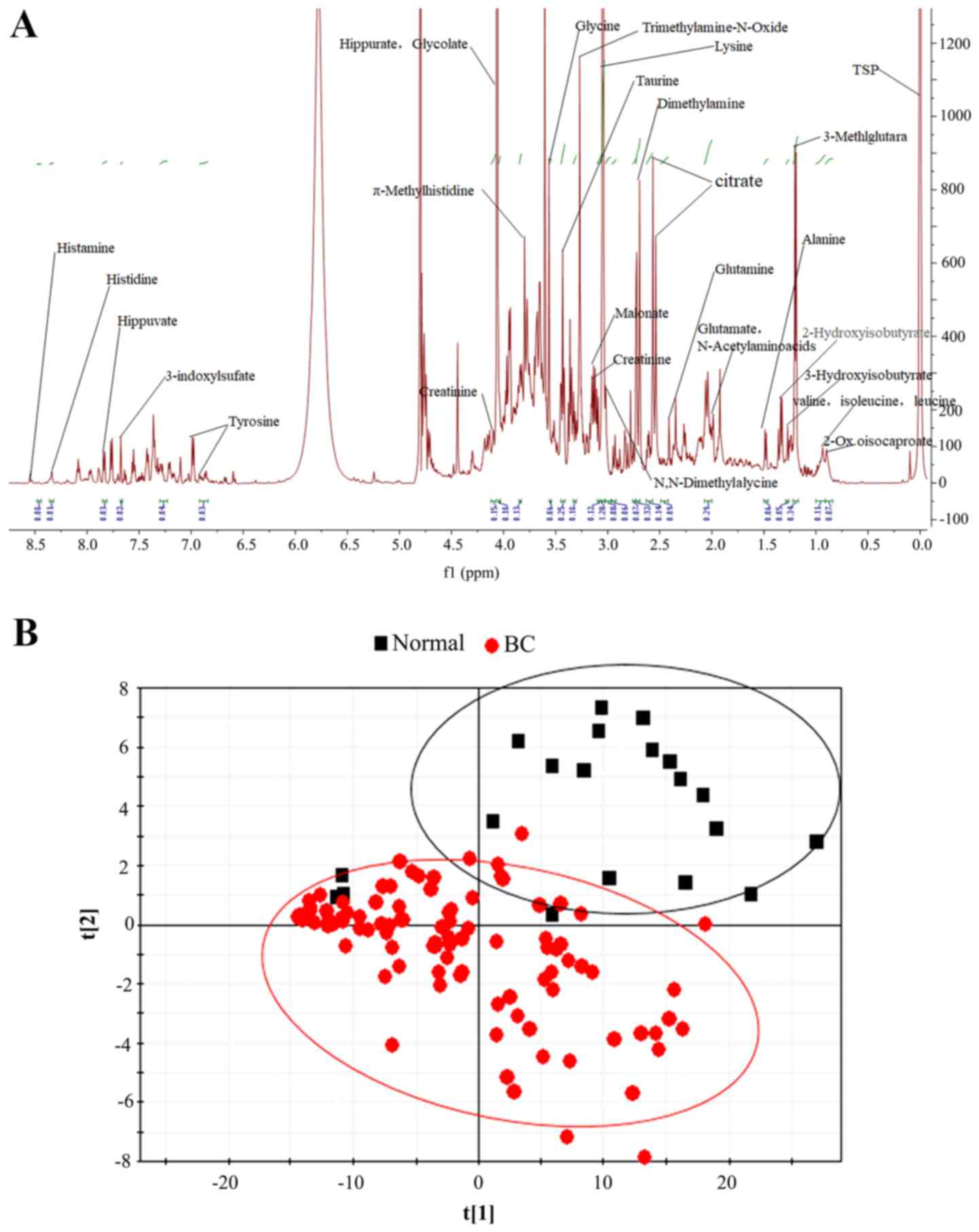
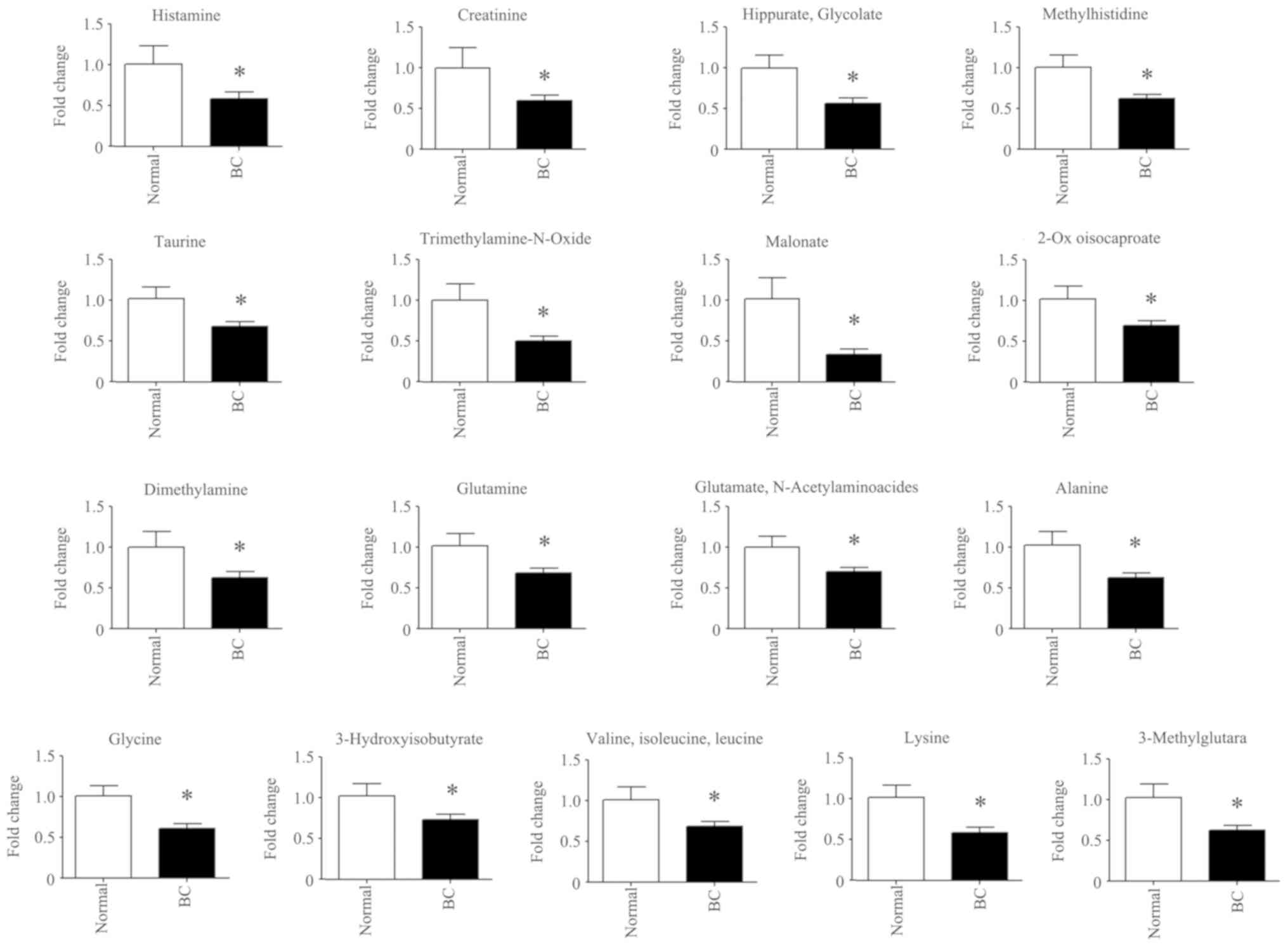
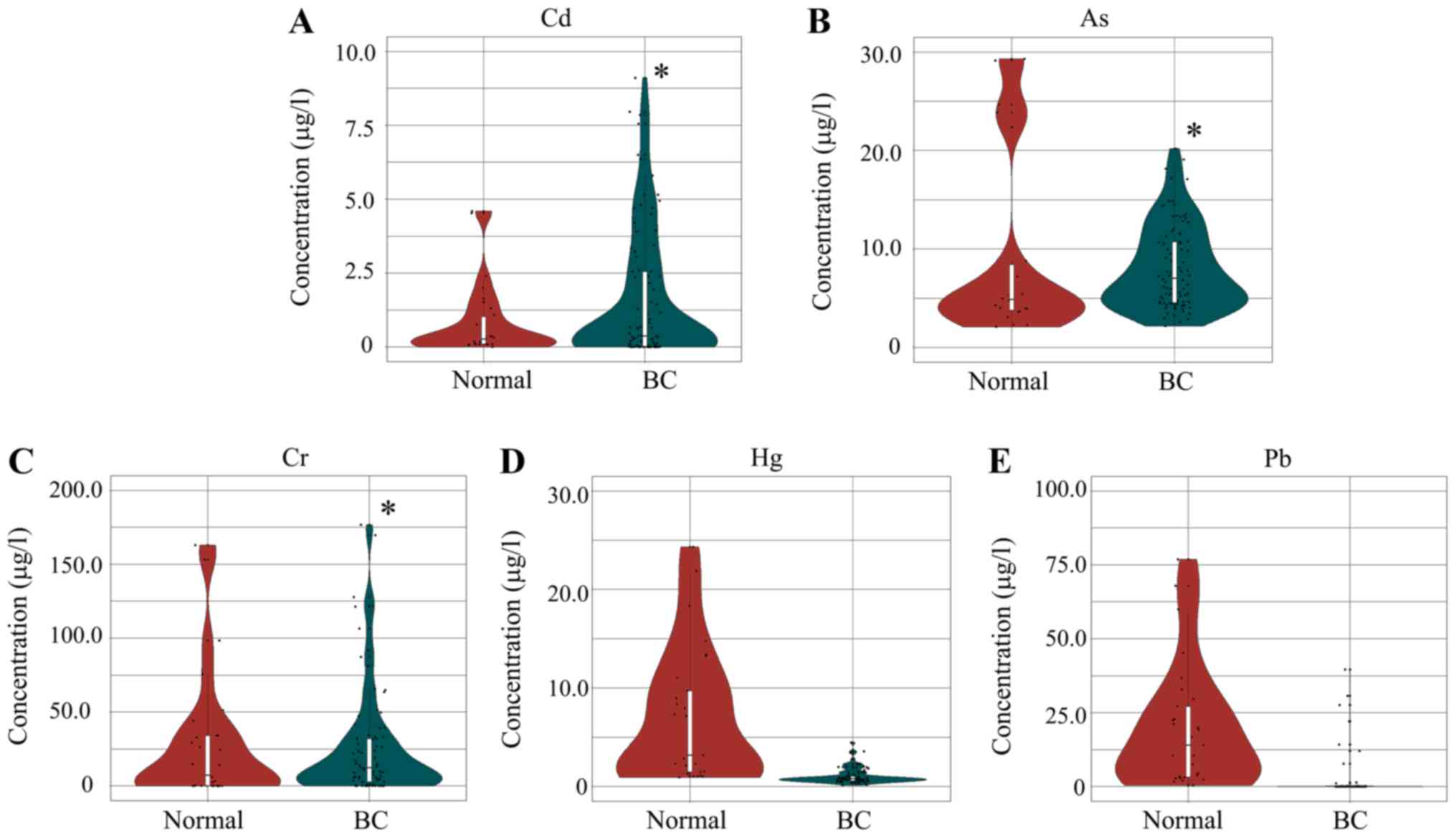
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M,
Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and
Bray F: GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, cancer incidence and mortality
worldwide: IARC cancer base no. 11 [Internet]. International Agency
for Research on Cancer; Lyon: 2014
|
|
2
|
Ledda C, Iavicoli I, Bracci M, Avola R,
Senia P, Santarelli L, Pomara C and Rapisarda V: Serum lipid,
lipoprotein and apolipoprotein profiles in workers exposed to low
arsenic levels: Lipid profiles and occupational arsenic exposure.
Toxicol Lett. 282:49–56. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 62:10–29. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Prüss-Üstün A and Corvalán C: Preventing
disease through healthy environments. Towards an estimate of the
environmental burden of disease. World Health Organization; France:
2006
|
|
5
|
Rzymski P, Tomczyk K, Rzymski P,
Poniedziałek B, Opala T and Wilczak M: Impact of heavy metals on
the female reproductive system. Ann Agric Environ Med. 22:259–264.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Howell A, Anderson AS, Clarke RB, Duffy
SW, Evans DG, Garcia-Closas M, Gescher AJ, Key TJ, Saxton JM and
Harvie MN: Risk determination and prevention of breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res. 16:4462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kruk J, Doskocz M, Jodłowska E,
Zacharzewska A, Łakomiec J, Czaja K and Kujawski J: NMR techniques
in metabolomic studies: A quick overview on examples of
utilization. Appl Magn Reson. 48:1–21. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Denkert C, Budczies J, Kind T, Weichert W,
Tablack P, Sehouli J, Niesporek S, Könsgen D, Dietel M and Fiehn O:
Mass spectrometry-based metabolic profiling reveals different
metabolite patterns in invasive ovarian carcinomas and ovarian
borderline tumors. Cancer Res. 66:10795–10804. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Burton C and Ma Y: Current trends in
cancer biomarker discovery using urinary metabolomics: Achievements
and new challenges. Curr Med Chem. 26:5–28. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cala M, Aldana J, Sánchez J, Guio J and
Meesters RJW: Urinary metabolite and lipid alterations in Colombian
Hispanic women with breast cancer: A pilot study. J Pharm Biomed
Anal. 152:234–241. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eriksen KT, McElroy JA, Harrington JM,
Levine KE, Pedersen C, Sørensen M, Tjønneland A, Meliker JR and
Raaschou-Nielsen O: Urinary cadmium and breast cancer: A
prospective danish cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 109(pii):
djw2042016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang T, Watson DG, Wang L, Abbas M,
Murdoch L, Bashford L, Ahmad I, Lam NY, Ng AC and Leung HY:
Application of holistic liquid chromatography-high resolution mass
spectrometry based urinary metabolomics or prostate cancer
detection and biomarker discovery. PLoS One. 8:e658802013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang A, Sun H, Wang P, Han Y and Wang X:
Modern analytical techniques in metabolomics analysis. Analyst.
137:293–300. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Suhre K, Shin SY, Petersen AK, Mohney RP,
Meredith D, Wägele B, Altmaier E, CARDIoGRA M, Deloukas P, Erdmann
J, et al: Human metabolic individuality in biomedical and
pharmaceutical research. Nature. 477:54–60. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bictash M, Ebbels TM, Chan Q, Loo RL, Yap
IK, Brown IJ, de Iorio M, Daviglus ML, Holmes E, Stamler J, et al:
Opening up the ‘Black Box’: Metabolic phenotyping and
metabolome-wide association studies in epidemiology. J Clin
Epidemiol. 63:970–979. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Claudino WM, Quattronem A, Biganzoli L,
Pestrin M, Bertini I and Di Leo A: Metabolomics: Available results,
current research projects in breast cancer, and future
applications. J Clin Oncol. 25:2840–2846. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Holmes E, Loo RL, Stamler J, Bictash M,
Yap IK, Chan Q, Ebbels T, De Iorio M, Brown IJ, Veselkov KA, et al:
Human metabolic phenotype diversity and its association with diet
and blood pressure. Nature. 453:396–400. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Norvig P, Relman DA and Goldstein DB: 2020
visions. Nature. 463:26–32. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N,
Mathew BB and Beeregowda KN: Toxicity, mechanism and health effects
of some heavy metals. Interdiscip Toxicol. 7:60–72. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vimercati L, Gatti MF, Gagliardi T,
Cuccaro F, De Maria L, Caputi A, Quarato M and Baldassarre A:
Environmental exposure to arsenic and chromium in an industrial
area. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 24:11528–11535. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vimercati L, Baldassarre A, Gatti MF,
Gagliardi T, Serinelli M, De Maria L, Caputi A, Dirodi AA, Galise
I, Cuccaro F and Assennato G: Non-occupational exposure to heavy
metals of the residents of an industrial area and biomonitoring.
Environ Monit Assess. 188:6732016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
IARC monographs on the evaluation of
carcinogenic risks to humans, . Chromium, nickel, and welding.
Chromium and chromium compounds; IARC, Lyon: 1990
|
|
23
|
Larsson SC, Orsini N and Wolk A: Urinary
cadmium concentration and risk of breast cancer: A systematic
review and dose-response meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol.
182:375–380. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wei XL, He JR, Cen YL, Su Y, Chen LJ, Lin
Y, Wu BH, Su FX, Tang LY and Ren ZF: Modified effect of urinary
cadmium on breast cancer risk by selenium. Clin Chim Acta.
438:80–85. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qin YC, Tang LY, Su Y, Chen LJ, Su FX, Lin
Y, Zhang AH and Ren ZF: Association of urinary cesium with breast
cancer risk. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:9785–9790. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Waalkes MP, Fox DA, States JC, Patierno SR
and McCabe MJ: Metals and disorders of cell accumulation:
Modulation of apoptosis and cell proliferation. Toxicol Sci.
56:255–261. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hayes RB: The carcinogenicity of metals in
humans. Cancer Causes Control. 8:371–385. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
IARC monographs on the evaluation of the
carcinogenic risk of chemicals to humans, . Some metals and
metallic compounds. Lyon; France: 1980
|
|
29
|
Gilman JPW and Smierenga SHH: Inorganic
carcinogenesis. Searle CE: Chemical carcinogens, ACS monograph.
(182)2. 1. American Chemical Society; Washington, DC: pp.
5771980
|
|
30
|
Norseth T: The carcinogenicity of
chromium. Environ Health Persp. 40:121–130. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Barlow SM and Sullivan FM: Reproductive
hazards and industrial chemicals. Ann Occup Hyg. 24:359–361.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Veronesi U, Zurrida S, Viale G, Galimberti
V, Arnone P and Nolè F: Rethinking TNM: A breast cancer
classification to guide to treatment and facilitate research.
Breast J. 15:291–295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang W, Zhao Y, Li F, Li L, Feng Y, Min
L, Ma D, Yu S, Liu J, Zhang H, et al: Zinc oxide nanoparticle
caused plasma metabolomic perturbations correlate with hepatic
steatosis. Front Pharmacol. 9:572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Soininen P, Kangas AJ, Würtz P, Tukiainen
T, Tynkkynen T, Laatikainen R, Järvelin MR, Kähönen M, Lehtimäki T,
Viikari J, et al: High-throughput serum NMR metabonomics for
cost-effective holistic studies on systemic metabolism. Analyst.
134:1781–1785. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee SH, Wang TY, Hong JH, Cheng TJ and Lin
CY: NMR-based metabolomics to determine acute inhalation effects of
nano- and fine-sized ZnO particles in rat lung. Nanotoxicology.
10:924–934. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao Y, Feng YN, Li L, Zhang HF, Zhang YN,
Zhang PF, Liu XQ, Zhang WD, Huang TT, Zhao L, et al:
Tissue-specific regulation of the contents and correlations of
mineral elements in hens by zinc oxide nanoparticles. Biol Trace
Elem Res. 177:353–366. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zimeri AM, Robb SW, Hassan SM, Hire RR and
Davis MB: Assessing heavy metal and PCB exposure from tap water by
measuring levels in plasma from sporadic breast cancer patients, a
pilot study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 12:15683–15691. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mäkinen VP, Soininen P, Forsblom C,
Parkkonen M, Ingman P, Kaski K, Groop PH; FinnDiane Study Group, ;
Ala-Korpela M: 1H NMR metabonomics approach to the disease
continuum of diabetic complications and premature death. Mol Syst
Biol. 4:1672008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yan G, Huang Y, Bu Q, Lv L, Deng P, Zhou
J, Wang Y, Yang Y, Liu Q, Cen X and Zhao Y: Zinc oxide
nanoparticles cause nephrotoxicity and kidney metabolism
alterations in rats. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst
Environ Eng. 47:577–588. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wan Q, He Q, Deng X, Hao F, Tang H and
Wang Y: Systemic metabolic responses of broiler chickens and
piglets to acute T-2 toxin intravenous exposure. J Agric Food Chem.
64:714–723. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wood RY and Della-Monica NR: Psychosocial
factors influencing breast cancer risk appraisal among older women.
Qual Health Res. 21:783–795. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Salhab M, Bismohun S and Mokbel K:
Risk-reducing strategies for women carrying BRCA1/2 mutations with
a focus on prophylactic surgery. BMC Womens Health. 10:282010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jevtic M, Velicki R, Popovic M,
Cemerlic-Adjic N, Babovic S and Velicki L: Dietary influence on
breast cancer. J BUON. 15:455–461. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ebrahim AM, Eltayeb M, Shaat M, Mohmed NM,
Eltayeb E and Ahmed AY: Study of selected trace elements in
cancerous and non-cancerous human breast tissues from Sudanese
subjects using instrumental neutron activation analysis. Sci Total
Environ. 383:52–58. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Florea AM and Büsselberg D: Metals and
breast cancer: Risk factors or healing agents? J Toxicol.
2011:1596192011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ilychova SA and Zaridze DG: Cancer
mortality among female and male workers occupationally exposed to
inorganic lead in the printing industry. Occup Environ Med.
69:87–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qu W, Tokar EJ, Kim AJ, Bell MW and
Waalkes MP: Chronic cadmium exposure in vitro causes acquisition of
multiple tumor cell characteristics in human pancreatic epithelial
cells. Environ Health Perspect. 120:1265–1271. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cheung MR: Blood lead concentration
correlates with all cause, all cancer and lung cancer mortality in
adults: A population based study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:3105–3108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Person RJ, Tokar EJ, Xu Y, Orihuela R,
Ngalame NN and Waalkes MP: Chronic cadmium exposure in vitro
induces cancer cell characteristics in human lung cells. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 273:281–288. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wadhwa SK, Kazi TG, Afridi HI, Talpur FN
and Naeemullah: Interaction between carcinogenic and
anti-carcinogenic trace elements in the scalp hair samples of
different types of Pakistani female cancer patients. Clin Chim
Acta. 439:178–184. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Byrne C, Divekar SD, Storchan GB, Parodi
DA and Martin MB: Metals and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 18:63–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gartell MJ, Craun JC, Podrebarae DS and
Gunderson ER: Pesticides, selected elements, and other chemicals in
adult total diet samples, October 1980-March 1982. J Assoc Off Anal
Chem. 69:146–159. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gartell MJ, Craun JC, Podrebarae DS and
Gunderson ER: Pesticides, selected elements, and other chemicals in
infant and toddler total diet samples, October 1980-March 1982. J
Assoc Off Anal Chem. 69:123–145. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lucas JM: Burea of mines. US Department of
the Interior. Cadmium. Bulletin. 6711980.
|
|
55
|
Núñez O, Fernández-Navarro P,
Martín-Méndez I, Bel-Lan A, Locutura JF and López-Abente G: Arsenic
and chromium topsoil levels and cancer mortality in Spain. Environ
Sci Pollut Res Int. 23:17664–17675. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Peralta-Videa JR, Lopez ML, Narayan M,
Saupe G and Gardea-Torresdey J: The biochemistry of environmental
heavy metal uptake by plants: Implications for the food chain. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:1665–1677. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Welling R, Beaumont JJ, Petersen SJ,
Alexeeff GV and Steinmaus C: Chromium VI and stomach cancer: A
meta-analysis of the current epidemiological evidence. Occup
Environ Med. 72:151–159. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
ATSDR, . Toxicological profile for
arsenic. Agency for toxic substances and disease registry (ATSDR).
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Atlanta: 2007
|
|
59
|
IARC Arsenic, metals, fibres and dusts.
IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans.
100c. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon: 2012
|
|
60
|
Muszyńska M, Jaworska-Bieniek K, Durda K,
Sukiennicki G, Gromowski T, Jakubowska A, Morawski A and Lubiński
J: Arsenic (As) and breast cancer risk. Hered Cancer Clin Pract.
10:2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Campo L, Vimercati L, Carrus A, Bisceglia
L, Pesatori AC, Bertazzi PA, Assennato G and Fustinoni S:
Environmental and biological monitoring of PAHs exposure in
coke-oven workers at the Taranto plant compared to two groups from
the general population of Apulia, Italy. Med Lav. 103:347–360.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|