|
1
|
Lam KO, Lee AW, Choi CW, Sze HC, Zietman
AL, Hopkins KI and Rosenblatt E: Global pattern of nasopharyngeal
cancer: Correlation of outcome with access to radiation therapy.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 94:1106–1112. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Peng H, Chen L, Zhang J, Li WF, Mao YP,
Zhang Y, Liu LZ, Tian L, Lin AH, Sun Y and Ma J: Induction
chemotherapy improved Long-term outcomes of patients with
locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A propensity
matched analysis of 5-year survival outcomes in the Era of
intensity-modulated radiotherapy. J Cancer. 8:371–377. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tan WL, Tan EH, Lim DW, Ng QS, Tan DS,
Jain A and Ang MK: Advances in systemic treatment for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin Clin Oncol. 5:212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kang M, Zhou P, Liao X, Xu M and Wang R:
Prognostic value of masticatory muscle involvement in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity-modulated
radiation therapy. Oral Oncol. 75:100–105. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ren XY, Zhou GQ, Jiang W, Sun Y, Xu YF, Li
YQ, Tang XR, Wen X, He QM, Yang XJ, et al: Low SFRP1 expression
correlates with poor prognosis and promotes cell invasion by
activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in NPC. Cancer Prev
Res (Phila). 8:968–977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tao Q and Chan AT: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: Molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic developments.
Expert Rev Mol Med. 9:1–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun R, Zhang Q, Guo L, Chen MY, Sun Y, Cao
B and Sun J: HGF stimulates proliferation through the HGF/c-Met
pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 3:1124–1128.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Low SY, Tan BS, Choo HL, Tiong KH, Khoo AS
and Leong CO: Suppression of BCL-2 synergizes cisplatin sensitivity
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 314:166–175. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lakhanpal M, Singh LC, Rahman T, Sharma J,
Singh MM, Kataki AC, Verma S, Chauhan PS, Singh YM, Wajid S, et al:
Contribution of susceptibility locus at HLA class I region and
environmental factors to occurrence of nasopharyngeal cancer in
Northeast India. Tumour Biol. 36:3061–3073. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cao Y, Miao XP, Huang MY, Deng L, Hu LF,
Ernberg I, Zeng YX, Lin DX and Shao JY: Polymorphisms of XRCC1
genes and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the Cantonese
population. BMC Cancer. 6:1672006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vercauteren SM, Sung S, Starczynowski DT,
Lam WL, Bruyere H, Horsman DE, Tsang P, Leitch H and Karsan A:
Array comparative genomic hybridization of peripheral blood
granulocytes of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome detects
karyotypic abnormalities. Am J Clin Pathol. 134:119–126. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang W, Guo Z, Wang W, Sun Y, Zhang C,
Wang X, Zhang L and Wang C: Application of single nucleotide
polymorphism microarray and fluorescence in situ hybridization
analysis for the prenatal diagnosis of a case with
Pallister-Killian syndrome. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi.
35:232–235. 2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu K, Kang M, Li J, Qin W and Wang R:
Prognostic value of the mRNA expression of members of the HSP90
family in non-small cell lung cancer. Exp Ther Med. 17:2657–2665.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen F, Shen C, Wang X, Wang H, Liu Y, Yu
C, Lv J, He J and Wen Z: Identification of genes and pathways in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma by bioinformatics analysis. Oncotarget.
8:63738–63749. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meng C, Shen X and Jiang W: Potential
biomarkers of HCC based on gene expression and DNA methylation
profiles. Oncol Lett. 16:3183–3192. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dodd LE, Sengupta S, Chen IH, den Boon JA,
Cheng YJ, Westra W, Newton MA, Mittl BF, McShane L, Chen CJ, et al:
Genes involved in DNA repair and nitrosamine metabolism and those
located on chromosome 14q32 are dysregulated in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 15:2216–2225. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu C, Wei W, Chen X, Woodman CB, Yao Y,
Nicholls JM, Joab I, Sihota SK, Shao JY, Derkaoui KD, et al: A
global view of the oncogenic landscape in nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
An integrated analysis at the genetic and expression levels. PLoS
One. 7:e410552012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(Database Issue):
D991–D995. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gene Ontology Consortium: The gene
ontology (GO) project in 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 34(Database
Issue): D322–D326. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi
M and Tanabe M: KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein
annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D457–D462. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic acids Res.
43(Database Issue): D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Su G, Morris JH, Demchak B and Bader GD:
Biological network exploration with Cytoscape 3. Curr Protoc
Bioinformatics. 47:8.13.11–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhai X, Yang Y, Wan J, Zhu R and Wu Y:
Inhibition of LDH-A by oxamate induces G2/M arrest, apoptosis and
increases radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Oncol
Rep. 30:2983–2991. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cao SM, Simons MJ and Qian CN: The
prevalence and prevention of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in China.
Chin J Cancer. 30:114–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wei KR, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Liang ZH, Li
ZM and Chen WQ: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in
China, 2013. Chin J Cancer. 36:902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brown NR, Korolchuk S, Martin MP, Stanley
WA, Moukhametzianov R, Noble MEM and Endicott JA: CDK1 structures
reveal conserved and unique features of the essential cell cycle
CDK. Nat Commun. 6:67692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chua MLK, Wee JTS, Hui EP and Chan ATC:
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 387:1012–1024. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Johnson N, Li YC, Walton ZE, Cheng KA, Li
D, Rodig SJ, Moreau LA, Unitt C, Bronson RT, Thomas HD, et al:
Compromised CDK1 activity sensitizes BRCA-proficient cancers to
PARP inhibition. Nat Med. 17:875–882. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kang J, Sergio CM, Sutherland RL and
Musgrove EA: Targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) but not
CDK4/6 or CDK2 is selectively lethal to MYC-dependent human breast
cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 14:322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wei-Shan H, Amit VC and Clarke DJ: Cell
cycle regulation of condensin Smc4. Oncotarget. 10:263–276. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou B, Yuan T, Liu M, Liu H, Xie J, Shen
Y and Chen P: Overexpression of the structural maintenance of
chromosome 4 protein is associated with tumor de-differentiation,
advanced stage and vascular invasion of primary liver cancer. Oncol
Rep. 28:1263–1268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Feng XD, Song Q, Li CW, Chen J, Tang HM,
Peng ZH and Wang XC: Structural maintenance of chromosomes 4 is a
predictor of survival and a novel therapeutic target in colorectal
cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:9459–9465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Morozumi Y, Boussouar F, Tan M, Chaikuad
A, Jamshidikia M, Colak G, He H, Nie L, Petosa C, de Dieuleveult M,
et al: Atad2 is a generalist facilitator of chromatin dynamics in
embryonic stem cells. J Mol Cell Biol. 8:349–362. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Caron C, Lestrat C, Marsal S, Escoffier E,
Curtet S, Virolle V, Barbry P, Debernardi A, Brambilla C, Brambilla
E, et al: Functional characterization of ATAD2 as a new
cancer/testis factor and a predictor of poor prognosis in breast
and lung cancers. Oncogene. 29:5171–5181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu G, Liu H, He H, Wang Y, Lu X, Yu Y, Xia
S, Meng X and Liu Y: miR-372 down-regulates the oncogene ATAD2 to
influence hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis.
BMC Cancer. 14:1072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wan WN, Zhang YX, Wang XM, Liu YJ, Zhang
YQ, Que YH and Zhao WJ: ATAD2 is highly expressed in ovarian
carcinomas and indicates poor prognosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:2777–2783. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Takahashi S, Fusaki N, Ohta S, Iwahori Y,
Iizuka Y, Inagawa K, Kawakami Y, Yoshida K and Toda M:
Downregulation of KIF23 suppresses glioma proliferation. J
Neurooncol. 106:519–529. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fischer M, Grundke I, Sohr S, Quaas M,
Hoffmann S, Knörck A, Gumhold C and Rother K: p53 and cell cycle
dependent transcription of kinesin family member 23 (KIF23) is
controlled via a CHR promoter element bound by DREAM and MMB
complexes. PLoS One. 8:e631872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou H, Kuang J, Zhong L, Kuo WL, Gray JW,
Sahin A, Brinkley BR and Sen S: Tumour amplified kinase STK15/BTAK
induces centrosome amplification, aneuploidy and transformation.
Nat Genet. 20:189–193. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Katayama H, Sasai K, Kawai H, Yuan ZM,
Bondaruk J, Suzuki F, Fujii S, Arlinghaus RB, Czerniak BA and Sen
S: Phosphorylation by aurora kinase A induces Mdm2-mediated
destabilization and inhibition of p53. Nat Genet. 36:55–62. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li J, Hong MJ, Chow JP, Man WY, Mak JP, Ma
HT and Poon RY: Co-inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 and Aurora
kinases promotes mitotic catastrophe. Oncotarget. 6:9327–9340.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ertych N, Stolz A, Stenzinger A, Weichert
W, Kaulfuß S, Burfeind P, Aigner A, Wordeman L and Bastians H:
Increased microtubule assembly rates influence chromosomal
instability in colorectal cancer cells. Nat Cell Biol. 16:779–791.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Katsha A, Soutto M, Sehdev V, Peng D,
Washington MK, Piazuelo MB, Tantawy MN, Manning HC, Lu P, Shyr Y,
et al: Aurora kinase A promotes inflammation and tumorigenesis in
mice and human gastric neoplasia. Gastroenterology.
145:1312–1322.e1-e8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang XX, Liu R, Jin SQ, Fan FY and Zhan
QM: Overexpression of Aurora-A kinase promotes tumor cell
proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma cell line. Cell Res. 16:356–366. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dutta-Simmons J, Zhang Y, Gorgun G, Gatt
M, Mani M, Hideshima T, Takada K, Carlson NE, Carrasco DE, Tai YT,
et al: Aurora kinase A is a target of Wnt/beta-catenin involved in
multiple myeloma disease progression. Blood. 114:2699–2708. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li JJ, Weroha SJ, Lingle WL, Papa D,
Salisbury JL and Li SA: Estrogen mediates Aurora-A overexpression,
centrosome amplification, chromosomal instability, and breast
cancer in female ACI rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:18123–18128.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zou Z, Yuan Z, Zhang Q, Long Z, Chen J,
Tang Z, Zhu Y, Chen S, Xu J, Yan M, et al: Aurora kinase A
inhibition-induced autophagy triggers drug resistance in breast
cancer cells. Autophagy. 8:1798–1810. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Park HS, Park WS, Bondaruk J, Tanaka N,
Katayama H, Lee S, Spiess PE, Steinberg JR, Wang Z, Katz RL, et al:
Quantitation of Aurora kinase A gene copy number in urine sediments
and bladder cancer detection. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:1401–1411.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sarfraz S, Hamid S, Ali S, Jafri W and
Siddiqui AA: Modulations of cell cycle checkpoints during HCV
associated disease. BMC Infect Dis. 9:1252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kops GJ, Kim Y, Weaver BA, Mao Y, McLeod
I, Yates JR III, Tagaya M and Cleveland DW: ZW10 links mitotic
checkpoint signaling to the structural kinetochore. J Cell Biol.
169:49–60. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang X, Xiao D, Wang Z, Zou Y, Huang L,
Lin W, Deng Q, Pan H, Zhou J, Liang C and He J: MicroRNA-26a/b
regulate DNA replication licensing, tumorigenesis, and prognosis by
targeting CDC6 in lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 12:1535–1546. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang H, Bierie B, Li AG, Pathania S,
Toomire K, Dimitrov SD, Liu B, Gelman R, Giobbie-Hurder A, Feunteun
J, et al: BRCA1/FANCD2/BRG1-Driven DNA repair stabilizes the
differentiation state of human mammary epithelial cells. Mol Cell.
63:277–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lu JH, Liao WT, Lee CH, Chang KL, Ke HL
and Yu HS: ΔNp63 promotes abnormal epidermal proliferation in
arsenical skin cancers. Toxicol In Vitro. 53:57–66. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wu Z, Wang S, Jiang F, Li Q, Wang C, Wang
H, Zhang W, Xue P and Wang SL: Mass spectrometric detection
combined with bioinformatic analysis identified possible protein
markers and key pathways associated with bladder cancer. Gene.
626:407–413. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang HJ, Tao J, Sheng L, Hu X, Rong RM,
Xu M and Zhu TY: Twist2 promotes kidney cancer cell proliferation
and invasion by regulating ITGA6 and CD44 expression in the
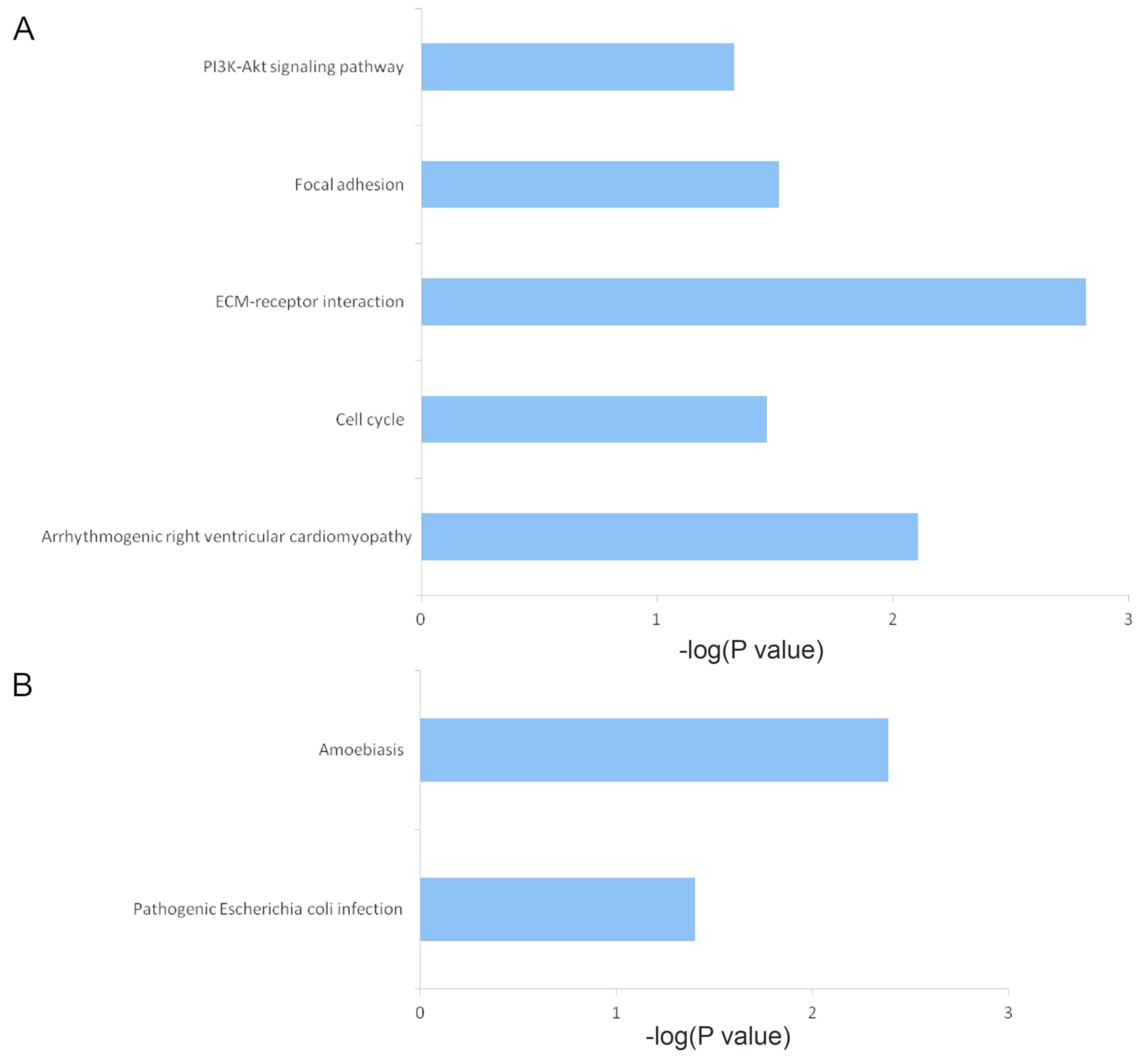
ECM-receptor interaction pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 9:1801–1812.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xu M, Bower KA, Chen G, Shi X, Dong Z, Ke
Z and Luo J: Ethanol enhances the interaction of breast cancer
cells over-expressing ErbB2 with fibronectin. Alcohol Clin Exp Res.
34:751–760. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ni Z and Yi J: Oxymatrine induces
nasopharyngeal cancer cell death through inhibition of PI3K/AKT and
NF-κB pathways. Mol Med Rep. 16:9701–9706. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu X, Takano C, Shimizu T, Yokobe S,
Abe-Kanoh N, Zhu B, Nakamura T, Munemasa S, Murata Y and Nakamura
Y: Inhibition of phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase ameliorates
antiproliferation by benzyl isothiocyanate in human colon cancer
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 491:209–216. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kaushik S, Shyam H, Sharma R and Balapure
AK: Dietary isoflavone daidzein synergizes centchroman action via
induction of apoptosis and inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway in
MCF-7/MDA MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine.
40:116–124. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Huang Y, Hua K, Zhou X, Jin H, Chen X, Lu
X, Yu Y, Zha X and Feng Y: Activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway
mediates FSH-stimulated VEGF expression in ovarian serous
cystadenocarcinoma. Cell Res. 18:780–791. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chen X, Yan CC, Zhang X and You ZH: Long
non-coding RNAs and complex diseases: From experimental results to
computational models. Brief Bioinform. 18:558–576. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen X and Yan GY: Novel human
lncRNA-disease association inference based on lncRNA expression
profiles. Bioinformatics. 29:2617–2624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chen X and Huang L: LRSSLMDA: Laplacian
regularized sparse subspace learning for MiRNA-disease association
prediction. PLoS Comput Biol. 13:e10059122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chen X, Xie D, Wang L, Zhao Q, You ZH and
Liu H: BNPMDA: Bipartite Network projection for MiRNA-disease
association prediction. Bioinformatics. 34:3178–3186. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen X, Wang L, Qu J, Guan NN and Li JQ:
Predicting miRNA-disease association based on inductive matrix
completion. Bioinformatics. 34:4256–4265. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|