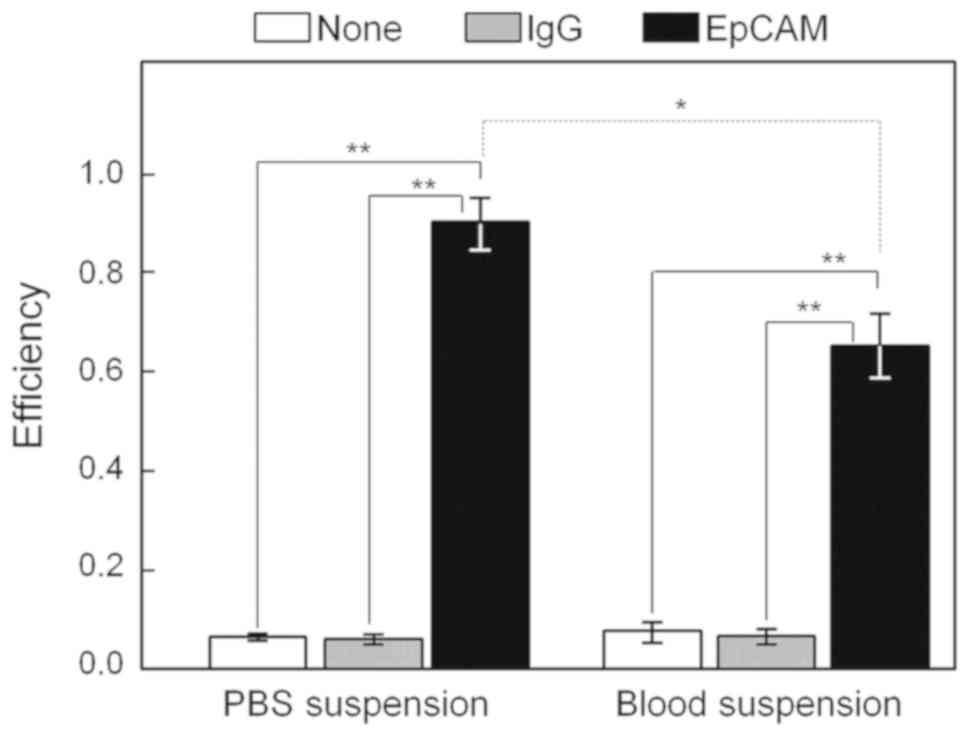
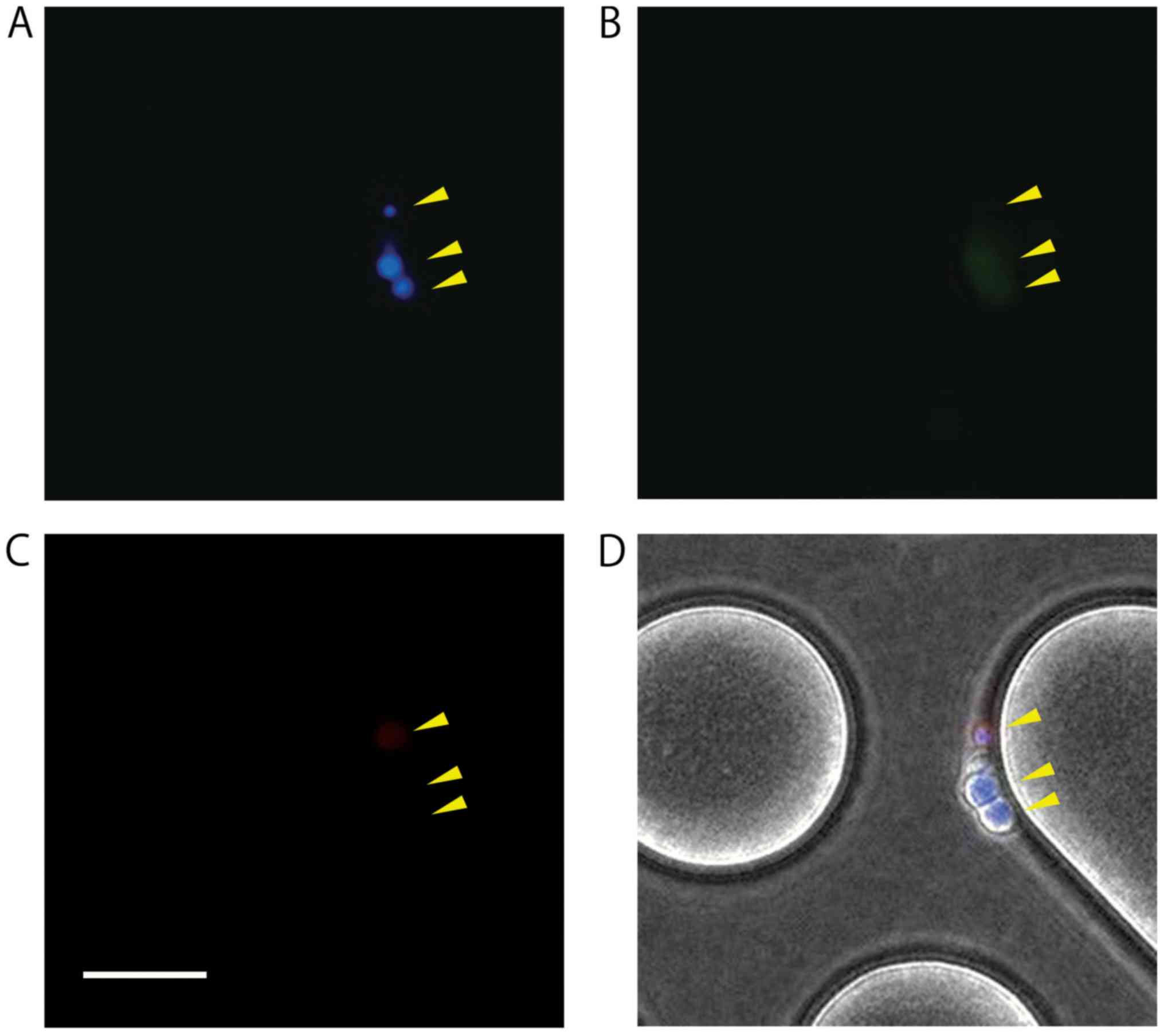
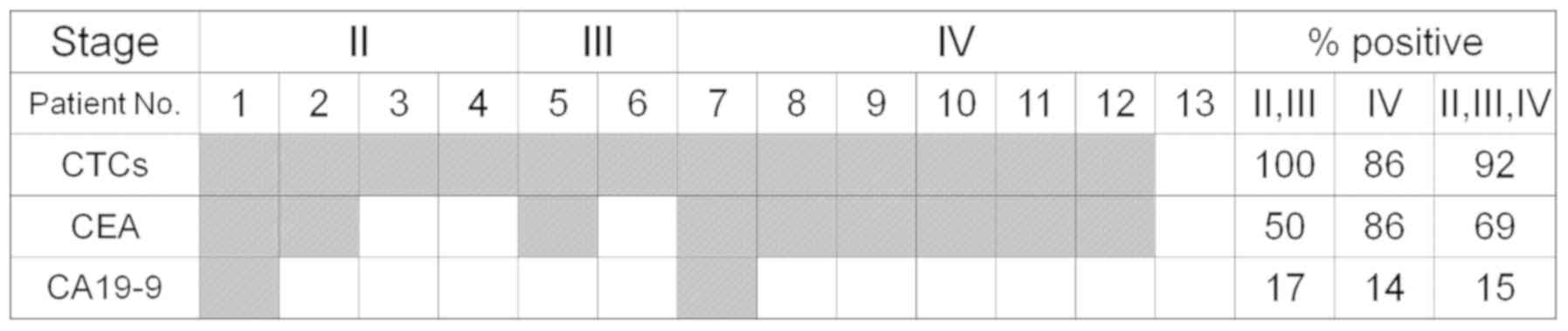
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Locker GY, Hamilton S, Harris J, Jessup
JM, Kemeny N, Macdonald JS, Somerfield MR, Hayes DF and Bast RC Jr;
ASCO, : ASCO 2006 update of recommendations for the use of tumor
markers in gastrointestinal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 24:5313–5327.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Racila E, Euhus D, Weiss AJ, Rao C,
McConnell J, Terstappen LW and Uhr JW: Detection and
characterization of carcinoma cells in the blood. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 95:4589–4594. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jacob K, Sollier C and Jabado N:
Circulating tumor cells: Detection, molecular profiling and future
prospects. Expert Rev Proteomics. 4:741–756. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Paterlini-Brechot P and Benali NL:
Circulating tumor cells (CTC) detection: Clinical impact and future
directions. Cancer Lett. 253:180–204. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ignatiadis M, Lee M and Jeffrey SS:
Circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA: Challenges and
opportunities on the path to clinical utility. Clin Cancer Res.
21:4786–4800. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Krivacic RT, Ladanyi A, Curry DN, Hsieh
HB, Kuhn P, Bergsrud DE, Kepros JF, Barbera T, Ho MY, Chen LB, et
al: A rare-cell detector for cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:10501–10504. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Allard WJ, Matera J, Miller MC, Repollet
M, Connelly MC, Rao C, Tibbe AG, Uhr JW and Terstappen LW: Tumor
cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but
not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases.
Clin Cancer Res. 10:6897–6904. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sato N, Hayashi N, Imamura Y, Tanaka Y,
Kinoshita K, Kurashige J, Saito S, Karashima R, Hirashima K, Nagai
Y, et al: Usefulness of transcription-reverse transcription
concerted reaction method for detecting circulating tumor cells in
patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:2060–2065.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Giannopoulou L, Kasimir-Bauer S and
Lianidou ES: Liquid biopsy in ovarian cancer: Recent advances on
circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. Clin Chem Lab
Med. 56:186–197. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kasimir-Bauer S, Hoffmann O, Wallwiener D,
Wallwiener D, Kimmig R and Fehm T: Expression of stem cell and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in primary breast cancer
patients with circulating tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res.
14:R152012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iinuma H, Okinaga K, Egami H, Mimori K,
Hayashi N, Nishida K, Adachi M, Mori M and Sasako M: Usefulness and
clinical significance of quantitative real-time RT-PCR to detect
isolated tumor cells in the peripheral blood and tumor drainage
blood of patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 28:297–306.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Iinuma H, Watanabe T, Mimori K, Adachi M,
Hayashi N, Tamura J, Matsuda K, Fukushima R, Okinaga K, Sasako M
and Mori M: Clinical significance of circulating tumor cells,
including cancer stem-like cells, in peripheral blood for
recurrence and prognosis in patients with Dukes' stage B and C
colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:1547–1555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gorges TM, Tinhofer I, Drosch M, Röse L,
Zollner TM, Krahn T and Ahsen O: Circulating tumour cells escape
from EpCAM-based detection due to epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. BMC Cancer. 12:1782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nagrath S, Sequist LV, Maheswaran S, Bell
DW, Irimia D, Ulkus L, Smith MR, Kwak EL, Digumarthy S, Muzikansky
A, et al: Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer
patients by microchip technology. Nature. 450:1235–1239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ankeny JS, Court CM, Hou S, Li Q, Song M,
Wu D, Chen JF, Lee T, Lin M, Sho S, et al: Circulating tumour cells
as a biomarker for diagnosis and staging in pancreatic cancer. Brit
J Cancer. 114:1367–1375. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Veridex, LLC: 510(k) Summary, .
CellSearch™ circulating tumor cell kit, premarket
notification-expanded indications for UseColorectal. Nov 20–2007,
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf7/k071729.pdfNovember
12–2018
|
|
18
|
Veridex, LLC: 510(k) Summary, .
CellSearch™ circulating tumor cell kit premarket
notification-expanded indications for use-metastatic prostate
cancer. Feb 27–2008, https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf7/K073338.pdfNovember
13–2008
|
|
19
|
Cristofanilli M, Budd GT, Ellis MJ,
Stopeck A, Matera J, Miller MC, Reuben JM, Doyle GV, Allard WJ,
Terstappen LW and Hayes DF: Circulating tumor cells, disease
progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J
Med. 351:781–791. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cristofanilli M, Hayes DF, Budd GT, Ellis
MJ, Stopeck A, Reuben JM, Doyle GV, Matera J, Allard WJ, Miller MC,
et al: Circulating tumor cells: A novel prognostic factor for newly
diagnosed metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:1420–1430.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cohen SJ, Punt CJ, Iannotti N, Saidman BH,
Sabbath KD, Gabrail NY, Picus J, Morse MA, Mitchell E, Miller MC,
et al: Relationship of circulating tumor cells to tumor response,
progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:3213–3221. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
De Bono JS, Scher HI, Montgomery RB,
Parker C, Miller MC, Tissing H, Doyle GV, Terstappen LW, Pienta KJ
and Raghavan D: Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit
from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:6302–6309. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miller MC, Doyle GV and Terstappen LW:
Significance of circulating tumor cells detected by the CellSearch
system in patients with metastatic breast colorectal and prostate
cancer. J Oncol. 2010:6174212010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lowes LE, Hedley BD, Keeney M and Allan
AL: User-defined protein marker assay development for
characterization of circulating tumor cells using the
CellSearch® system. Cytometry A. 81:983–995. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Reeh M, Effenberger KE, Koenig AM,
Riethdorf S, Eichstädt D, Vettorazzi E, Uzunoglu FG, Vashist YK,
Izbicki JR, Pantel K and Bockhorn M: Circulating tumor cells as a
biomarker for preoperative prognostic staging in patients with
esophageal cancer. Ann Surg. 261:1124–1130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sato N, Hayashi N, Imamura Yu, Tanaka Y,
Kinoshita K, Kurashige J, Saito S, Karashima R, Hirashima K, Nagai
Y, et al: Usefulness of transcription-reverse transcription
concerted reaction method for detecting circulating tumor cells in
patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:2060–2065.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Viswanath B, Kim S and Lee K: Recent
insights into nanotechnology development for detection and
treatment of colorectal cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 11:2491–2504.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo W, Yang X, Sun YF, Shen MN, Ma XL, Wu
J, Zhang CY, Zhou Y, Xu Y, Hu B, et al: Clinical significance of
EpCAM mRNA-positive circulating tumor cells in hepatocellular
carcinoma by an optimized negative enrichment and qRT-PCR-based
platform. Clin Cancer Res. 20:4794–4805. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kelley RK, Magbanua MJ, Butler TM,
Collisson EA, Hwang J, Sidiropoulos N, Evason K, McWhirter RM,
Hameed B, Wayne EM, et al: Circulating tumor cells in
hepatocellular carcinoma: A pilot study of detection, enumeration,
and next-generation sequencing in cases and controls. BMC Cancer.
15:2062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hiraiwa K, Takeuchi H, Hasegawa H, Saikawa
Y, Suda K, Ando T, Kumagai K, Irino T, Yoshikawa T, Matsuda S, et
al: Clinical significance of circulating tumor cells in blood from
patients with gastrointestinal cancers. Ann Surg Oncol.
15:3092–3100. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sequist LV, Nagrath S, Toner M, Haber DA
and Lynch TJ: The CTC-chip: An exciting new tool to detect
circulating tumor cells in lung cancer patients. J Thorac Oncol.
4:281–283. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ohnaga T, Shimada Y, Moriyama M, Kishi H,
Obata T, Takata K, Okumura T, Nagata T, Muraguchi A and Tsukada K:
Polymeric microfluidic devices exhibiting sufficient capture of
cancer cell line for isolation of circulating tumor cells. Biomed
Microdevices. 15:611–616. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ohnaga T, Shimada Y, Takata K, Obata T,
Okumura T, Nagata T, Kishi H, Muraguchi A and Tsukada K: Capture of
esophageal and breast cancer cells with polymeric microfluidic
devices for CTC isolation. Mol Clin Oncol. 4:599–602. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chikaishi Y, Yoneda K, Ohnaga T and Tanaka
F: EpCAM-independent capture of circulating tumor cells with a
‘universal CTC-chip’. Oncol Rep. 37:77–82. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yoneda K, Chikaishi Y, Kuwata T, Ohnaga T
and Tanaka F: Capture of mesothelioma cells with ‘universal’
CTC-chip. Oncol Lett. 15:2635–2640. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ohnaga T, Takei Y, Nagata T and Shimada Y:
Highly efficient capture of cancer cells expressing EGFR by
microfluidic methods based on antigen-antibody association. Sci
Rep. 8:120052018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
Ch: TNM classification of malignant tumours. 7th. Oxford, UK:
Wiley-Blackwell; 2009
|
|
38
|
Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon
and Rectum (JSCCR): Japanese classification of colorectal
carcinoma. 2nd English. Kanehara and Co. Ltd; Tokyo: 2009
|
|
39
|
Thomsen M, Skovlund E, Sorbye H, Bolstad
N, Nustad KJ, Glimelius B, Pfeiffer P, Kure EH, Johansen JS, Tveit
KM, et al: Prognostic role of carcinoembryonic antigen and
carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in metastatic colorectal cancer: A
BRAF-mutant subset with high CA 19-9 level and poor outcome. Br J
Cancer. 118:1609–1616. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Stojkovic Lalosevic M, Stankovic S,
Stojkovic M, Markovic V, Dimitrijevic I, Lalosevic J, Petrovic J,
Brankovic M, Pavlovic Markovic A and Krivokapic Z: Can preoperative
CEA and CA19-9 serum concentrations suggest metastatic disease in
colorectal cancer patients? Hell J Nuc Med. 20:41–45. 2017.
|
|
41
|
Watanabe M, Takemasa I, Kaneko N, Yokoyama
Y, Matsuo E, Iwasa S, Mori M, Matsuura N, Monden M and Nishimura O:
Clinical significance of circulating galectins as colorectal cancer
markers. Oncol Rep. 25:1217–1226. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pecot CV, Bischoff FZ, Mayer JA, Wong KL,
Pham T, Bottsford-Miller J, Stone RL, Lin YG, Jaladurgam P, Roh JW,
et al: A novel platform for detection of CK+ and CK- CTCs. Cancer
Discov. 1:580–586. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
R Core Team, . R: A language and
environment for statistical computing. R foundation for statistical
computing; Vienna, Austria: https://www.R-project.org/2016
|
|
44
|
Lu YT, Zhao L, Shen Q, Garcia MA, Wu D,
Hou S, Song M, Xu X, Ouyang WH, Ouyang WW, et al: NanoVelcro Chip
for CTC enumeration in prostate cancer patients. Methods.
64:144–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Galletti G, Sung MS, Vahdat LT, Shah MA,
Santana SM, Altavilla G, Kirby BJ and Giannakakou P: Isolation of
breast cancer and gastric cancer circulating tumor cells by use of
an anti HER2-based microfluidic device. Lab Chip. 14:147–156. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gleghorn JP, Pratt ED, Denning D, Liu H,
Bander NH, Tagawa ST, Nanus DM, Giannakakou PA and Kirby BJ:
Capture of circulating tumor cells from whole blood of prostate
cancer patients using geometrically enhanced differential
immunocapture (GEDI) and a prostate-specific antibody. Lab Chip.
10:27–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Maheswaran S, Sequist LV, Nagrath S, Ulkus
L, Brannigan B, Collura CV, Inserra E, Diederichs S, Iafrate AJ,
Bell DW, et al: Detection of mutations in EGFR in circulating
lung-cancer cells. N Engl J Med. 359:366–377. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|