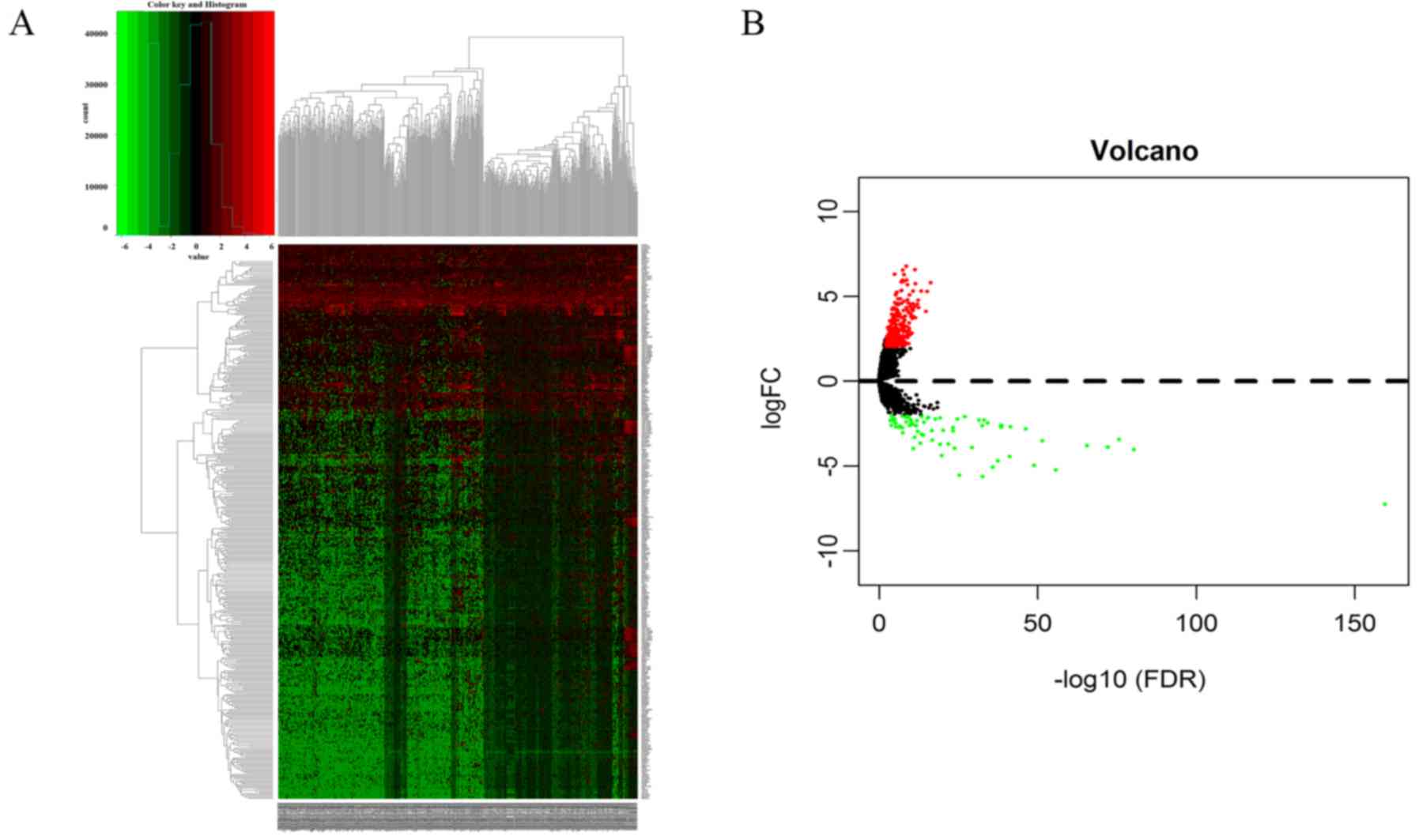
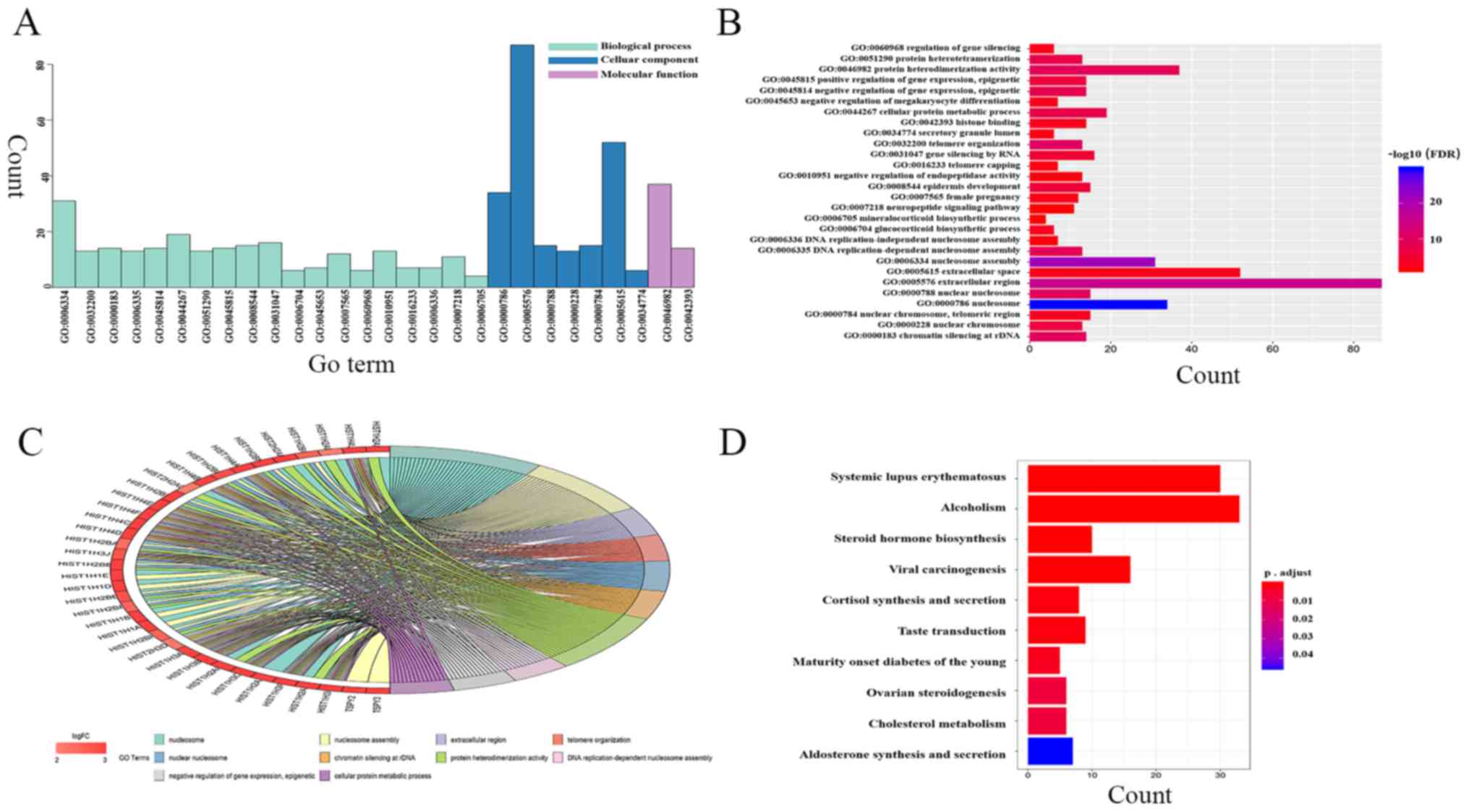
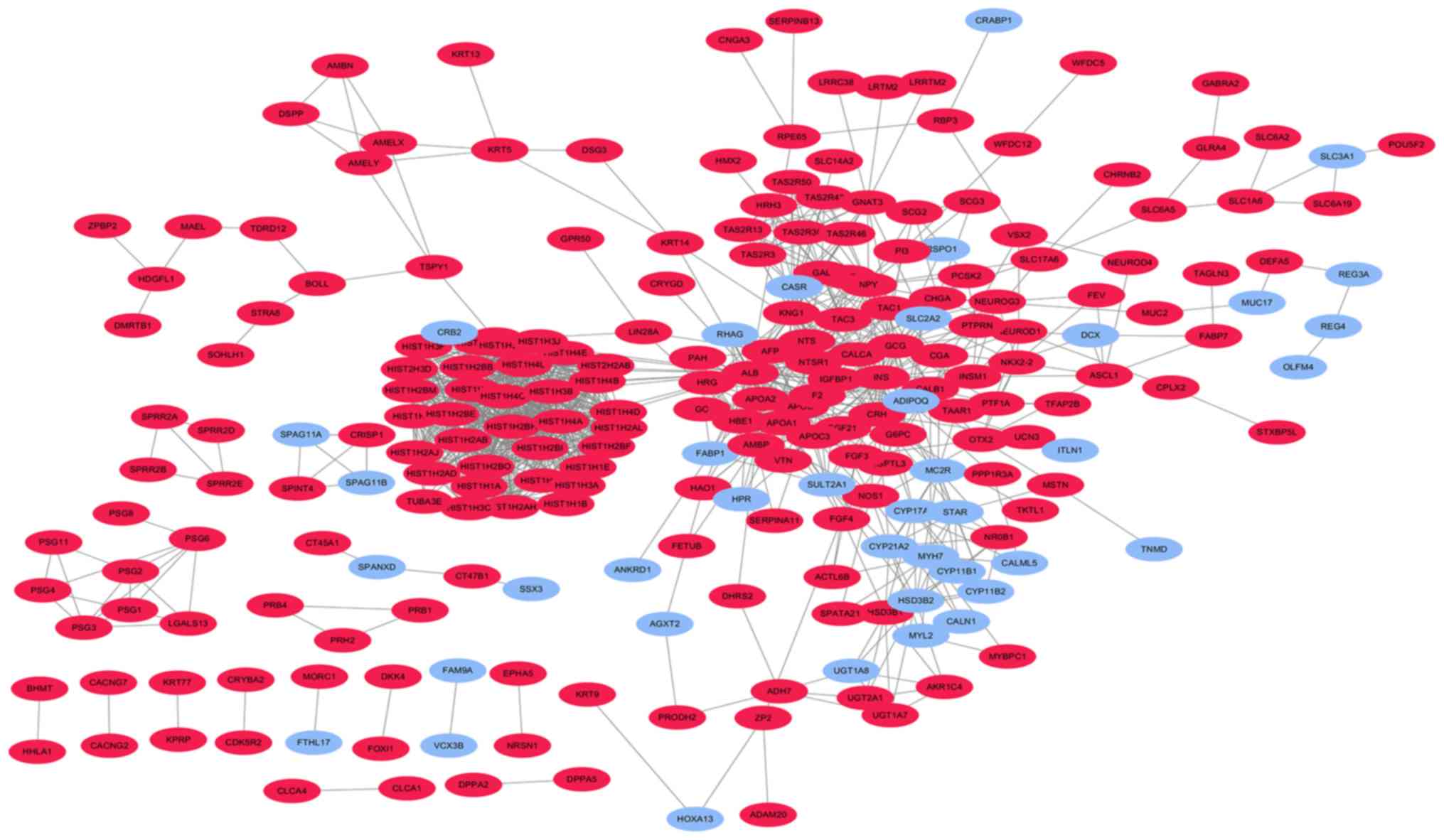
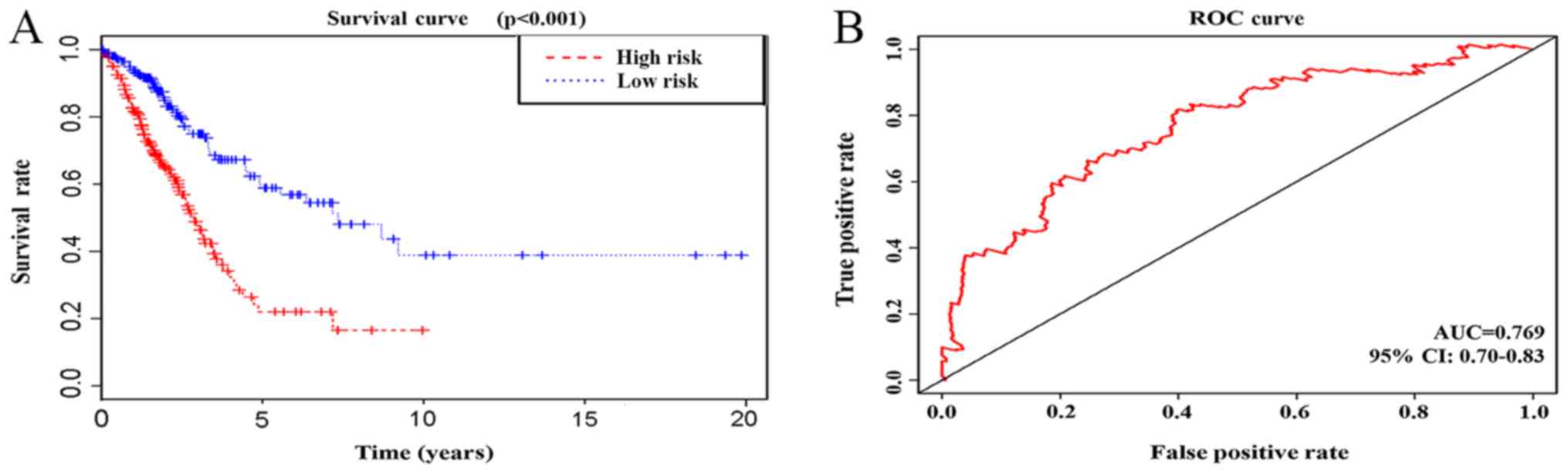
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V,
Harewood R, Matz M, Nikšić M, Bonaventure A, Valkov M, Johnson CJ,
Estève J, et al: Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival
2000–14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of individual records for 37 513 025
patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based
registries in 71 countries. Lancet. 391:1023–1075. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wei S, Zhang ZY, Fu SL, Xie JG, Liu XS, Xu
YJ, Zhao JP and Xiong WN: Hsa-miR-623 suppresses tumor progression
in human lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 7:e23882016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Promotion H: Let's make the next
generation tobacco-free: Your guide to the 50th anniversary Surgeon
General's Report on Smoking and Health. Health Promotion. 1964.
|
|
5
|
Prevention NCfCD, Smoking HPOo, Health, .
The Health Consequences of Smoking-50 Years of Progress: A report
of the surgeon general. Usnational Library of Medicine. 2014.
|
|
6
|
USA USDoH, Services H. How tobacco smoke
causes disease, . The biology and behavioral basis for
smoking-attributable disease. A report of the Surgeon General.
2010.
|
|
7
|
Homa DM, Neff LJ, King BA, Caraballo RS,
Bunnell RE, Babb SD, Garrett BE, Sosnoff CS and Wang L; Centers for
Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), : Vital signs: Disparities in
nonsmokers' exposure to secondhand smoke-United States, 1999–2012.
MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 64:103–108. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Subramanian J and Govindan R: Lung cancer
in never smokers: A review. J Clin Oncol. 25:561–570. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Casal-Mouriño A, Valdés L, Barros-Dios JM
and Ruano- Ravina A: Lung cancer survival among never smokers.
Cancer Lett. 451:142–149. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun S, Schiller JH and Gazdar AF: Lung
cancer in never smokers-a different disease. Nat Rev Cancer.
7:778–790. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Patel MI, Cheng I and Gomez SL: US lung
cancer trends by histologic type. Cancer. 121:1150–1152. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ryan BM: Lung cancer health disparities.
Carcinogenesis. 39:741–751. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu J, Wang Y, Liu X, Yuan Q, Zhang Y and
Li Y: Novel molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) multiple sensors
for endogenous redox couples determination and their applications
in lung cancer diagnosis. Talanta. 199:573–580. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiao ZY, Tian Q, Li N, Wang HB and Li KZ:
Plasma long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) serve as potential biomarkers
for predicting breast cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:1994–1999. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang Y, Wu L, Shu X, Lu Y, Shu XO, Cai Q,
Beeghly-Fadiel A, Li B, Ye F, Berchuck A, et al: Genetic data from
nearly 63,000 women of European descent predicts DNA methylation
biomarkers and epithelial ovarian cancer risk. Cancer Res.
79:505–517. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Carleton NM, Zhu G, Gorbounov M, Miller
MC, Pienta KJ, Resar LMS and Veltri RW: PBOV1 as a potential
biomarker for more advanced prostate cancer based on protein and
digital histomorphometric analysis. Prostate. 78:547–559. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou Q, Eldakhakhny S, Conforti F, Crosbie
EJ, Melino G and Sayan BS: Pir2/Rnf144b is a potential endometrial
cancer biomarker that promotes cell proliferation. Cell death Dis.
9:5042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Irimie AI, Braicu C, Cojocneanu R, Magdo
L, Onaciu A, Ciocan C, Mehterov N, Dudea D, Buduru S and
Berindan-Neagoe I: Differential effect of smoking on gene
expression in head and neck cancer patients. Int J Environ Res
Public Health. 15(pii): E15582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li X, Li J, Wu P, Zhou L, Lu B, Ying K,
Chen E, Lu Y and Liu P: Smoker and non-smoker lung adenocarcinoma
is characterized by distinct tumor immune microenvironments.
Oncoimmunology. 7:e14946772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mathewos T, Yingling CM, Yushi L, Tellez
CS, Leander VN, Baylin SS and Belinsky SA: Genome-wide unmasking of
epigenetically silenced genes in lung adenocarcinoma from smokers
and never smokers. Carcinogenesis. 35:1248–1257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41(Database Issue): D808–D815. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D607–D613. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rajput A, Thakur A, Sharma S and Kumar M:
aBiofilm: A resource of anti-biofilm agents and their potential
implications in targeting antibiotic drug resistance. Nucleic Acids
Res. 46:D894–D900. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hillis SL: Equivalence of binormal
likelihood-ratio and bi-chi-squared ROC curve models. Stat Med.
35:2031–2057. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xiao F, Yang M, Xu Y and Vongsangnak W:
Comparisons of prostate cancer inhibitors abiraterone and TOK-001
binding with CYP17A1 through molecular dynamics. Comput Struct
Biotec. 13:520–527. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gomez L, Kovac JR and Lamb DJ: CYP17A1
inhibitors in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Steroids.
95:80–87. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Olivo-Marston SE, Mechanic LE, Mollerup S,
Bowman ED, Remaley AT, Forman MR, Skaug V, Zheng YL, Haugen A and
Harris CC: Serum estrogen and tumor-positive estrogen
receptor-alpha are strong prognostic classifiers of non-small-cell
lung cancer survival in both men and women. Carcinogenesis.
31:1778–1786. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Y, Hua S, Zhang A, Kong X, Jiang C,
Deng D and Wenlong B: Association between polymorphisms in COMT,
PLCH1, and CYP17A1, and Non-small-cell lung cancer risk in Chinese
nonsmokers. Clin Lung Cancer. 14:45–49. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kang S, Thompson Z, McClung EC, Abdallah
R, Lee JK, Gonzalez-Bosquet J, Wenham RM and Chon HS: Gene
expression signature-based prediction of lymph node metastasis in
patients with endometrioid endometrial cancer. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 28:260–266. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chien J, Sicotte H, Fan JB, Humphray S,
Cunningham JM, Kalli KR, Oberg AL, Hart SN, Li Y, Davila JI, et al:
TP53 mutations, tetraploidy and homologous recombination repair
defects in early stage high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Nucleic
Acids Res. 43:6945–6958. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Harrison EH: Mechanisms of transport and
delivery of vitamin A and carotenoids to the retinal pigment
epithelium. Mol Nutr Food Res. e18010462019.doi:
10.1002/mnfr.201801046 (Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu Z, Galmiche A, Liu J, Stadler N, Wendum
D, Segal-Bendirdjian E, Paradis V and Forgez P: Neurotensin
regulation induces overexpression and activation of EGFR in HCC and
restores response to erlotinib and sorafenib. Cancer Lett.
388:73–84. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu S, Tian H, Niu X, Wang J, Li X, Jiang
N, Wen S, Chen X, Ren S, Xu C, et al: Neurotensin and its receptors
mediate neuroendocrine transdifferentiation in prostate cancer.
Oncogene. 38:4875–4884. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu Z, Fournel L, Stadler N, Liu J,
Boullier A, Hoyeau N, Fléjou JF, Duchatelle V, Djebrani-Oussedik N,
Agopiantz M, et al: Modulation of lung cancer cell plasticity and
heterogeneity with the restoration of cisplatin sensitivity by
neurotensin antibody. Cancer Lett. 444:147–161. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kralisch S, Hoffmann A, Lössner U,
Kratzsch J, Blüher M, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M and Ebert T:
Regulation of the novel adipokines/hepatokines fetuin A and fetuin
B in gestational diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 68:88–94. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Khammanivong A, Anandharaj A, Qian X, Song
JM, Upadhyaya P, Balbo S, Bandyopadhyay D, Dickerson EB, Hecht SS
and Kassie F: Transcriptome profiling in oral cavity and esophagus
tissues from (S)-N′-nitrosonornicotine-treated rats reveals
candidate genes involved in human oral cavity and esophageal
carcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog. 55:2168–2182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Diao WQ, Shen N, Du YP, Liu BB, Sun XY, Xu
M and He B: Fetuin-B (FETUB): A plasma biomarker candidate related
to the severity of lung function in COPD. Sci Rep. 6:300452016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zheng F, Tang Q, Zheng XH, Wu J, Huang H,
Zhang H and Hann SS: Inactivation of Stat3 and crosstalk of
miRNA155-5p and FOXO3a contribute to the induction of IGFBP1
expression by beta-elemene in human lung cancer. Exp Mol Med.
50:1212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Major JM, Laughlin GA, Kritz-Silverstein
D, Wingard DL and Barrett-Connor E: Insulin-like growth factor-I
and cancer mortality in older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
95:1054–1059. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tang Q, Wu J, Zheng F, Hann SS and Chen Y:
Emodin increases expression of insulin-like growth factor binding
protein 1 through activation of MEK/ERK/AMPKα and interaction of
PPARγ and Sp1 in lung cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:339–357.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nyce JW: Detection of a novel,
primate-specific ‘kill switch’ tumor suppression mechanism that may
fundamentally control cancer risk in humans: An unexpected twist in
the basic biology of TP53. Endocr Relat Cancer. 25:R497–R517. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Guo T, Chen T, Gu C, Li B and Xu C:
Genetic and molecular analyses reveal G6PC as a key element
connecting glucose metabolism and cell cycle control in ovarian
cancer. Tumor Biol. 36:7649–7658. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Gjorgjieva M, Calderaro J, Monteillet L,
Silva M, Raffin M, Brevet M, Romestaing C, Roussel D, Zucman-Rossi
J, Mithieux G, et al: Dietary exacerbation of metabolic stress
leads to accelerated hepatic carcinogenesis in glycogen storage
disease type Ia. J Hepatol. 69:1074–1087. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim GY, Kwon JH, Cho J-H, Zhang L,
Mansfield BC and Chou JY: Downregulation of pathways implicated in
liver inflammation and tumorigenesis of glycogen storage disease
type Ia mice receiving gene therapy. Hum Mol Genet. 26:1890–1899.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|