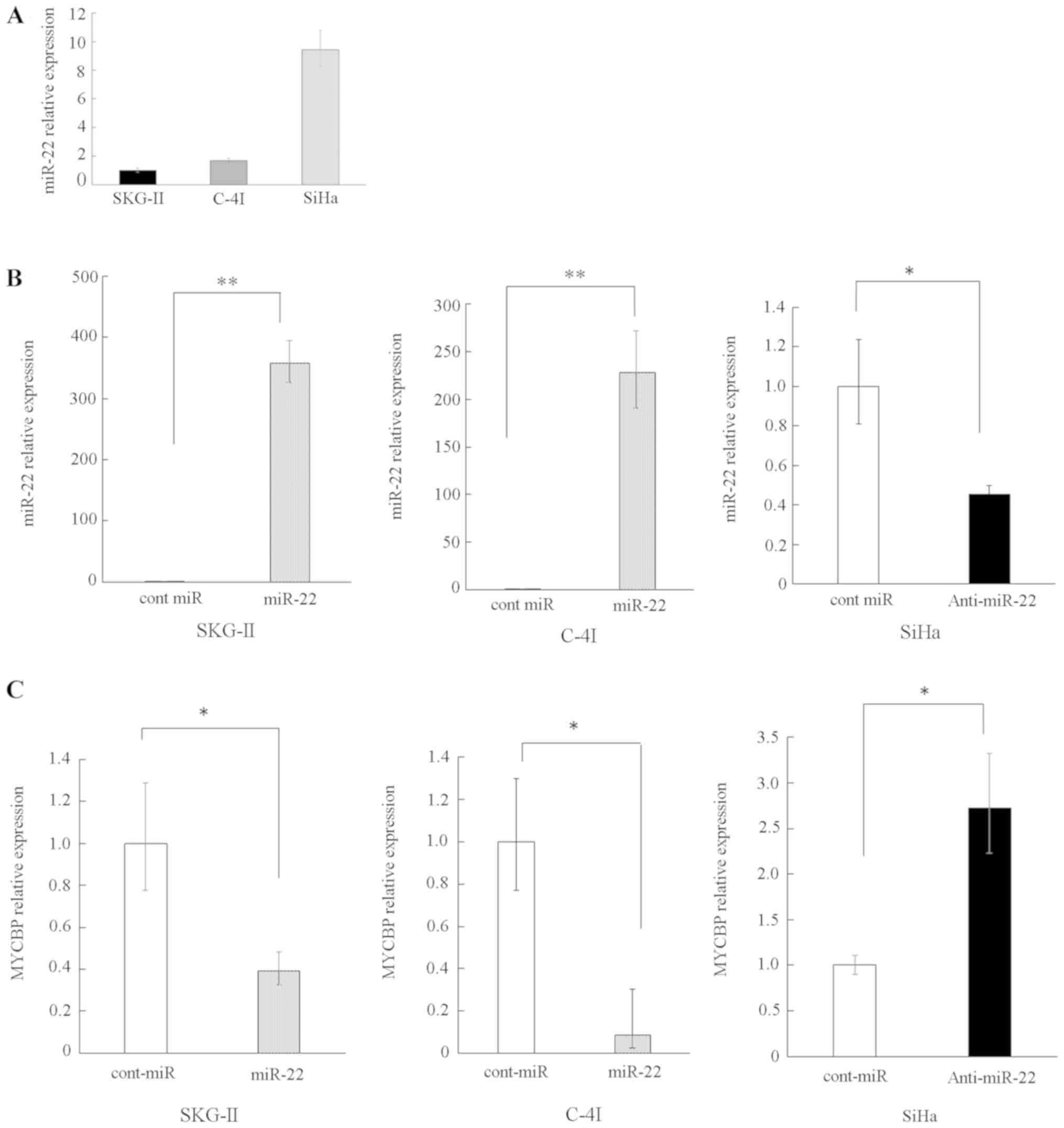
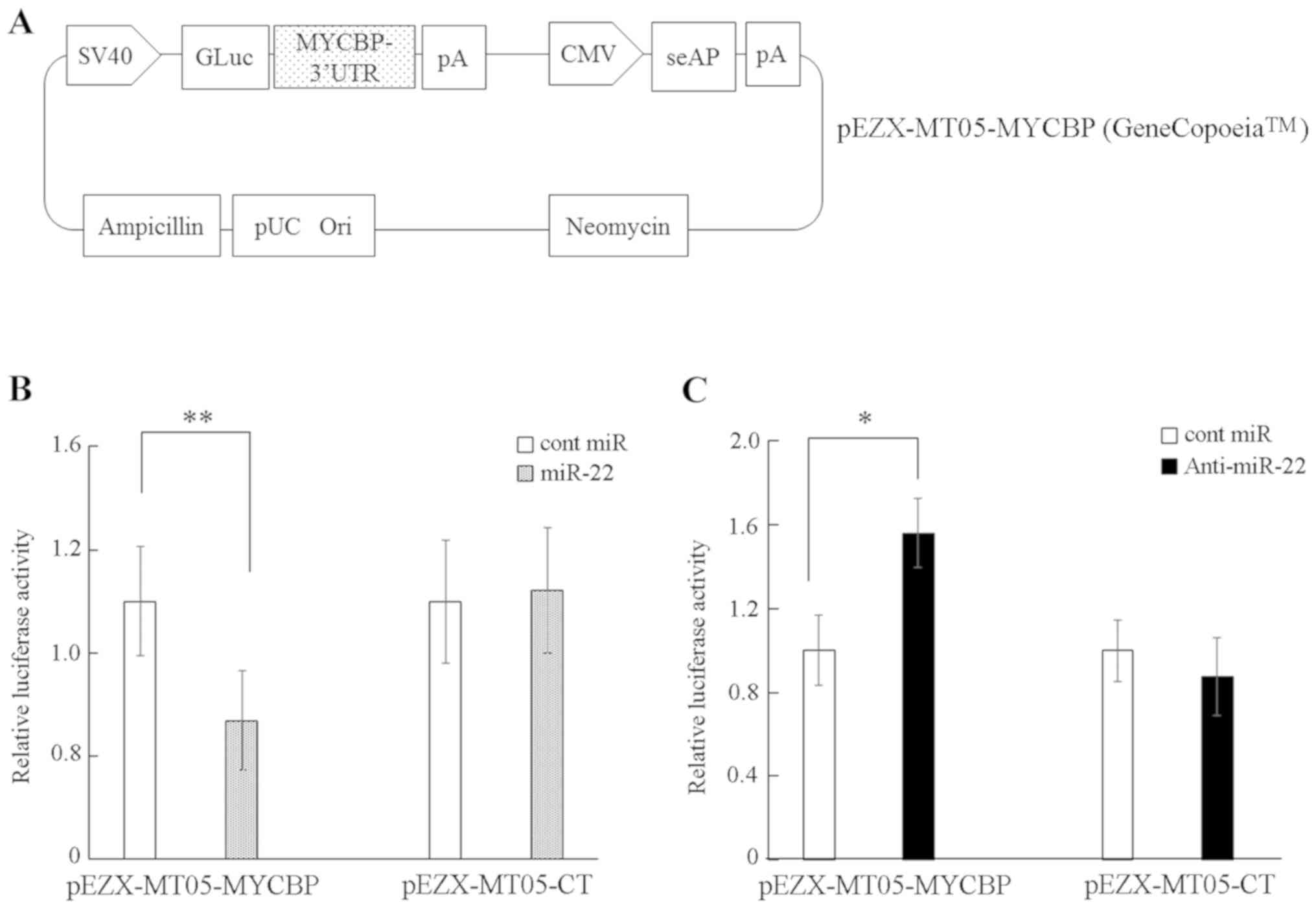
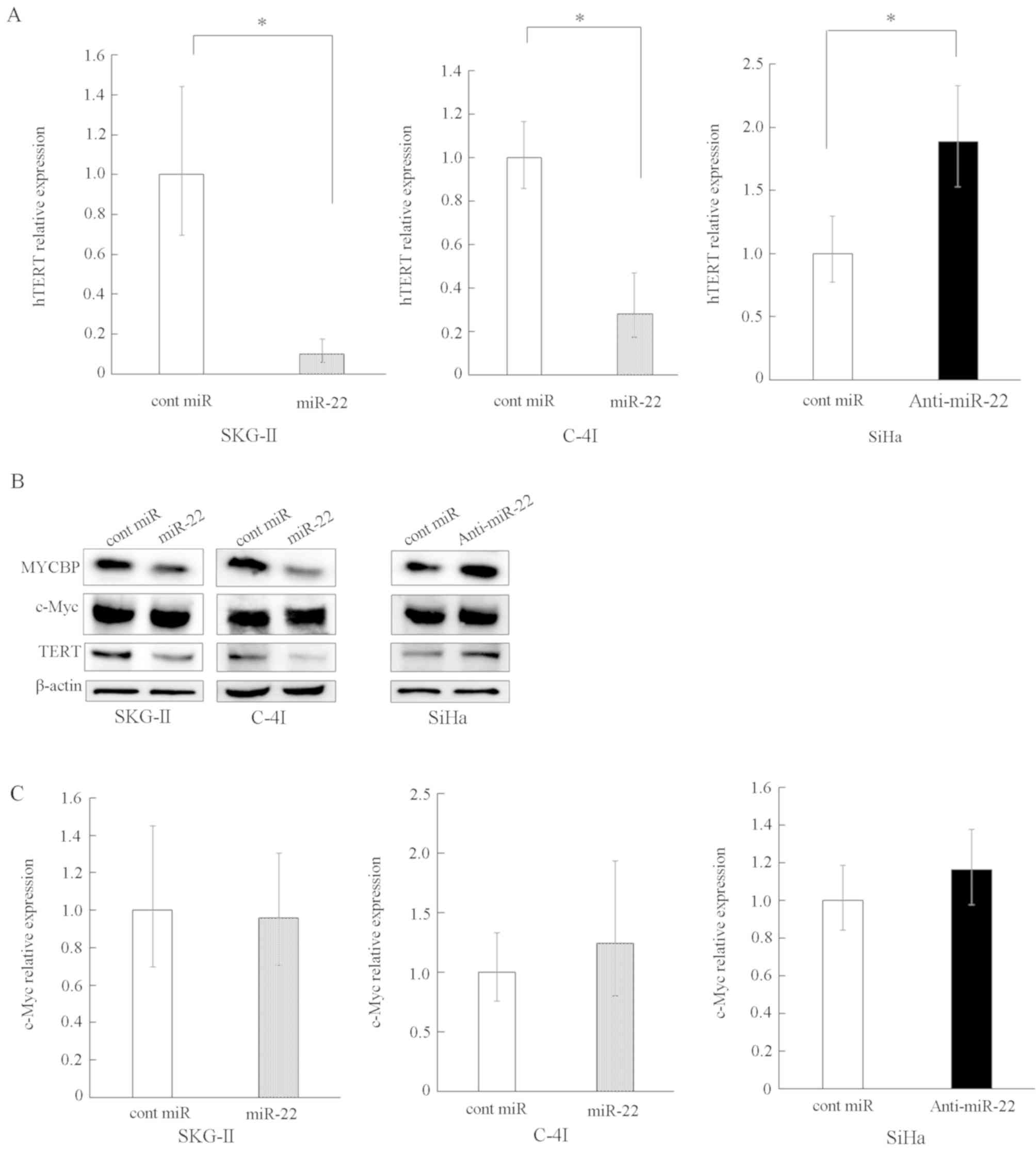
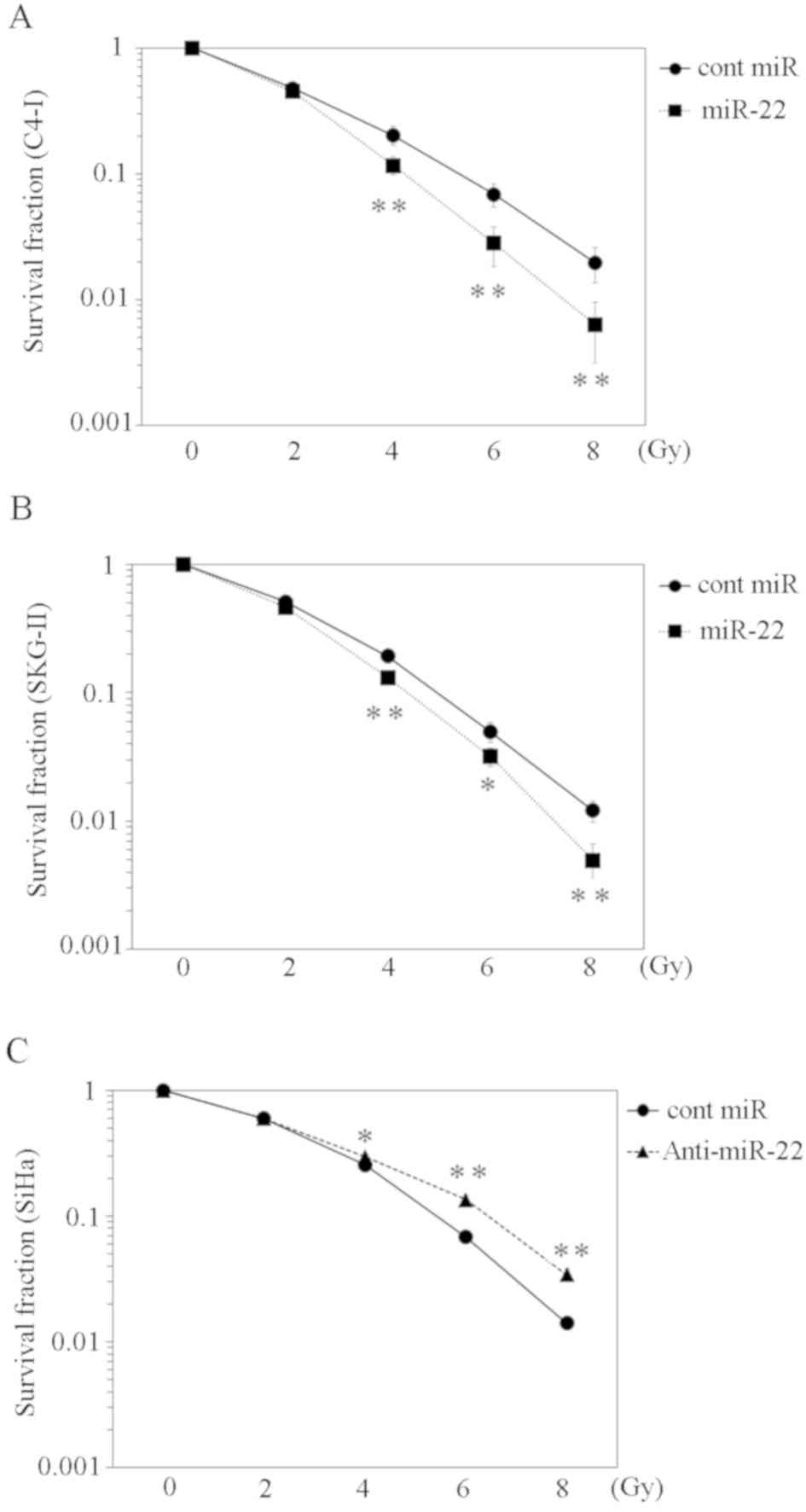
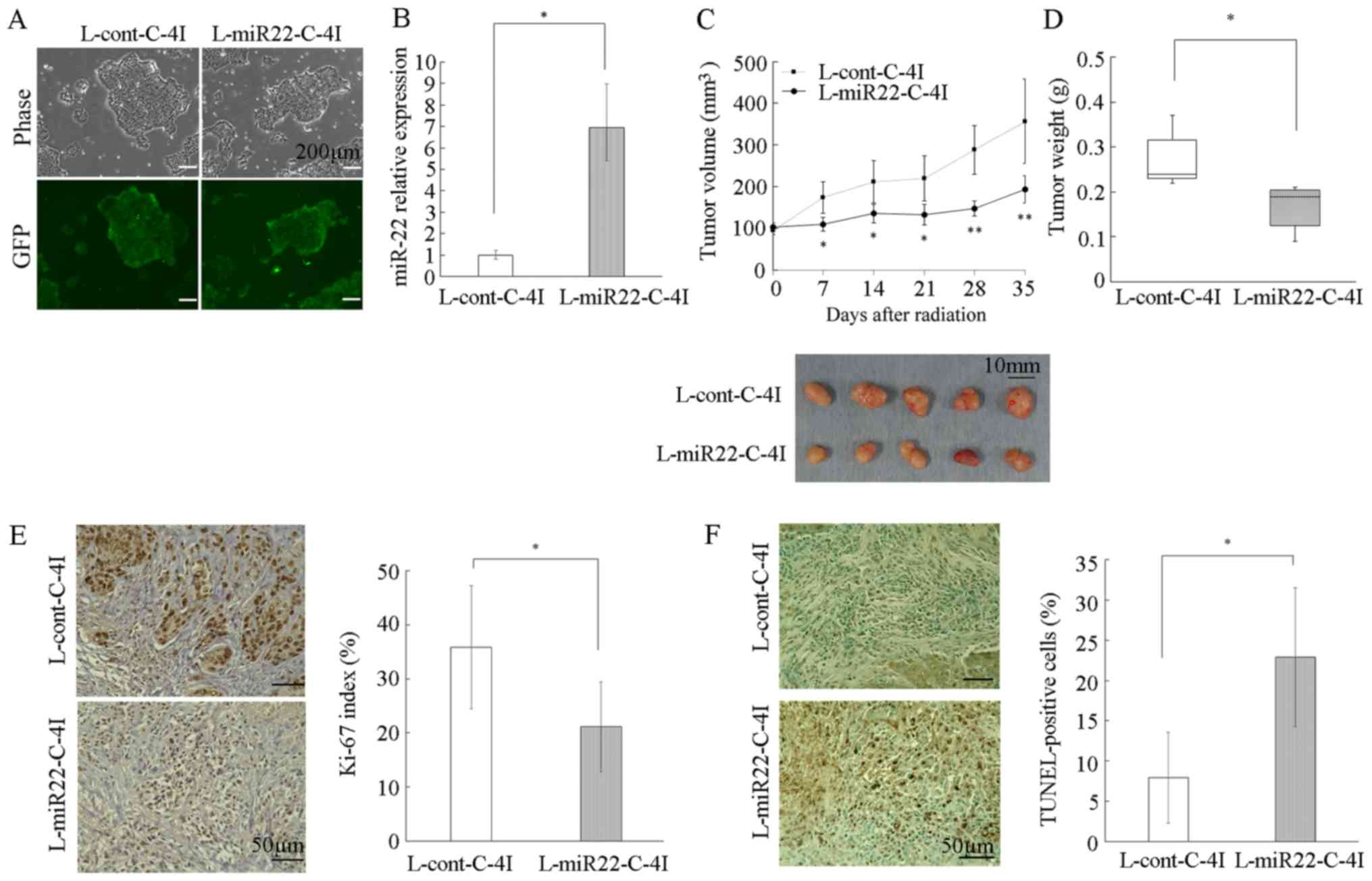
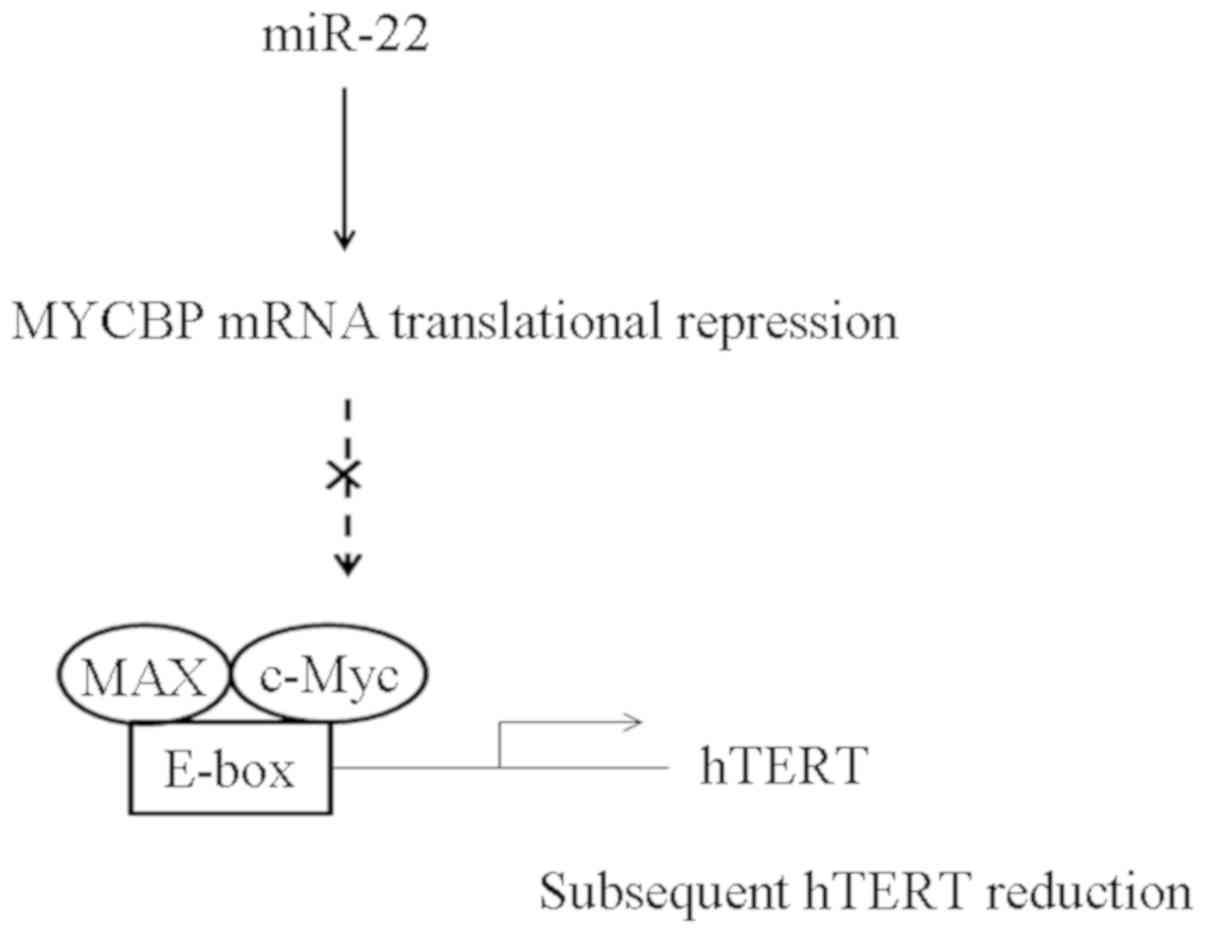
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 coutries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yagi A, Ueda Y, Kakuda M, Tanaka Y, Ikeda
S, Matsuzaki S, Kobayashi E, Morishima T, Miyashiro I, Fukui K, et
al: Epidemiologic and clinical analysis of cervical cancer using
data from the population-based Osaka cancer regstry. Cancer Res.
79:1252–1259. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fokom Domgue J and Schmeler KM:
Conservative management of cervical cancer: Current status and
obstetrical implications. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol.
55:79–92. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chohen PA, Jhingran A, Oaknin A and Denny
L: Cercvical cancer. Lancet. 393:169–182. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wright JD, Matsuo K, Huang Y, Tergas AI,
Hou JY, Khoury-Collado F, St Clair CM, Ananth CV, Neugut AI and
Hershman DL: Prognostic performance of the 2018 international
federation of gynecololgy and obstetrics cervical cancer staging
guidelines. Obstet Gynecol. 134:49–57. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pal J, Gold JS, Munshi NC and Shammas MA:
Biology of telomeres: Importance in etiology of esophageal cancer
and as therapeutic target. Transl Res. 162:364–370. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lord RV, Salonga D, Danenberg KD, Peters
JH, DeMeester TR, Park JM, Johansson J, Skinner KA, Chandrasoma P,
DeMeester SR, et al: Telomerase reverse transcriptase expression is
increased early in the Barrett's metaplasia, dysplasia,
adenocarcinoma sequence. J Gastrointest Surg. 4:135–142. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hoang-Vu C, Boltze C, Gimm O, Poremba C,
Dockhorn-Dworniczak B, Köhrle J, Rath FW and Dralle H: Expression
of telomerase genes in thyroid carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 21:265–272.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang R, Lin F, Wang X, Gao P, Dong K, Wei
SH, Cheng SY and Zhang HZ: The therapeutic potential of survivin
promoter-driven siRNA on suppressing tumor growth and enhancing
radiosensitivity of human cervical carcinoma cells via
downregulating hTERT gene expression. Cancer Biol Ther.
6:1295–1301. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kyo S, Takakura M, Taira T, Kanaya T, Itoh
H, Yutsudo M, Ariga H and Inoue M: Sp1 cooperates with c-Myc to
activate transcription of the human telomerase reverse
transcriptase gene (hTERT). Nucleic Acids Res. 28:669–677. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ambros V: MicroRNAs: Tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kaur A, Mackin ST, Schlosser K, Wong FL,
Elharram M, Delles C, Stewart DJ, Dayan N, Landry T and Pilote L:
Systemativ review of microRNA biomarkers in acute coronary syndrome
and stable coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Res. (pii):
cvz3022019.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ji C and Guo X: The clinical potential of
circulating microRNAs in obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 15:731–743.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang L, Chen B and Ding D: Decreased
microRNA-22 is associated with poor prognosis in cervical cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 10:9515–9520. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiong J, Du Q and Liang Z:
Tumor-suppressive microRNA-22 inhibits the transcription of
E-box-containing c-Myc target genes by silencing c-Myc binding
protein. Oncogene. 29:4980–4988. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Grimson A, Farh KK, Johnston WK,
Garrett-Engele P, Lim LP and Bartel DP: MicroRNA targeting
specificity in mammals: Determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol Cell.
27:91–105. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wong N and Wang X: MiRDB: An online
resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43((Database Issue)): D146–D152. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schimittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ono YJ, Hayashi M, Tanabe A, Hayashi A,
Kanemura M, Terai Y and Ohmichi M: Estradiol-mediated hepatocyte
growth factor is involved in the implantation of endometriotic
cells via the mesothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the
peritoneum. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 308:E950–E959. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman
J and van Bree C: Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc.
1:2315–2319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Taira T, Maeda J, Onishi T, Kitaura H,
Yoshida S, Kato H, Ikeda M, Tamai K, Iguchi-Ariga SM and Ariga H:
AMY-1, a novel C-MYC binding protein that stimulates transcription
activity of C-MYC. Genes Cells. 3:549–565. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu KJ, Grandori C, Amacker M, Simon-Vermot
N, Polack A, Lingner J and Dalla-Favera R: Direct activation of
TERT transcription by c-MYC. Nat Genet. 21:220–224. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang W and Xing L: RNAi gene therapy of
SiHa cells via targeting human TERT induces growth inhibition and
enhances radiosensitivity. Int J Oncol. 43:1228–1234. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakatani F, Ferracin M, Manara MC, Ventura
S, Del Monaco V, Ferrari S, Alberghini M, Grilli A, Knuutila S,
Schaefer KL, et al: MiR-34a predicts survival of Ewing's sarcoma
patients and directly influences cell chemo-sensitivity and
malignancy. J Pathol. 226:796–805. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xin M, Qiao Z, Li J, Liu J, Song S, Zhao
X, Miao P, Tang T, Wang L, Liu W, et al: MiR-22 inhibits tumor
growth and metastasis by targeting ATP citrate lyase: Evidence in
osteosarcoma, prostate cancer, cervical cancer and lung cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:44252–44265. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Liang S, Yu H, Zhang J, Ma D and Lu
X: An inhibitory effect of miR-22 on cell migration and invasion in
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 119:543–538. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zuo QF, Cao LY, Yu T, Gong L, Wang LN,
Zhao YL, Xiao B and Zou QM: MicroRNA-22 inhibits tumor growth and
metastasis in gastric cancer by directly targeting MMP14 and Snail.
Cell Death Dis. 6:e20002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang H, Tang J, Li C, Kong J, Wang J, Wu
Y, Xu E and Lai M: MiR-22 regulates 5-FU sensitivity by inhibiting
autophagy and promoting apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 356:781–790. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang T, Xue X and Peng H: Therapeutic
delivery of miR-29b enhances radiosensitivity in cervical cancer.
Mol Ther. 27:1183–1194. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pedroza-Torres A, Campos-Parra AD,
Millan-Catalan O, Loissell-Baltazar YA, Zamudio-Meza H, Cantú de
León D, Montalvo-Esquivel G, Isla-Ortiz D, Herrera LA,
Ángeles-Zaragoza Ó, et al: MicroRNA-125 modulates radioresistance
through targeting p21 in cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 39:1532–1540.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Li Y, Wang D and Wei X: MiR-22
suppresses tumorigenesis and improves radiosensitivity of breast
cancer cells by targeting Sirt1. Biol Res. 50:272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Z, Li T, Deng S, Fu S, Zhou X and He
Y: Radiation induces apoptosis and osteogenic impairment through
miR-22-mediated intracellular oxidative stress in bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2018:58454022018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sakamuro D and Prendergast GC: New
Myc-interacting proteins: A second Myc network emerges. Oncogene.
18:2942–2954. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang H, Yan X, Ji LY, Ji XT, Wang P, Guo
SW and Li SZ: MiR-139 functions as an antioncomir to repress glioma
progression through targeting IGF-1 R, AMY-1, and PGC-1β. Technol
Cancer Res Treat. 16:497–511. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gong L, Xia Y, Qian Z, Shi J, Luo J, Song
G, Xu J and Ye Z: Overexpression of MYC binding protein promotes
invasion and migration in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:5243–5249.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|