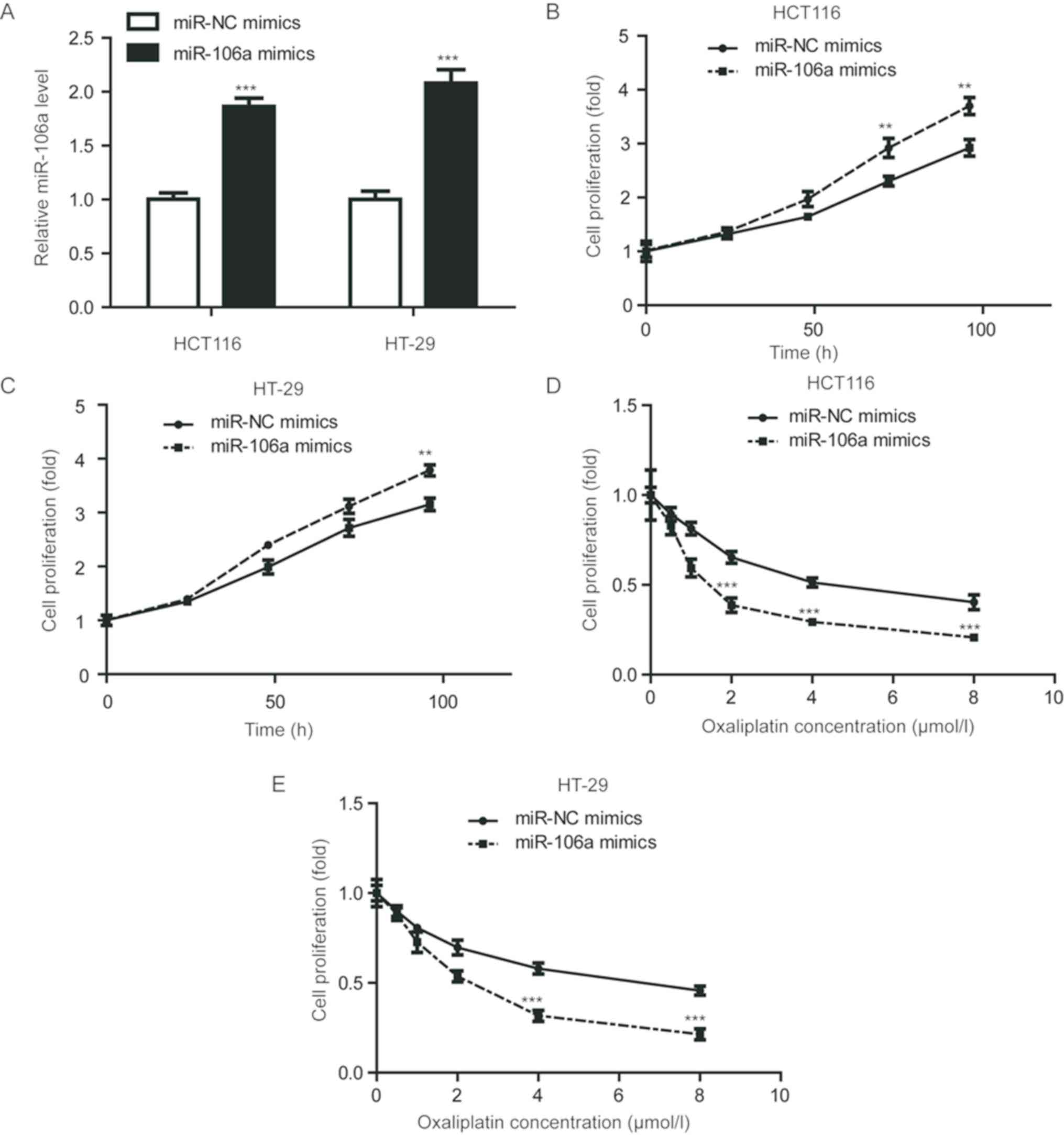
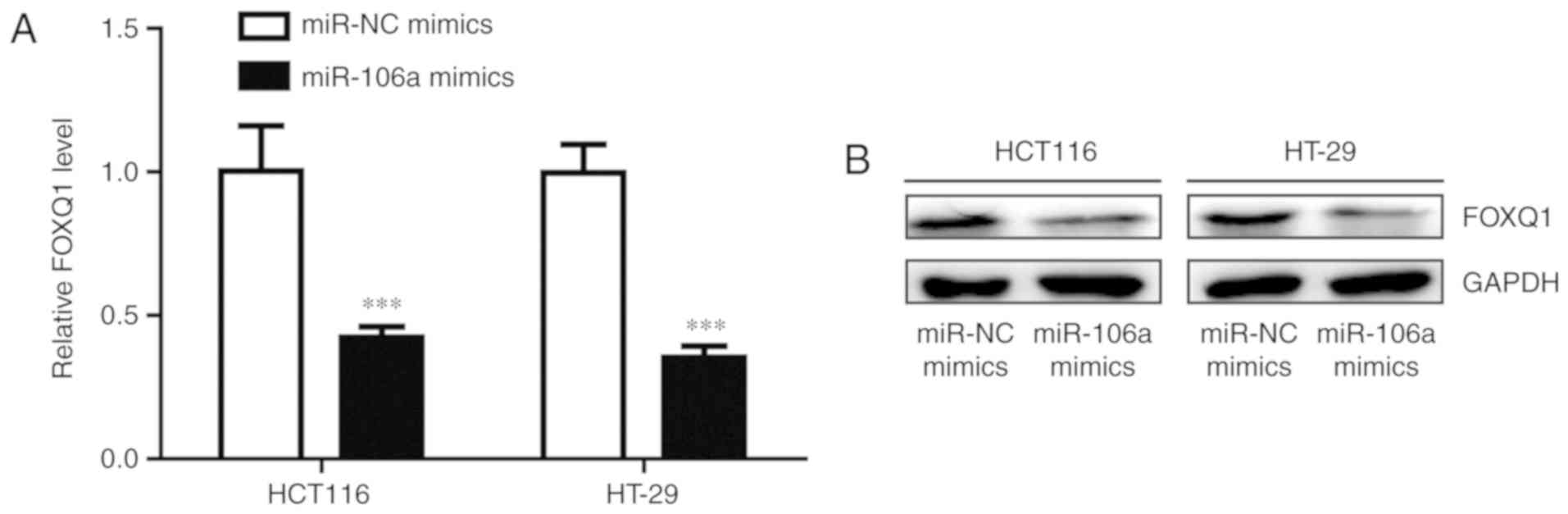
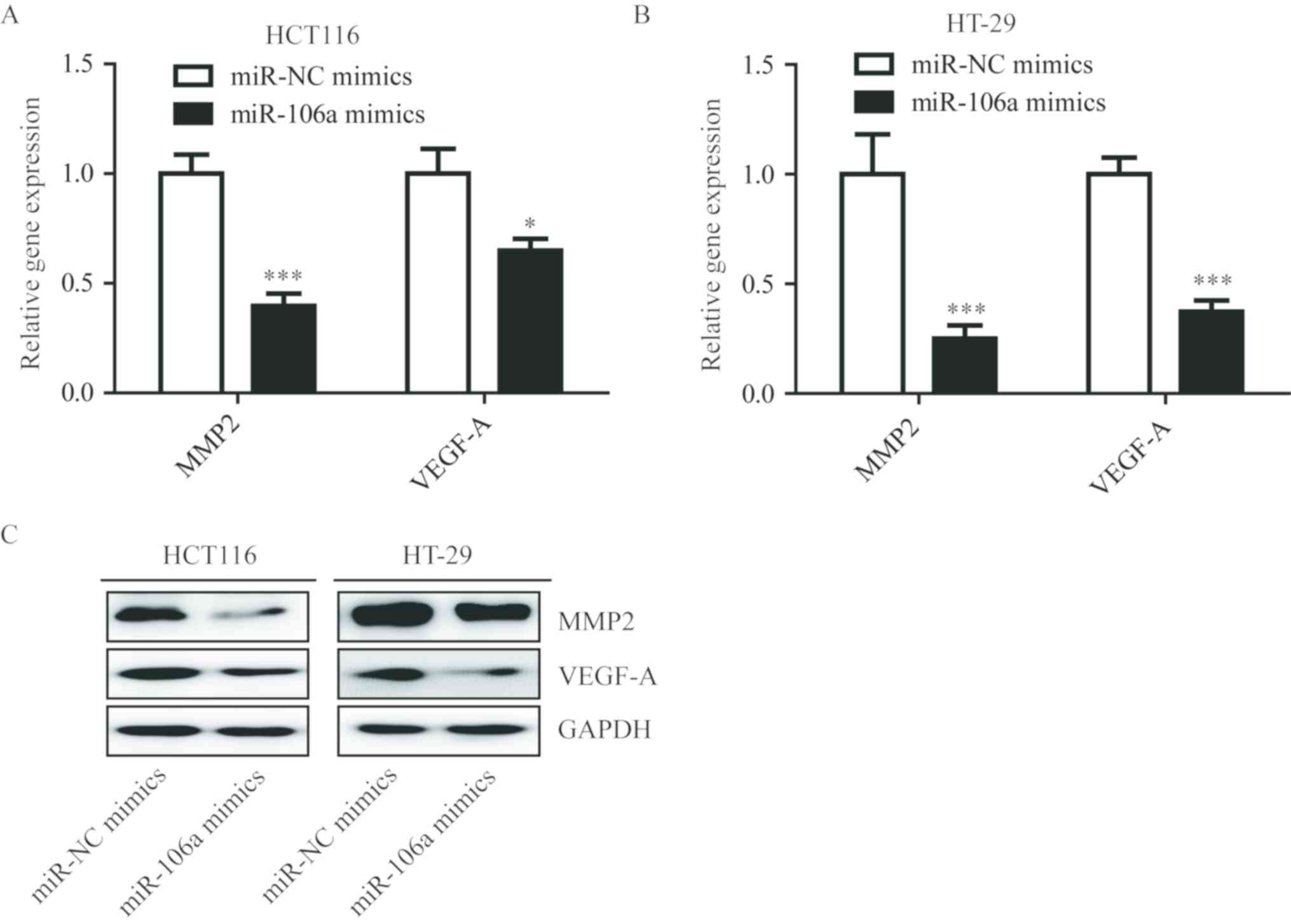
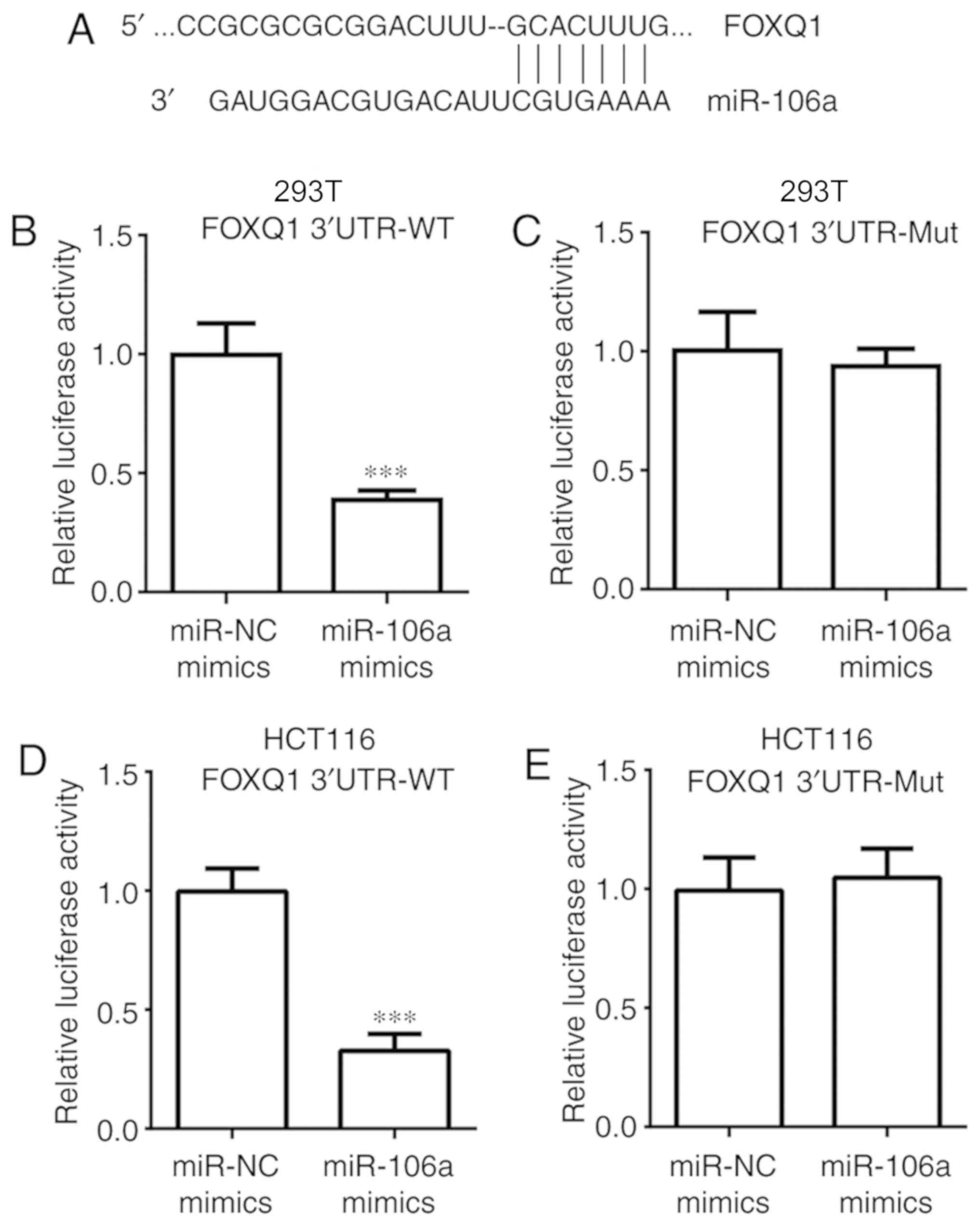
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
André T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L,
Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Zaninelli M, Clingan
P, Bridgewater J, et al: Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin
as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2343–2351. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Raymond E, Faivre S, Chaney S, Woynarowski
J and Cvitkovic E: Cellular and molecular pharmacology of
oxaliplatin. Mol Cancer Ther. 1:227–235. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rabik CA and Dolan ME: Molecular
mechanisms of resistance and toxicity associated with platinating
agents. Cancer Treat Rev. 33:9–23. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ambros V: microRNAs: Tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ardekani AM and Naeini MM: The role of
microRNAs in human diseases. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2:161–179.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Du B, Wu D, Yang X, Wang T, Shi X, Lv Y,
Zhou Z, Liu Q and Zhang W: The expression and significance of
microRNA in different stages of colorectal cancer. Medicine
(Baltimore). 97:e96352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Emami SS, Akbari A, Zare AA, Agah S,
Masoodi M, Talebi A, Minaeian S, Fattahi A and Moghadamnia F:
MicroRNA expression levels and histopathological features of
colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Cancer. 50:276–284. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Hu X, Miao X, Zhu K, Cui S, Meng
Q, Sun J and Wang T: MicroRNA-425-5p regulates chemoresistance in
colorectal cancer cells via regulation of programmed cell death 10.
J Cell Mol Med. 20:360–369. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou Y, Wan G, Spizzo R, Ivan C, Mathur R,
Hu X, Ye X, Lu J, Fan F, Xia L, et al: miR-203 induces oxaliplatin
resistance in colorectal cancer cells by negatively regulating ATM
kinase. Mol Oncol. 8:83–92. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ayers D and Vandesompele J: Influence of
microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in cancer chemoresistance. Genes
(Basel). 8(pii): E952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Feng B, Dong TT, Wang LL, Zhou HM, Zhao
HC, Dong F and Zheng MH: Colorectal cancer migration and invasion
initiated by microRNA-106a. PLoS One. 7:e434522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Koga Y, Yamazaki N, Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto
S, Saito N, Kakugawa Y, Otake Y, Matsumoto M and Matsumura Y: Fecal
miR-106a is a useful marker for colorectal cancer patients with
false-negative results in immunochemical fecal occult blood test.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 22:1844–1852. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu GH, Zhou ZG, Chen R, Wang MJ, Zhou B,
Li Y and Sun XF: Serum miR-21 and miR-92a as biomarkers in the
diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol.
34:2175–2181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Diaz R, Silva J, Garcia JM, Lorenzo Y,
García V, Peña C, Rodríguez R, Muñoz C, García F, Bonilla F and
Domínguez G: Deregulated expression of miR-106a predicts survival
in human colon cancer patients. Genes Chromosomes Cance.
47:794–802. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Overdier DG, Porcella A and Costa RH: The
DNA-binding specificity of the hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/forkhead
domain is influenced by amino-acid residues adjacent to the
recognition helix. Mol Cell Biol. 14:2755–2766. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu H: Targeting forkhead box
transcription factors FOXM1 and FOXO in leukemia (Review). Oncol
Rep. 32:1327–1334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaneda H, Arao T, Tanaka K, Tamura D,
Aomatsu K, Kudo K, Sakai K, De Velasco MA, Matsumoto K, Fujita Y,
et al: FOXQ1 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and enhances
tumorigenicity and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 70:2053–2063. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weng W, Okugawa Y, Toden S, Toiyama Y,
Kusunoki M and Goel A: FOXM1 and FOXQ1 are promising prognostic
biomarkers and novel targets of tumor-suppressive miR-342 in human
colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:4947–4957. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Christensen J, Bentz S, Sengstag T,
Shastri VP and Anderle P: FOXQ1, a novel target of the Wnt pathway
and a new marker for activation of Wnt signaling in solid tumors.
PLoS One. 8:e600512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vishnubalaji R, Hamam R, Yue S, Al-Obeed
O, Kassem M, Liu FF, Aldahmash A and Alajez NM: MicroRNA-320
suppresses colorectal cancer by targeting SOX4, FOXM1, and FOXQ1.
Oncotarget. 7:35789–35802. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Calnan DR and Brunet A: The FoxO code.
Oncogene. 27:2276–2288. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Codony-Servat J, Cuatrecasas M, Asensio E,
Montironi C, Martínez-Cardús A, Marín-Aguilera M, Horndler C,
Martínez-Balibrea E, Rubini M, Jares P, et al: Nuclear IGF-1R
predicts chemotherapy and targeted therapy resistance in metastatic
colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 117:1777–1786. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ju HQ, Lu YX, Wu QN, Liu J, Zeng ZL, Mo
HY, Chen Y, Tian T, Wang Y, Kang TB, et al: Disrupting
G6PD-mediated Redox homeostasis enhances chemosensitivity in
colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 36:6282–6292. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Peng X, Luo Z, Kang Q, Deng D, Wang Q,
Peng H, Wang S and Wei Z: FOXQ1 mediates the crosstalk between
TGF-β and Wnt signaling pathways in the progression of colorectal
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 16:1099–1109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Davies JM and Goldberg RM: First-line
therapeutic strategies in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncology
(Williston Park). 22:1470–1479. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hector S, Bolanowska-Higdon W, Zdanowicz
J, Hitt S and Pendyala L: In vitro studies on the mechanisms of
oxaliplatin resistance. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 48:398–406.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li J, Chen Y, Zhao J, Kong F and Zhang Y:
miR-203 reverses chemoresistance in p53-mutated colon cancer cells
through downregulation of Akt2 expression. Cancer Lett. 304:52–59.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sau A, Pellizzari Tregno F, Valentino F,
Federici G and Caccuri AM: Glutathione transferases and development
of new principles to overcome drug resistance. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 500:116–122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thomas J, Ohtsuka M, Pichler M and Ling H:
MicroRNAs: Clinical relevance in colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
16:28063–28076. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bovell LC, Shanmugam C, Putcha BD,
Katkoori VR, Zhang B, Bae S, Singh KP, Grizzle WE and Manne U: The
prognostic value of microRNAs varies with patient race/ethnicity
and stage of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 19:3955–3965.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li J, Liu Y, Wang C, Deng T, Liang H, Wang
Y, Huang D, Fan Q, Wang X, Ning T, et al: Serum miRNA expression
profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal
adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 5:129212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qin Y, Huo Z, Song X, Chen X, Tian X and
Wang X: mir-106a regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of
colon cancer cells through targeting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling
pathway. Oncol Lett. 15:3197–3201. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hao H, Liu L, Zhang D, Wang C, Xia G,
Zhong F and Hu X: Diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-106a in
colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 8:5038–5047. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Zhang Y, Yao Z, Li S, Yin Z and Xu
M: Forkhead box Q1: A key player in the pathogenesis of tumors
(Review). Int J Oncol. 49:51–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qiao Y, Jiang X, Lee ST, Karuturi RK, Hooi
SC and Yu Q: FOXQ1 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
human cancers. Cancer Res. 71:3076–3086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|