|
1
|
Adès L, Itzykson R and Fenaux P:
Myelodysplastic syndromes. Lancet. 383:2239–2252. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shastri A, Will B, Steidl U and Verma A:
Stem and progenitor cell alterations in myelodysplastic syndromes.
Blood. 129:1586–1594. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferrer RA, Wobus M, List C, Wehner R,
Schönefeldt C, Brocard B, Mohr B, Rauner M, Schmitz M, Stiehler M,
et al: Mesenchymal stromal cells from patients with myelodyplastic
syndrome display distinct functional alterations that are
modulatedbylenalidomide. Haematologica. 98:1677–1685. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Medyouf H, Mossner M, Jann JC, Nolte F,
Raffel S, Herrmann C, Lier A, Eisen C, Nowak V, Zens B, et al:
Myelodysplastic cells in patients reprogram mesenchymal stromal
cells to establisha transplantable stem cell niche disease unit.
Cell Stem Cell. 14:824–837. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zambetti NA, Ping Z, Chen S, Kenswil KJG,
Mylona MA, Sanders MA, Hoogenboezem RM, Bindels EMJ, Adisty MN, Van
Strien PMH, et al: Mesenchymal inflammation drives genotoxic
stressin hematopoietic stem cells and predicts diseaseevolution in
human pre-leukemia. Cell Stem Cell. 19:613–627. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Raaijmakers MH, Mukherjee S, Guo S, Zhang
S, Kobayashi T, Schoonmaker JA, Ebert BL, Al-Shahrour F, Hasserjian
RP, Scadden EO, et al: Bone progenitor dysfunction induces
myelodysplasia andsecondary leukemia. Nature. 464:852–857. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Y, Chen X, Cao W and Shi Y:
Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells inimmunomodulation:
Pathological andtherapeutic implications. Nat Immunol.
15:1009–10016. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bagley RG, Weber W, Rouleau C, Yao M,
Honma N, Kataoka S, Ishida I, Roberts BL and Teicher BA: Human
mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow express tumor endothelial
and stromal markers. Int J Oncol. 34:619–627. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao Y, Wu D, Fei C, Guo J, Gu S, Zhu Y,
Xu F, Zhang Z, Wu L, Li X and Chang C: Down-regulation of Dicer1
promotes cellular senescence and decreases the differentiation and
stem cell-supporting capacities of mesenchymal stromal cells in
patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Haematologica. 100:194–204.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Geyh S, Oz S, Cadeddu RP, Fröbel J,
Brückner B, Kündgen A, Fenk R, Bruns I, Zilkens C, Hermsen D, et
al: Insufficient stromal support in MDS results from molecular
andfunctional deficits of mesenchymal stromal cells. Leukemia.
27:1841–1851. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pang Y, Deng C, Geng S, Weng J, Lai P,
Liao P, Zeng L, Lu Z, Zhang J and Du X: Premature exhaustion of
mesenchymal stromal cellsfrom myelodysplastic syndrome patients. Am
J Transl Res. 9:3462–3468. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pavlaki K, Pontikoglou CG, Demetriadou A,
Batsali AK, Damianaki A, Simantirakis E, Kontakis M, Galanopoulos
A, Kotsianidis I, Kastrinaki MC and Papadaki HA: Impaired
proliferative potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells in
patients with myelodysplastic syndromes is associated with abnormal
wnt signaling pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 23:1568–1581. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Falconi G, Fabiani E, Fianchi L, Criscuolo
M, Raffaelli CS, Bellesi S, Hohaus S, Voso MT, D'Alò F and Leone G:
Impairment of PI3K/AKT and WNT/β-catenin pathways in bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells isolated from patients with myelodysplastic
syndromes. Exp Hematol. 44:75–83.e1-4. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Roulois D, Loo Yau H, Singhania R, Wang Y,
Danesh A, Shen SY, Han H, Liang G, Jones PA, Pugh TJ, et al:
DNA-demethylating agents target colorectal cancer cells by inducing
viral mimicry by endogenous transcripts. Cell. 162:961–973. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chiba N, Furukawa K, Takayama S, Asari T,
Chin S, Harada Y, Kumagai G, Wada K, Tanaka T, Ono A, et al:
Decreased DNA methylation in the promoter region of the WNT5A and
GDNF genes may promote the osteogenicity of mesenchymal stemcells
from patients with ossified spinal ligaments. J Pharmacol Sci.
127:467–473. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Teklemariam T, Purandare B, Zhao L and
Hantash BM: Inhibition of DNA methylation enhances HLA-G expression
in human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
452:753–759. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning
RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, Harris NL, Le Beau MM,
Hellström-Lindberg E, Tefferi A and Bloomfield CD: The 2008
revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification
ofmyeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: Rationale and important
changes. Blood. 114:937–951. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
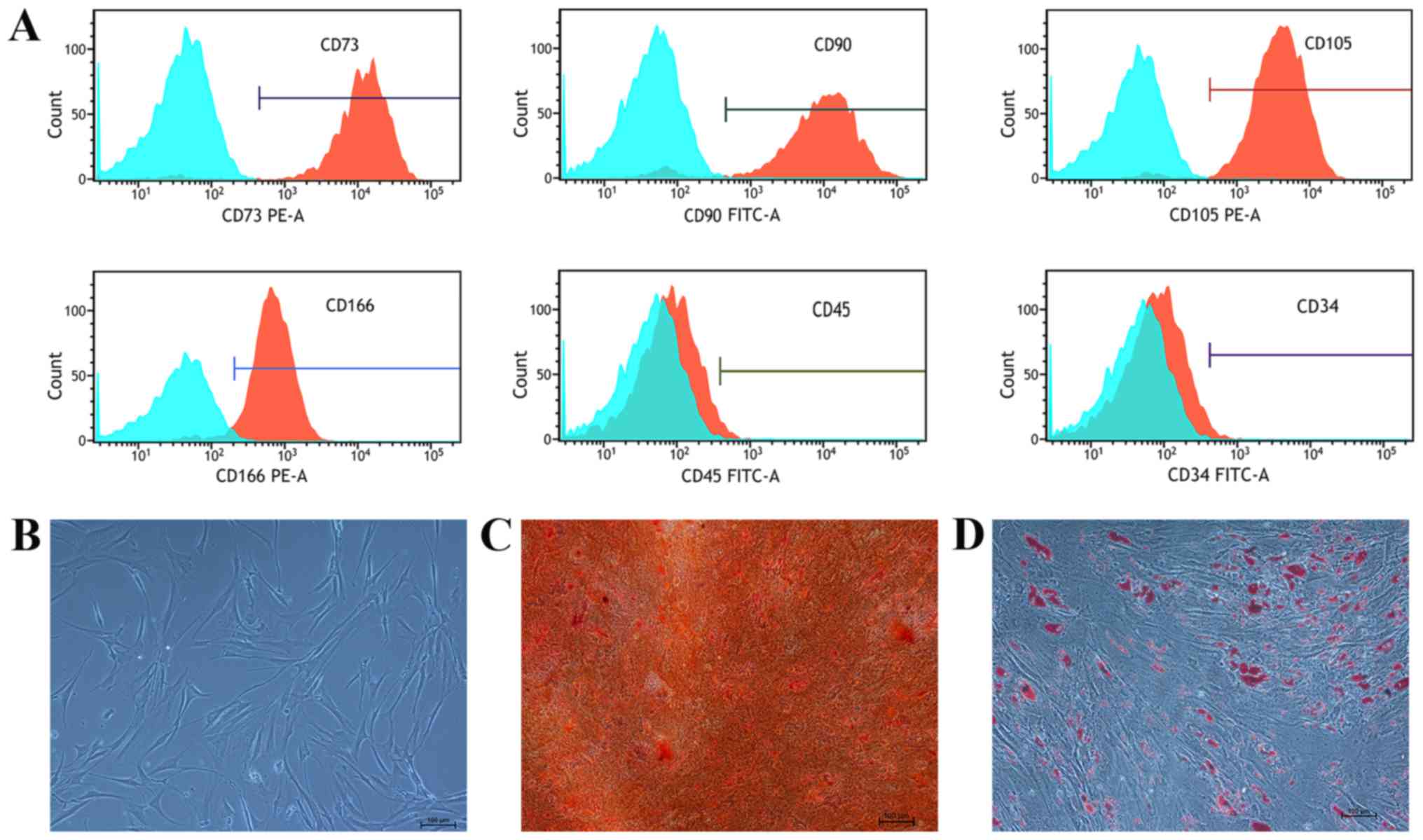
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop DJ and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. The international society for cellular
therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fei C, Zhao Y, Guo J, Gu S, Li X and Chang
C: Senescence of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells is
accompanied by activation of p53/p21 pathway inmyelodysplastic
syndromes. Eur J Haematol. 93:476–486. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tsai HC, Li H, Van Neste L, Cai Y, Robert
C, Rassool FV, Shin JJ, Harbom KM, Beaty R, Pappou E, et al:
Transient low doses of DNA-demethylating agents exert durable
antitumor effects on hematological and epithelial tumor cells.
Cancer Cell. 21:430–446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yao Y, Zhou J, Wang L, Gao X, Ning Q,
Jiang M, Wang J, Wang L and Yu L: Increased PRAME-specific CTL
killing of acute myeloid leukemia cells by either a novel histone
deacetylase inhibitor chidamide alone or combined treatment with
decitabine. PLoS One. 8:e705222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
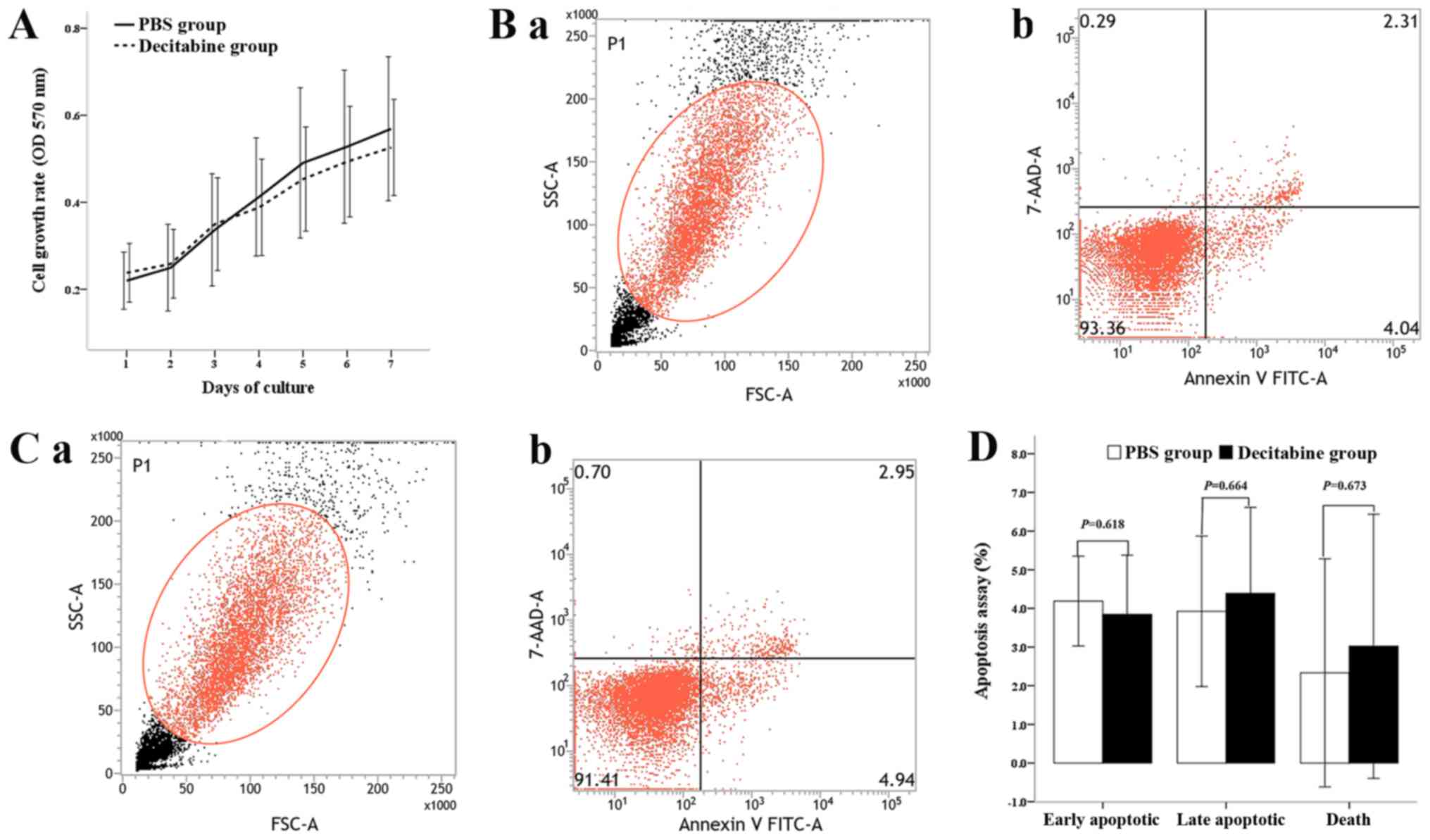
Ding K, Fu R, Liu H, Nachnani DA and Shao
ZH: Effects of decitabine on megakaryocyte maturation in patients
with myelodysplastic syndromes. Oncol Lett. 11:2347–2352. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Armand P: Immune checkpoint blockade in
hematologic malignancies. Blood. 125:3393–3400. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chiappinelli KB, Strissel PL, Desrichard
A, Li H, Henke C, Akman B, Hein A, Rote NS, Cope LM, Snyder A, et
al: Inhibiting DNA methylation causes an interferon response in
cancer via dsRNA including endogenous retroviruses. Cell.
169:3612017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
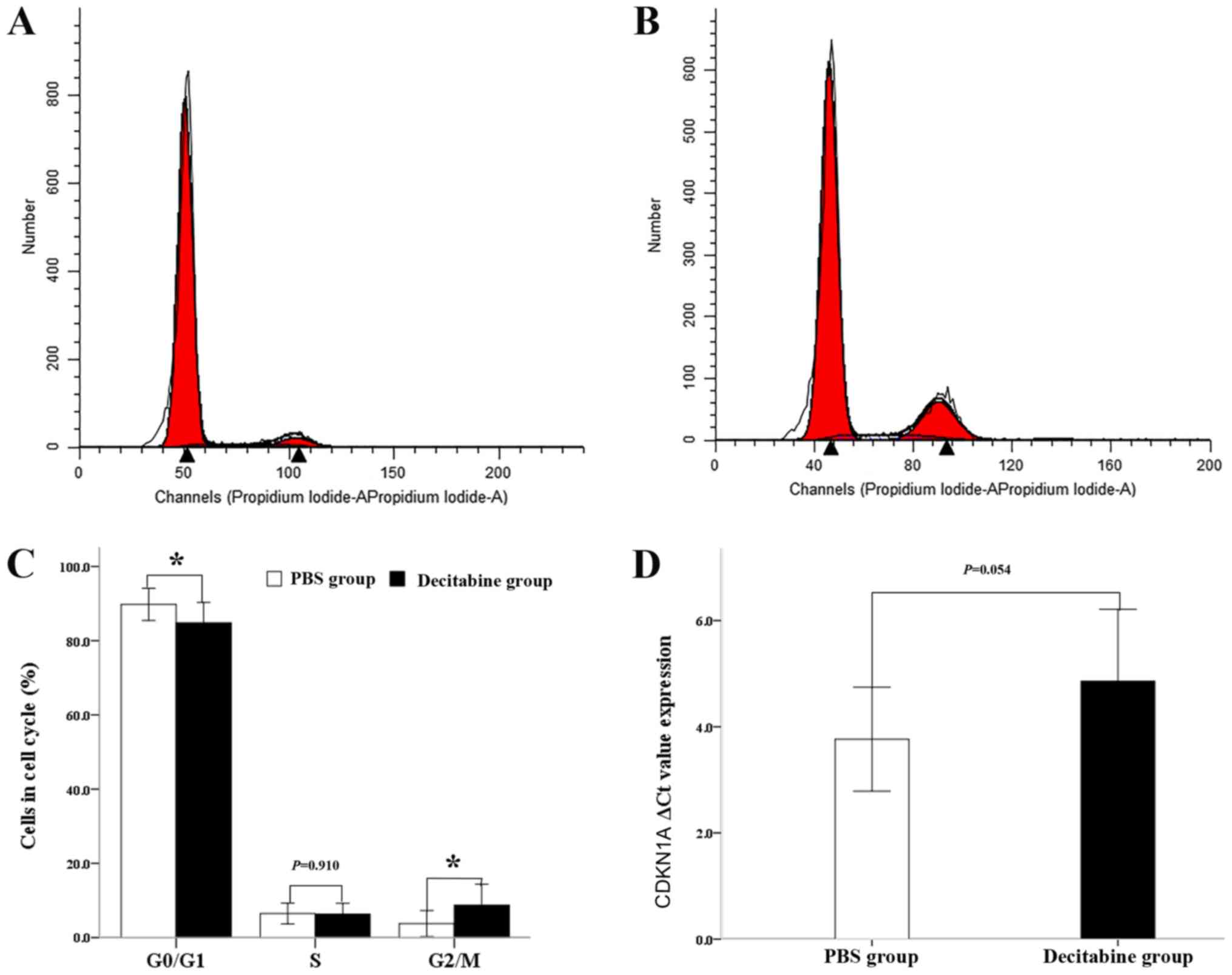
Shin DY, Sung Kang H, Kim GY, Kim WJ, Yoo
YH and Choi YH: Decitabine, a DNA methyltransferases inhibitor,
induces cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase through p53-independent
pathway in human cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 67:305–311.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shang D, Han T, Xu X and Liu Y: Decitabine
induces G2/M cell cycle arrest by suppressing p38/NF-κB signaling
inhuman renal clear cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:11140–11148. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Diesch J, Zwick A, Garz AK, Palau A,
Buschbeck M and Götze KS: A clinical-molecular update
onazanucleoside-based therapy for thetreatment of hematologic
cancers. Clin Epigenetics. 8:712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Reinisch A, Etchart N, Thomas D, Hofmann
NA, Fruehwirth M, Sinha S, Chan CK, Senarath-Yapa K, Seo EY, Wearda
T, et al: Epigenetic and in vivo comparison of diverse MSC sources
reveals an endochondral signature for human hematopoietic niche
formation. Blood. 125:249–260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chan CK, Chen CC, Luppen CA, Kim JB,
DeBoer AT, Wei K, Helms JA, Kuo CJ, Kraft DL and Weissman IL:
Endochondral ossification is required for haematopoietic stem-cell
niche formation. Nature. 457:490–494. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mao Z, Ke Z, Gorbunova V and Seluanov A:
Replicatively senescent cells are arrested in G1 and G2 phases.
Aging (Albany NY). 4:431–435. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kordasti SY, Ingram W, Hayden J, Darling
D, Barber L, Afzali B, Lombardi G, Wlodarski MW, Maciejewski JP,
Farzaneh F and Mufti GJ: CD4+CD25high Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in
myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood. 110:847–850. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao Z, Wang Z, Li Q, Li W, You Y and Zou
P: The different immunoregulatory functions of mesenchymal stem
cells in patients with low-risk or high-risk myelodysplastic
syndromes. PLoS One. 7:e456752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang H, Bueso-Ramos C, DiNardo C, Estecio
MR, Davanlou M, Geng QR, Fang Z, Nguyen M, Pierce S, Wei Y, et al:
Expression of PD-L1, PD-L2, PD-1 and CTLA4 in myelodysplastic
syndromes is enhanced by treatment with hypomethylating agents.
Leukemia. 28:1280–1288. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
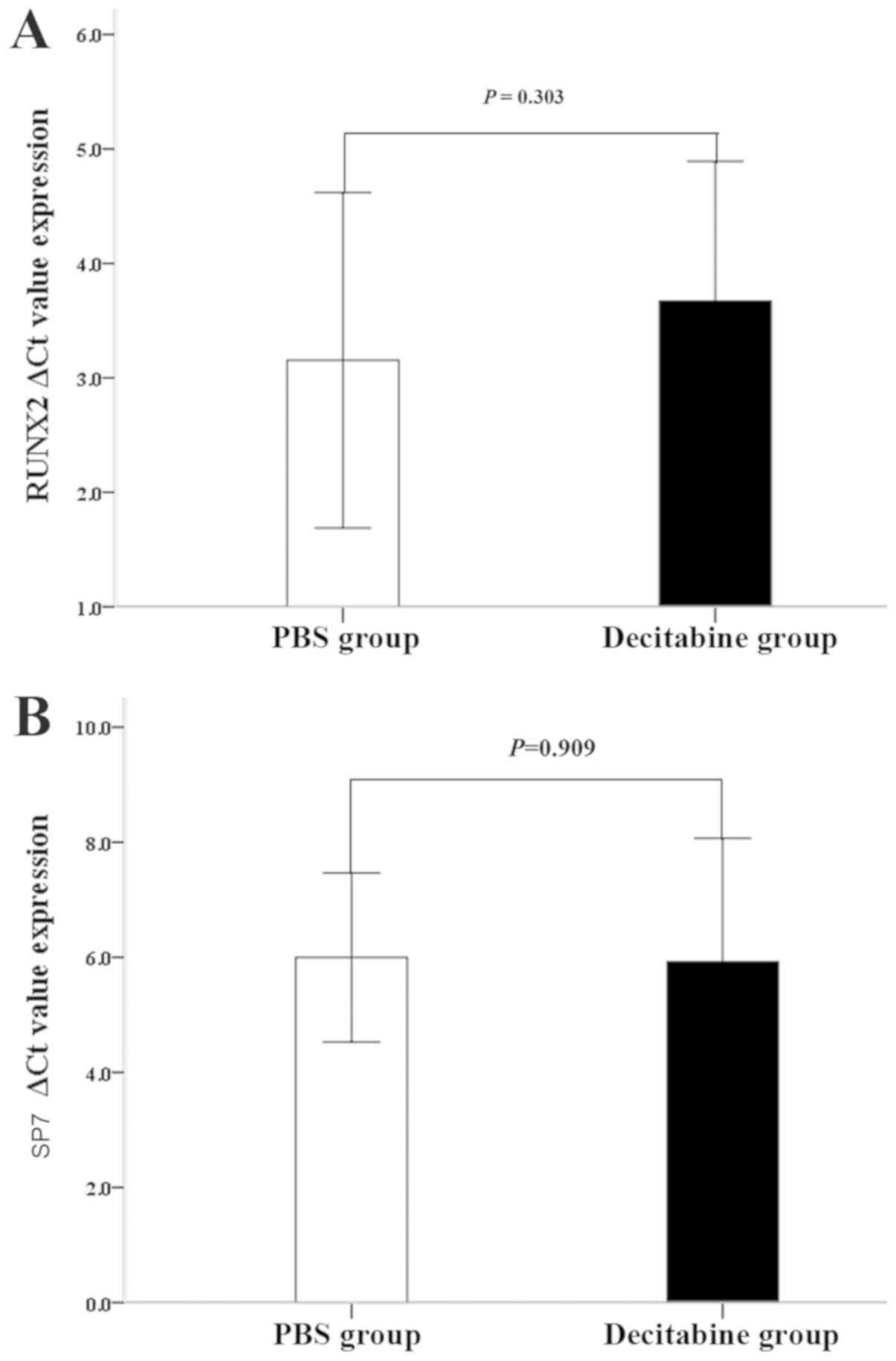
Pleyer L, Valent P and Greil R:
Mesenchymal stem and progenitor cells in normaland dysplastic
hematopoiesis-masters of survivaland clonality? Int J Mol Sci.
17(pii): E10092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|