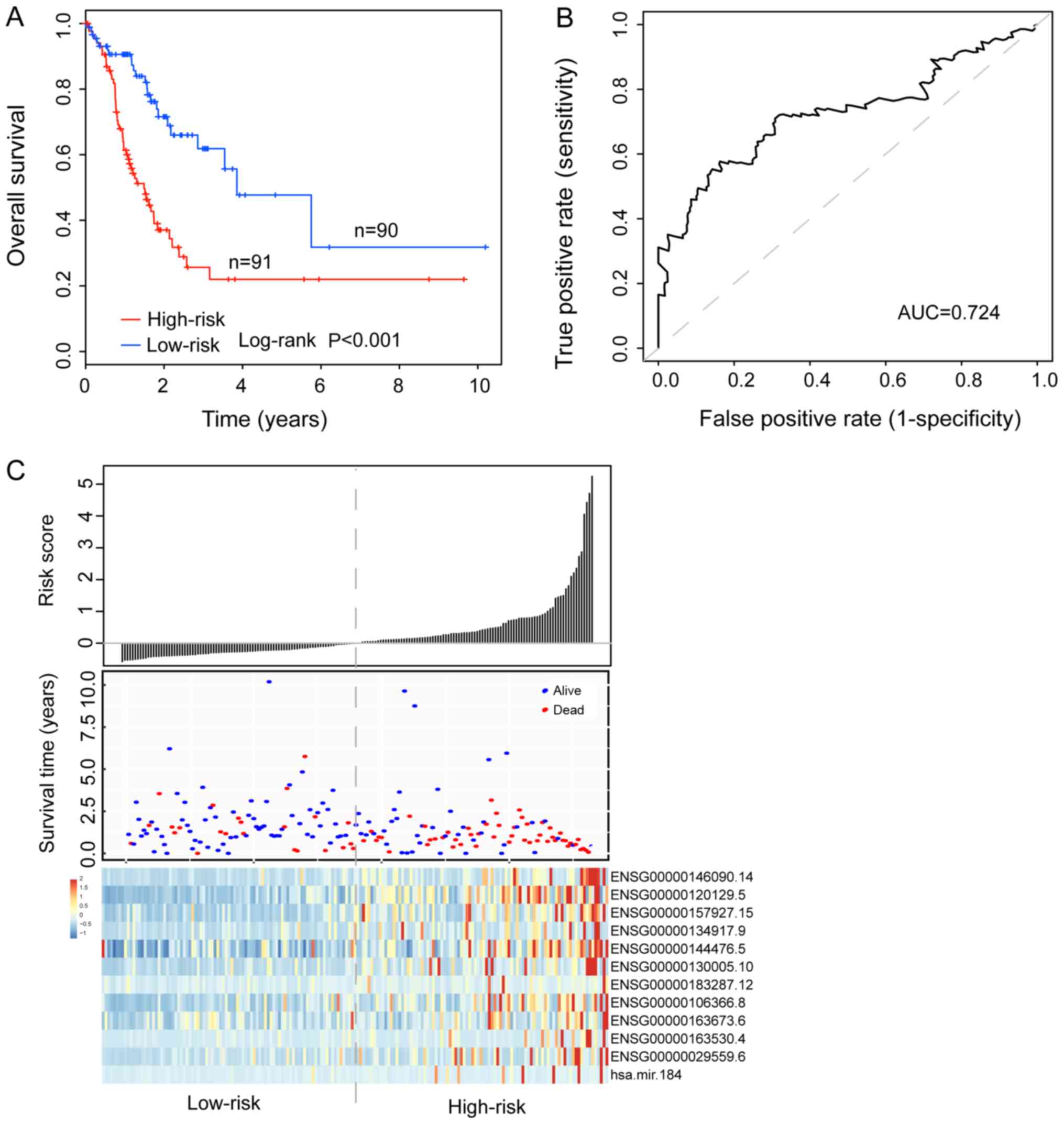
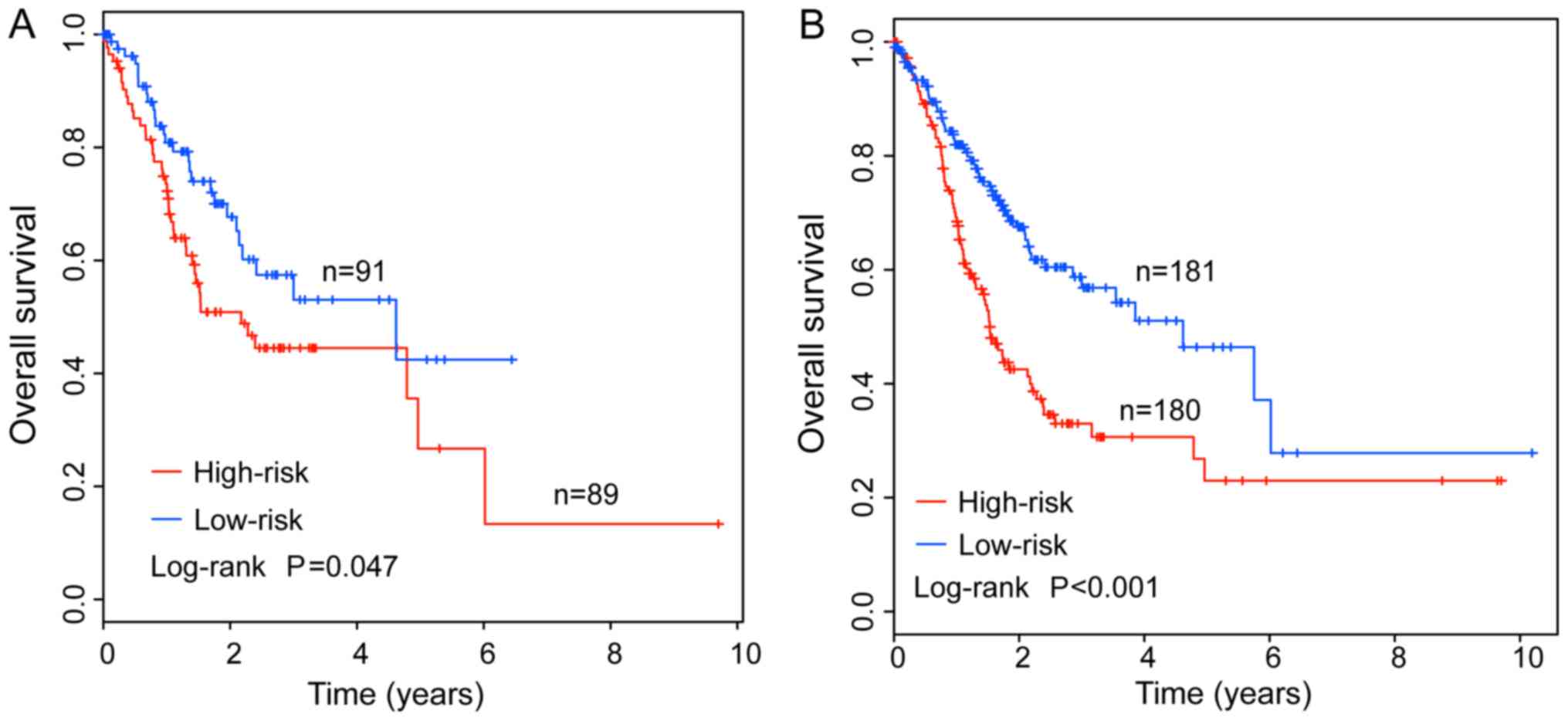
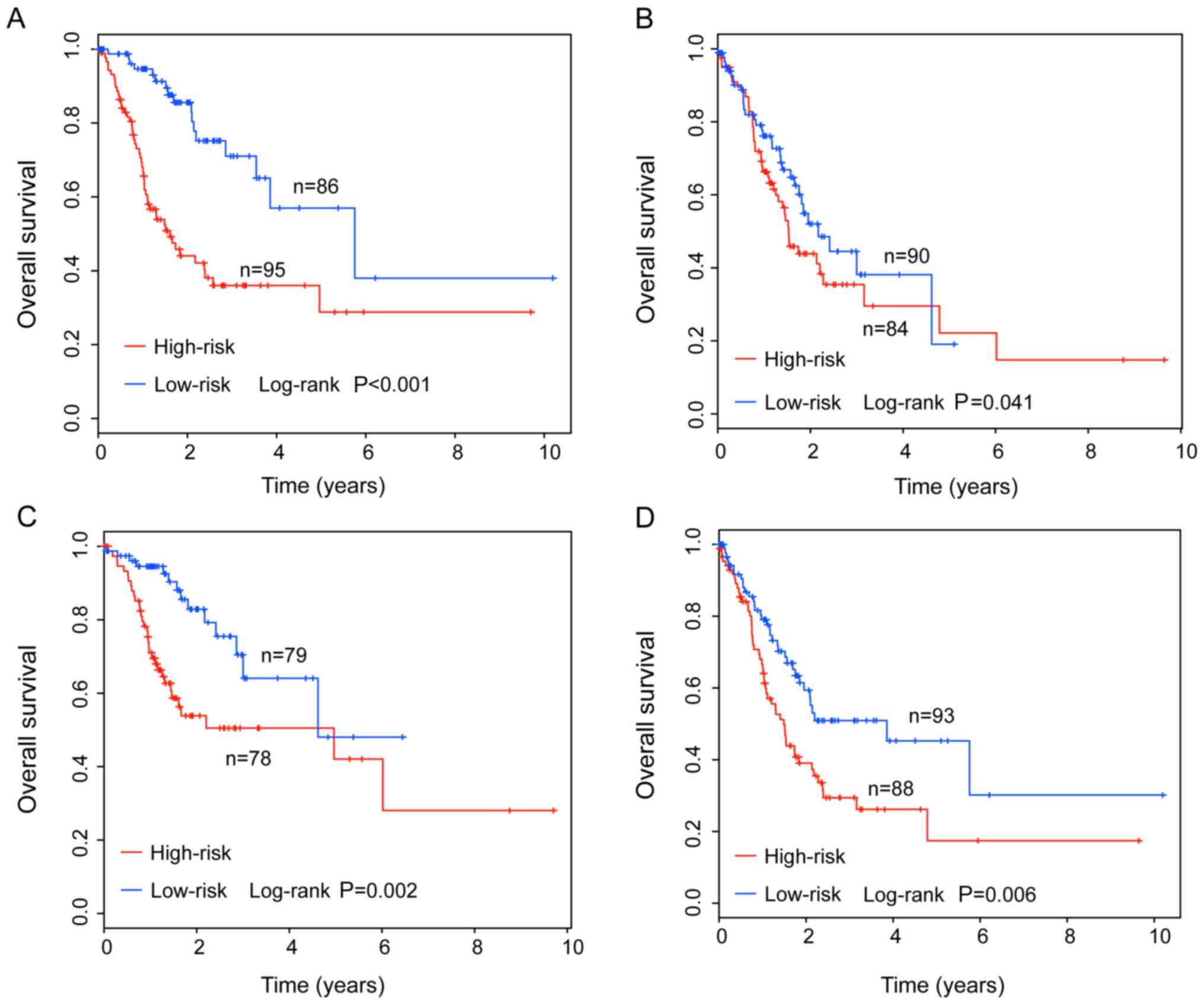
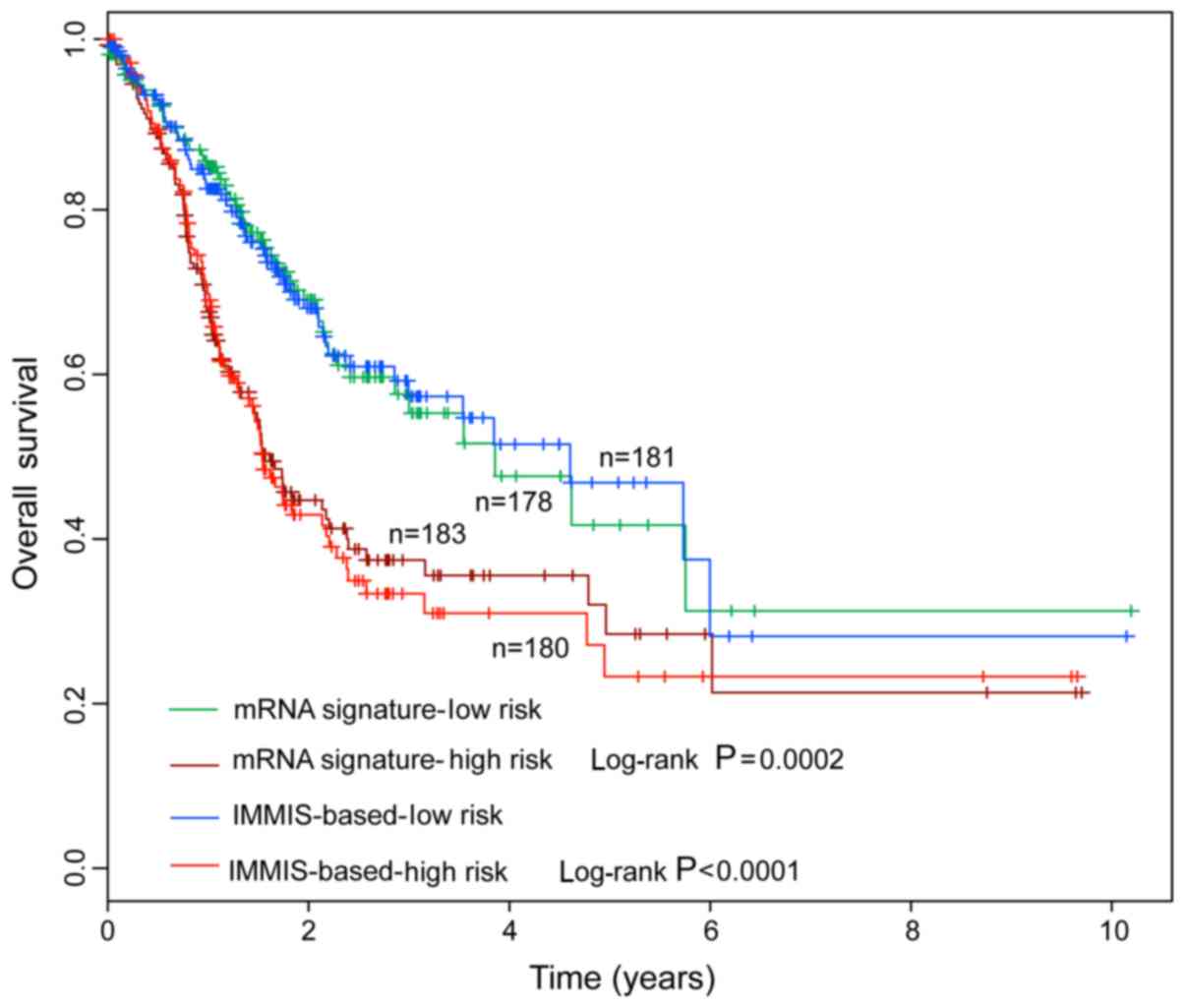
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hu B, El Hajj N, Sittler S, Lammert N,
Barnes R and Meloni-Ehrig A: Gastric cancer: Classification,
histology and application of molecular pathology. J Gastrointest
Oncol. 3:251–261. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Orditura M, Galizia G, Sforza V,
Gambardella V, Fabozzi A, Laterza MM, Andreozzi F, Ventriglia J,
Savastano B, Mabilia A, et al: Treatment of gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:1635–1649. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen CN, Lin JJ, Chen JJ, Lee PH, Yang CY,
Kuo ML, Chang KJ and Hsieh FJ: Gene expression profile predicts
patient survival of gastric cancer after surgical resection. J Clin
Oncol. 23:7286–7295. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cho JY, Lim JY, Cheong JH, Park YY, Yoon
SL, Kim SM, Kim SB, Kim H, Hong SW, Park YN, et al: Gene expression
signature-based prognostic risk score in gastric cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:1850–1857. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ding B, Gao X, Li H, Liu L and Hao X: A
novel microRNA signature predicts survival in stomach
adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:28144–28153. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiong Y, Wang R, Peng L, You W, Wei J,
Zhang S, Wu X, Guo J, Xu J, Lv Z and Fu Z: An integrated lncRNA,
microRNA and mRNA signature to improve prognosis prediction of
colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 8:85463–85478. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Volinia S and Croce CM: Prognostic
microRNA/mRNA signature from the integrated analysis of patients
with invasive breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:7413–7417.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bing Z, Tian J, Zhang J, Li X, Wang X and
Yang K: An integrative model of miRNA and mRNA expression signature
for patients of breast invasive carcinoma with radiotherapy
prognosis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 31:253–260. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun J, Chen X, Wang Z, Guo M, Shi H, Wang
X, Cheng L and Zhou M: A potential prognostic long non-coding RNA
signature to predict metastasis-free survival of breast cancer
patients. Sci Rep. 5:165532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun J, Cheng L, Shi H, Zhang Z, Zhao H,
Wang Z and Zhou M: A potential panel of six-long non-coding RNA
signature to improve survival prediction of diffuse large-B-cell
lymphoma. Sci Rep. 6:278422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou M, Guo M, He D, Wang X, Cui Y, Yang
H, Hao D and Sun J: A potential signature of eight long non-coding
RNAs predicts survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
J Transl Med. 13:2312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou M, Xu W, Yue X, Zhao H, Wang Z, Shi
H, Cheng L and Sun J: Relapse-related long non-coding RNA signature
to improve prognosis prediction of lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget.
7:29720–29738. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou M, Zhang Z, Zhao H, Bao S and Sun J:
A novel lncRNA-focus expression signature for survival prediction
in endometrial carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 18:392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou M, Zhang Z, Zhao H, Bao S, Cheng L
and Sun J: An immune-related six-lncRNA signature to improve
prognosis prediction of glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Neurobiol.
55:3684–3697. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou M, Zhong L, Xu W, Sun Y, Zhang Z,
Zhao H, Yang L and Sun J: Discovery of potential prognostic long
non-coding RNA biomarkers for predicting the risk of tumor
recurrence of breast cancer patients. Sci Rep. 6:310382016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
R Core Team. R, . A language and
environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical
Computing; Vienna: 2012, http://www.R-project.org/
|
|
20
|
Liu JY, Peng CW, Yang XJ, Huang CQ and Li
Y: The prognosis role of AJCC/UICC 8th edition staging system in
gastric cancer, a retrospective analysis. Am J Transl Res.
10:2922018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chia NY and Tan P: Molecular
classification of gastric cancer. Ann Oncol. 27:763–769. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang HB, Yang TJ, Lu P and Ma YJ: Gene
expression profiling of gastric cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
18:2109–2115. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marimuthu A, Jacob HK, Jakharia A,
Subbannayya Y, Keerthikumar S, Kashyap MK, Goel R, Balakrishnan L,
Dwivedi S, Pathare S, et al: Gene expression profiling of gastric
cancer. J Proteomics Bioinform. 4:74–82. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Takeno A, Takemasa I, Doki Y, Yamasaki M,
Miyata H, Takiguchi S, Fujiwara Y, Matsubara K and Monden M:
Integrative approach for differentially overexpressed genes in
gastric cancer by combining large-scale gene expression profiling
and network analysis. Br J Cancer. 99:1307–1315. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ishimoto T, Baba H, Izumi D, Sugihara H,
Kurashige J, Iwatsuki M and Tan P: Current perspectives toward the
identification of key players in gastric cancer microRNA
dysregulation. Int J Cancer. 138:1337–1349. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pan HW, Li SC and Tsai KW: MicroRNA
dysregulation in gastric cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 19:1273–1284.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu WK, Lee CW, Cho CH, Fan D, Wu K, Yu J
and Sung JJ: MicroRNA dysregulation in gastric cancer: A new player
enters the game. Oncogene. 29:5761–5771. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou M, Hu L, Zhang Z, Wu N, Sun J and Su
J: Recurrence-associated long non-coding RNA signature for
determining the risk of recurrence in patients with colon cancer.
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 12:518–529. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou M, Zhao H, Wang X, Sun J and Su J:
Analysis of long noncoding RNAs highlights region-specific altered
expression patterns and diagnostic roles in Alzheimer's disease.
Brief Bioinform:. 20:598–608. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo L, Peng Y, Meng Y, Liu Y, Yang S, Jin
H and Li Q: Expression profiles analysis reveals an integrated
miRNA-lncRNA signature to predict survival in ovarian cancer
patients with wild-type BRCA1/2. Oncotarget. 8:68483–68492.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shen J, Zhang Y, Yu H, Shen B, Liang Y,
Jin R, Liu X, Shi L and Cai X: Role of DUSP1/MKP1 in tumorigenesis,
tumor progression and therapy. Cancer Med. 5:2061–2068. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Teng F, Xu Z, Chen J, Zheng G, Zheng G, Lv
H, Wang Y, Wang L and Cheng X: DUSP1 induces apatinib resistance by
activating the MAPK pathway in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep.
40:1203–1222. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou M, Zhao H, Xu W, Bao S, Cheng L and
Sun J: Discovery and validation of immune-associated long
non-coding RNA biomarkers associated with clinically molecular
subtype and prognosis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Mol Cancer.
16:162017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kilic MO, Aynekin B, Kara A, Icen D and
Demircan K: Differentially regulated ADAMTS1, 8, and 18 in gastric
adenocarcinoma. Bratisl Lek Listy. 118:71–76. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim N, Baek SW, Ryu H, Choi YS, Song IC,
Yun HJ, Jo DY, Kim SY and Lee HJ: Atypical chemokine receptor ACKR3
expression is associated with aggressive behavior and poor
prognosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 76 (Suppl
14):39472016.
|
|
36
|
Tian GA, Zhu CC, Zhang XX, Zhu L, Yang XM,
Jiang SH, Li RK, Tu L, Wang Y, Zhuang C, et al: CCBE1 promotes GIST
development through enhancing angiogenesis and mediating resistance
to imatinib. Sci Rep. 6:310712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cheng Z, Wang HZ, Li X, Wu Z, Han Y, Li Y,
Chen G, Xie X, Huang Y, Du Z and Zhou Y: MicroRNA-184 inhibits cell
proliferation and invasion, and specifically targets TNFAIP2 in
Glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu G, Liu J, Wu Z, Wu X and Yao X:
MicroRNA-184 inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis in human
colorectal cancer by directly targeting IGF-1R. Oncol Lett.
14:3215–3222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|