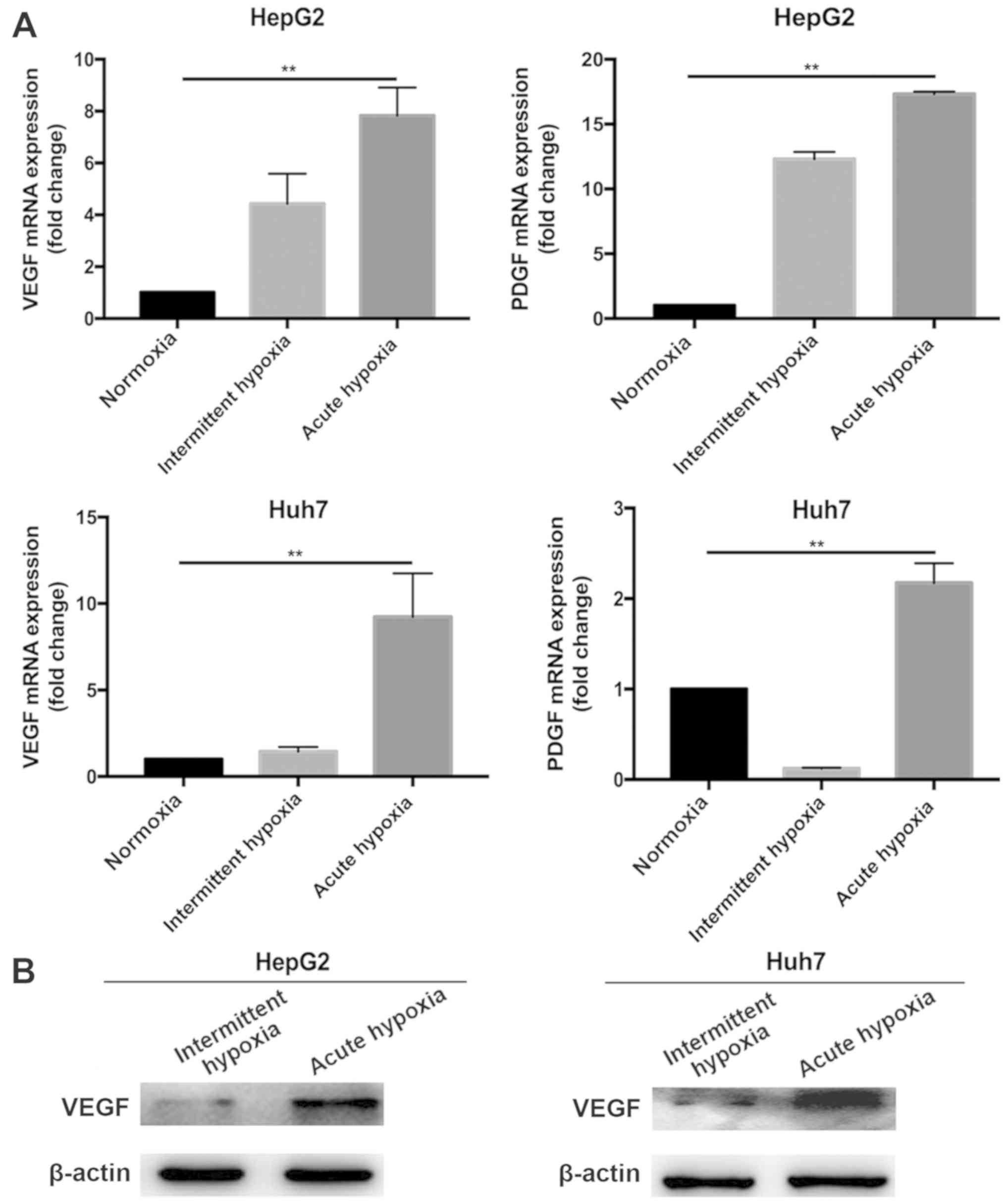
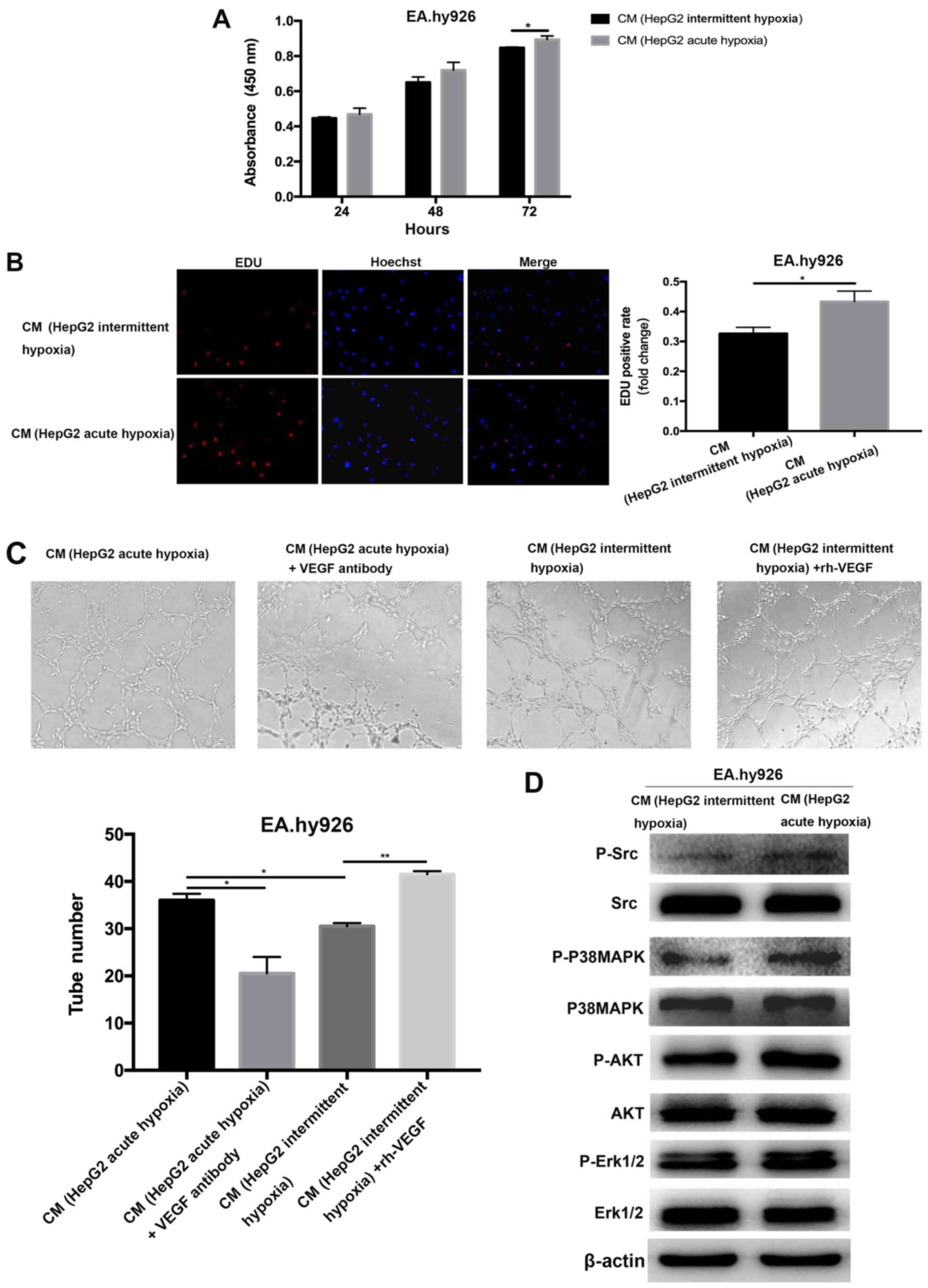
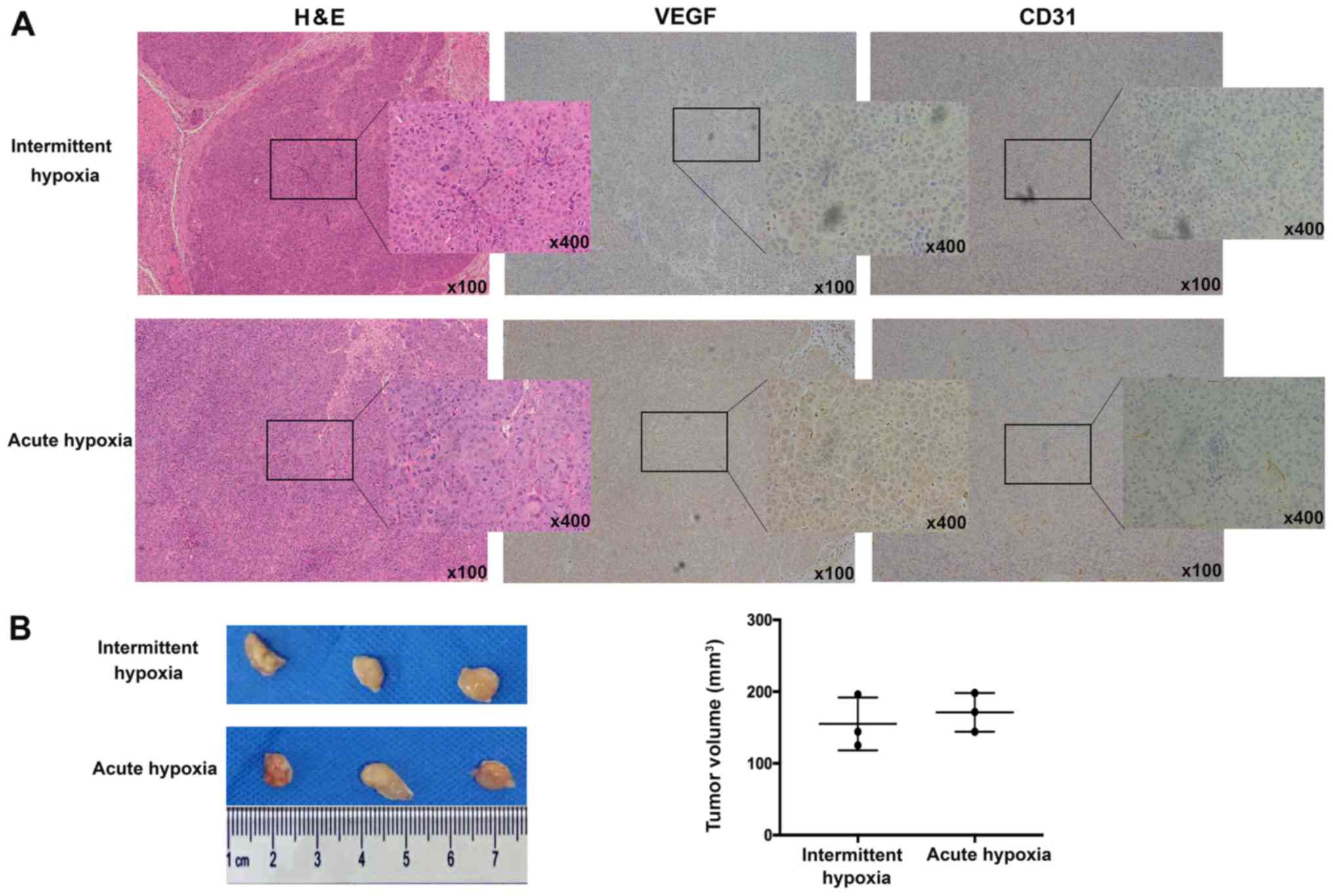
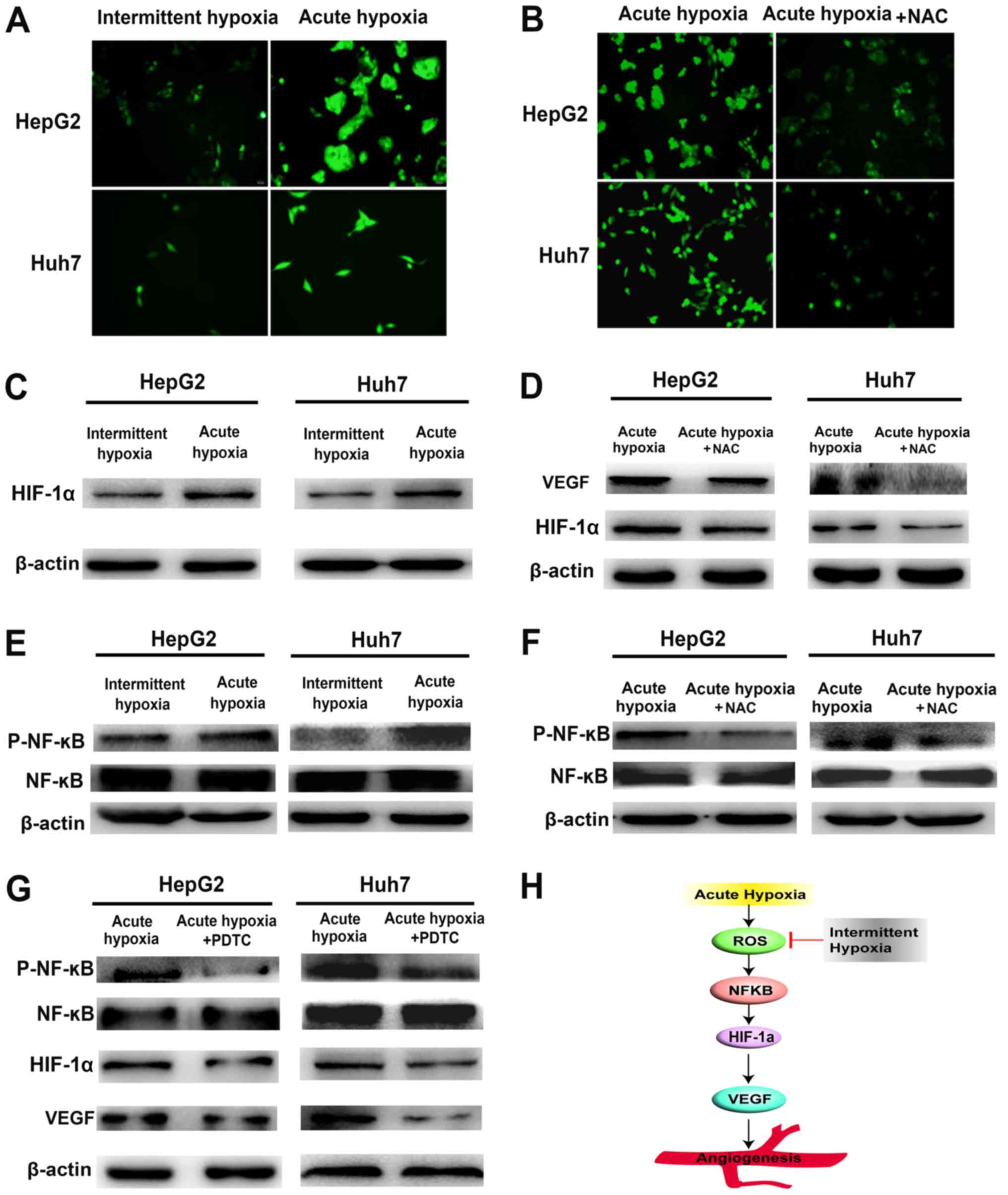
|
1
|
Chua CW and Choo SP: Targeted therapy in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Hepatol. 2011:1–11. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhang ZM, Guo JX, Zhang ZC, Jiang N, Zhang
ZY and Pan LJ: Therapeutic options for intermediate-advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 17:1685–1689.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang YH, Wu JC, Chen SC, Chen CH, Chiang
JH, Huo TI, Lee PC, Chang FY and Lee SD: Survival benefit of
transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 10 cm in diameter. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 23:129–135. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guan YS, He Q and Wang MQ: Transcatheter
arterial chemoembolization: History for more than 30 years. ISRN
Gastroenterol. 2012:4806502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pleguezuelo M, Marelli L, Misseri M,
Germani G, Calvaruso V, Xiruochakis E, Manousou P and Burroughs AK:
TACE versus TAE as therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 8:1623–1641. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y and Lai Y: A combination of
anti-angiogenesis with endostatin and transcatheter arterial
chemoembolization (TACE) enhances antitumour effects in a rabbit
VX2 liver tumor. Radiol Soc North Am 2010 Sci Assembly Meeting.
2010.
|
|
7
|
Hanks BA, Suhocki PV, DeLong DM, Doan PL,
Liu E, Tsai AL, Burke CT, Bernard SA, O'Neil BH and Morse MA: The
efficacy and tolerability of transarterial chemo-embolization
(TACE) compared with transarterial embolization (TAE) for patients
with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J Clin Oncol.
26:45952008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sergio A, Cristofori C, Cardin R, Pivetta
G, Ragazzi R, Baldan A, Girardi L, Cillo U, Burra P, Giacomin A and
Farinati F: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): The role of angiogenesis and
invasiveness. Am J Gastroenterol. 103:914–921. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chao Y, Wu CY, Kuo CY, Wang JP, Luo JC,
Kao CH, Lee RC, Lee WP and Li CP: Cytokines are associated with
postembolization fever and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma
patients receiving transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
Hepatol Int. 7:883–892. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jia ZZ, Jiang GM and Feng YL: Serum
HIF-1alpha and VEGF levels pre- and post-TACE in patients with
primary liver cancer. Chin Med Sci J. 26:158–162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu K, Min XL, Peng J, Yang K, Yang L and
Zhang XM: The changes of HIF-1α and VEGF expression after TACE in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Med Res. 8:297–302.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jia ZZ, Jiang GM and Feng YL: Serum
HIF-1alpha and VEGF levels pre- and post-TACE in patients with
primary liver cancer. Chin Med Sci J. 26:158–162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Britten CD, Gomes AS, Wainberg ZA,
Elashoff D, Amado R, Xin Y, Busuttil RW, Slamon DJ and Finn RS:
Transarterial chemoembolization plus or minus intravenous
bevacizumab in the treatment of hepatocellular cancer: A pilot
study. BMC Cancer. 12:162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pinter M, Ulbrich G, Sieghart W,
Kölblinger C, Reiberger T, Li S, Ferlitsch A, Müller C, Lammer J
and Peck-Radosavljevic M: Hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase II
randomized controlled double-blind trial of transarterial
chemoembolization in combination with biweekly intravenous
administration of bevacizumab or a placebo. Radiology. 277:903–912.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin B, Wang D, Lewandowski RJ, Riaz A, Ryu
RK, Sato KT, Larson AC, Salem R and Omary RA: Chemoembolization
endpoints: Effect on survival among patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 196:919–928. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu D, Liao Y, Zhu SH, Chen QC, Xie DM,
Liao JJ, Feng X, Jiang MH and He W: Bone-derived Nestin-positive
mesenchymal stem cells improve cardiac function via recruiting
cardiac endothelial cells after myocardial infarction. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 10:1272019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu M, Ning X, Li R, Yang Z, Yang X, Sun S
and Qian Q: Signalling pathways involved in hypoxia-induced renal
fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. 21:1248–1259. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rius J, Guma M, Schachtrup C, Akassoglou
K, Zinkernagel AS, Nizet V, Johnson RS, Haddad GG and Karin M:
NF-kappaB links innate immunity to the hypoxic response through
transcriptional regulation of HIF-1alpha. Nature. 453:807–811.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang Q, Zhan L, Cao H, Li J, Lyu Y, Guo
X, Zhang J, Ji L, Ren T, An J, et al: Increased mitochondrial
fission promotes autophagy and hepatocellular carcinoma cell
survival through the ROS-modulated coordinated regulation of the
NFKB and TP53 pathways. Autophagy. 12:999–1014. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bonello S, Zähringer C, BelAiba RS,
Djordjevic T, Hess J, Michiels C, Kietzmann T and Görlach A:
Reactive oxygen species activate the HIF-1alpha promoter via a
functional NFkappaB site. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
27:755–761. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Diebold I, Djordjevic T, Hess J and
Görlach A: Rac-1 promotes pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell
proliferation by upregulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1:
Role of NFkappaB-dependent hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
transcription. Thromb Haemost. 100:1021–1028. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
El-Halawany MS, Ismail HM, Zeeneldin AA,
Elfiky A, Tantawy M, Kobaisi MH, Hamed I and Abdel Wahab AH:
Investigating the pretreatment miRNA expression patterns of
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients in association with
response to TACE treatment. Biomed Res Int. 2015:6497502015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Petrillo M, Patella F, Pesapane F, Suter
MB, Ierardi AM, Angileri SA, Floridi C, de Filippo M and
Carrafiello G: Hypoxia and tumor angiogenesis in the era of
hepatocellular carcinoma transarterial loco-regional treatments.
Future Oncol. 14:2957–2967. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ahluwalia A, Jones MK, Matysiak-Budnik T
and Tarnawski AS: VEGF and colon cancer growth beyond angiogenesis:
Does VEGF directly mediate colon cancer growth via a non-angiogenic
mechanism? Curr Pharm Des. 20:1041–1044. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Petersen W, Pufe T, Stärke C, Fuchs T,
Kopf S, Neumann W, Zantop T, Paletta J, Raschke M and Becker R: The
effect of locally applied vascular endothelial growth factor on
meniscus healing: Gross and histological findings. Arch Orthop
Trauma Surg. 127:235–240. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Olszewska-Pazdrak B, Hein TW, Olszewska P
and Carney DH: Chronic hypoxia attenuates VEGF signaling and
angiogenic responses by downregulation of KDR in human endothelial
cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 296:C1162–C1170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee G, Won HS, Lee YM, Choi JW, Oh TI,
Jang JH, Choi DK, Lim BO, Kim YJ, Park JW, et al: Oxidative
dimerization of PHD2 is responsible for its inactivation and
contributes to metabolic reprogramming via HIF-1α activation. Sci
Rep. 6:189282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen A, Sceneay J, Gödde N, Kinwel T, Ham
S, Thompson EW, Humbert PO and Möller A: Intermittent hypoxia
induces a metastatic phenotype in breast cancer. Oncogene.
37:4214–4225. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Louie E, Nik S, Chen JS, Schmidt M, Song
B, Pacson C, Chen XF, Park S, Ju J and Chen EI: Identification of a
stem-like cell population by exposing metastatic breast cancer cell
lines to repetitive cycles of hypoxia and reoxygenation. Breast
Cancer Res. 12:R942010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|