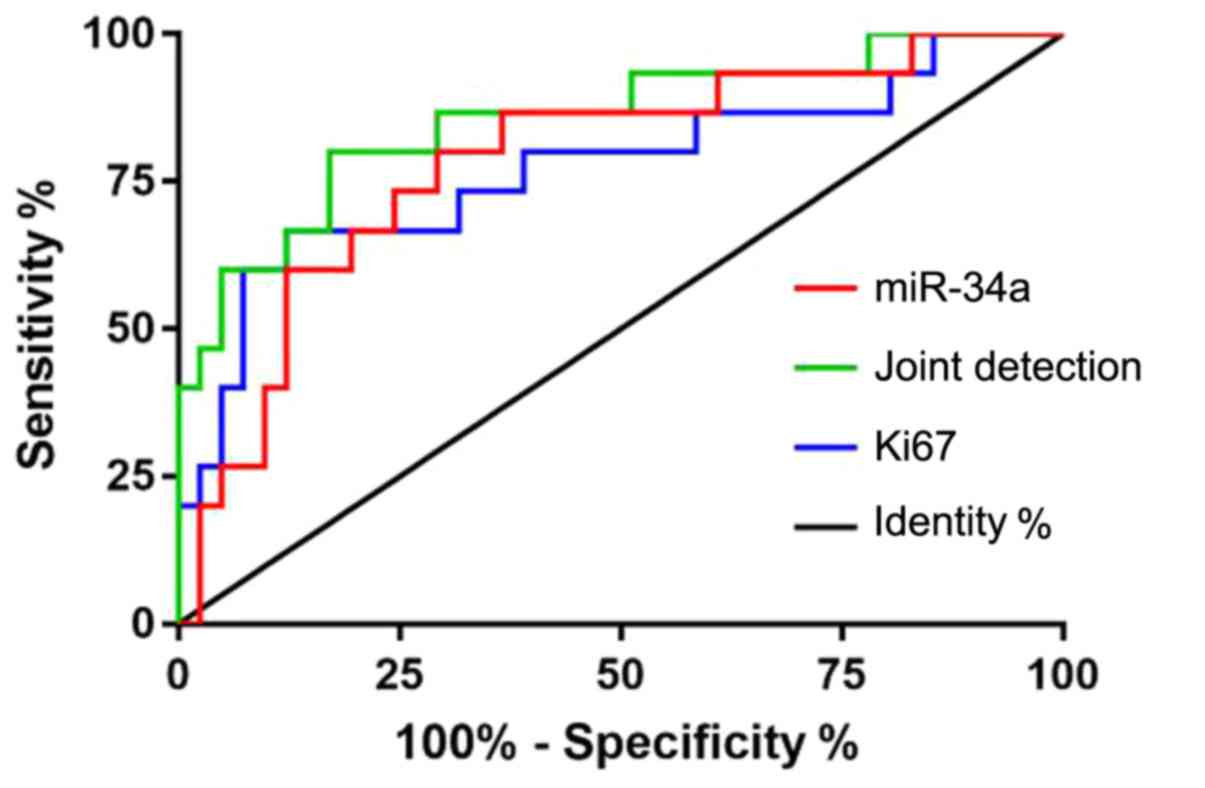
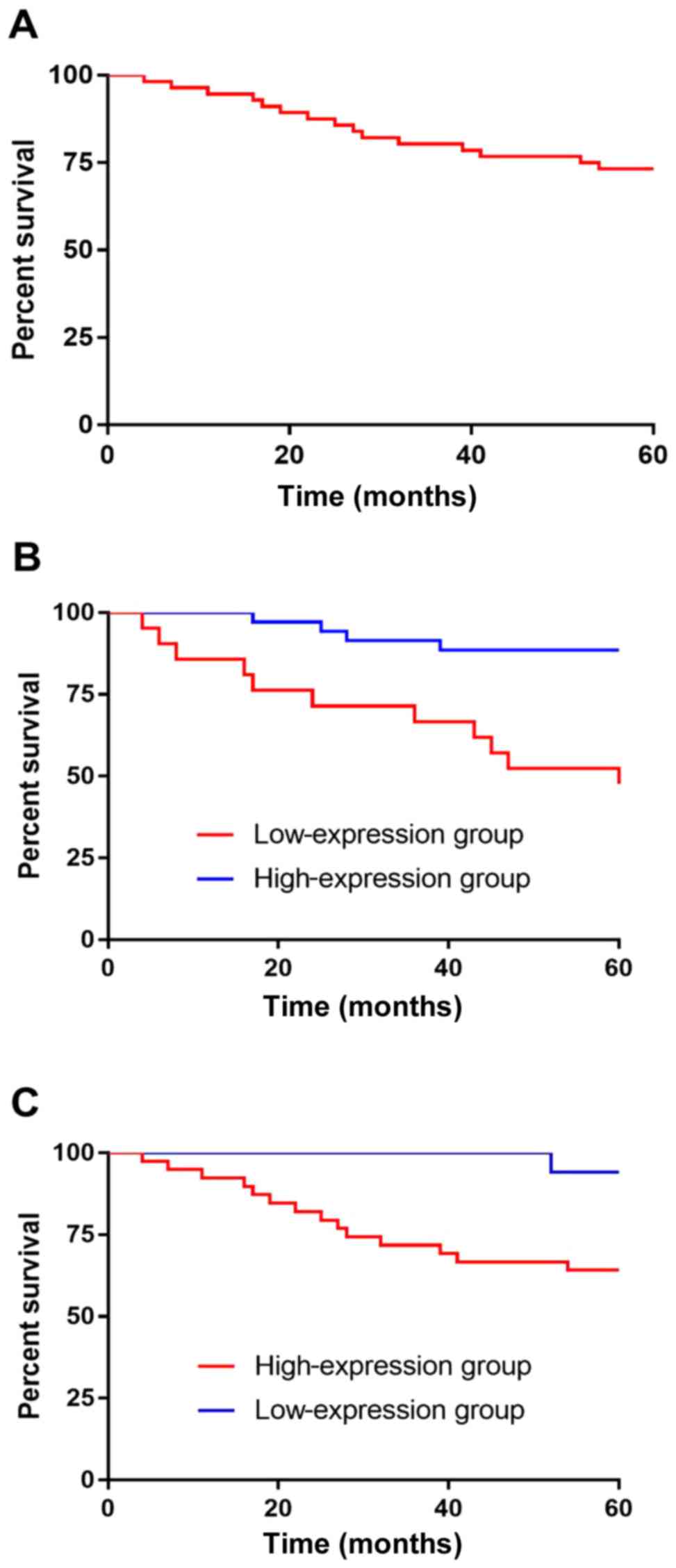
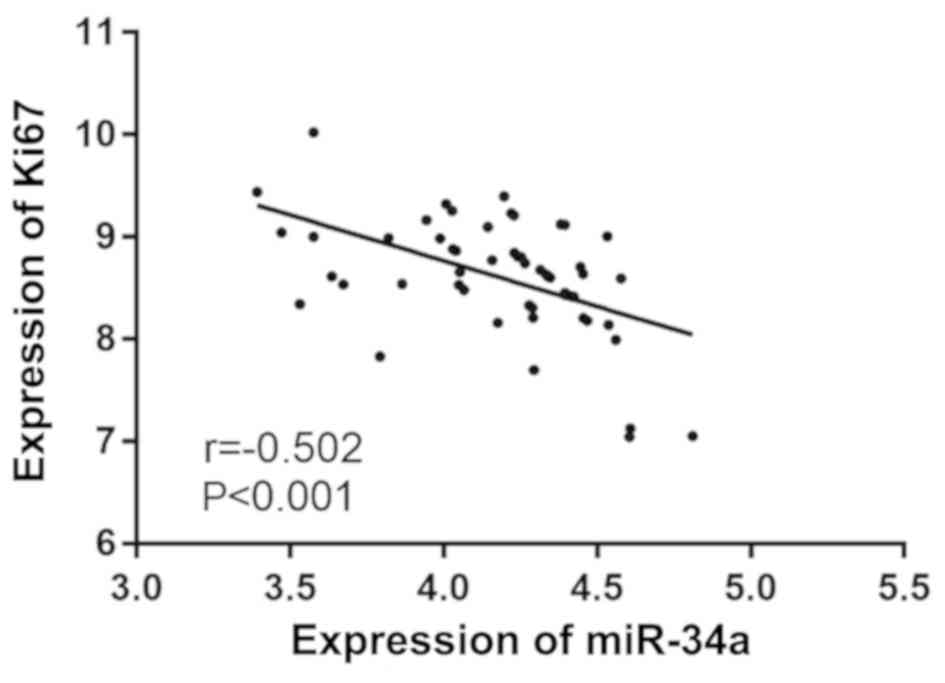
|
1
|
Paul P, Deka H, Malakar AK, Halder B and
Chakraborty S: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Understanding its
molecular biology at a fine scale. Eur J Cancer Prev. 27:33–41.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fu ZT, Guo XL, Zhang SW, Zeng HM, Sun KX,
Chen WQ and He J: Incidence and mortality of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma in China, 2014. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 40:566–571.
2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kong L, Li X, Wang H, He G and Tang A:
Calycosin inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by influencing
EWSAT1 expression to regulate the TRAF6-related pathways. Biomed
Pharmacother. 106:342–348. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang WB, Chan JYW and Liu DL: Human
papillomavirus and World Health Organization type III
nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Multicenter study from an endemic area in
Southern China. Cancer. 124:530–536. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fangzheng W, Chuner J, Lei W, Weijun C,
Min X, Quanquan S, Tongxin L, Aizawa R, Sakamoto M and Zhenfu F:
Outcome and long-term efficacy of four facio-cervical fields
conformal radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:39756–39765. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu LR, Liu YT, Jiang N, Fan YX, Wen J,
Huang SF, Guo WJ, Bian XH, Wang FJ, Li F, et al: Ten-year survival
outcomes for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma receiving
intensity-modulated radiotherapy: An analysis of 614 patients from
a single center. Oral Oncol. 69:26–32. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou Y, Xia L, Lin J, Wang H, Oyang L, Tan
S, Tian Y, Su M, Wang H, Cao D, et al: Exosomes in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. J Cancer. 9:767–777. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Witwer KW and Halushka MK: Toward the
promise of microRNAs - Enhancing reproducibility and rigor in
microRNA research. RNA Biol. 13:1103–1116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng C, Xiaohua W, Ning J, Dan Z,
Chengyun Y, Lijun Z, Li Y, Shengfu H, Hong J and He X: MiR-122
exerts anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects on nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Mol Biol.
64:21–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen L, Gao H, Liang J, Qiao J, Duan J,
Shi H, Zhen T, Li H, Zhang F, Zhu Z, et al: miR-203a-3p promotes
colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting PDE4D.
Am J Cancer Res. 8:2387–2401. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li YY, Tao YW, Gao S, Li P, Zheng JM,
Zhang SE, Liang J and Zhang Y: Cancer-associated fibroblasts
contribute to oral cancer cells proliferation and metastasis via
exosome-mediated paracrine miR-34a-5p. EBioMedicine. 36:209–220.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang C, Zhang J, Ding M, Xu K, Li L, Mao L
and Zheng J: Ki67 targeted strategies for cancer therapy. Clin
Transl Oncol. 20:570–575. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang J, Liu Y, Deng Y, He J, Lang J and
Fan J: Ki67 and nm23 are potential prognostic markers in patients
with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 9:6350–6356.
2016.
|
|
14
|
Chen Q, Guo Z, Liu S, Quan P, Cao X, Guo
L, Zhang S and Sun X: The cancer incidence and mortality among
children and adolescents during the period of 2010–2014 in Henan
Province, China. Cancer Med. 8:814–823. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Wang L, Lou GH, Zeng HR, Hu J,
Huang QW, Peng W and Yang XB: Coptidis Rhizoma: A comprehensive
review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry,
pharmacology and toxicology. Pharm Biol. 57:193–225. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
DeBord LC, Pathak RR, Villaneuva M, Liu
HC, Harrington DA, Yu W, Lewis MT and Sikora AG: The chick
chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) as a versatile patient-derived
xenograft (PDX) platform for precision medicine and preclinical
research. Am J Cancer Res. 8:1642–1660. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Jia L, Tsang CM and Tsao SW: EBV
infection and glucose metabolism in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 1018:75–90. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fangzheng W, Chuner J, Quanquan S, Zhimin
Y, Tongxin L, Jiping L, Sakamoto M, Peng W, Kaiyuan S, Weifeng Q,
et al: Addition of chemotherapy to intensity-modulated radiotherapy
does not improve survival in stage II nasopharyngeal carcinoma
patients. J Cancer. 9:2030–2037. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sanchez Calle A, Kawamura Y, Yamamoto Y,
Takeshita F and Ochiya T: Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in
cancer. Cancer Sci. 109:2093–2100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang G, Du MY, Zhu H, Zhang N, Lu ZW,
Qian LX, Zhang W, Tian X, He X and Yin L: MiRNA-34a reversed
TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via suppression of
SMAD4 in NPC cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 106:217–224. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klöppel G and La Rosa S: Ki67 labeling
index: Assessment and prognostic role in gastroenteropancreatic
neuroendocrine neoplasms. Virchows Arch. 472:341–349. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shan GP, Wang BB, Zheng P, Du FL and Yang
YW: Efficacy and safety of chemotherapy combined with stereotactic
radiotherapy in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Med Sci
Monit. 23:5630–5636. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guan GF, Zhang DJ, Wen LJ, Yu DJ, Zhao Y,
Zhu L, Guo YY and Zheng Y: Prognostic value of TROP2 in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:10995–11004.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao L, Chen H, Hu B, Zhang H and Lin Q:
Prognostic significance of Ki67 expression and the derived
neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer
Manag Res. 10:1919–1926. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao Y and Shen L, Huang X, Jing D, Huang
D, Fu J, Li Z, Zhang G and Shen L: High expression of Ki-67 acts a
poor prognosis indicator in locally advanced nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 494:390–396. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|