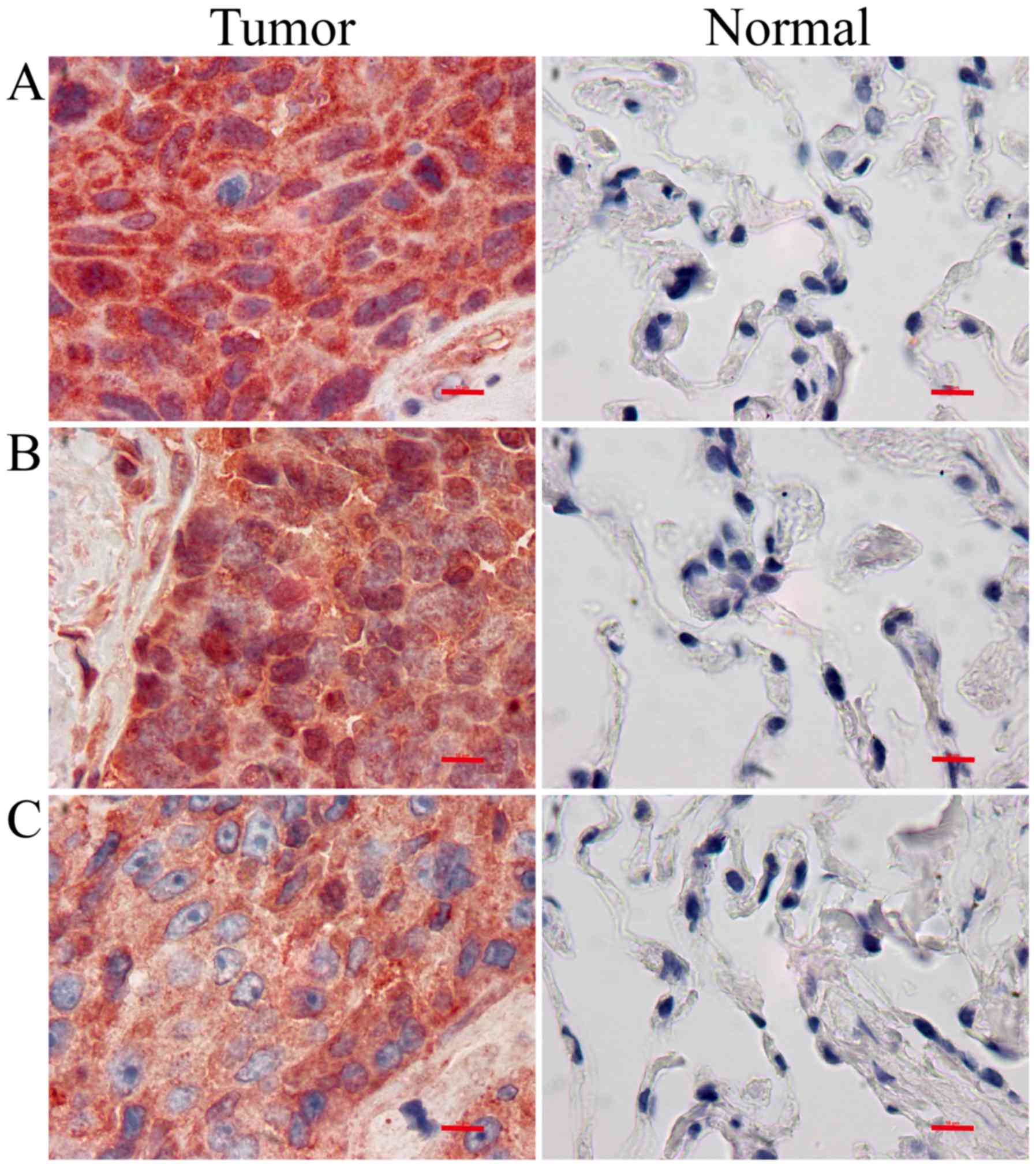
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E and Li QK:
Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical
markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma
(NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin
Cancer Biol. 52:103–109. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kikuchi T, Hassanein M, Amann JM, Liu Q,
Slebos RJ, Rahman SM, Kaufman JM, Zhang X, Hoeksema MD, Harris BK,
et al: In-depth proteomic analysis of nonsmall cell lung cancer to
discover molecular targets and candidate biomarkers. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 11:916–932. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Uribarri M, Hormaeche I, Zalacain R,
Lopez-Vivanco G, Martinez A, Nagore D and Ruiz-Argüello MB: A new
biomarker panel in bronchoalveolar lavage for an improved lung
cancer diagnosis. J Thorac Oncol. 9:1504–1512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shimura T, Iwasaki H, Kitagawa M, Ebi M,
Yamada T, Yamada T, Katano T, Nisie H, Okamoto Y, Ozeki K, et al:
Urinary cysteine-rich protein 61 and trefoil factor 3 as diagnostic
biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Transl Oncol. 12:539–544. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ahn JM, Sung HJ, Yoon YH, Kim BG, Yang WS,
Lee C, Park HM, Kim BJ, Kim BG, Lee SY, et al: Integrated
glycoproteomics demonstrates fucosylated serum paraoxonase 1
alterations in small cell lung cancer. Mol Cell Proteomics.
13:30–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Abdullah-Soheimi SS, Lim BK, Hashim OH and
Shuib AS: Patients with ovarian carcinoma excrete different altered
levels of urine CD59, kininogen-1 and fragments of
inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 and albumin. Proteome
Sci. 8:582010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu JS, Chen YT, Chiang WF, Hsiao YC, Chu
LJ, See LC, Wu CS, Tu HT, Chen HW, Chen CC, et al: Saliva protein
biomarkers to detect oral squamous cell carcinoma in a high-risk
population in Taiwan. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:11549–11554.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J, Wang X, Lin S, Chen C, Wang C, Ma
Q and Jiang B: Identification of kininogen-1 as a serum biomarker
for the early detection of advanced colorectal adenoma and
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e705192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Briones-Orta MA, Avendaño-Vázquez SE,
Aparicio-Bautista DI, Coombes JD, Weber GF and Syn WK: Osteopontin
splice variants and polymorphisms in cancer progression and
prognosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1868:93–108A. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao H, Chen Q, Alam A, Cui J, Suen KC,
Soo AP, Eguchi S, Gu J and Ma D: The role of osteopontin in the
progression of solid organ tumour. Cell Death Dis. 9:3562018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang W, Wang S and Zhang M: Identification
of urine biomarkers associated with lung adenocarcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:38517–38529. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Y, Miao L, Yu M, Shi M, Wang Y, Yang J,
Xiao Y and Cai H: α1-antitrypsin promotes lung adenocarcinoma
metastasis through upregulating fibronectin expression. Int J
Oncol. 50:1955–1964. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liang Y, Ma T, Thakur A, Yu H, Gao L, Shi
P, Li X, Ren H, Jia L, Zhang S, et al: Differentially expressed
glycosylated patterns of alpha-1-antitrypsin as serum biomarkers
for the diagnosis of lung cancer. Glycobiology. 25:331–340. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu S, Meng Q, Hu H and Zhang M:
Correlation of ANXA1 expression with drug resistance and relapse in
bladder cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:5538–5548. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pastor MD, Nogal A, Molina-Pinelo S,
Quintanal-Villalonga Á, Meléndez R, Ferrer I, Romero-Romero B, De
Miguel MJ, López-Campos JL, Corral J, et al: IL-11 and CCL-1: Novel
protein diagnostic biomarkers of lung adenocarcinoma in
bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). J Thorac Oncol. 11:2183–2192.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Doustjalali SR, Yusof R, Yip CH, Looi LM,
Pillay B and Hashim OH: Aberrant expression of acute-phase reactant
proteins in sera and breast lesions of patients with malignant and
benign breast tumors. Electrophoresis. 25:2392–2401. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abdul-Rahman PS, Lim BK and Hashim OH:
Expression of high-abundance proteins in sera of patients with
endometrial and cervical cancers: Analysis using 2-DE with silver
staining and lectin detection methods. Electrophoresis.
28:1989–1996. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mu AK, Lim BK, Hashim OH and Shuib AS:
Identification of O-glycosylated proteins that are aberrantly
excreted in the urine of patients with early stage ovarian cancer.
International journal of molecular sciences. 14:7923–7931. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sandim V, Pereira Dde A, Kalume DE,
Oliveira-Carvalho AL, Ornellas AA, Soares MR, Alves G and Zingali
RB: Proteomic analysis reveals differentially secreted proteins in
the urine from patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol
Oncol. 34:5.e11–25. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xu J, Fang J, Cheng Z, Fan L, Hu W, Zhou F
and Shen H: Overexpression of the Kininogen-1 inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis of glioma cells. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 37:1802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schrödter S, Braun M, Syring I, Klümper N,
Deng M, Schmidt D, Perner S, Müller SC and Ellinger J:
Identification of the dopamine transporter SLC6A3 as a biomarker
for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 15:102016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang W, Zhang L, Guo Q, Wang H, Ma M, Sun
J and Chen C: Identification of the pathogenic biomarkers for
hepatocellular carcinoma based on RNA-seq analyses. Pathol Oncol
Res. 25:1207–1213. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu W, Liu B, Cai Q, Li J, Chen X and Zhu
Z: Proteomic identification of serum biomarkers for gastric cancer
using multi-dimensional liquid chromatography and 2D differential
gel electrophoresis. Clinica Chimica Acta. 413:1098–1106. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Quesada-Calvo F, Massot C, Bertrand V,
Longuespée R, Blétard N, Somja J, Mazzucchelli G, Smargiasso N,
Baiwir D, De Pauw-Gillet MC, et al: OLFM4, KNG1 and Sec24C
identified by proteomics and immunohistochemistry as potential
markers of early colorectal cancer stages. Clin Proteomics.
14:92017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao B, Yu T, Xue D, Sun B, Shao Q,
Choudhry H, Marcus V, Ragoussis J, Zhang Y, Zhang W and Gao ZH: A
multidimensional integration analysis reveals potential bridging
targets in the process of colorectal cancer liver metastasis. PLoS
One. 12:e01787602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Navaneethan U, Lourdusamy V, Gk Venkatesh
P, Willard B, Sanaka MR and Parsi MA: Bile proteomics for
differentiation of malignant from benign biliary strictures: A
pilot study. Gastroenterol Rep. 3:136–143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li S, Yang R, Sun X, Miao S, Lu T, Wang Y,
Wo Y and Jiao W: Identification of SPP1 as a promising biomarker to
predict clinical outcome of lung adenocarcinoma individuals. Gene.
679:398–404. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin Q, Guo L, Lin G, Chen Z, Chen T, Lin
J, Zhang B and Gu X: Clinical and prognostic significance of OPN
and VEGF expression in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.
Cancer Epidemiol. 39:539–544. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kothari AN, Arffa ML, Chang V, Blackwell
RH, Syn WK, Zhang J, Mi Z and Kuo PC: Osteopontin-a master
regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Med.
5:E392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zou C, Luo Q, Qin J, Shi Y, Yang L, Ju B
and Song G: Osteopontin promotes mesenchymal stem cell migration
and lessens cell stiffness via integrin β1, FAK, and ERK pathways.
Cell Biochem Biophys. 65:455–462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Marotta LL, Almendro V, Marusyk A,
Shipitsin M, Schemme J, Walker SR, Bloushtain-Qimron N, Kim JJ,
Choudhury SA, Maruyama R, et al: The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway
is required for growth of CD44+CD24− stem
cell-like breast cancer cells in human tumors. J Clin Invest.
121:2723–2735. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rouanne M, Adam J, Goubar A, Robin A,
Ohana C, Louvet E, Cormier J, Mercier O, Dorfmüller P, Fattal S, et
al: Osteopontin and thrombospondin-1 play opposite roles in
promoting tumor aggressiveness of primary resected non-small cell
lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 16:4832016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ostheimer C, Schweyer F, Reese T, Bache M
and Vordermark D: The relationship between tumor volume changes and
serial plasma osteopontin detection during radical radiotherapy of
non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 12:3449–3456. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Y, Yang J, Liu H, Bi JR, Liu Y, Chen
YY, Cao JY and Lu YJ: The association between osteopontin and
survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients: A meta-analysis of
13 cohorts. Onco Targets Ther. 8:3513–3521. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mack PC, Redman MW, Chansky K, Williamson
SK, Farneth NC, Lara PN Jr, Franklin WA, Le QT, Crowley JJ and
Gandara DR; SWOG, : Lower osteopontin plasma levels are associated
with superior outcomes in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy: SWOG Study S0003. J
Clin Oncol. 26:4771–4776. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang SH, Cho KC, Yu KN, Hong SH, Park S,
Lee AY, Kim S, Lee S, Kang JW, Chae C, et al: Alpha 1-antitrypsin
activates lung cancer cell survival by acting on cap-dependent
protein translation, vesicle-mediated transport, and metastasis.
Oncotarget. 2016.
|
|
38
|
Rodríguez-Piñeiro AM, Blanco-Prieto S,
Sánchez-Otero N, Rodríguez-Berrocal FJ and de la Cadena MP: On the
identification of biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer in
serum and pleural effusion. J Proteomics. 73:1511–1522. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
El-Akawi ZJ, Abu-Awad AM, Sharara AM and
Khader Y: The importance of alpha-1 antitrypsin (alpha1-AT) and
neopterin serum levels in the evaluation of non-small cell lung and
prostate cancer patients. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 31:113–116.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chang YH, Lee SH, Liao IC, Huang SH, Cheng
HC and Liao PC: Secretomic analysis identifies alpha-1 antitrypsin
(A1AT) as a required protein in cancer cell migration, invasion,
and pericellular fibronectin assembly for facilitating lung
colonization of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Proteomics.
11:1320–1339. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kataoka H, Uchino H, Iwamura T, Seiki M,
Nabeshima K and Koono M: Enhanced tumor growth and invasiveness in
vivo by a carboxyl-terminal fragment of alpha1-proteinase inhibitor
generated by matrix metalloproteinases: A possible modulatory role
in natural killer cytotoxicity. Am J Pathol. 154:457–468. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zelvyte I, Sjögren HO and Janciauskiene S:
Effects of native and cleaved forms of alpha1-antitrypsin on ME
1477 tumor cell functional activity. Cancer Detect Prev.
26:256–265. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zelvyte I, Lindgren S and Janciauskiene S:
Multiple effects of alpha1-antitrypsin on breast carcinoma MDA-MB
468 cell growth and invasiveness. Eur J Cancer Prev. 12:117–124.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang P, Sun Z, Krowka MJ, Aubry MC, Bamlet
WR, Wampfler JA, Thibodeau SN, Katzmann JA, Allen MS, Midthun DE,
et al: Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency carriers, tobacco smoke,
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and lung cancer risk. Arch
Intern Med. 168:1097–1103. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Higashiyama M, Doi O, Kodama K, Yokouchi H
and Tateishi R: An evaluation of the prognostic significance of
alpha-1-antitrypsin expression in adenocarcinomas of the lung: An
immunohistochemical analysis. Br J Cancer. 65:300–302. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|