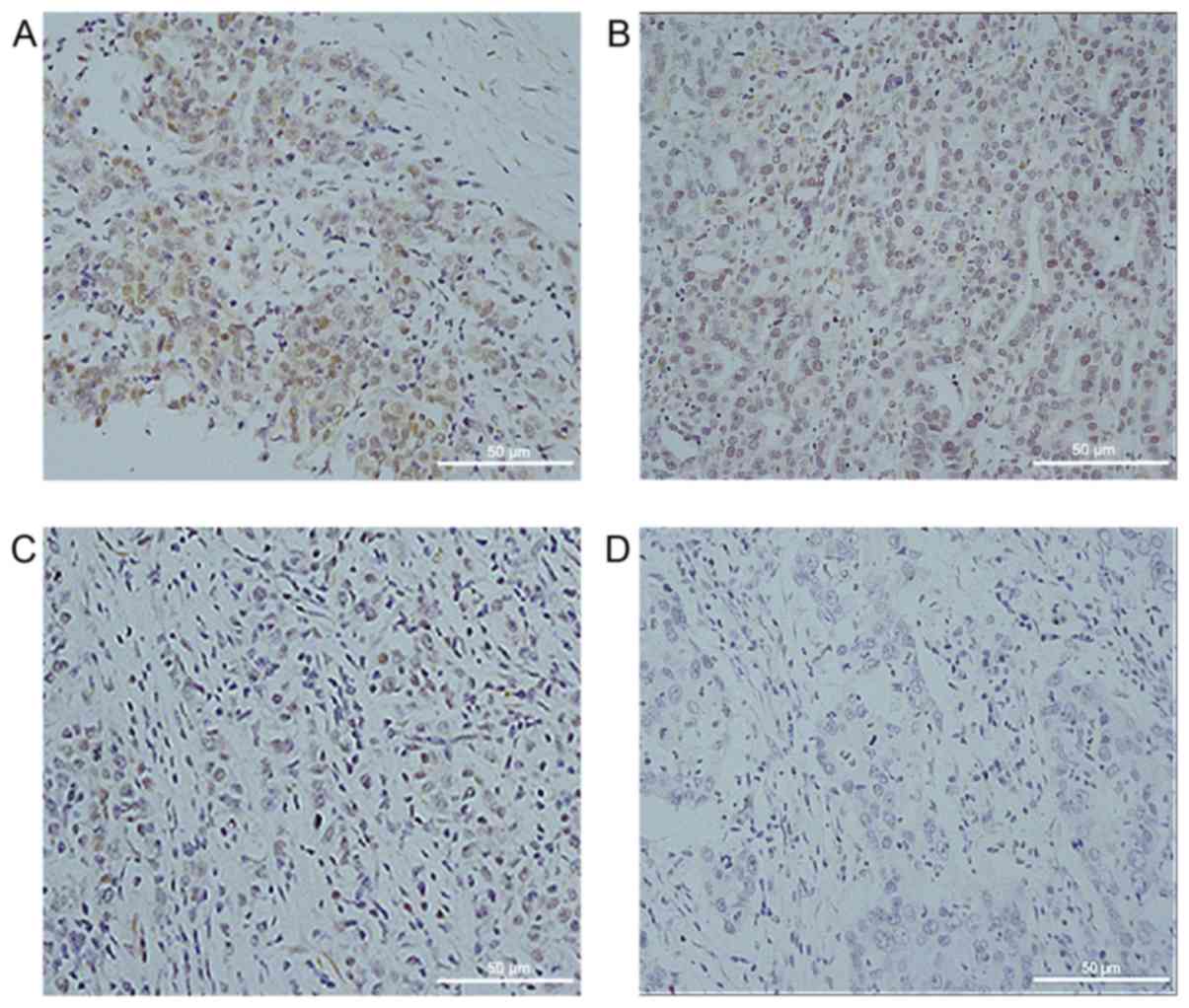
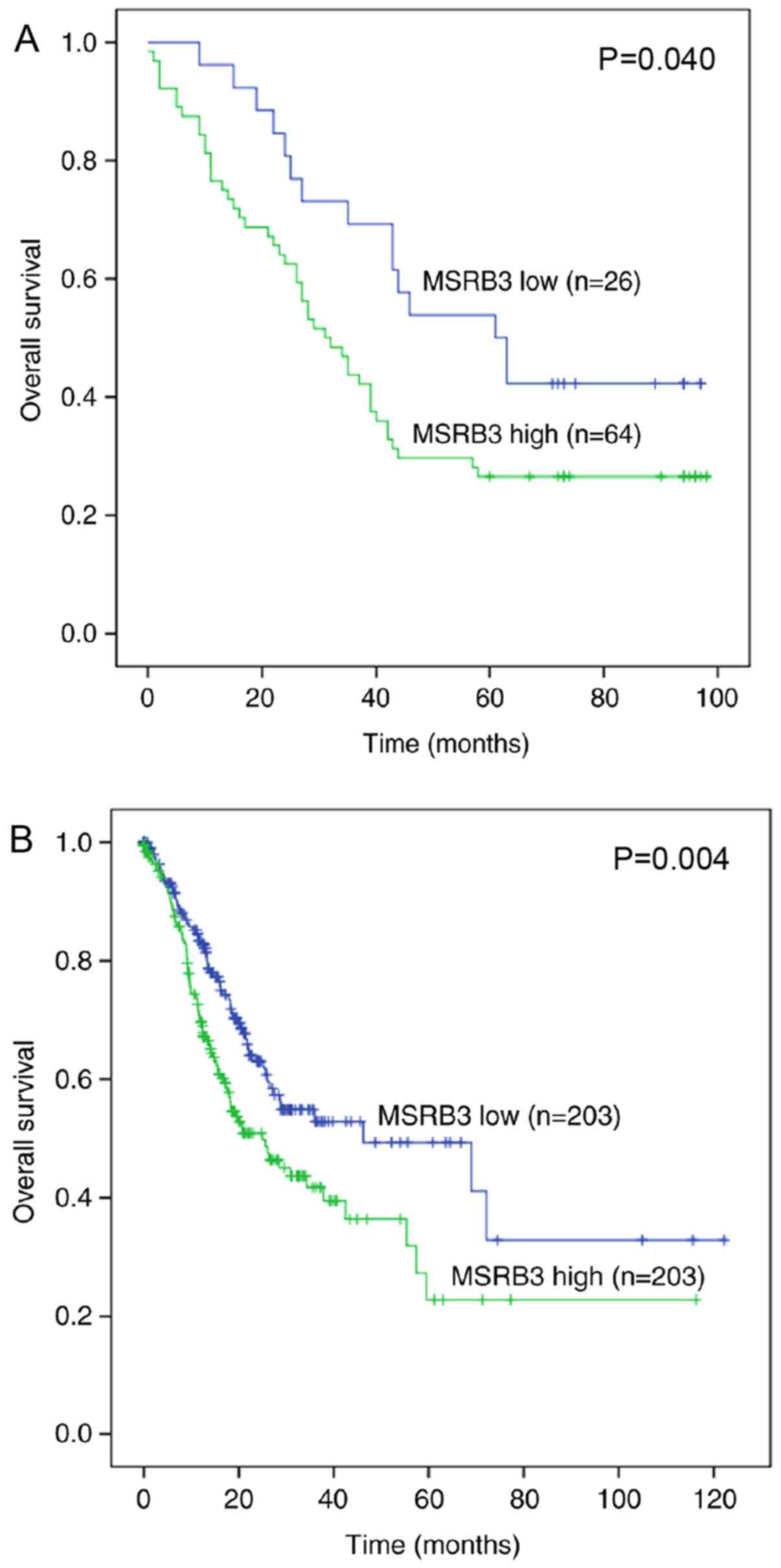
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shen YH, Xie ZB, Yue AM, Wei QD, Zhao HF,
Yin HD, Mai W, Zhong XG and Huang SR: Expression level of
microRNA-195 in the serum of patients with gastric cancer and its
relationship with the clinicopathological staging of the cancer.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:1283–1287. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Miao R, Guo X, Zhi Q, Shi Y, Li L, Mao X,
Zhang L and Li C: VEZT, a novel putative tumor suppressor,
suppresses the growth and tumorigenicity of gastric cancer. PLoS
One. 8:e744092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen Y, Pan K, Li S, Xia J, Wang W, Chen
J, Zhao J, Lü L, Wang D, Pan Q, et al: Decreased expression of
V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 1 (VSIG1) is associated
with poor prognosis in primary gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol.
106:286–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee J, Lim DH, Kim S, Park SH, Park JO,
Park YS, Lim HY, Choi MG, Sohn TS, Noh JH, et al: Phase III trial
comparing capecitabine plus cisplatin versus capecitabine plus
cisplatin with concurrent capecitabine radiotherapy in completely
resected gastric cancer with D2 lymph node dissection: The ARTIST
trial. J Clin Oncol. 30:268–273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matés JM, Pérez-Gómez C and Núñez de
Castro I: Antioxidant enzymes and human diseases. Clin Biochem.
32:595–603. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Krause KH: Aging: A revisited theory based
on free radicals generated by NOX family NADPH oxidases. Exp
Gerontol. 42:256–262. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Valko M, Izakovic M, Mazur M, Rhodes CJ
and Telser J: Role of oxygen radicals in DNA damage and cancer
incidence. Mol Cell Biochem. 266:37–56. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schumacker PT: Reactive oxygen species in
cancer cells: Live by the sword, die by the sword. Cancer Cell.
10:175–176. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pelicano H, Carney D and Huang P: ROS
stress in cancer cells and therapeutic implications. Drug Resist
Updat. 7:97–110. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT,
Mazur M and Telser J: Free radicals and antioxidants in normal
physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
39:44–84. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M
and Mazur M: Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative
stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact. 160:1–40. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M and Lunec
J: Oxidative DNA damage: Mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB
J. 17:1195–1214. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Klaunig JE and Kamendulis LM: The role of
oxidative stress in carcinogenesis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
44:239–267. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Halliwell B: Antioxidants in human health
and disease. Annu Rev Nutr. 16:33–50. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim HY and Gladyshev VN: Methionine
sulfoxide reductases: Selenoprotein forms and roles in antioxidant
protein repair in mammals. Biochem J. 407:321–329. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kwak GH, Kim TH and Kim HY:
Down-regulation of MsrB3 induces cancer cell apoptosis through
reactive oxygen species production and intrinsic mitochondrial
pathway activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 483:468–474. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim HY: The methionine sulfoxide reduction
system: Selenium utilization and methionine sulfoxide reductase
enzymes and their functions. Antioxid Redox Signal. 19:958–969.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lim DH, Han JY, Kim JR, Lee YS and Kim HY:
Methionine sulfoxide reductase B in the endoplasmic reticulum is
critical for stress resistance and aging in Drosophila. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 419:20–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim HY and Gladyshev VN: Role of
structural and functional elements of mouse methionine-S-sulfoxide
reductase in its subcellular distribution. Biochemistry.
44:8059–8067. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim G, Cole NB, Lim JC, Zhao H and Levine
RL: Dual sites of protein initiation control the localization and
myristoylation of methionine sulfoxide reductase A. J Biol Chem.
285:18085–18094. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vougier S, Mary J and Friguet B:
Subcellular localization of methionine sulphoxide reductase A
(MsrA): Evidence for mitochondrial and cytosolic isoforms in rat
liver cells. Biochem J. 373:531–537. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim HY and Gladyshev VN: Methionine
sulfoxide reduction in mammals: Characterization of
methionine-R-sulfoxide reductases. Mol Biol Cell. 15:1055–1064.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kwak GH, Lim DH, Han JY, Lee YS and Kim
HY: Methionine sulfoxide reductase B3 protects from endoplasmic
reticulum stress in Drosophila and in mammalian cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 420:130–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang C, Jia P, Jia Y, Li Y, Webster KA,
Huang X, Achary M, Lemanski SL and Lemanski LF: Anoxia, acidosis,
and intergenic interactions selectively regulate methionine
sulfoxide reductase transcriptions in mouse embryonic stem cells. J
Cell Biochem. 112:98–106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Morel AP, Ginestier C, Pommier RM, Cabaud
O, Ruiz E, Wicinski J, Devouassoux-Shisheboran M, Combaret V,
Finetti P, Chassot C, et al: A stemness-related ZEB1-MSRB3 axis
governs cellular pliancy and breast cancer genome stability. Nat
Med. 23:568–578. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hansel A, Jung S, Hoshi T and Heinemann
SH: A second human methionine sulfoxide reductase (hMSRB2) reducing
methionine-R-sulfoxide displays a tissue expression pattern
distinct from hMSRB1. Redox Rep. 8:384–388. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oakley GJ, Fuhrer K and Seethala RR:
Brachyury, SOX-9, and podoplanin, new markers in the skull base
chordoma vs chondrosarcoma differential: A tissue microarray-based
comparative analysis. Mod Pathol. 21:1461–1469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Washington K: 7th edition of the AJCC
cancer staging manual: Stomach. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:3077–3079. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tomczak K, Czerwińska P and Wiznerowicz M:
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of
knowledge. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 19:A68–A77. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiang YZ, Yu KD, Zuo WJ, Peng WT and Shao
ZM: GATA3 mutations define a unique subtype of luminal-like breast
cancer with improved survival. Cancer. 120:1329–1337. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Liang L, Dai W, Cai G, Xu Y, Li X,
Li Q and Cai S: Prognostic impact of programed cell death-1 (PD-1)
and PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in cancer cells and tumor
infiltrating lymphocytes in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer.
15:552016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ueno H, Jones AM, Wilkinson KH, Jass JR
and Talbot IC: Histological categorisation of fibrotic cancer
stroma in advanced rectal cancer. Gut. 53:581–586. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Espejo Romero H and Navarrete Siancas J:
Classification of stomach adenocarcinomas. Rev Gastroenterol Peru.
23:199–212. 2003.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kwak GH, Kim JR and Kim HY: Expression,
subcellular localization, and antioxidant role of mammalian
methionine sulfoxide reductases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BMB
Rep. 42:113–118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kwon TJ, Cho HJ, Kim UK, Lee E, Oh SK, Bok
J, Bae YC, Yi JK, Lee JW, Ryoo ZY, et al: Methionine sulfoxide
reductase B3 deficiency causes hearing loss due to stereocilia
degeneration and apoptotic cell death in cochlear hair cells. Hum
Mol Genet. 23:1591–1601. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ahmed ZM, Yousaf R, Lee BC, Khan SN, Lee
S, Lee K, Husnain T, Rehman AU, Bonneux S, Ansar M, et al:
Functional null mutations of MSRB3 encoding methionine sulfoxide
reductase are associated with human deafness DFNB74. Am J Hum
Genet. 88:19–29. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kwak GH, Kim KY and Kim HY: Methionine
sulfoxide reductase B3 deficiency stimulates heme oxygenase-1
expression via ROS-dependent and Nrf2 activation pathways. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 473:1033–1038. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee E, Kwak GH, Kamble K and Kim HY:
Methionine sulfoxide reductase B3 deficiency inhibits cell growth
through the activation of p53-p21 and p27 pathways. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 547:1–5. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ran Q, Liang H, Gu M, Qi W, Walter CA,
Roberts LJ II, Herman B, Richardson A and Van Remmen H: Transgenic
mice overexpressing glutathione peroxidase 4 are protected against
oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 279:55137–55146.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Torres M: Mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathways in redox signaling. Front Biosci. 8:d369–d391. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kwak GH and Kim HY: MsrB3 deficiency
induces cancer cell apoptosis through p53-independent and ER
stress-dependent pathways. Arch Biochem Biophys. 621:1–5. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Murakami D, Tsujitani S, Osaki T, Saito H,
Katano K, Tatebe S and Ikeguchi M: Expression of phosphorylated Akt
(pAkt) in gastric carcinoma predicts prognosis and efficacy of
chemotherapy. Gastric Cancer. 10:45–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yokota T, Ishiyama S, Saito T, Teshima S,
Narushima Y, Murata K, Iwamoto K, Yashima R, Yamauchi H and Kikuchi
S: Lymph node metastasis as a significant prognostic factor in
gastric cancer: A multiple logistic regression analysis. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 39:380–384. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|