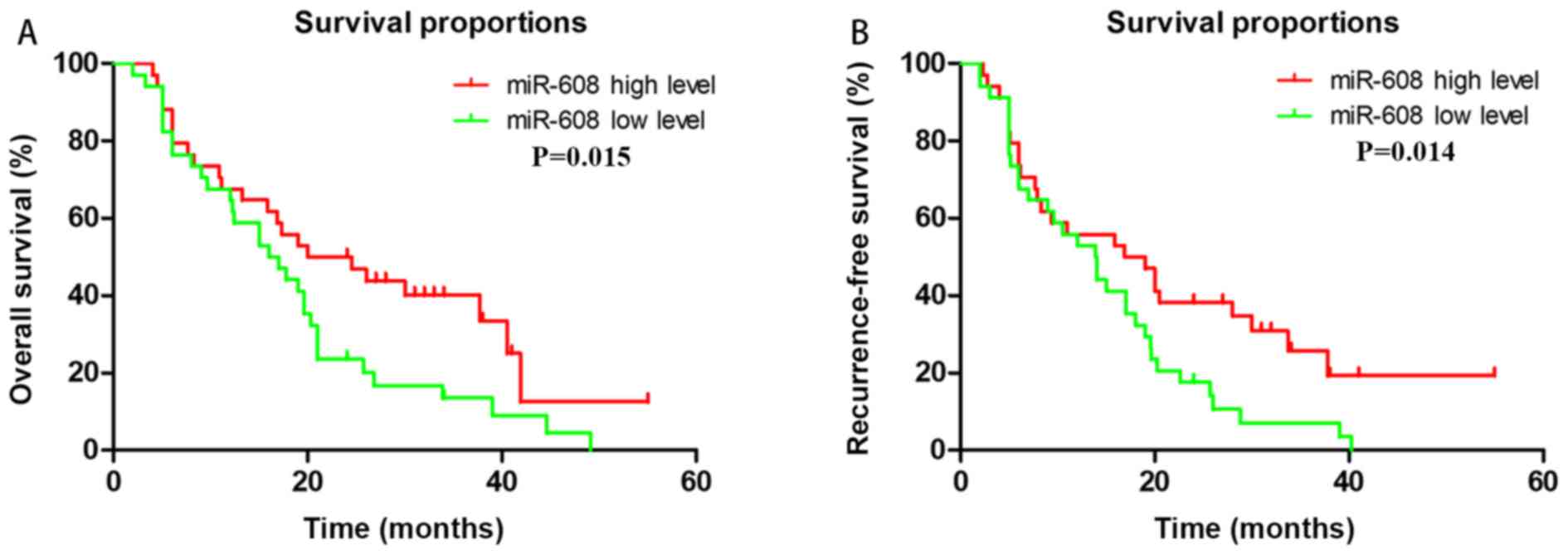
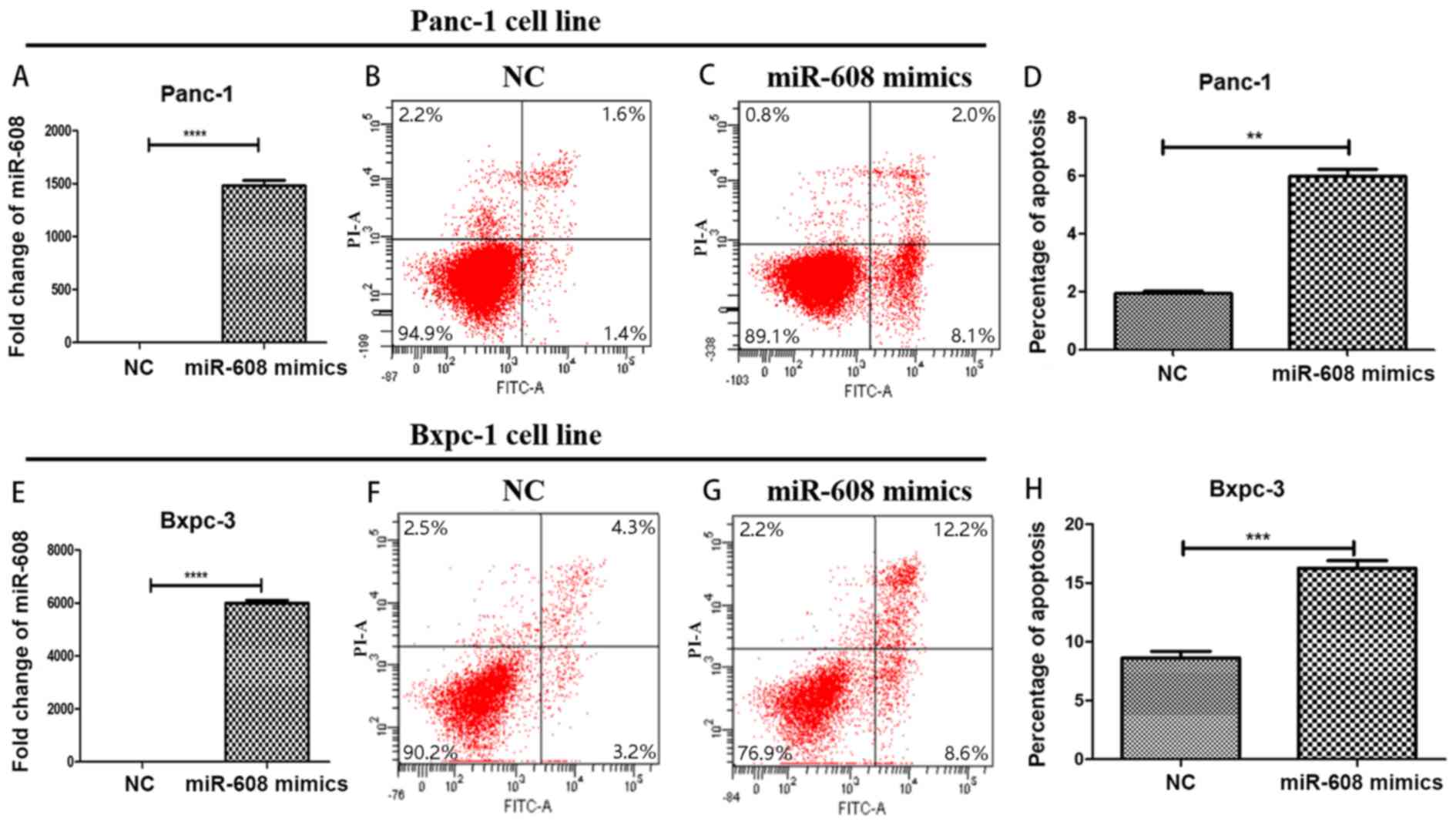
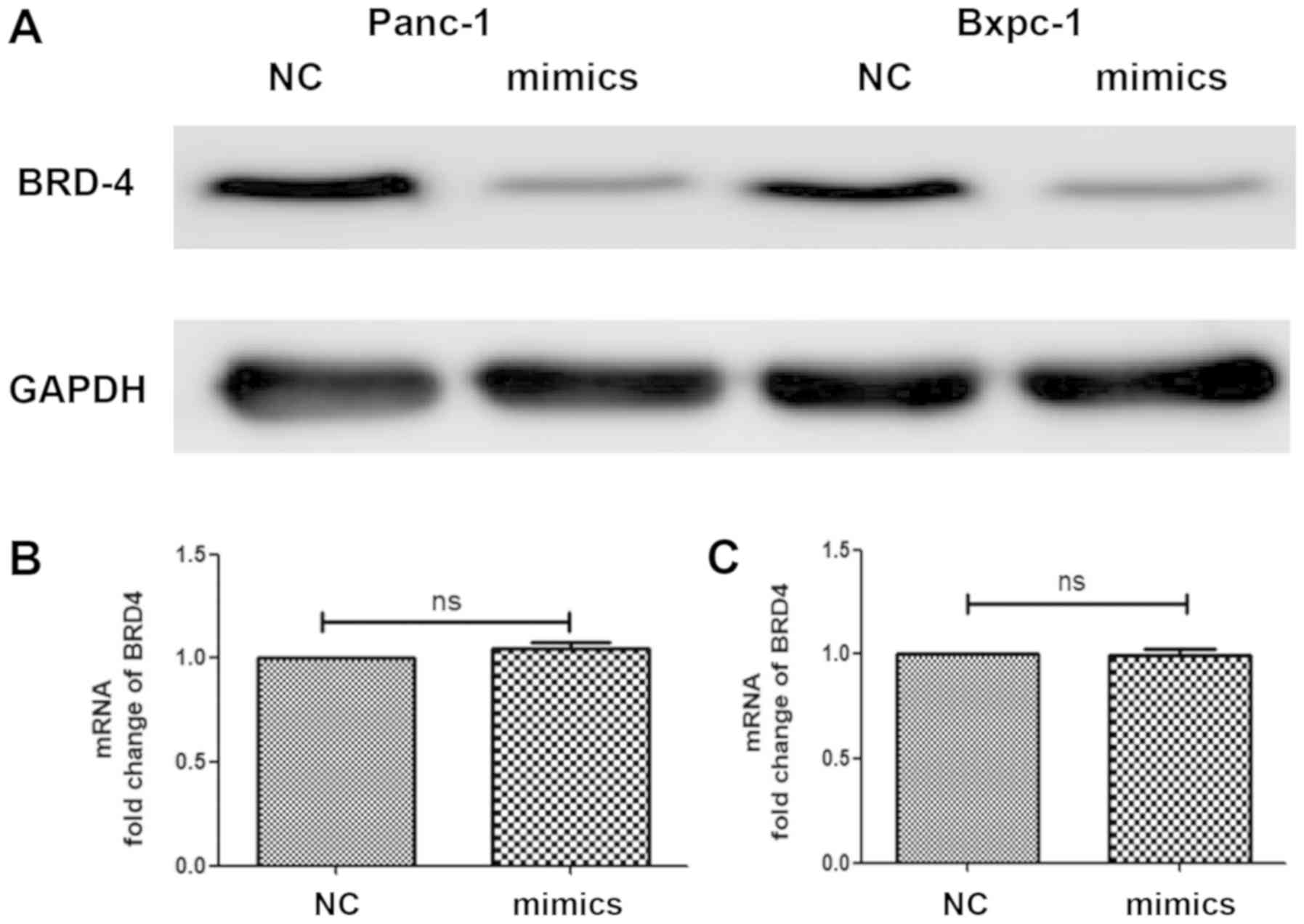
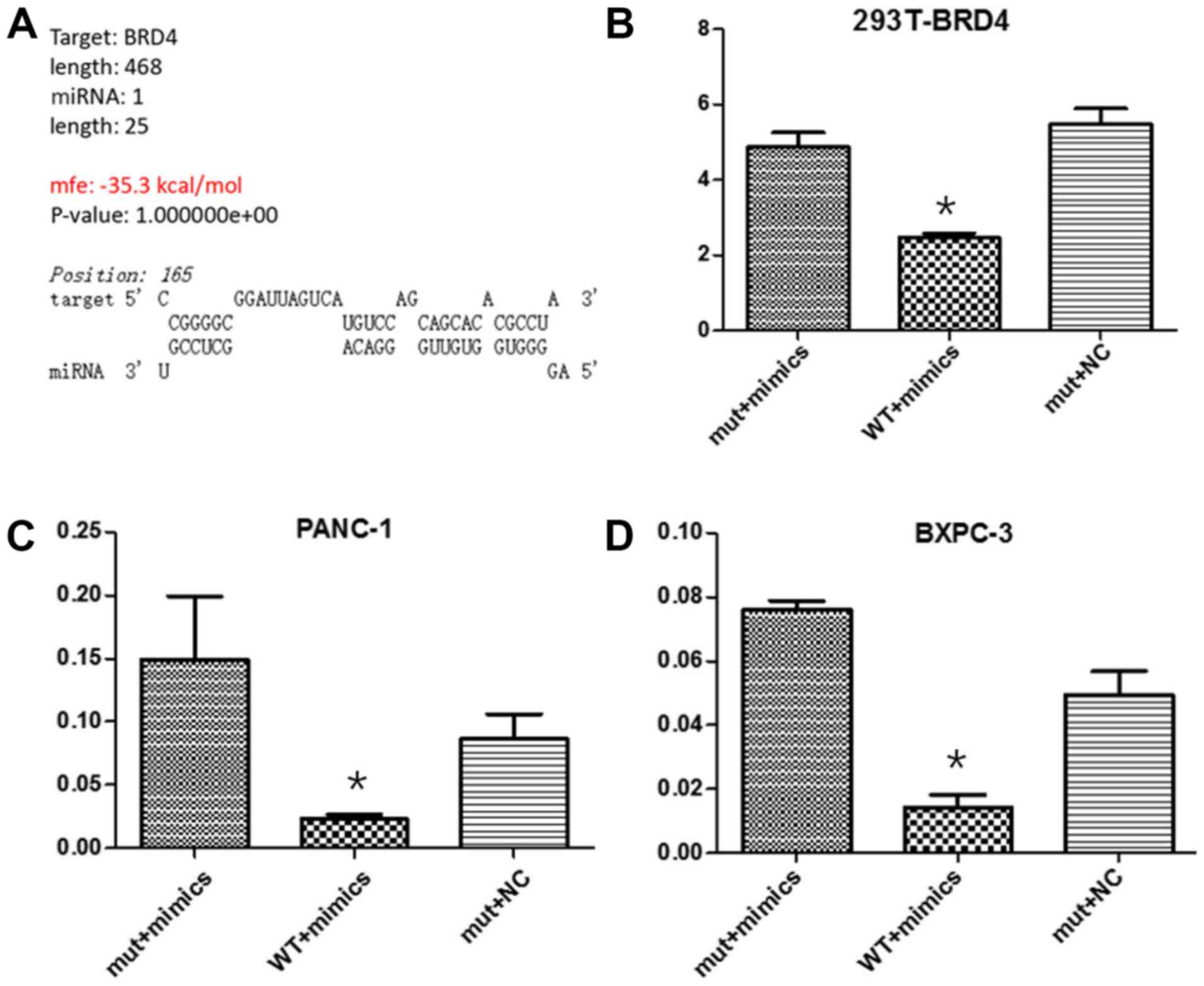
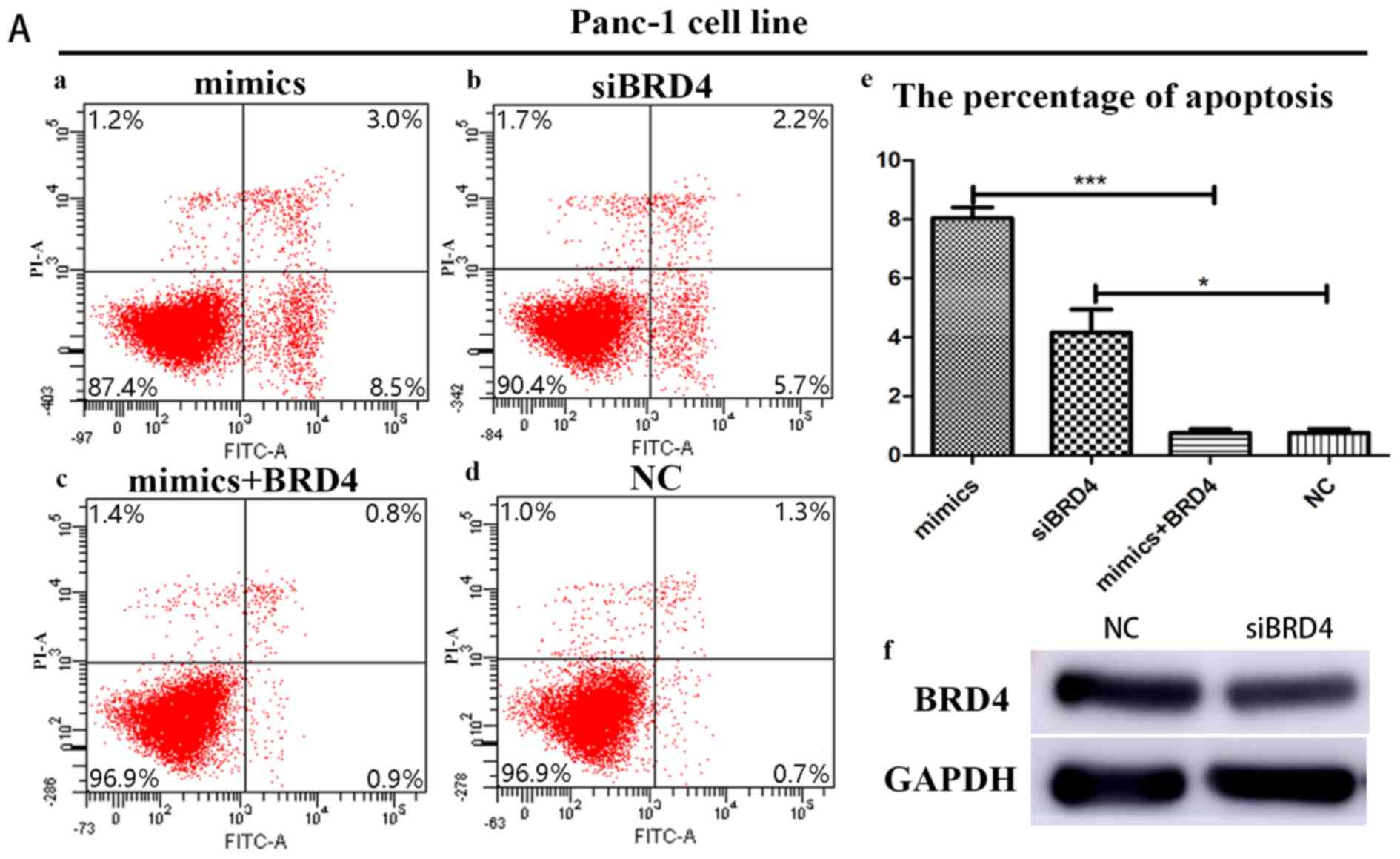
|
1
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Berezikov E, van Tetering G, Verheul M,
van de Belt J, van Laake L, Vos J, Verloop R, van de Wetering M,
Guryev V, Takada S, et al: Many novel mammalian microRNA candidates
identified by extensive cloning and RAKE analysis. Genome Res.
16:1289–1298. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hata A and Lieberman J: Dysregulation of
microRNA biogenesis and gene silencing in cancer. Sci Signal.
8:re32015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stratford JK, Bentrem DJ, Anderson JM, Fan
C, Volmar KA, Marron JS, Routh ED, Caskey LS, Samuel JC, Der CJ, et
al: A six-gene signature predicts survival of patients with
localized pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. PLoS Med.
7:e10003072010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Collisson EA, Sadanandam A, Olson P, Gibb
WJ, Truitt M, Gu S, Cooc J, Weinkle J, Kim GE, Jakkula L, et al:
Subtypes of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and their differing
responses to therapy. Nat Med. 17:500–503. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Donahue TR, Tran LM, Hill R, Li Y,
Kovochich A, Calvopina JH, Patel SG, Wu N, Hindoyan A, Farrell JJ,
et al: Integrative survival-based molecular profiling of human
pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1352–1363. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
AJCC 7th Edition Cancer Staging Manual.
https://cancerstaging.org/references-tools/deskreferences/Documents/AJCC%207th%20Ed%20Cancer%20Staging%20Manual.pdfApril
10–2019
|
|
12
|
Li D, Liu H, Li Y, Yang M, Qu C, Zhang Y,
Liu Y and Zhang X: Identification of suitable endogenous control
genes for quantitative RT-PCR analysis of miRNA in bovine solid
tissues. Mol Biol Rep. 41:6475–6480. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma W, Li T, Wu S, Li J, Wang X and Li H:
LOX and ACSL5 as potential relapse markers for pancreatic cancer
patients. Cancer Biol Ther. 20:787–798. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jung M, Gelato KA, Fernández-Montalván A,
Siegel S and Haendler B: Targeting BET bromodomains for cancer
treatment. Epigenomics. 7:487–501. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sahraei M, Chaube B, Liu Y, Sun J, Kaplan
A, Price NL, Ding W, Oyaghire S, García-Milian R, Mehta S, et al:
Suppressing miR-21 activity in tumor-associated macrophages
promotes an antitumor immune response. J Clin Invest.
129:5518–5536. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Juang V, Chang CH, Wang CS, Wang HE and Lo
YL: pH-Responsive PEG-shedding and targeting peptide-modified
nanoparticles for dual-delivery of irinotecan and microRNA to
enhance tumor-specific therapy. Small. 15:e19032962019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Basu A, Jiang X, Negrini M and Haldar S:
MicroRNA-mediated regulation of pancreatic cancer cell
proliferation. Oncol Lett. 1:565–568. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liang Z, Wang X, Xu X, et al: MicroRNA-608
inhibits proliferation of bladder cancer via AKT/FOXO3a signaling
pathway. Mol Cancer. 16:962017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang H, Li Q, Niu J, Li B, Jiang D, Wan Z,
Yang Q, Jiang F, Wei P and Bai S: microRNA-342-5p and miR-608
inhibit colon cancer tumorigenesis by targeting NAA10. Oncotarget.
7:2709–2720. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Z, Xue Y, Wang P, Zhu J and Ma J:
MiR-608 inhibits the migration and invasion of glioma stem cells by
targeting macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Oncol Rep.
35:2733–2742. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang K, Liang Q, Wei L, Zhang W and Zhu P:
MicroRNA-608 acts as a prognostic marker and inhibits the cell
proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by macrophage migration
inhibitory factor. Tumour Biol. 37:3823–3830. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Othman N and Nagoor NH: miR-608 regulates
apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma via regulation of AKT2. Int
J Oncol. 51:1757–1764. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Filippakopoulos P, Qi J, Picaud S, Shen Y,
Smith WB, Fedorov O, Morse EM, Keates T, Hickman TT, Felletar I, et
al: Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature.
468:1067–1073. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Delmore JE, Issa GC, Lemieux ME, et al:
BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target
c-Myc. Cell. 146:904–917. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:1202–1207. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Seggerson K, Tang L and Moss EG: Two
genetic circuits repress the Caenorhabditis elegans heterochronic
gene lin-28 after translation initiation. Dev Biol. 243:215–225.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|