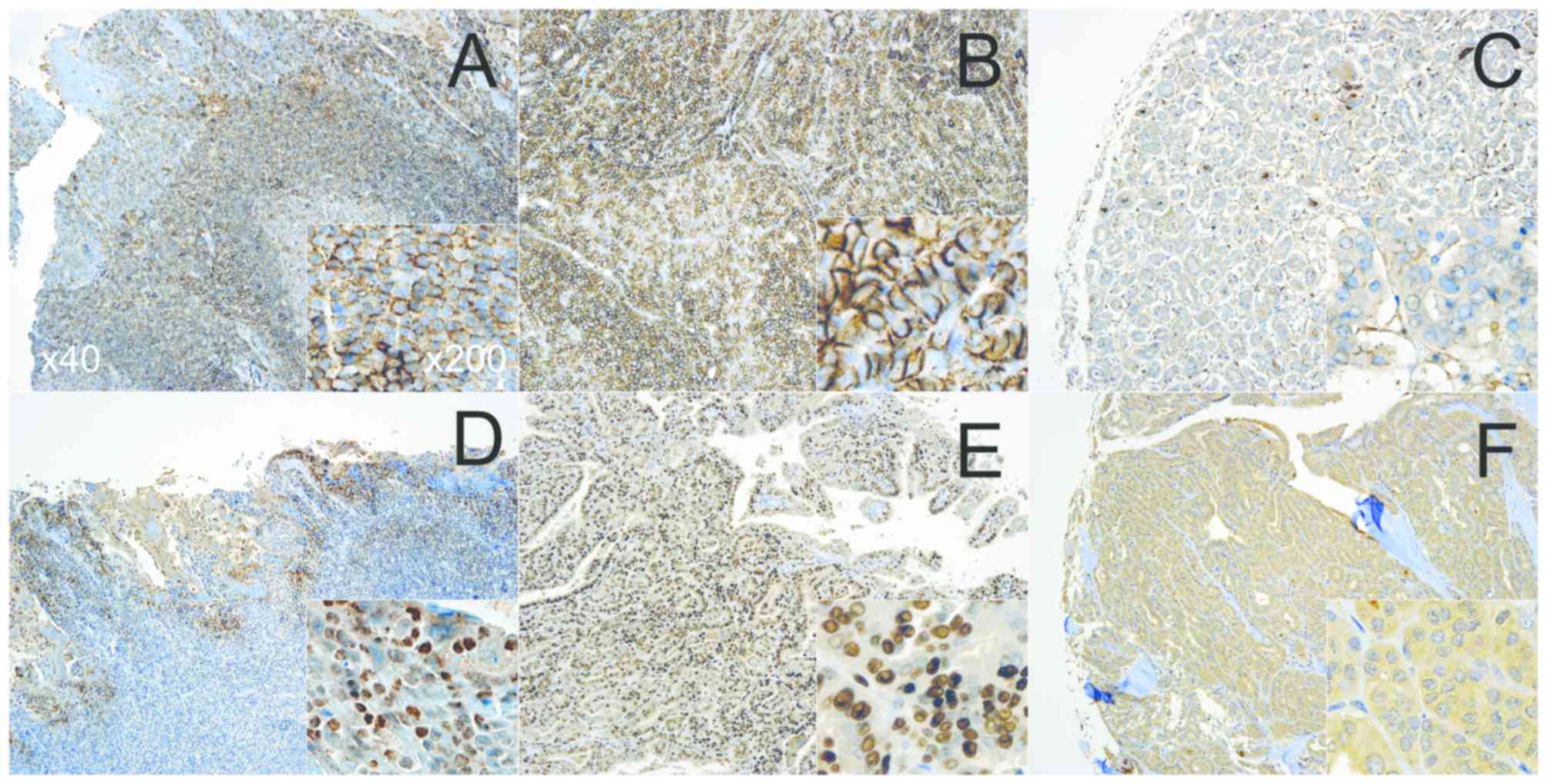
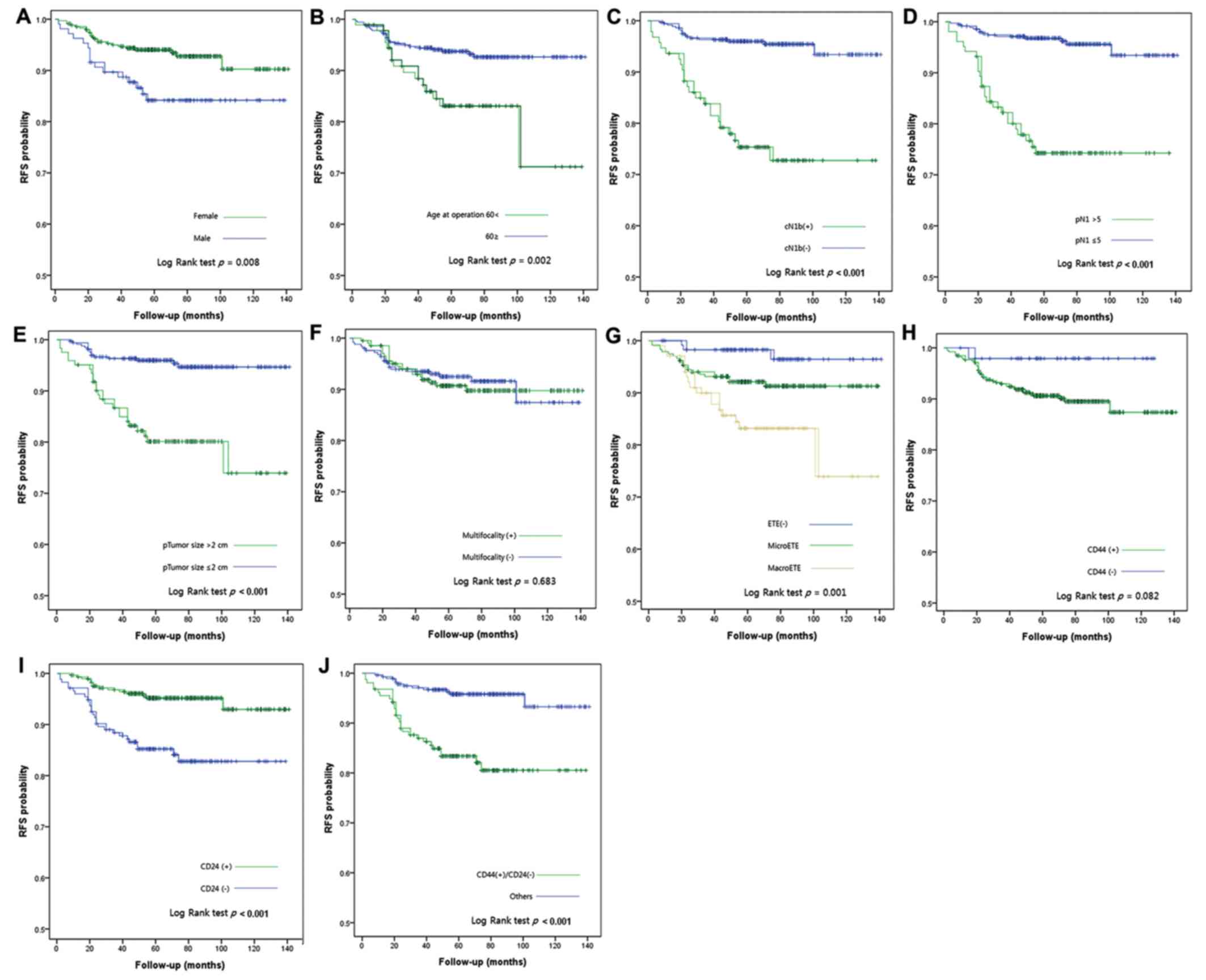
|
1
|
Ito Y, Nikiforov YE, Schlumberger M and
Vigneri R: Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer: Controversies
explored. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 9:178–184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
National_Cancer_Information_Center, .
Korea cancer registry statistics 2014National Cancer Information
Center; Goyang: 2016
|
|
3
|
Cho BY, Choi HS, Park YJ, Lim JA, Ahn HY,
Lee EK, Kim KW, Yi KH, Chung JK, Youn YK, et al: Changes in the
clinicopathological characteristics and outcomes of thyroid cancer
in Korea over the past four decades. Thyroid. 23:797–804. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty
GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, Pacini F, Randolph GW, Sawka AM,
Schlumberger M, et al: 2015 American thyroid association management
guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and
differentiated thyroid cancer the American thyroid association
guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid
cancer. Thyroid. 26:1–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moharil RB, Dive A, Khandekar S and
Bodhade A: Cancer stem cells: An insight. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol.
21:4632017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ahn SH, Henderson YC, Williams MD, Lai SY
and Clayman GL: Detection of thyroid cancer stem cells in papillary
thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 99:536–544. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fedchenko N and Reifenrath J: Different
approaches for interpretation and reporting of immunohistochemistry
analysis results in the bone tissue-a review. Diagn Pathol.
9:2212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Perrier ND, Brierley JD and Tuttle RM:
Differentiated and anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: Major changes in
the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer
staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:55–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tubiana M, Schlumberger M, Rougier P,
Laplanche A, Benhamou E, Gardet P, Caillou B, Travagli JP and
Parmentier C: Long-term results and prognostic factors in patients
with differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Cancer. 55:794–804. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Coburn M, Teates D and Wanebo HJ:
Recurrent thyroid cancer. Role of surgery versus radioactive iodine
(I131). Ann Surg. 219:587–595. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim WG, Kim EY, Yim JH, Han JM, Jeon MJ,
Kim TY, Ryu JS, Gong G, Hong SJ, Kim WB and Shong YK: Comparison of
different staging systems for predicting recurrence of papillary
thyroid carcinoma. Endocrinol Metab. 26:53–61. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hwangbo Y, Kim JM, Park YJ, Lee EK, Lee
YJ, Park DJ, Choi YS, Lee KD, Sohn SY, Kim SW, et al: Long-term
recurrence of small papillary thyroid cancer and its risk factors
in a Korean multicenter study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
102:625–633. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nagayama Y, Shimamura M and Mitsutake N:
Cancer stem cells in the thyroid. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
7:202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zito G, Richiusa P, Bommarito A, Carissimi
E, Russo L, Coppola A, Zerilli M, Rodolico V, Criscimanna A, Amato
M, et al: In vitro identification and characterization of
CD133(pos) cancer Stem-like cells in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
cell lines. PLoS One. 3:e35442008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Friedman S, Lu M, Schultz A, Thomas D and
Lin RY: CD133+ anaplastic thyroid cancer cells initiate tumors in
immunodeficient mice and are regulated by thyrotropin. PLoS One.
4:e53952009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sahlberg SH, Spiegelberg D, Glimelius B,
Stenerlöw B and Nestor M: Evaluation of cancer stem cell markers
CD133, CD44, CD24: Association with AKT isoforms and radiation
resistance in colon cancer cells. PLoS One. 9:e946212014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tuttle RM, Haugen B and Perrier ND:
Updated American Joint Committee on Cancer/Tumor-Node-Metastasis
staging system for differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancer
(Eighth edition): What changed and why? Thyroid. 27:751–756. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bi Y, Meng Y, Wu H, Cui Q, Luo Y and Xue
X: Expression of the potential cancer stem cell markers CD133 and
CD44 in medullary thyroid carcinoma: A ten-year follow-up and
prognostic analysis. J Surg Oncol. 113:144–151. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Horimoto Y, Arakawa A, Sasahara N, Tanabe
M, Sai S, Himuro T and Saito M: Combination of cancer stem cell
markers CD44 and CD24 is superior to ALDH1 as a prognostic
indicator in breast cancer patients with distant metastases. PLoS
One. 11:e01652532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eramo A, Haas TL and De Maria R: Lung
cancer stem cells: Tools and targets to fight lung cancer.
Oncogene. 29:4625–4635. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC,
Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, Meyer L, Gress DM, Byrd DR and
Winchester DP: The eighth edition AJCC cancer staging manual:
Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more
‘personalized’ approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin.
67:93–99. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|