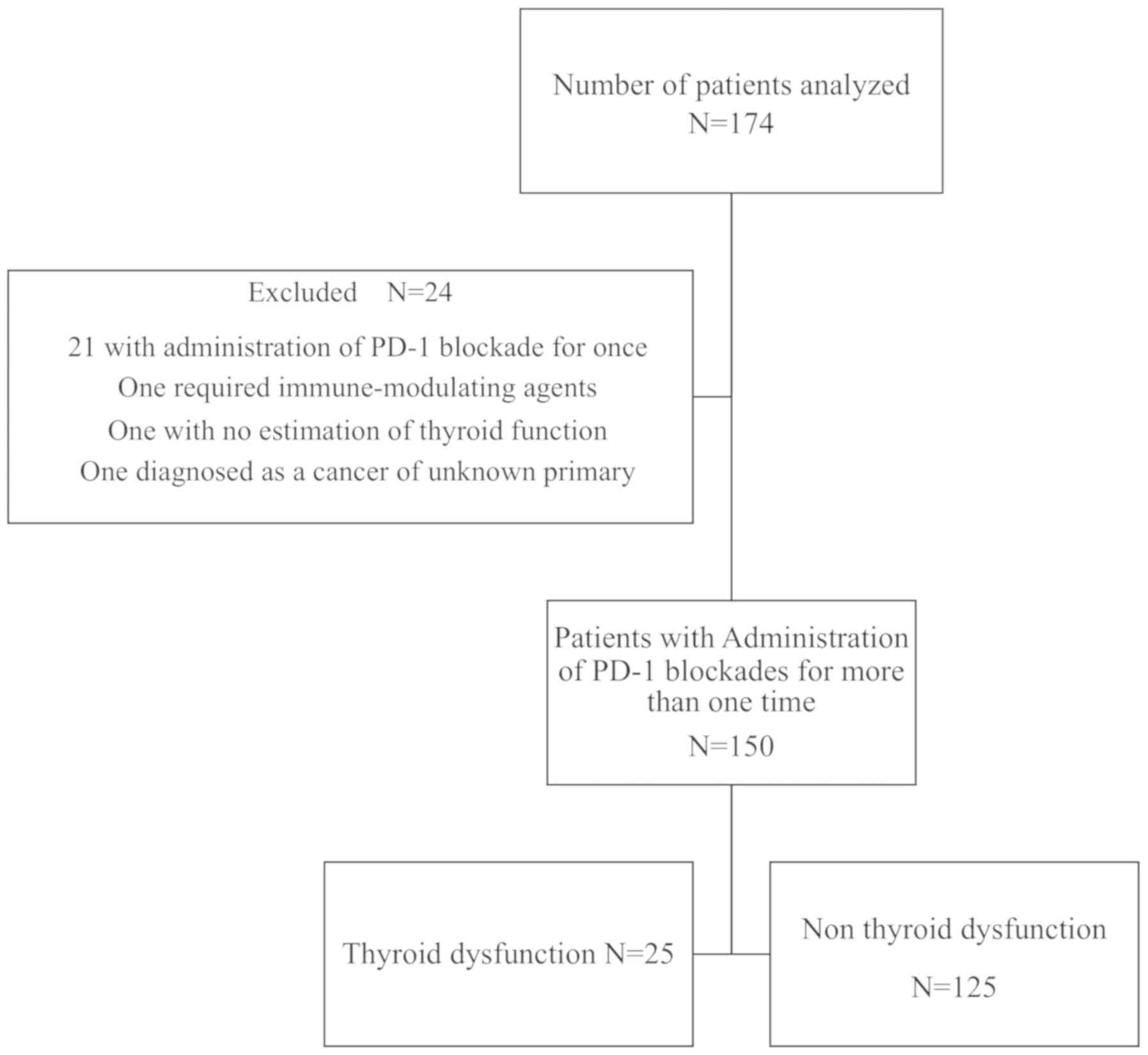
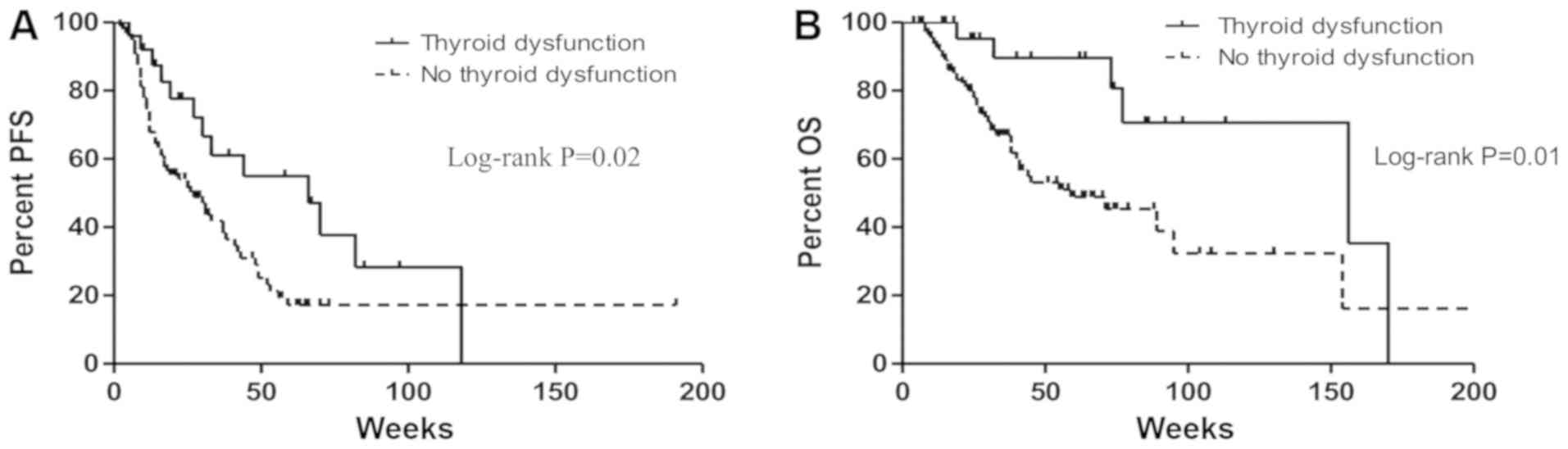
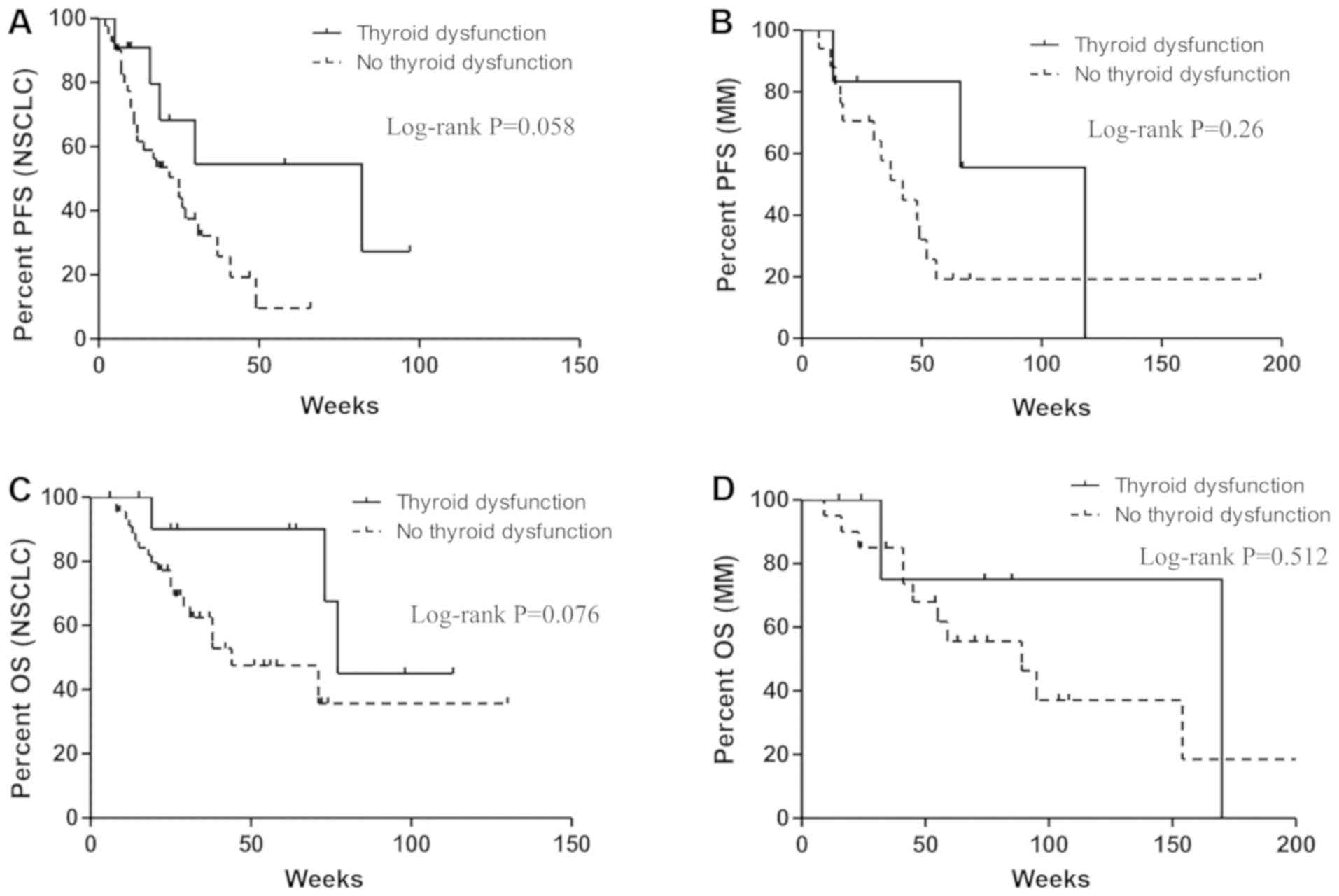
|
1
|
Robert C, Long GV, Brady B, Dutriaux C,
Maio M, Mortier L, Hassel JC, Rutkowski P, McNeil C,
Kalinka-Warzocha E, et al: Nivolumab in previously untreated
melanoma without BRAF mutation. N Engl J Med. 372:320–330. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR,
Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, et al:
Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:1627–1639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF,
George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S, Tykodi SS, Sosman JA, Procopio G,
Plimack ER, et al: Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 373:1803–1813. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferris RL, Blumenschein G Jr, Fayette J,
Guigay J, Colevas AD, Licitra L, Harrington K, Kasper S, Vokes EE,
Even C, et al: Nivolumab for recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of
the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 375:1856–1867. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I,
Halwani A, Scott EC, Gutierrez M, Schuster SJ, Millenson MM, Cattry
D, Freeman GJ, et al: PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or
refractory hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 372:311–319. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kang YK, Boku N, Satoh T, Ryu MH, Chao Y,
Kato K, Chung HC, Chen JS, Muro K, Kang WK, et al: Nivolumab in
patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction
cancer refractory to, or intolerant of, at least two previous
chemotherapy regimens (ONO-4538-12, ATTRACTION-2): A randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet.
390:2461–2471. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rizvi NA, Hellmann MD, Snyder A, Kvistborg
P, Makarov V, Havel JJ, Lee W, Yuan J, Wong P, Ho TS, et al:
Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in
non-small cell lung cancer. Science. 348:124–128. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Boutros C, Tarhini A, Routier E, Lambotte
O, Ladurie FL, Carbonnel F, Izzeddine H, Marabelle A, Champiat S,
Berdelou A, et al: Safety profiles of anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1
antibodies alone and in combination. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
13:473–486. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Friedman CF, Proverbs-Singh TA and Postow
MA: Treatment of the immune-related adverse effects of immune
checkpoint inhibitors: A review. JAMA Oncol. 2:1346–1353. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Postow MA, Sidlow R and Hellmann MD:
Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint
blockade. N Engl J Med. 378:158–168. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sanlorenzo M, Vujic I, Daud A, Algazi A,
Gubens M, Luna SA, Lin K, Quaglino P, Rappersberger K and
Ortiz-Urda S: Pembrolizumab cutaneous adverse events and their
association with disease progression. JAMA Dermatol. 151:1206–1212.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakamura Y, Tanaka R, Asami Y, Teramoto Y,
Imamura T, Sato S, Maruyama H, Fujisawa Y, Matsuya T, Fujimoto M
and Yamamoto A: Correlation between vitiligo occurrence and
clinical benefit in advanced melanoma patients treated with
nivolumab: A multi-institutional retrospective study. J Dermatol.
44:117–122. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Teulings H-E, Limpens J, Jansen SN,
Zwinderman AH, Reitsma JB, Spuls PI and Luiten RM: Vitiligo-like
depigmentation in patients with stage III–IV melanoma receiving
immunotherapy and its association with survival: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 33:773–781. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Haratani K, Hayashi H, Chiba Y, Kudo K,
Yonesaka K, Kato R, Kaneda H, Hasegawa Y, Tanaka K, Takeda M and
Nakagawa K: Association of immune-related adverse events with
nivolumab efficacy in non-small-cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol.
4:374–378. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R,
Grob JJ, Cowey CL, Lao CD, Schadendorf D, Dummer R, Smylie M,
Rutkowski P, et al: Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or
monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 373:23–34. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Osorio JC, Ni A, Chaft JE, Pollina R,
Kasler MK, Stephens D, Rodriguez C, Cambridge L, Rizvi H, Wolchok
JD, et al: Antibody-mediated thyroid dysfunction during T-cell
checkpoint blockade in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.
Ann Oncol. 28:583–589. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kobayashi T, Iwama S, Yasuda Y, Okada N,
Tsunekawa T, Onoue T, Takagi H, Hagiwara D, Ito Y, Morishita Y, et
al: Patients with antithyroid antibodies are prone to develop
destructive thyroiditis by nivolumab: A prospective study. J Endocr
Soc. 2:241–251. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J,
Davis TE, McFadden ET and Carbone PP: Toxicity and response
criteria of the eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin
Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
de Filette J, Jansen Y, Schreuer M,
Everaert H, Velkeniers B, Neyns B and Bravenboer B: Incidence of
thyroid-related adverse events in melanoma patients treated with
pembrolizumab. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 101:4431–4439. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jaafar J, Fernandez E, Alwan H and
Philippe J: Programmed cell death-1 and programmed cell death
ligand-1 antibodies-induced dysthyroidism. Endocr Connect.
7:R196–R211. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pearce SHS, Brabant G, Duntas LH, Monzani
F, Peeters RP, Razvi S and Wemeau JL: 2013 ETA guideline:
Management of subclinical hypothyroidism. Eur Thyroid J. 2:215–228.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garber JR, Cobin RH, Gharib H, Hennessey
JV, Klein I, Mechanick JI, Pessah-Pollack R, Singer PA and Woeber
KA: Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults:
Cosponsored by the american association of clinical
endocrinologists and the american thyroid association. Endocr
Pract. 18:988–1028. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Morganstein DL, Lai Z, Spain L, Diem S,
Levine D, Mace C, Gore M and Larkin J: Thyroid abnormalities
following the use of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 and
programmed death receptor protein-1 inhibitors in the treatment of
melanoma. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 86:614–620. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sato K, Akamatsu H, Murakami E, Sasaki S,
Kanai K, Hayata A, Tokudome N, Akamatsu K, Koh Y, Ueda H, et al:
Correlation between immune-related adverse events and efficacy in
non-small cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab. Lung Cancer.
115:71–74. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Freeman-Keller M, Kim Y, Cronin H,
Richards A, Gibney G and Weber JS: Nivolumab in resected and
unresectable metastatic melanoma: Characteristics of immune-related
adverse events and association with outcomes. Clin Cancer Res.
22:886–894. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim HI, Kim M, Lee SH, Park SY, Kim YN,
Kim H, Jeon MJ, Kim TY, Kim SW, Kim WB, et al: Development of
thyroid dysfunction is associated with clinical response to PD-1
blockade treatment in patients with advanced non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncoimmunology. 7:e13756422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|