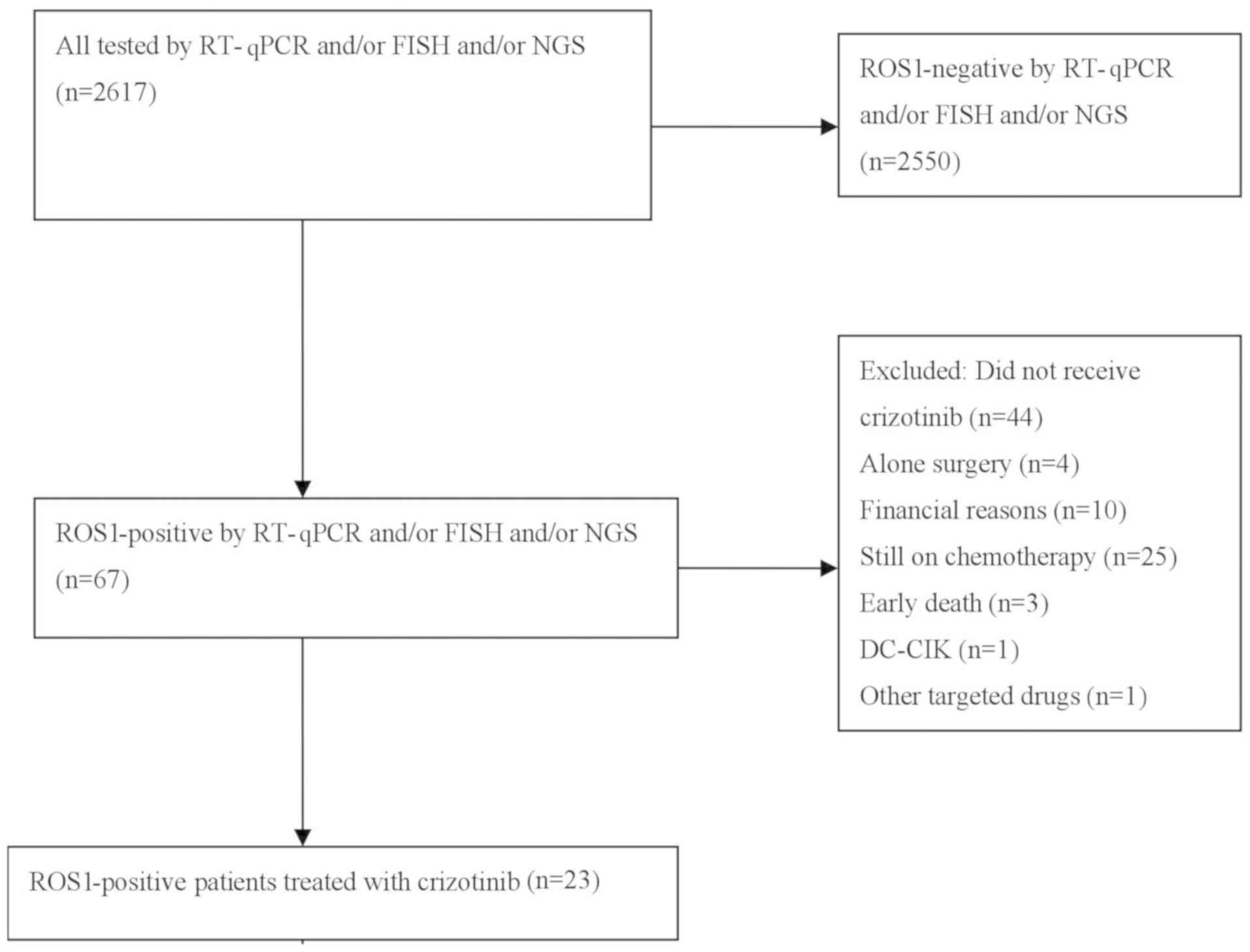
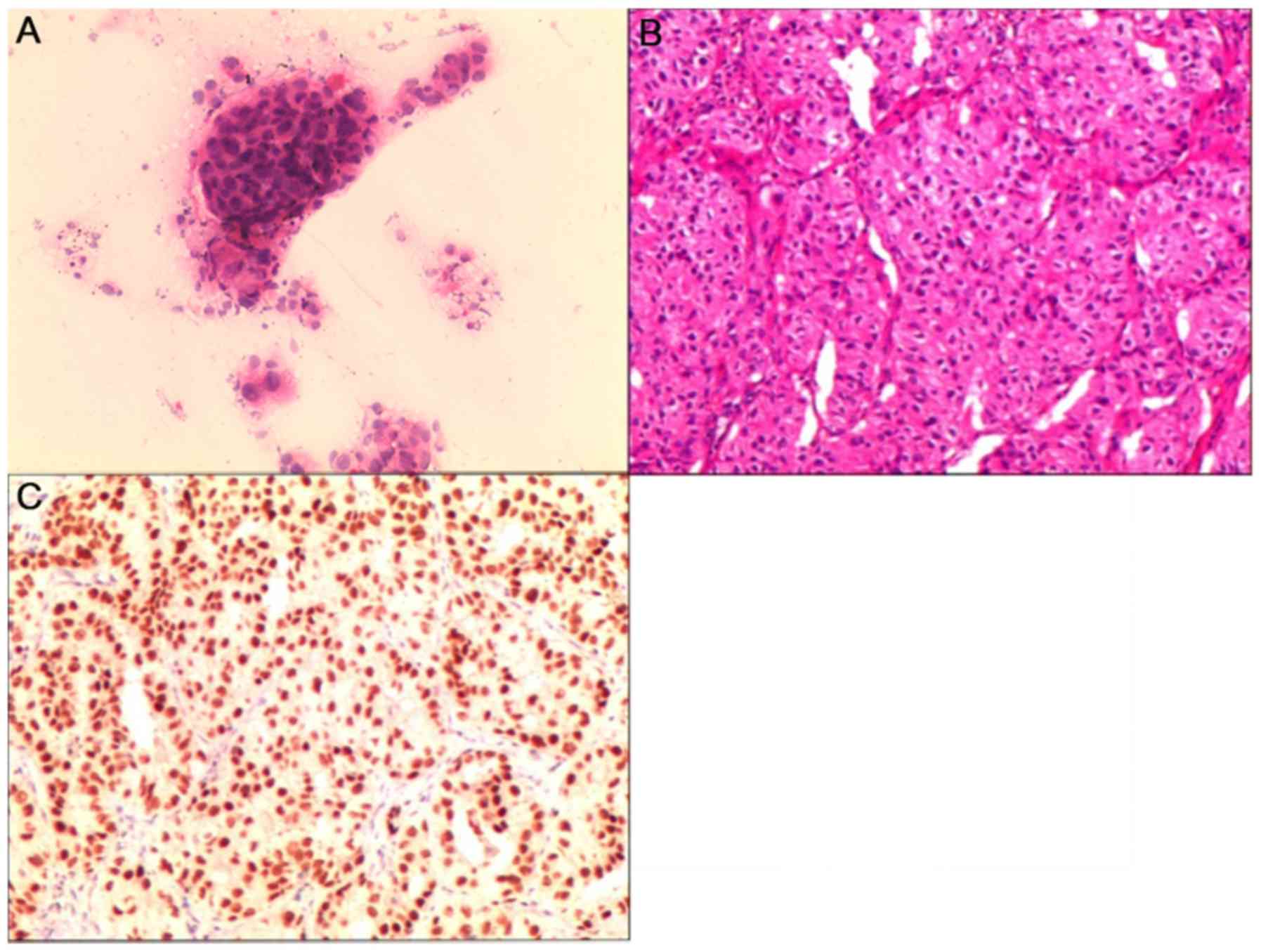
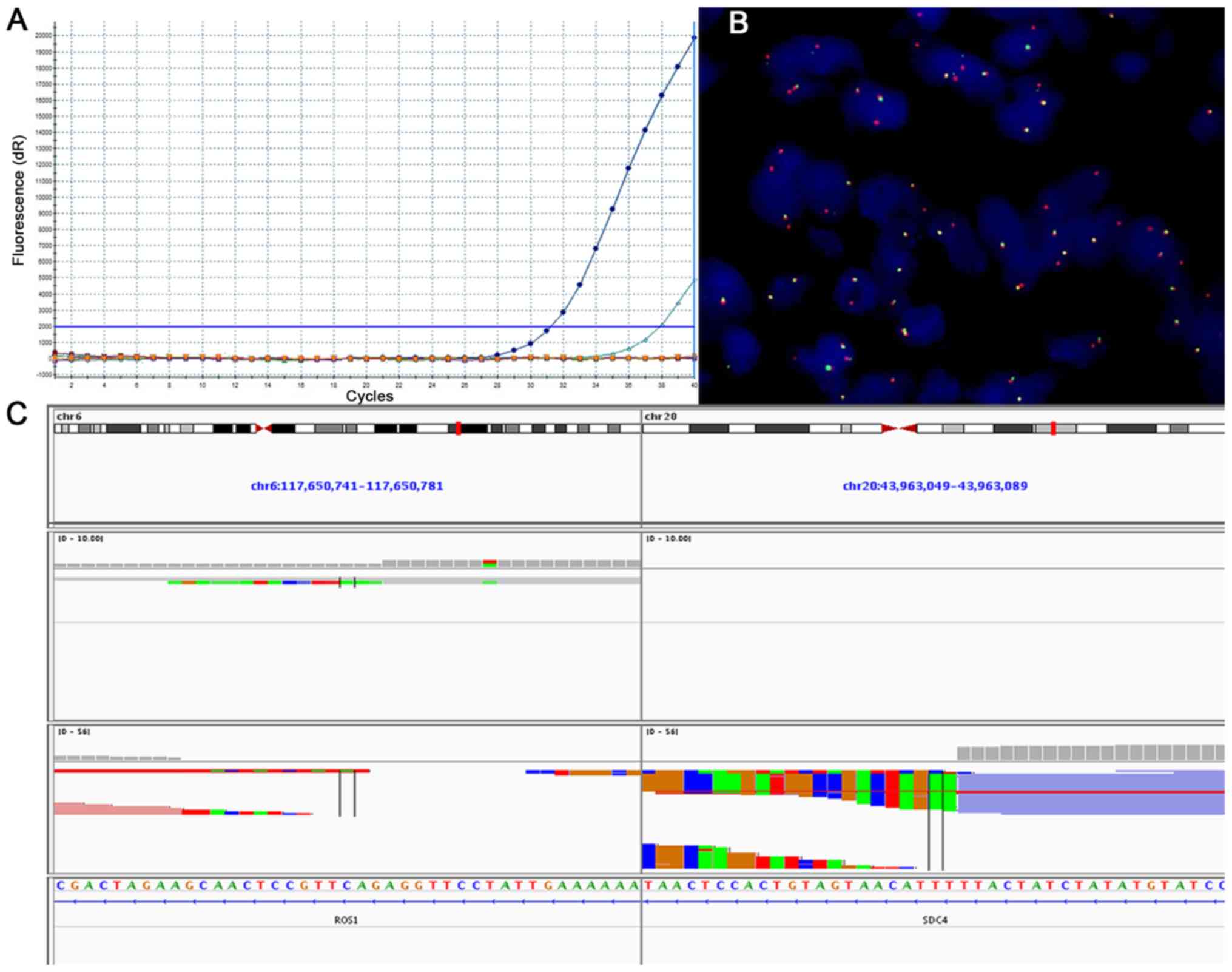
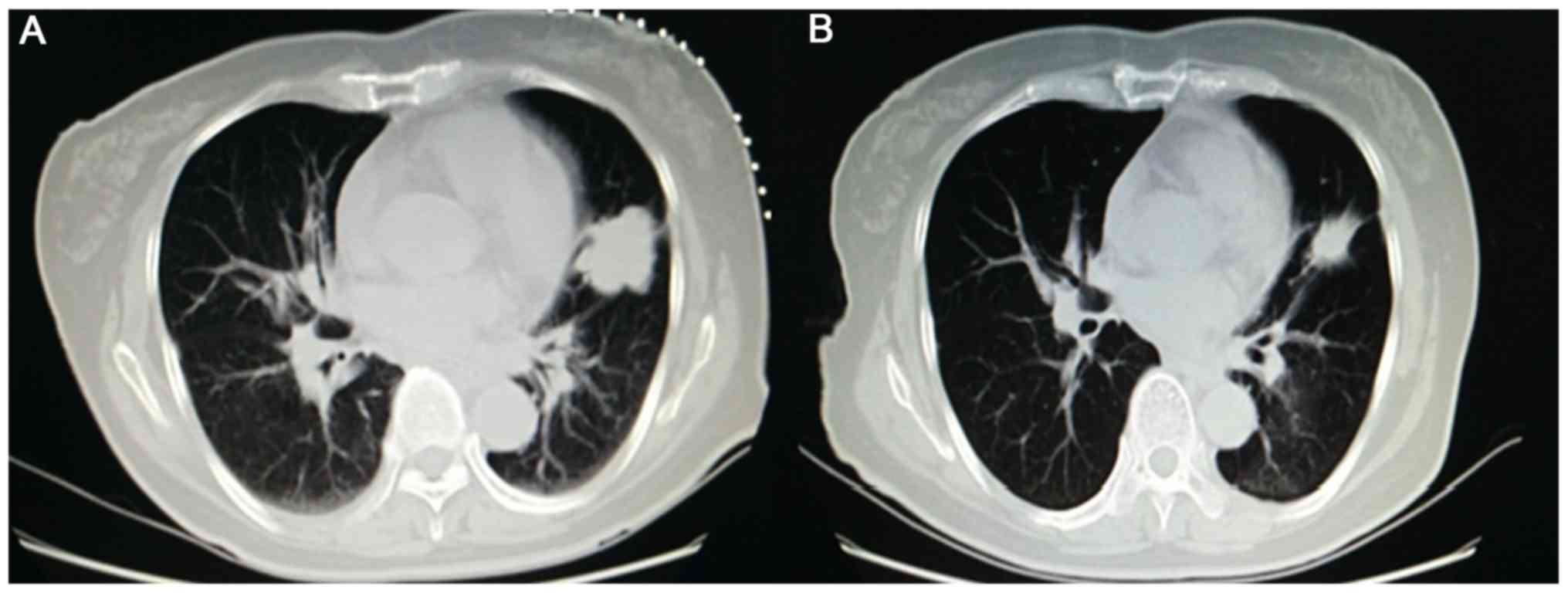
|
1
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R,
Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat
SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al: Activating mutations in the
epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of
non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med.
350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S, Srinivasan
S, Tsai CM, Khoa MT, Heeroma K, Itoh Y, Cornelio G and Yang PC: A
prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in
Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of
adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol. 9:154–162.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Beasley MB, Chitale
DA, Dacic S, Giaccone G, Jenkins RB, Kwiatkowski DJ, Saldivar JS,
Squire J, et al: Molecular testing guideline for selection of lung
cancer patients for EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors:
Guideline from the College of American pathologists, international
association for the study of lung cancer, and association for
molecular pathology. J Thorac Oncol. 8:823–859. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wood K, Hensing T, Malik R and Salgia R:
Prognostic and predictive value in KRAS in non-small-cell lung
cancer: A review. JAMA Oncol. 2:805–812. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Ou SH, Katayama R,
Lovly CM, McDonald NT, Massion PP, Siwak-Tapp C, Gonzalez A, Fang
R, et al: ROS1 rearrangements define a unique molecular class of
lung cancers. J Clin Oncol. 30:863–870. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davies KD, Le AT, Theodoro MF, Skokan MC,
Aisner DL, Berge EM, Terracciano LM, Cappuzzo F, Incarbone M,
Roncalli M, et al: Identifying and targeting ROS1 gene fusions in
non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:4570–4579. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network:
Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature.
511:543–550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ou SH, Chalmers ZR, Azada MC, Ross JS,
Stephens PJ, Ali SM and Miller VA: Identification of a novel
TMEM106B-ROS1 fusion variant in lung adenocarcinoma by
comprehensive genomic profiling. Lung Cancer. 88:352–354. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu VW, Upadhyay D, Schrock AB, Gowen K,
Ali SM and Ou SH: TPD52L1-ROS1, a new ROS1 fusion variant in lung
adenosquamous cell carcinoma identified by comprehensive genomic
profiling. Lung Cancer. 97:48–50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara
S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, Gemma A, Harada M, Yoshizawa H, Kinoshita I,
et al: Geftinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with
mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 362:2380–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shaw AT, Ou SH, Bang YJ, Camidge DR,
Solomon BJ, Salgia R, Riely GJ, Varella-Garcia M, Shapiro GI, Costa
DB, et al: Crizotinib in ROS1-rearranged non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 371:1963–1971. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mazières J, Zalcman G, Crinò L, Biondani
P, Barlesi F, Filleron T, Dingemans AM, Léna H, Monnet I,
Rothschild SI, et al: Crizotinib therapy for advanced lung
adenocarcinoma and a ROS1 rearrangement: Results from the EUROS1
cohort. J Clin Oncol. 33:992–999. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chansky K, Detterbeck FC, Nicholson AG,
Rusch VW, Vallières E, Groome P, Kennedy C, Krasnik M, Peake M,
Shemanski L, et al: The IASLC lung cancer staging project: External
validation of the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the eighth
edition of the TNM classification of lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol.
12:1109–1121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, Possemato A, Yu
J, Haack H, Nardone J, Lee K, Reeves C, Li Y, et al: Global survey
of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung
cancer. Cell. 131:1190–1203. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rimkunas VM, Crosby KE, Li D, Hu Y, Kelly
ME, Gu TL, Mack JS, Silver MR, Zhou X and Haack H: Analysis of
receptor tyrosine kinase ROS1-positive tumors in non-small cell
lung cancer: Identification of a FIG-ROS1 fusion. Clin Cancer Res.
18:4449–4457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen YF, Hsieh MS, Wu SG, Chang YL, Shih
JY, Liu YN, Tsai MF, Tsai TH, Yu CJ, Yang JC and Yang PC: Clinical
and the prognostic characteristics of lung adenocarcinoma patients
with ROS1 fusion in comparison with other driver mutations in East
Asian populations. J Thorac Oncol. 9:1171–1179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu S, Wang J, Zhou L, Su D, Liu Y, Liang
X, Zhang S and Zeng X: Clinicopathological characteristics and
outcomes of ROS1-rearranged patients with lung adenocarcinoma
without EGFR, KRAS mutations and ALK rearrangements. Thorac Cancer.
6:413–420. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Takeuchi K, Soda M, Togashi Y, Suzuki R,
Sakata S, Hatano S, Asaka R, Hamanaka W, Ninomiya H, Uehara H, et
al: RET, ROS1 and ALK fusions in lung cancer. Nat Med. 18:378–381.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mescam-Mancini L, Lantuéjoul S,
Moro-Sibilot D, Rouquette I, Souquet PJ, Audigier-Valette C,
Sabourin JC, Decroisette C, Sakhri L, Brambilla E and McLeer-Florin
A: On the relevance of a testing algorithm for the detection of
ROS1-rearranged lung adenocarcinomas. Lung Cancer. 83:168–173.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Song Z, Zheng Y, Wang X, Su H, Zhang Y and
Song Y: ALK and ROS1 rearrangements, coexistence and treatment in
epidermal growth factor receptor-wild type lung adenocarcinoma: A
multicenter study of 732 cases. J Thorac Dis. 9:3919–3926. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu YC, Liao XH, Wang WX, Xu CW, Zhuang W,
Wei JG and Du KQ: Dual drive coexistence of EML4-ALK and TPM3-ROS1
fusion in advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Thorac Cancer. 9:324–327.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu YC, Lin XP, Li XF, Wu LX, Chen HF,
Wang WX, Xu CW, Shen JF, Wei JG and Du KQ: Concurrent ROS1 gene
rearrangement and KRAS mutation in lung adenocarcinoma: A case
report and literature review. Thorac Cancer. 9:159–163. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu YC, Xu CW, Ye XQ, Yin MX, Zhang JX, Du
KQ, Zhang ZH and Hu J: Lung cancer with concurrent EGFR mutation
and ROS1 rearrangement: A case report and review of the literature.
Onco Targets Ther. 9:4301–4305. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Uguen A, Schick U and Quéré G: A rare case
of ROS1 and ALK double rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. J
Thorac Oncol. 12:e71–e72. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pan W, Yang Y, Zhu H, Zhang Y, Zhou R and
Sun X: KRAS mutation is a weak, but valid predictor for poor
prognosis and treatment outcomes in NSCLC: A meta-analysis of 41
studies. Oncotarget. 7:8373–8388. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou J, Mo W, Zhao J, Zheng J, Ding W and
Zhou J: Clinicopathological features associated with EGFR gene
mutation in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 94:2332–2336. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cai W, Li X, Su C, Fan L, Zheng L, Fei K,
Zhou C, Manegold C and Schmid-Bindert G: ROS1 fusions in Chinese
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 24:1822–1827.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang L, Jiang T, Zhao C, Li W, Li X, Zhao
S, Liu X, Jia Y, Yang H, Ren S and Zhou C: Efficacy of crizotinib
and pemetrexed-based chemotherapy in Chinese NSCLC patients with
ROS1 rearrangement. Oncotarget. 7:75145–75154. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH,
Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, et
al: Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary
adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 361:947–957. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han JY, Kim SH, Lee YS, Lee SY, Hwang JA,
Kim JY, Yoon SJ and Lee GK: Comparison of targeted next-generation
sequencing with conventional sequencing for predicting the
responsiveness to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase
inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) therapy in never-smokers with lung
adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 85:161–167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lin JJ and Shaw AT: Recent advances in
targeting ROS1 in lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 12:1611–1625. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pekar-Zlotin M, Hirsch FR, Soussan-Gutman
L, Ilouze M, Dvir A, Boyle T, Wynes M, Miller VA, Lipson D, Palmer
GA, et al: Fluorescence in situ hybridization immunohistochemistry,
next-generation sequencing for detection of EML4-ALK rearrangement
in lung cancer. Oncologist. 20:316–322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu YL, Yang JC, Kim DW, Lu S, Zhou J, Seto
T, Yang JJ, Yamamoto N, Ahn MJ, Takahashi T, et al: Phase II study
of crizotinib in East asian patients with ROS1-positive advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 36:1405–1411. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Song A, Kim TM, Kim DW, Kim S, Keam B, Lee
SH and Heo DS: Molecular changes associated with acquired
resistance to crizotinib in ROS1-rearranged non-small cell lung
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:2379–2387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|