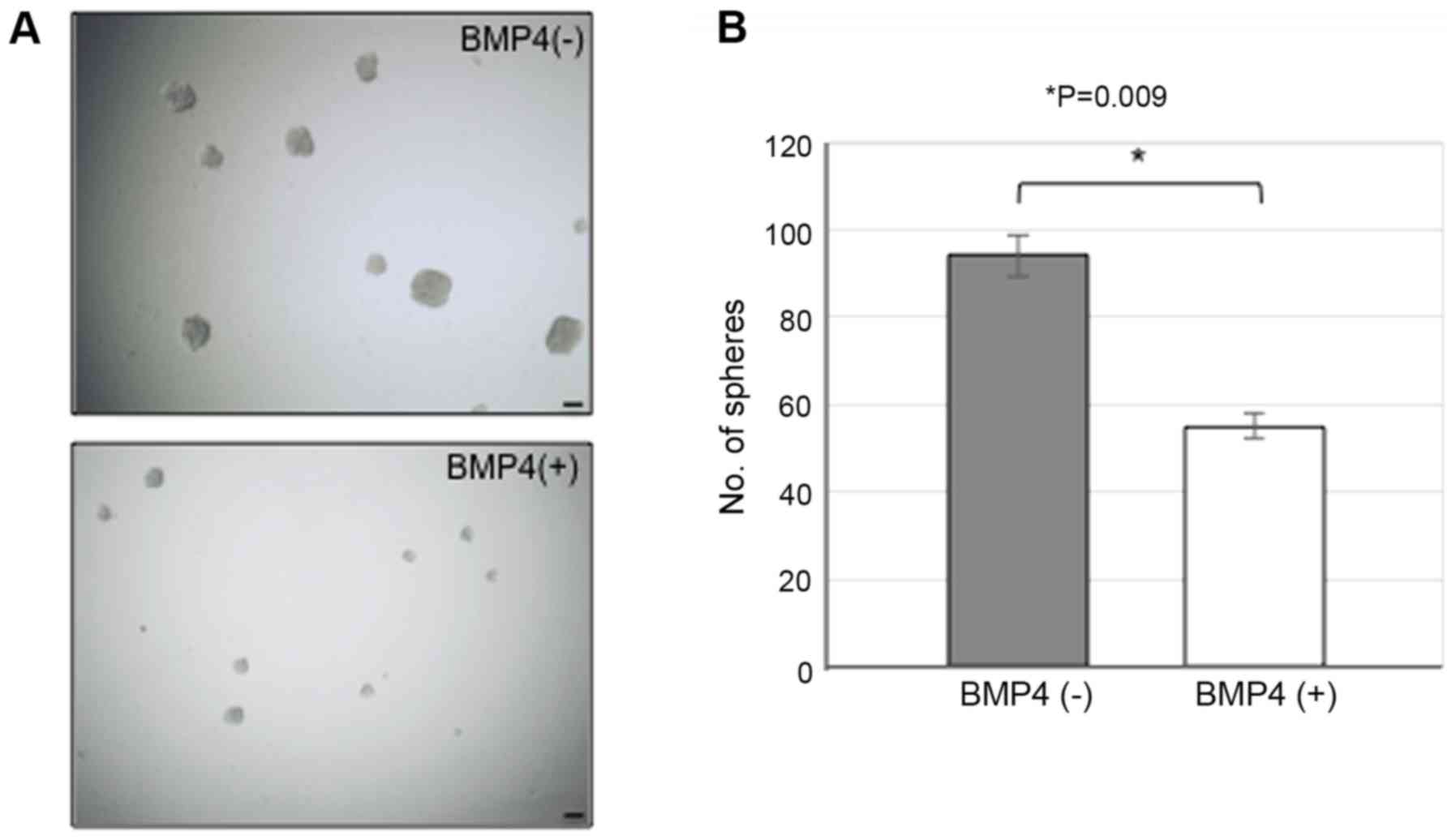
|
1
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent
MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B,
Belanger K, et al: Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and
adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in
glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of
the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:459–466. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rasras S, Zibara K, Vosughi T and Zayeri
ZD: Genetics and epigenetics of glioblastoma: Therapeutic
challenges. Clin Cancer Invest J. 7:43–49. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Deris Zayeri Z, Tahmasebi Birgani M,
Mohammadi Asl J, Kashipazha D and Hajjari M: A novel infram
deletion in MSH6 gene in glioma: Conversation on MSH6 mutations in
brain tumors. J Cell Physiol. 234:11092–11102. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Antoniou A, Hébrant A, Dom G, Dumont JE
and Maenhaut C: Cancer stem cells, a fuzzy evolving concept: A cell
population or a cell property? Cell Cycle. 12:3743–3748. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dalerba P, Cho RW and Clarke MF: Cancer
stem cells: Models and concepts. Annu Rev Med. 58:267–284. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang T, Shigdar S, Gantier MP, Hou Y, Wang
L, Li Y, Shamaileh HA, Yin W, Zhou SF, Zhao X and Duan W: Cancer
stem cell targeted therapy: Progress amid controversies.
Oncotarget. 6:44191–44206. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Soeda A, Hara A, Kunisada T, Yoshimura S,
Iwama T and Park DM: The evidence of glioblastoma heterogeneity.
Sci Rep. 5:79792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA,
Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman RM, Cusimano MD and Dirks PB:
Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature.
432:396–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sampetrean O and Saya H: Characteristics
of glioma stem cells. Brain Tumor Pathol. 30:209–214. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q,
Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Glioma stem
cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA
damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bleau AM, Hambardzumyan D, Ozawa T,
Fomchenko EI, Huse JT, Brennan CW and Holland EC: PTEN/PI3K/Akt
pathway regulates the side population phenotype and ABCG2 activity
in glioma tumor stem-like cells. Cell Stem Cell. 4:226–235. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cheng L, Bao S and Rich JN: Potential
therapeutic implications of cancer stem cells in glioblastoma.
Biochem Pharmacol. 80:654–665. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sunayama J, Sato A, Matsuda K, Tachibana
K, Watanabe E, Seino S, Suzuki K, Narita Y, Shibui S, Sakurada K,
et al: FoxO3a functions as a key integrator of cellular signals
that control glioblastoma stem-like cell differentiation and
tumorigenicity. Stem Cells. 29:1327–1337. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sato A, Sunayama J, Okada M, Watanabe E,
Seino S, Shibuya K, Suzuki K, Narita Y, Shibui S, Kayama T and
Kitanaka C: Glioma-initiating cell elimination by metformin
activation of FOXO3 via AMPK. Stem Cells Transl Med. 1:811–824.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bidlingmaier S, Zhu X and Liu B: The
utility and limitations of glycosylated human CD133 epitopes in
defining cancer stem cells. J Mol Med (Berl). 86:1025–1032. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: Identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bao S, Wu Q, Li Z, Sathornsumetee S, Wang
H, McLendon RE, Hjelmeland AB and Rich JN: Targeting cancer stem
cells through L1CAM suppresses glioma growth. Cancer Res.
68:6043–6048. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dreesen O and Brivanlou AH: Signaling
pathways in cancer and embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. 3:7–17.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eyler CE, Foo WC, LaFiura KM, McLendon RE,
Hjelmeland AB and Rich JN: Brain cancer stem cells display
preferential sensitivity to Akt inhibition. Stem Cells.
26:3027–3036. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gallia GL, Tyler BM, Hann CL, Siu IM,
Giranda VL, Vescovi AL, Brem H and Riggins GJ: Inhibition of Akt
inhibits growth of glioblastoma and glioblastoma stem-like cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 8:386–393. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fan X, Khaki L, Zhu TS, Soules ME, Talsma
CE, Gul N, Koh C, Zhang J, Li YM, Maciaczyk J, et al: NOTCH pathway
blockade depletes CD133-positive glioblastoma cells and inhibits
growth of tumor neurospheres and xenografts. Stem Cells. 28:5–16.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xiao YT, Xiang LX and Shao JZ: Bone
morphogenetic protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 362:550–553.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiao L, Michalski N, Kronander E, Gjoni E,
Genoud C, Knott G and Schneggenburger R: BMP signaling specifies
the development of a large and fast CNS synapse. Nat Neurosci.
16:856–864. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lim DA, Tramontin AD, Trevejo JM, Herrera
DG, García-Verdugo JM and Alvarez-Buylla A: Noggin antagonizes BMP
signaling to create a niche for adult neurogenesis. Neuron.
28:713–726. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Johnston MA and Lim DA: Keeping them
quiet: BMPs maintain adult neural stem cell quiescence. Cell Stem
Cell. 7:9–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qi X, Li TG, Hao J, Hu J, Wang J, Simmons
H, Miura S, Mishina Y and Zhao GQ: BMP4 supports self-renewal of
embryonic stem cells by inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:6027–6032. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xi G, Best B, Mania-Farnell B, James CD
and Tomita T: Therapeutic potential for bone morphogenetic protein
4 in human malignant glioma. Neoplasia. 19:261–270. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee J, Son MJ, Woolard K, Donin NM, Li A,
Cheng CH, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Walling J, Ahn S, et al:
Epigenetic-mediated dysfunction of the bone morphogenetic protein
pathway inhibits differentiation of glioblastoma-initiating cells.
Cancer Cell. 13:69–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bonaguidi MA: LIF and BMP signaling
generate separate and discrete types of GFAP-expressing cells.
Development. 132:5503–5514. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Piccirillo SG, Reynolds BA, Zanetti N,
Lamorte G, Binda E, Broggi G, Brem H, Olivi A, Dimeco F and Vescovi
AL: Bone morphogenetic proteins inhibit the tumorigenic potential
of human brain tumour-initiating cells. Nature. 444:761–765. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Morrison SJ and Kimble J: Asymmetric and
symmetric stem-cell divisions in development and cancer. Nature.
441:1068–1074. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bajaj J, Zimdahl B and Reya T: Fearful
symmetry: Subversion of asymmetric division in cancer development
and progression. Cancer Res. 75:792–797. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wakimoto H, Mohapatra G, Kanai R, Curry WT
Jr, Yip S, Nitta M, Patel AP, Barnard ZR, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO,
Louis DN, et al: Maintenance of primary tumor phenotype and
genotype in glioblastoma stem cells. Neuro Oncol. 14:132–144. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lathia JD, Hitomi M, Gallagher J, Gadani
SP, Adkins J, Vasanji A, Liu L, Eyler CE, Heddleston JM, Wu Q, et
al: Distribution of CD133 reveals glioma stem cells self-renew
through symmetric and asymmetric cell divisions. Cell Death Dis.
2:e2002011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Beier D, Hau P, Proescholdt M, Lohmeier A,
Wischhusen J, Oefner PJ, Aigner L, Brawanski A, Bogdahn U and Beier
CP: CD133(+) and CD133(−) glioblastoma-derived cancer stem cells
show differential growth characteristics and molecular profiles.
Cancer Res. 67:4010–4015. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Joo KM, Kim SY, Jin X, Song SY, Kong DS,
Lee JI, Jeon JW, Kim MH, Kang BG, Jung Y, et al: Clinical and
biological implications of CD133-positive and CD133-negative cells
in glioblastomas. Lab Invest. 88:808–815. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Makyio H, Ohgi M, Takei T, Takahashi S,
Takatsu H, Katoh Y, Hanai A, Ueda T, Kanaho Y, Xie Y, et al:
Structural basis for Arf6-MKLP1 complex formation on the Flemming
body responsible for cytokinesis. EMBO J. 31:2590–2603. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu B, Chen Q, Tian D, Wu L, Dong H, Wang
J, Ji B, Zhu X, Cai Q, Wang L and Zhang S: BMP4 reverses multidrug
resistance through modulation of BCL-2 and GDNF in glioblastoma.
Brain Res. 1507:115–124. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rahman M, Azari H, Deleyrolle L, Millette
S, Zeng H and Reynolds BA: Controlling tumor invasion: Bevacizumab
and BMP4 for glioblastoma. Future Oncol. 9:1389–1396. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang J, Sakariassen PØ, Tsinkalovsky O,
Immervoll H, Bøe SO, Svendsen A, Prestegarden L, Røsland G, Thorsen
F, Stuhr L, et al: CD133 negative glioma cells form tumors in nude
rats and give rise to CD133 positive cells. Int J Cancer.
122:761–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wei Y, Jiang Y, Zou F, Liu Y, Wang S, Xu
N, Xu W, Cui C, Xing Y, Liu Y, et al: Activation of PI3K/Akt
pathway by CD133-p85 interaction promotes tumorigenic capacity of
glioma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:6829–6834. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li Z: CD133: A stem cell biomarker and
beyond. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2:172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Izumi H, Li Y, Shibaki M, Mori D, Yasunami
M, Sato S, Matsunaga H, Mae T, Kodama K, Kamijo T, et al: Recycling
endosomal CD133 functions as an inhibitor of autophagy at the
pericentrosomal region. Sci Rep. 9:22362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Neumüller RA and Knoblich JA: Dividing
cellular asymmetry: Asymmetric cell division and its implications
for stem cells and cancer. Genes Dev. 23:2675–2699. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cicalese A, Bonizzi G, Pasi CE, Faretta M,
Ronzoni S, Giulini B, Brisken C, Minucci S, Di Fiore PP and Pelicci
PG: The tumor suppressor p53 regulates polarity of self-renewing
divisions in mammary stem cells. Cell. 138:1083–1095. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen G, Kong J, Tucker-Burden C, Anand M,
Rong Y, Rahman F, Moreno CS, Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG and Brat
DJ: Human Brat ortholog TRIM3 is a tumor suppressor that regulates
asymmetric cell division in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 74:4536–4548.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tominaga K, Minato H, Murayama T, Sasahara
A, Nishimura T, Kiyokawa E, Kanauchi H, Shimizu S, Sato A, Nishioka
K, et al: Semaphorin signaling via MICAL3 induces symmetric cell
division to expand breast cancer stem-like cells. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 116:625–630. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Spike BT and Wahl GM: p53, Stem cells, and
reprogramming: Tumor suppression beyond guarding the genome. Genes
Cancer. 2:404–419. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|