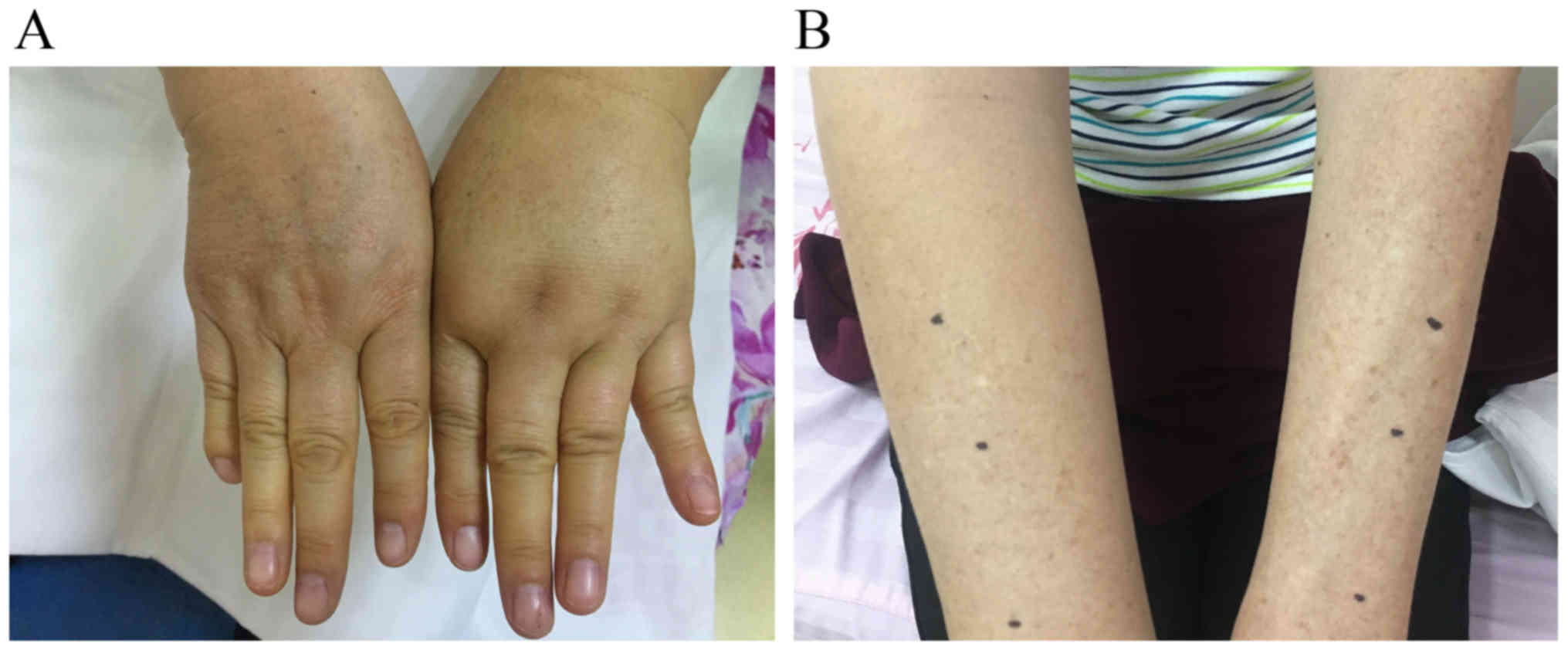
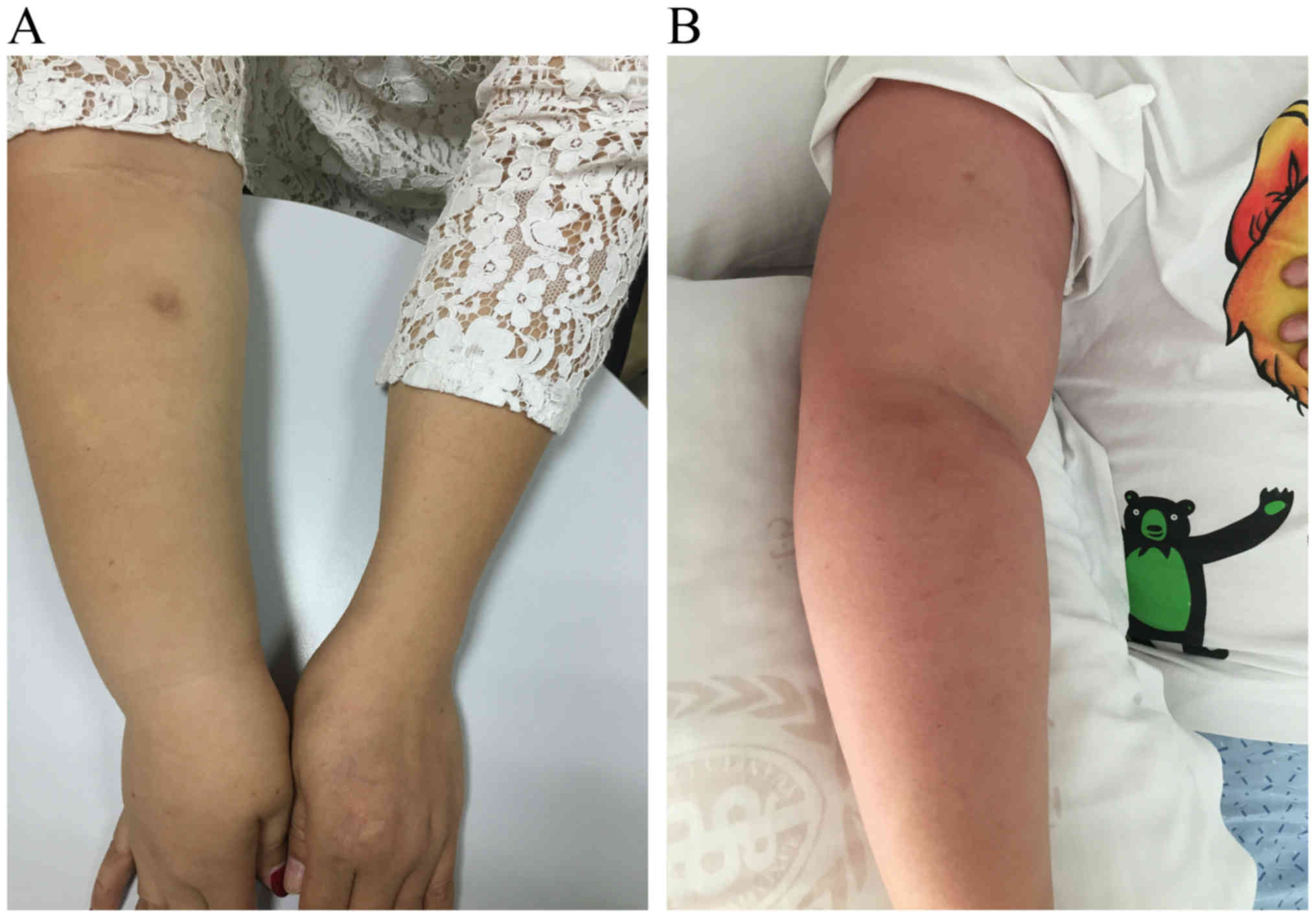
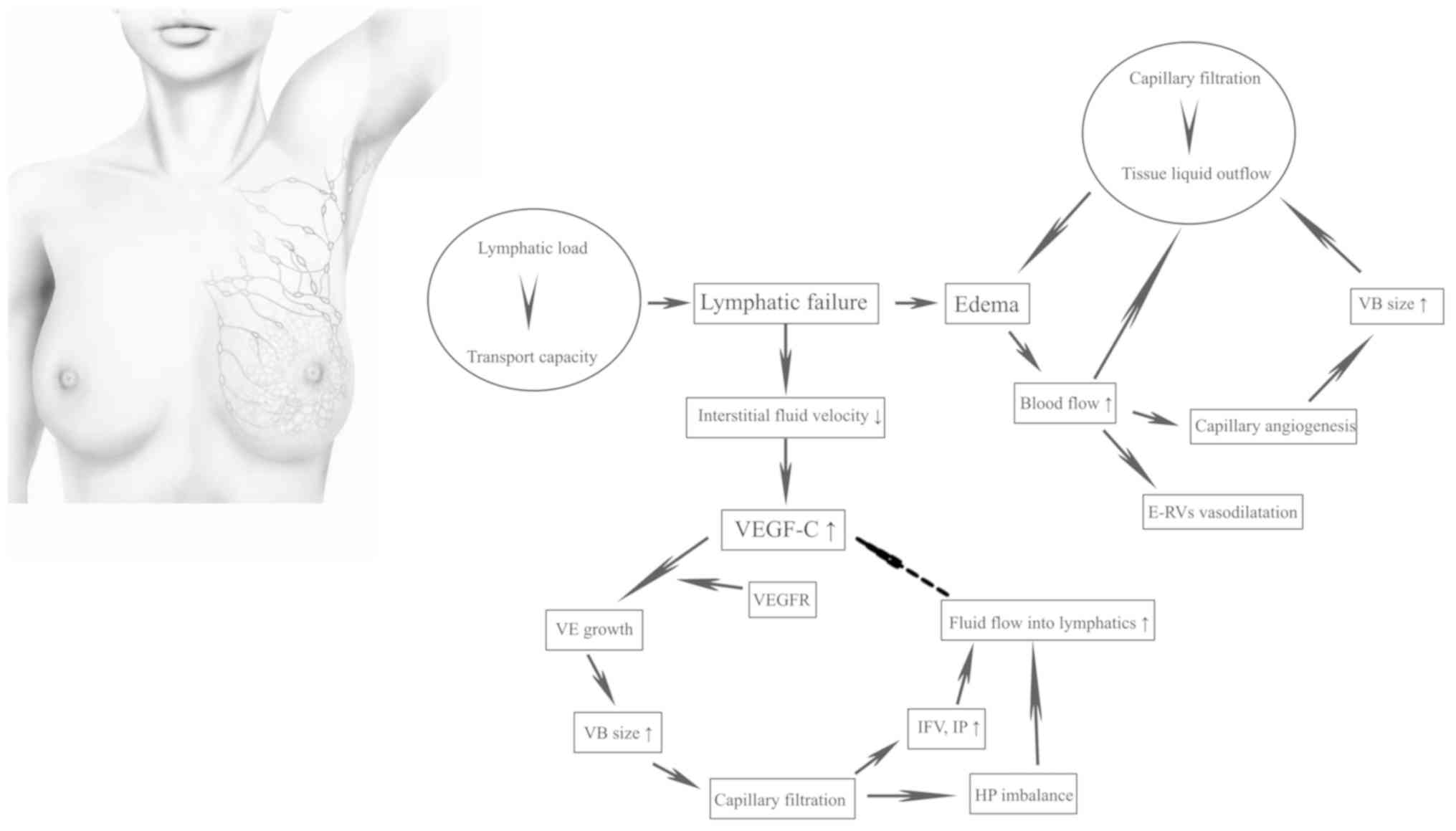
|
1
|
Rockson SG: Lymphedema after Breast Cancer
Treatment. N Eng J Med. 379:1937–1944. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Armer JM, Ballman KV, McCall L, Armer NC,
Sun Y, Udmuangpia T, Hunt KK, Mittendorf EA, Byrd DR, Julian TB and
Boughey JC: Lymphedema symptoms and limb measurement changes in
breast cancer survivors treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and
axillary dissection: Results of American college of surgeons
oncology group (ACOSOG) Z1071 (Alliance) substudy. Support Care
Cancer. 27:495–503. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Velanovich V and Szymanski W: Quality of
life of breast cancer patients with lymphedema. Am J Surg.
177:184–187. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Casley-Smith JR and Casley-Smith JR:
Modern treatment of lymphoedema II. The benzopyrones. Australas J
Dermatol. 33:69–74. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
MM H: Functional and psychosocial aspects
of lymphedema in women treated for breast cancer. Innov Breast
Cancer Care. 3:97–100. 17–18.
|
|
6
|
Armer JM and Mallinckrodt BR: Post-breast
cancer treatment lymphedema. The secret epidemic Scope Phlebolog
Lympholog. 9:334–341. 2002.
|
|
7
|
Carter BJ: Womens experiences of
lymphedema. Oncol Nurs Forum. 24:875–882. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Newman ML, Brennan M and Passik S:
Lymphedema complicated by pain and psychological distress: A case
with complex treatment needs. J Pain Symptom Manage. 12:376–379.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Passik SD and McDonald MV: Psychosocial
aspects of upper extremity lymphedema in women treated for breast
carcinoma. Cancer. 83 (12 Suppl American):2817–2820. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tobin MB, Lacey HJ, Meyer L and Mortimer
PS: The psychological morbidity of breast cancer-related arm
swelling. Psychological morbidity of lymphoedema. Cancer.
72:3248–3252. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
DiSipio T, Rye S, Newman B and Hayes S:
Incidence of unilateral arm lymphoedema after breast cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 14:500–515.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Specht MC, Miller CL, Russell TA, Horick
N, Skolny MN, OToole JA, Jammallo LS, Niemierko A, Sadek BT,
Shenouda MN, et al: Defining a threshold for intervention in breast
cancer-related lymphedema: What level of arm volume i ncrease
predicts progression? Breast cancer research and treatment.
140:485–494. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rockson SG and Rivera KK: Estimating the
population burden of lymphedema. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1131:147–154.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hayes S, Cornish B and Newman B:
Comparison of methods to diagnose lymphoedema among breast cancer
survivors: 6-month follow-up. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 89:221–226.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Denlinger CS, Sanft T, Baker KS, Broderick
G, Demark-Wahnefried W, Friedman DL, Goldman M, Hudson M, Khakpour
N, King A, et al: Survivorship, version 2.2018, NCCN clinical
practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw.
16:1216–1247. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
International Society of Lymphology: The
diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema. 2009 concensus
document of the international society of lymphology. Lymphology.
42:51–60. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lawenda BD, Mondry TE and Johnstone PA:
Lymphedema: A primer on the identification and management of a
chronic condition in oncologic treatment. CA Cancer J Clin.
59:8–24. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mortimer PS: The pathophysiology of
lymphedema. Cancer. 83 (12 Suppl American):2798–2802. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Goldman J, Conley KA, Raehl A, Bondy DM,
Pytowski B, Swartz MA, Rutkowski JM, Jaroch DB and Ongstad EL:
Regulation of lymphatic capillary regeneration by interstitial flow
in skin. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 292:H2176–H2183. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Joukov V, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A, Chilov
D, Lahtinen I, Kukk E, Saksela O, Kalkkinen N and Alitalo K: A
novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for
the Flt4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor tyrosine kinases.
EMBO J. 15:290–298. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pajusola, Kaipainen, Chilov, Lahtinen,
Kukk, Saksela O, Kalkkinen N and Alitalo K: 2, 199621. Bates DO: An
interstitial hypothesis for breast cancer related lymphoedema.
Pathophysiology. 17:289–294. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McDuff SGR, Mina AI, Brunelle CL, Salama
L, Warren LEG, Abouegylah M, Swaroop M, Skolny MN, Asdourian M,
Gillespie T, et al: Timing of lymphedema after treatment for breast
cancer: When are patients most at risk? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 103:62–70. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Asdourian MS, Swaroop MN, Sayegh HE,
Brunelle CL, Mina AI, Zheng H, Skolny MN and Taghian AG:
Association between precautionary behaviors and breast
cancer-related lymphedema in patients undergoing bilateral surgery.
J Clin Oncol. 35:3934–3941. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Iyigun ZE, Duymaz T, Ilgun AS, Alco G,
Ordu C, Sarsenov D, Aydin AE, Celebi FE, Izci F, Eralp Y and Ozmen
V: Preoperative lymphedema-related risk factors in early-stage
breast cancer. Lymphat Res Biol. 16:28–35. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Network NL: Lymphedema risk reduction
practices. http://wwwlymphnetorg/pdfDocs/nlnriskreductionpdf2012
|
|
26
|
Ferguson CM, Swaroop MN, Horick N, Skolny
MN, Miller CL, Jammallo LS, Brunelle C, OToole JA, Salama L, Specht
MC and Taghian AG: Impact of ipsilateral blood draws, injections,
blood pressure measurements, and air travel on the risk of
lymphedema for patients treated for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
34:691–698. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Clark B, Sitzia J and Harlow W: Incidence
and risk of arm oedema following treatment for breast cancer: A
three-year follow-up study. QJM. 98:343–348. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Geller BM, Vacek PM, OBrien P and
Secker-Walker RH: Factors associated with arm swelling after breast
cancer surgery. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 12:921–930. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Armer J and Fu MR: Age differences in
post-breast cancer lymphedema signs and symptoms. Cancer Nurs.
28:200–207; quiz208-209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Larson D, Weinstein M, Goldberg I, Silver
B, Recht A, Cady B, Silen W and Harris JR: Edema of the arm as a
function of the extent of axillary surgery in patients with stage
I–II carcinom a of the breast treated with primary radiotherapy.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 12:1575–1582. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Engel J, Kerr J, Schlesinger-Raab A, Sauer
H and Holzel D: Axilla surgery severely affects quality of life:
Results of a 5-year prospective study in breast cancer patients.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 79:47–57. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Paskett ED, Naughton MJ, McCoy TP, Case LD
and Abbott JM: The epidemiology of arm and hand swelling in
premenopausal breast cancer survivors. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 16:775–782. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pezner RD, Patterson MP, Hill LR, Lipsett
JA, Desai KR, Vora N, Wong JY and Luk KH: Arm lymphedema in
patients treated conservatively for breast cancer: Relationship to
patient age and axillary node dissection technique. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 12:2079–2083. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cariati M, Bains SK, Grootendorst MR,
Suyoi A, Peters AM, Mortimer P, Ellis P, Harries M, Van Hemelrijck
M and Purushotham AD: Adjuvant taxanes and the development of
breast cancer-related arm lymphoedema. Br J Surg. 102:1071–1078.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Penn IW, Chang YC, Chuang E, Chen CM,
Chung CF, Kuo CY and Chuang TY: Risk factors and prediction model
for persistent breast-cancer-related lymphedema: A 5-year cohort
study. Support Care Cancer. 27:991–1000. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Swaroop MN, Ferguson CM, Horick NK, Skolny
MN, Miller CL, Jammallo LS, Brunelle CL, OToole JA, Isakoff SJ,
Specht MC and Taghian AG: Impact of adjuvant taxane-based
chemotherapy on development of breast cancer-related lymphedema:
Results from a large prospective cohort. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
151:393–403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Czerniec SA, Ward LC and Kilbreath SL:
Breast cancer-related arm lymphedema: Fluctuation over six months
and the effect of the weather. Lymphat Res Biol. 14:148–155. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rockson SG: Precipitating factors in
lymphedema: Myths and realities. Cancer. 83 (12 Suppl
American):2814–2846. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Meeske KA, Sullivan-Halley J, Smith AW,
McTiernan A, Baumgartner KB, Harlan LC and Bernstein L: Risk
factors for arm lymphedema following breast cancer diagnosis in
Black women and White women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 113:383–391.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Visser J, van Geel M, Cornelissen AJM, van
der Hulst RRWJ and Qiu SS: Breast cancer-related lymphedema and
genetic predisposition: A systematic review of the literature.
Lymphat Res Biol. 17:288–293. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Newman B, Lose F, Kedda MA, Francois M,
Ferguson K, Janda M, Yates P, Spurdle AB and Hayes SC: Possible
genetic predisposition to lymphedema after breast cancer. Lymphat
Res Biol. 10:2–13. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tandra P, Kallam A and Krishnamurthy J:
Identification and management of lymphedema in patients with breast
cancer. J Oncol pract. 15:255–262. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tsai RJ, Dennis LK, Lynch CF, Snetselaar
LG, Zamba GK and Scott-Conner C: The risk of developing arm
lymphedema among breast cancer survivors: A meta-analysis of
treatment factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:1959–1972. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gentilini O and Veronesi U: Abandoning
sentinel lymph node biopsy in early breast cancer? A new trial in
progress at the European institute of oncology of milan (SOUND:
Sentinel node vs observation after axillary UltraSouND). Breast.
21:678–681. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cardoso F, vant Veer LJ, Bogaerts J,
Slaets L, Viale G, Delaloge S, Pierga JY, Brain E, Causeret S,
DeLorenzi M, et al: 70-Gene signature as an aid to treatment
decisions in early-stage breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 375:717–729.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sparano JA, Gray RJ, Makower DF, Pritchard
KI, Albain KS, Hayes DF, Geyer CE Jr, Dees EC, Perez EA, Olson JA
Jr, et al: Prospective validation of a 21-gene expression assay in
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:2005–2014. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gradishar WJ, Anderson BO, Balassanian R,
Blair SL, Burstein HJ, Cyr A, Elias AD, Farrar WB, Forero A,
Giordano SH, et al: NCCN guidelines insights: Breast cancer,
version 1.2017. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 15:433–451. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Levenhagen K, Davies C, Perdomo M, Ryans K
and Gilchrist L: Diagnosis of upper quadrant lymphedema secondary
to cancer: Clinical practice guideline from the oncology section of
the American physical therapy association. Phys Ther. 97:729–745.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lyman GH, Somerfield MR, Bosserman LD,
Perkins CL, Weaver DL and Giuliano AE: Sentinel lymph node biopsy
for patients with early-stage breast cancer: American society of
clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol.
35:561–564. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
International Society of Lymphology: The
diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema: 2013 Consensus
document of the international society of lymphology. Lymphology.
46:1–11. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hughes KS, Schnaper LA, Bellon JR,
Cirrincione CT, Berry DA, McCormick B, Muss HB, Smith BL, Hudis CA,
Winer EP and Wood WC: Lumpectomy plus tamoxifen with or without
irradiation in women age 70 years or older with early breast
cancer: Long-term follow-up of CALGB 9343. J Clin Oncol.
31:2382–2387. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Czerniec SA, Ward LC, Refshauge KM, Beith
J, Lee MJ, York S and Kilbreath SL: Assessment of breast
cancer-related arm lymphedema--comparison of physical measurement
methods and self-report. Cancer Invest. 28:54–62. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cormier JN, Xing Y, Zaniletti I, Askew RL,
Stewart BR and Armer JM: Minimal limb volume change has a
significant impact on breast cancer survivors. Lymphology.
42:161–175. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Thompson M, Korourian S, Henry-Tillman R,
Adkins L, Mumford S, Westbrook KC and Klimberg VS: Axillary reverse
mapping (ARM): A new concept to identify and enhance lymphatic
preservation. Ann Surg Oncol. 14:1890–1895. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nos C, Lesieur B, Clough KB and Lecuru F:
Blue dye injection in the arm in order to conserve the lymphatic
drainage of the arm in breast cancer patients requiring an axillary
dissection. Ann Surg Oncol. 14:2490–2496. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Pavlista D and Eliska O: Analysis of
direct oil contrast lymphography of upper limb lymphatics
traversing the axilla - a lesson from the past - contribution to
the concept of axillary reverse mapping. Eur J Surg Oncol.
38:390–394. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gennaro M, Maccauro M, Sigari C, Casalini
P, Bedodi L, Conti AR, Caraceni A and Bombardieri E: Selective
axillary dissection after axillary reverse mapping to prevent
breast-cancer-related lymphoedema. Eur J Surg Oncol. 39:1341–1345.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Pasko JL, Garreau J, Carl A, Ansteth M,
Glissmeyer M and Johnson N: Axillary reverse lymphatic mapping
reduces patient perceived incidence of lymphedema after axillary
dissection in breast cancer. Am J Surg. 209:890–895. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yue T, Zhuang D, Zhou P, Zheng L, Fan Z,
Zhu J, Hou L, Yu F, Dong X, Xiao L and He Q: A prospective study to
assess the feasibility of axillary reverse mapping and evaluate its
effect on preventing lymphedema in breast cancer patients. Clin
Breast Cancer. 15:301–306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Noguchi M, Noguchi M, Ohno Y, Morioka E,
Nakano Y, Kosaka T, Kurose N and Minato H: Feasibility study of
axillary reverse mapping for patients with clinically node-negative
breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 42:650–656. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Beek MA, Gobardhan PD, Klompenhouwer EG,
Rutten HJ, Voogd AC and Luiten EJ: Axillary reverse mapping (ARM)
in clinically node positive breast cancer patients. Eur J Surg
Oncol. 41:59–63. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
McLaughlin SA, Staley AC, Vicini F,
Thiruchelvam P, Hutchison NA, Mendez J, MacNeill F, Rockson SG,
DeSnyder SM, Klimberg S, et al: Considerations for clinicians in
the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of breast cancer-related
lymphedema: Recommendations from a multidisciplinary expert ASBrS
panel: Part 1: Definitions, assessments, education, and future
directions. Ann Surg Oncol. 24:2818–2826. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bok SK, Jeon Y and Hwang PS:
Ultrasonographic evaluation of the effects of progressive resistive
exercise in breast cancer-related lymphedema. Lymphat Res Biol.
14:18–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Engin O, Akalin E, Saribay E, Aslan C,
Sahin E and Alper S: Easy volumeter in detection of breast
cancer-related lymphedema: A validity study. Lymphat Res Biol.
17:543–549. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cornish BH, Chapman M, Thomas BJ, Ward LC,
Bunce IH and Hirst C: Early diagnosis of lymphedema in postsurgery
breast cancer patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 904:571–575. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Cornish BH, Chapman M, Hirst C, Mirolo B,
Bunce IH, Ward LC and Thomas BJ: Early diagnosis of lymphedema
using multiple frequency bioimpedance. Lymphology. 34:2–11.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bundred NJ, Stockton C, Keeley V, Riches
K, Ashcroft L, Evans A, Skene A, Purushotham A, Bramley M and
Hodgkiss T; Investigators of BEA/PLACE studies, : Comparison of
multi-frequency bioimpedance with perometry for the early detection
and intervention of lymphoedema after axillary node clearance for
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 151:121–129. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Fu MR, Cleland CM, Guth AA, Kayal M, Haber
J, Cartwright F, Kleinman R, Kang Y, Scagliola J and Axelrod D:
L-dex ratio in detecting breast cancer-related lymphedema:
Reliability, sensitivity, and specificity. Lymphology. 46:85–96.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Barrio AV, Eaton A and Frazier TG: A
prospective validation study of bioimpedance with volume
displacement in early-stage breast cancer patients at risk for
lymphedema. Ann Surg Oncol. 22 (Suppl 3):S370–S375. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Czerniec SA, Ward LC, Lee MJ, Refshauge
KM, Beith J and Kilbreath SL: Segmental measurement of breast
cancer-related arm lymphoedema using perometry and bioimpedance
spectroscopy. Support Care Cancer. 19:703–710. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Qin ES, Bowen MJ and Chen WF: Diagnostic
accuracy of bioimpedance spectroscopy in patients with lymphedema:
A retrospective cohort analysis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg.
71:1041–1050. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Soran A, Ozmen T, McGuire KP, Diego EJ,
McAuliffe PF, Bonaventura M, Ahrendt GM, DeGore L and Johnson R:
The importance of detection of subclinical lymphedema for the
prevention of breast cancer-related clinical lymphedema after
axillary lymph node dissection; A prospective observational study.
Lymphat Res Biol. 12:289–294. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Newman AL, Rosenthall L, Towers A, Hodgson
P, Shay CA, Tidhar D, Vigano A and Kilgour RD: Determining the
precision of dual energy x-ray absorptiometry and bioelectric
impedance spectroscopy in the assessment of breast cancer-related
lymphedema. Lymphat Res Biol. 11:104–109. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gjorup C, Zerahn B and Hendel HW:
Assessment of volume measurement of breast cancer-related
lymphedema by three methods: Circumference measurement, water
displacement, and dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Lymphat Res
Biol. 8:111–119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bae JS, Yoo RE, Choi SH, Park SO, Chang H,
Suh M and Cheon GJ: Evaluation of lymphedema in upper extremities
by MR lymphangiography: Comparison with lymphoscintigraphy. Magn
Reson Imaging. 49:63–70. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Partsch H: Practical aspects of indirect
lymphography and lymphoscintigraphy. Lymphat Res Biol. 1:71–73;
discussion 73–74. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Mihara M, Hara H, Araki J, Kikuchi K,
Narushima M, Yamamoto T, Iida T, Yoshimatsu H, Murai N, Mitsui K,
et al: Indocyanine green (ICG) lymphography is superior to
lymphoscintigraphy for diagnostic imaging of early lymphedema of
the upper limbs. PloS One. 7:e381822012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Szuba A, Razavi M and Rockson SG:
Diagnosis and treatment of concomitant venous obstruction in
patients with secondary lymphedema. J Vasc Interv Radiol.
13:799–803. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Rockson SG: Lymphedema after breast cancer
treatment. N Engl J Med. 380:6942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen WF, Zhao H, Yamamoto T, Hara H and
Ding J: Indocyanine green lymphographic evidence of surgical
efficacy following microsurgical and supermicrosurgical lymphedema
reconstructions. J Reconstr Microsurg. 32:688–698. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yamamoto T, Matsuda N, Doi K, Oshima A,
Yoshimatsu H, Todokoro T, Ogata F, Mihara M, Narushima M, Iida T
and Koshima I: The earliest finding of indocyanine green
lymphography in asymptomatic limbs of lower extremity lymphedema
patients secondary to cancer treatment: The modified dermal
backflow stage and concept of subclinical lymphedema. Plast
Reconstr Surg. 128:314e–321e. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Yamamoto T, Yoshimatsu H, Narushima M,
Yamamoto N, Hayashi A and Koshima I: Indocyanine green lymphography
findings in primary leg lymphedema. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg.
49:95–102. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Torres Lacomba M, Yuste Sánchez MJ, Zapico
Goñi A, Prieto Merino D, Mayoral del Moral O, Cerezo Téllez E and
Minayo Mogollón E: Effectiveness of early physiotherapy to prevent
lymphoedema after surgery for breast cancer: Randomised, single
blinded, clinical trial. BMJ. 340:b53962010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Stout NL, Pfalzer LA, Springer B, Levy E,
McGarvey CL, Danoff JV, Gerber LH and Soballe PW: Breast
cancer-related lymphedema: Comparing direct costs of a prospective
surveillance model and a traditional model of care. Phys Ther.
92:152–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Stout Gergich NL, Pfalzer LA, McGarvey C,
Springer B, Gerber LH and Soballe P: Preoperative assessment
enables the early diagnosis and successful treatment of lymphedema.
Cancer. 112:2809–2819. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Boccardo FM, Ansaldi F, Bellini C, Accogli
S, Taddei G, Murdaca G, Campisi CC, Villa G, Icardi G, Durando P,
et al: Prospective evaluation of a prevention protocol for
lymphedema following surgery for breast cancer. Lymphology. 42:1–9.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Box RC, Reul-Hirche HM, Bullock-Saxton JE
and Furnival CM: Physiotherapy after breast cancer surgery: Results
of a randomised controlled study to minimise lymphoedema. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 75:51–64. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Czerniec SA, Ward LC and Kilbreath SL:
Assessment of breast cancer-related lymphedema: A comparison of
moisture meter and spot bioimpedance measurement. Lymphat Res Biol.
13:10–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Cacchio A, Prencipe R, Bertone M, De
Benedictis L, Taglieri L, DElia E, Centoletti C and Di Carlo G:
Effectiveness and safety of a product containing diosmin, coumarin,
and arbutin (Linfadren®) in addit ion to complex
decongestive therapy on management of breast cancer-related
lymphedema. Support Care Cancer. 27:1471–1480. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Duyur Cakit B, Pervane Vural S and Ayhan
FF: Complex decongestive therapy in breast cancer-related
lymphedema: Does obesity affect the outcome negatively? Lymphat Res
Biol. 17:45–50. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Huang TW, Tseng SH, Lin CC, Bai CH, Chen
CS, Hung CS, Wu CH and Tam KW: Effects of manual lymphatic drainage
on breast cancer-related lymphedema: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World J Surg Oncol.
11:152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Ezzo J, Manheimer E, McNeely ML, Howell
DM, Weiss R, Johansson KI, Bao T, Bily L, Tuppo CM, Williams AF and
Karadibak D: Manual lymphatic drainage for lymphedema following
breast cancer treatment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
21:CD0034752015.
|
|
93
|
Johansson K, Albertsson M, Ingvar C and
Ekdahl C: Effects of compression bandaging with or without manual
lymph drainage treatment in patients with postoperative arm
lymphedema. Lymphology. 32:103–110. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Pujol-Blaya V, Salinas-Huertas S, Catasus
ML, Pascual T and Belmonte R: Effectiveness of a precast adjustable
compression system compared to multilayered compression bandages in
the treatment of breast cancer-related lymphoedema: A randomized,
single-blind clinical trial. Clin Rehabil. 33:631–641. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Mobarakeh ZS, Mokhtari-Hesari P,
Lotfi-Tokaldany M, Montazeri A, Heidari M and Zekri F: Combined
decongestive therapy and reduction of pain and heaviness in
patients with breast cancer-related lymphedema. Support Care
Cancer. 27:3805–3811. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Moffatt CJ, Doherty DC, Franks PJ and
Mortimer PS: Community-based treatment for chronic edema: An
effective service model. Lymphat Res Biol. 16:92–99. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ochalek K, Partsch H, Gradalski T and
Szygula Z: Do compression sleeves reduce the incidence of arm
lymphedema and improve quality of life? two-year results from a
prospective randomized trial in breast cancer survivors. Lymphat
Res Biol. 17:70–77. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Shao Y, Qi K, Zhou QH and Zhong DS:
Intermittent pneumatic compression pump for breast cancer-related
lymphedema: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. Oncol Res Treat. 37:170–174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Karaca-Mandic P, Hirsch AT, Rockson SG and
Ridner SH: The cutaneous, net clinical, and health economic
benefits of advanced pneumatic compression devices in patients with
lymphedema. JAMA Dermatol. 151:1187–1193. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hayes SC, Reul-Hirche H and Turner J:
Exercise and secondary lymphedema: Safety, potential benefits, and
research issues. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 41:483–489. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Ahmed RL, Thomas W, Yee D and Schmitz KH:
Randomized controlled trial of weight training and lymphedema in
breast cancer survivors. J Clin Oncol. 24:2765–2772. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Harris SR and Niesen-Vertommen SL:
Challenging the myth of exercise-induced lymphedema following
breast cancer: A series of case reports. J Surg Oncol. 74:95–98,
Discussion 98–99. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Lane K, Jespersen D and McKenzie DC: The
effect of a whole body exercise programme and dragon boat training
on arm volume and arm circumference in women treated for breast
cancer. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 14:353–358. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
McKenzie DC and Kalda AL: Effect of upper
extremity exercise on secondary lymphedema in breast cancer
patients: A pilot study. J Clin Oncol. 21:463–466. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Panchik D, Masco S, Zinnikas P, Hillriegel
B, Lauder T, Suttmann E, Chinchilli V, McBeth M and Hermann W:
Effect of exercise on breast cancer-related lymphedema: What the
lymphatic surgeon needs to know. J Reconstr Microsurg. 35:37–45.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Keilani M, Hasenoehrl T, Neubauer M and
Crevenna R: Resistance exercise and secondary lymphedema in breast
cancer survivors-a systematic review. Support Care Cancer.
24:1907–1916. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Markkula SP, Leung N, Allen VB and Furniss
D: Surgical interventions for the prevention or treatment of
lymphoedema after breast cancer treatment. Cochrane Database Syst
Rev. 2:CD0114332019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Cornelissen AJM, Beugels J, Ewalds L,
Heuts EM, Keuter XHA, Piatkowski A, van der Hulst RRWJ and Qiu Shao
SS: Effect of lymphaticovenous anastomosis in breast cancer-related
lymphedema: A review of the literature. Lymphat Res Biol.
16:426–434. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Winters H, Tielemans HJP, Verhulst AC,
Paulus VAA, Slater NJ and Ulrich DJO: The long-term patency of
lymphaticovenular anastomosis in breast cancer-related lymphedema.
Ann Plast Surg. 82:196–200. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Granzow JW, Soderberg JM, Kaji AH and
Dauphine C: Review of current surgical treatments for lymphedema.
Ann Surg Oncol. 21:1195–1201. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Chan VS, Narushima M, Hara H, Yamamoto T,
Mihara M, Iida T and Koshima I: Local anesthesia for
lymphaticovenular anastomosis. Ann Plast Surg. 72:180–183. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Boccardo F, Casabona F, De Cian F,
Friedman D, Murelli F, Puglisi M, Campisi CC, Molinari L, Spinaci
S, Dessalvi S and Campisi C: Lymphatic microsurgical preventing
healing approach (LYMPHA) for primary surgical prevention of breast
cancer-related lymphedema: Over 4 years follow-up. Microsurgery.
34:421–424. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Boccardo F, Casabona F, De Cian F,
Friedman D, Villa G, Bogliolo S, Ferrero S, Murelli F and Campisi
C: Lymphedema microsurgical preventive healing approach: A new
technique for primary prevention of arm lymphedema after
mastectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:703–708. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Ozmen T, Lazaro M, Zhou Y, Vinyard A and
Avisar E: Evaluation of simplified lymphatic microsurgical
preventing healing approach (S-LYMPHA) for the prevention of breast
cancer-related clinical lymphedema after axillary lymph node
dissection. Ann Surg. 270:1156–1160. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Khan AA, Hernan I, Adamthwaite JA and
Ramsey KWD: Feasibility study of combined dynamic imaging and
lymphaticovenous anastomosis surgery for breast cancer-related
lymphoedema. Br J Surg. 106:100–110. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Seki Y, Kajikawa A, Yamamoto T, Takeuchi
T, Terashima T and Kurogi N: The dynamic-lymphaticovenular
anastomosis method for breast cancer treatment-related lymphedema:
Creation of functional lymphaticovenular anastomoses with use of
preoperative dynamic ultrasonography. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet
Surg. 72:62–70. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Pappalardo M, Patel K and Cheng MH:
Vascularized lymph node transfer for treatment of extremity
lymphedema: An overview of current controversies regarding donor
sites, recipient sites and outcomes. J Surg Oncol. 117:1420–1431.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Liu HL, Pang SY and Lee CC: Donor limb
assessment after vascularized groin lymph node transfer for the
treatment of breast cancer-related lymphedema: Clinical and
lymphoscintigraphy findings. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg.
72:216–224. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Brorson H and Svensson H: Liposuction
combined with controlled compression therapy reduces arm lymphedema
more effectively than controlled compression therapy alone. Plast
Reconstr Surg. 102:1058–1067; discussion 1068. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Brorson H and Svensson H: Complete
reduction of lymphoedema of the arm by liposuction after breast
cancer. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 31:137–143. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Brorson H OK, Olsson G and Svensson B:
Liposuction of postmastectomy arm lymphedema completely removes
excess volume: A thirteen-year study (Quad erat demonstrandum). Eur
J Lymphol. 17:92007.
|
|
122
|
Brorson H, Svensson H, Norrgren K and
Thorsson O: Liposuction reduces arm lymphedema without
significantly altering the already impaired lymph transport.
Lymphology. 31:156–172. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Brorson H: Liposuction in lymphedema
treatment. J Reconstr Microsurg. 32:56–65. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Lamprou DA, Voesten HG, Damstra RJ and
Wikkeling OR: Circumferential suction-assisted lipectomy in the
treatment of primary and secondary end-stage lymphoedema of the
leg. Br J Surg. 104:84–89. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Damstra RJ, Voesten HG, Klinkert P and
Brorson H: Circumferential suction-assisted lipectomy for
lymphoedema after surgery for breast cancer. Br J Surg. 96:859–864.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Schaverien MV, Munro KJ, Baker PA and
Munnoch DA: Liposuction for chronic lymphoedema of the upper limb:
5 Years of experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 65:935–942.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Brorson H: Complete reduction of arm
lymphedema following breast cancer - A prospective twenty-one years
study. Plast Reconstructive Surg. 136 (4 Suppl):S134–S135. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Boyages J, Kastanias K, Koelmeyer LA,
Winch CJ, Lam TC, Sherman KA, Munnoch DA, Brorson H, Ngo QD,
Heydon-White A, et al: Liposuction for advanced lymphedema: A
multidisciplinary approach for complete reduction of arm and leg
swelling. Ann Surg Oncol. 22 (Suppl 3):S1263–S1270. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Brorson H and Svensson H: Skin blood flow
of the lymphedematous arm before and after liposuction. Lymphology.
30:165–172. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Frick A, Hoffmann JN, Baumeister RG and
Putz R: Liposuction technique and lymphatic lesions in lower legs:
Anatomic study to reduce risks. Plast Reconstr Surg. 103:1868–1873;
discussion 1874–1875. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Lee D, Piller N, Hoffner M, Manjer J and
Brorson H: Liposuction of postmastectomy arm lymphedema decreases
the incidence of erysipelas. Lymphology. 49:85–92. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Schaverien MV, Munnoch DA and Brorson H:
Liposuction treatment of lymphedema. Semin Plast Surg. 32:42–47.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Alitalo K: The lymphatic vasculature in
disease. Nat Med. 17:1371–1380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Karkkainen MJ, Saaristo A, Jussila L,
Karila KA, Lawrence EC, Pajusola K, Bueler H, Eichmann A, Kauppinen
R, Kettunen MI, et al: A model for gene therapy of human hereditary
lymphedema. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 98:12677–12682. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Kriederman BM, Myloyde TL, Witte MH,
Dagenais SL, Witte CL, Rennels M, Bernas MJ, Lynch MT, Erickson RP,
Caulder MS, et al: FOXC2 haploinsufficient mice are a model for
human autosomal dominant lymphedema-distichiasis syndrome. Hum Mol
Genet. 12:1179–1185. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Norrmen C, Tammela T, Petrova TV and
Alitalo K: Biological basis of therapeutic lymphangiogenesis.
Circulation. 123:1335–1351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Tammela T, Saaristo A, Holopainen T,
Lyytikkä J, Kotronen A, Pitkonen M, Abo-Ramadan U, Ylä-Herttuala S,
Petrova TV and Alitalo K: Therapeutic differentiation and
maturation of lymphatic vessels after lymph node dissection and
transplantation. Nat Med. 13:1458–1466. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Lahteenvuo M, Honkonen K, Tervala T,
Tammela T, Suominen E, Lähteenvuo J, Kholová I, Alitalo K,
Ylä-Herttuala S and Saaristo A: Growth factor therapy and
autologous lymph node transfer in lymphedema. Circulation.
123:613–620. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Shimizu Y, Shibata R, i Shintani S, Ishii
M and Murohara T: Therapeutic lymphangiogenesis with implantation
of adipose-derived regenerative cells. J Am Heart Assoc.
1:e0008772012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Conrad C, Niess H, Huss R, Huber S, von
Luettichau I, Nelson PJ, Ott HC, Jauch KW and Bruns CJ: Multipotent
mesenchymal stem cells acquire a lymphendothelial phenotype and
enhance lymphatic regeneration in vivo. Circulation. 119:281–289.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Hwang JH, Kim IG and Lee JY, Piao S, Lee
DS, Lee TS, Ra JC and Lee JY: Therapeutic lymphangiogenesis using
stem cell and VEGF-C hydrogel. Biomaterials. 32:4415–4423. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Toyserkani NM, Jensen CH, Andersen DC,
Sheikh SP and Sørensen JA: Treatment of breast cancer-related
lymphedema with adipose-derived regenerative cells and fat grafts:
A feasibility and safety study. Stem Cells Transl Med. 6:1666–1672.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Toyserkani NM, Jensen CH, Tabatabaeifar S,
Jørgensen MG, Hvidsten S, Simonsen JA, Andersen DC, Sheikh SP and
Sørensen JA: Adipose-derived regenerative cells and fat grafting
for treating breast cancer-related lymphedema: Lymphoscintigraphic
evaluation with 1 year of follow-up. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg.
72:71–77. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|