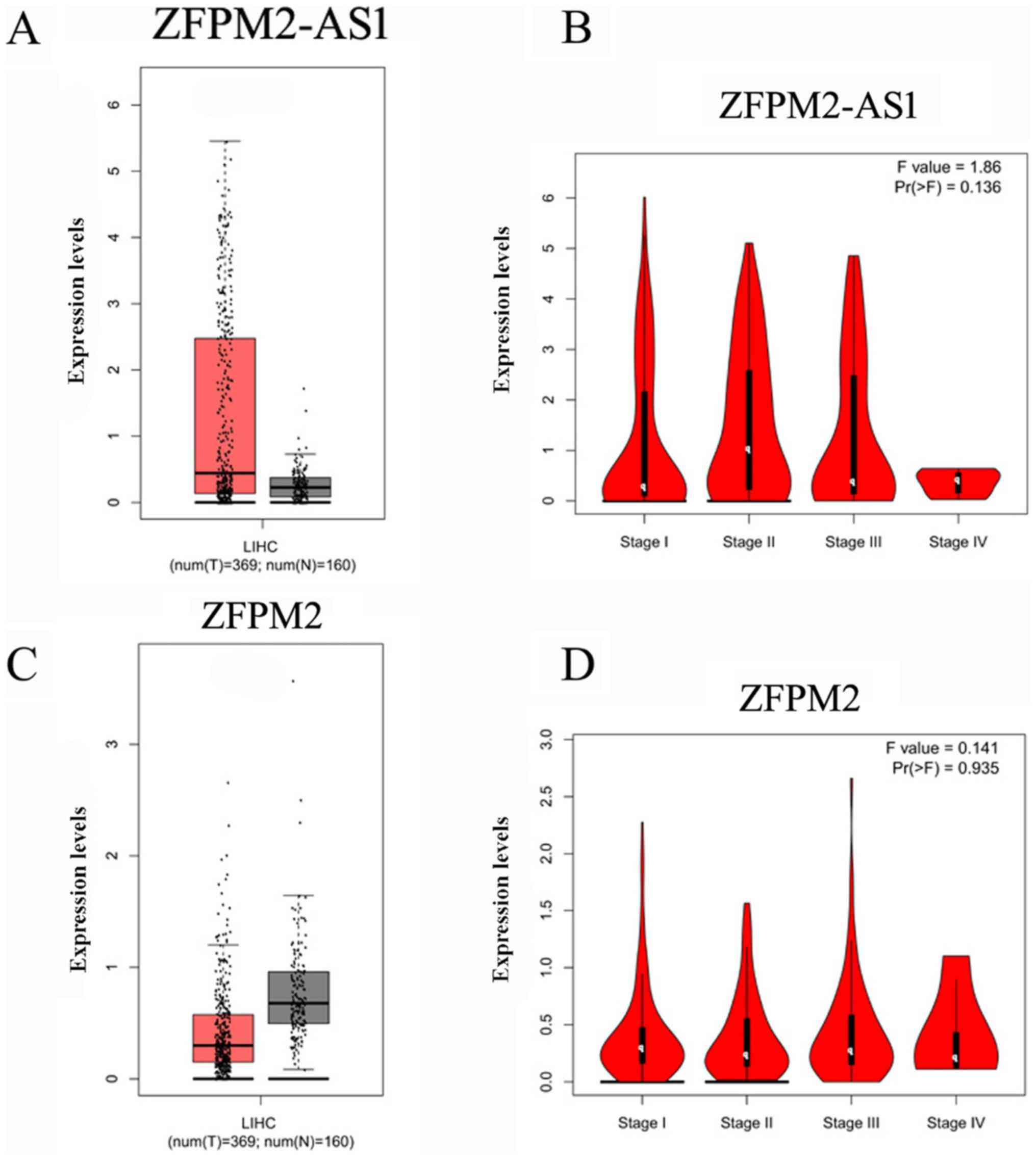
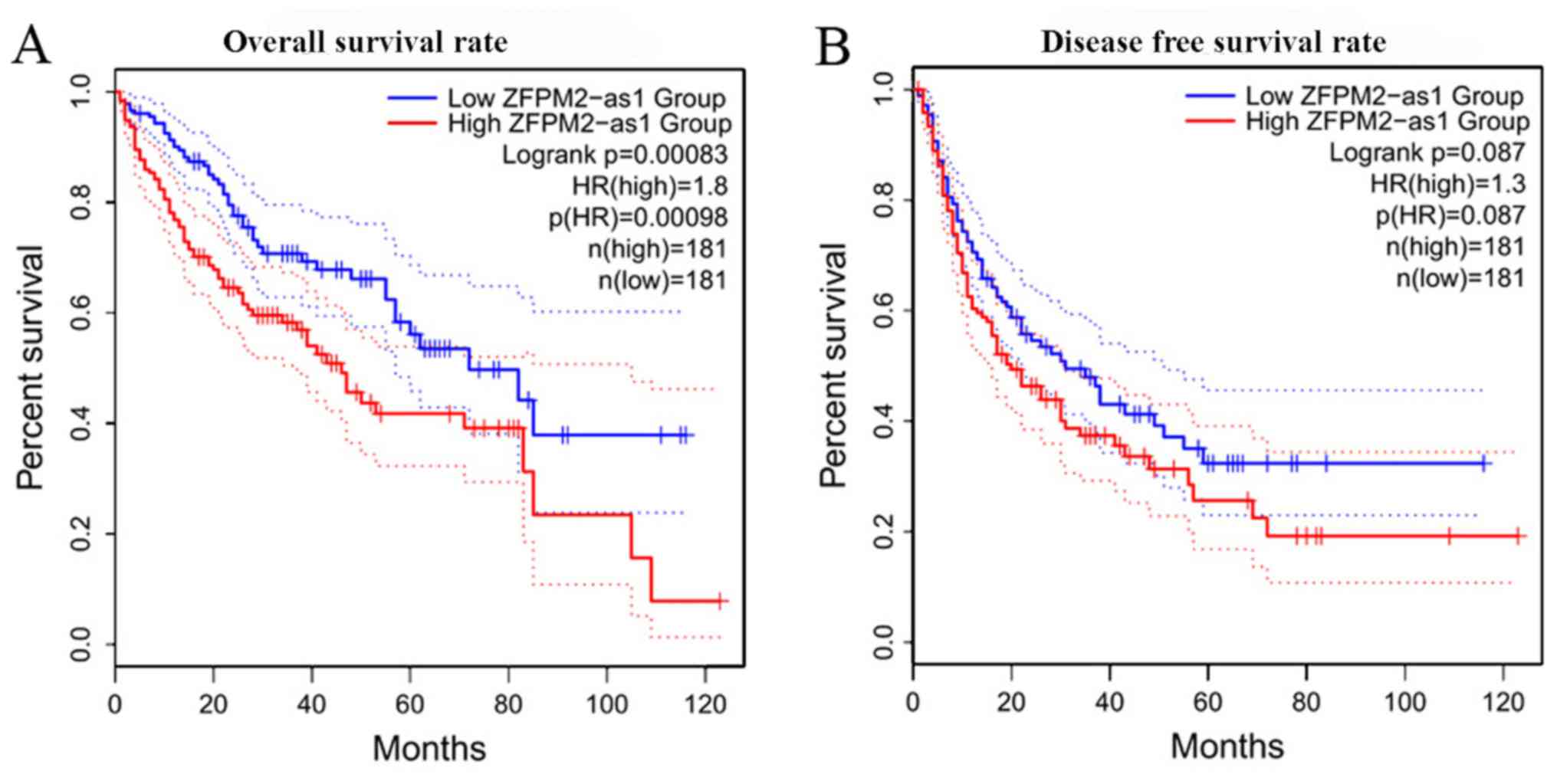
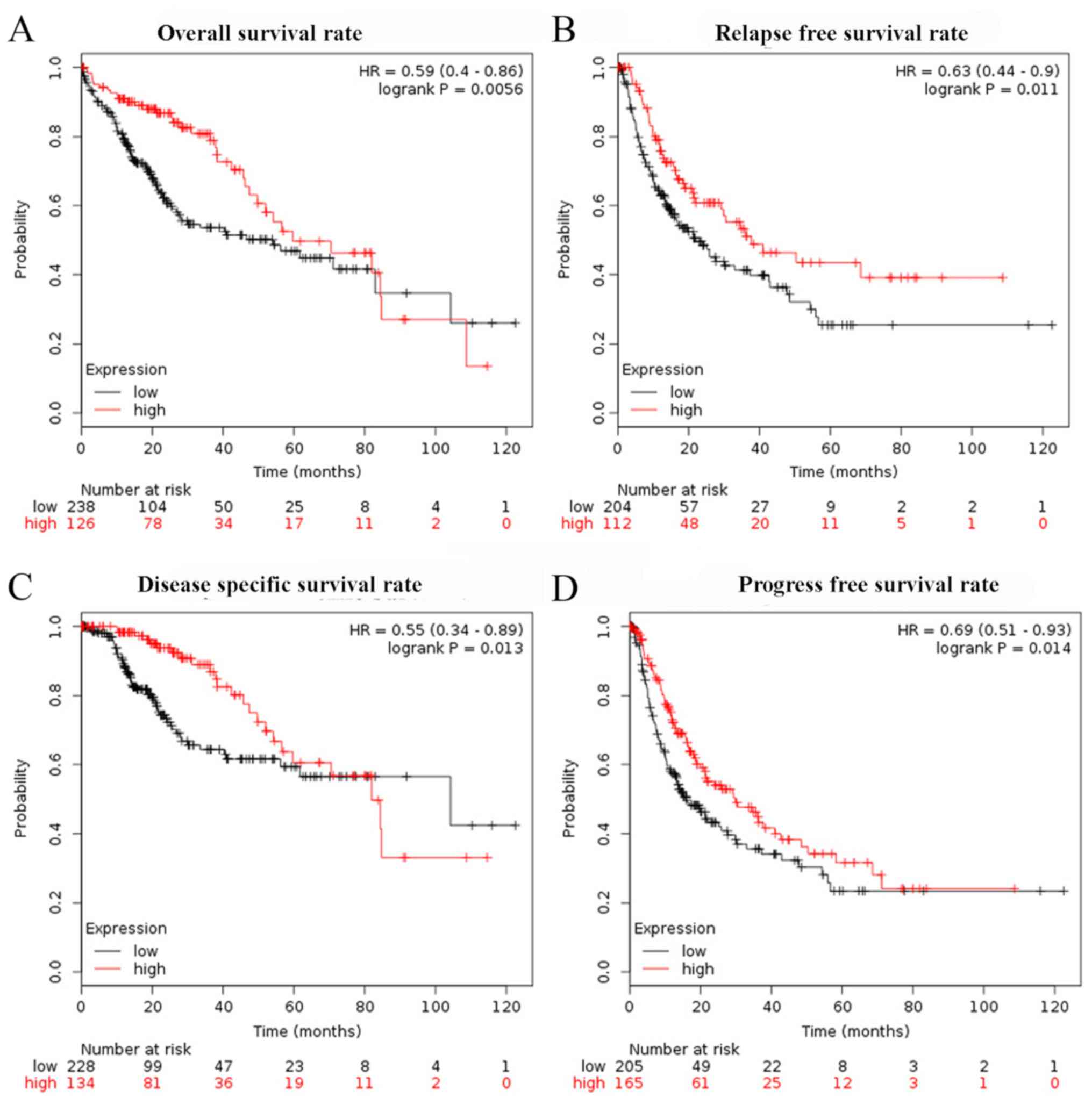
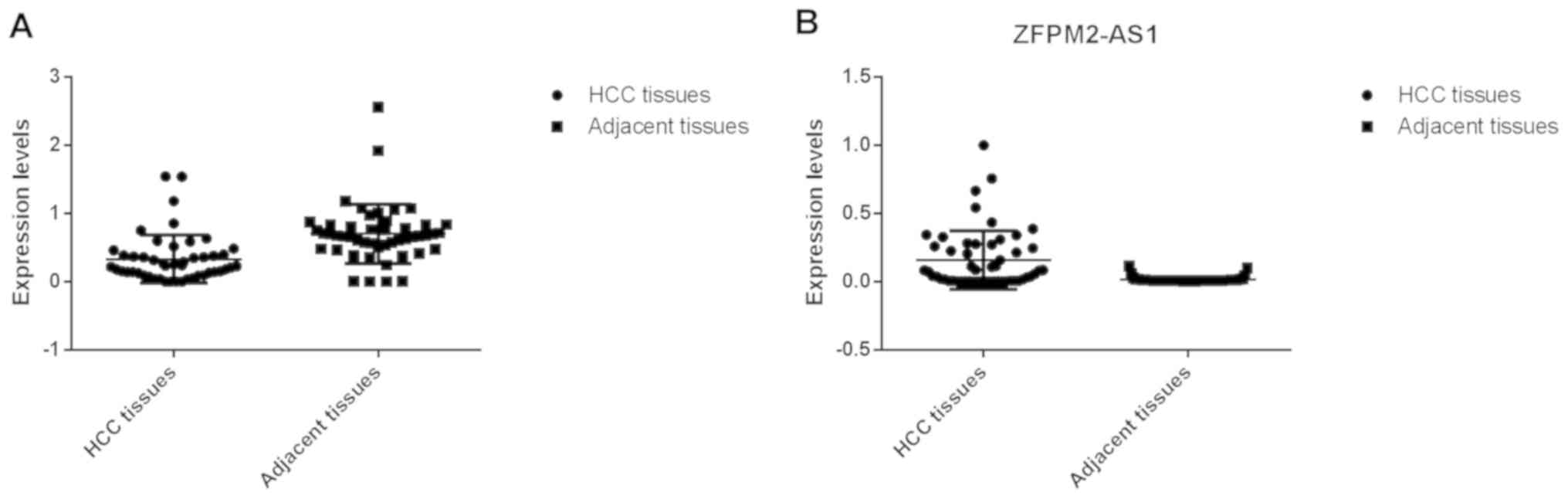
|
1
|
Forner A, Gilabert M, Bruix J and Raoul
JL: Treatment of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 11:525–535. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu RX, Seto WK, Lai CL and Yuen MF:
Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in the Asia-pacific
region. Gut Liver. 10:332–339. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators, .
Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282
causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980-2017: A
systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017.
Lancet. 392:1736–1788. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fatica A and Bozzoni I: Long non-coding
RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev
Genet. 15:7–21. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Beermann J, Piccoli MT, Viereck J and Thum
T: Non-coding RNAs in development and disease: Background,
mechanisms, and therapeutic approaches. Physiol Rev. 96:1297–1325.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mai H, Zhou B, Liu L, Yang F, Conran C, Ji
Y, Hou J and Jiang D: Molecular pattern of lncRNAs in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:1982019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao J, Wu L, Meng X, Yang H, Ni S, Wang Q,
Zhou J, Zhang Q, Su K, Shao L, et al: Profiling,
clinicopathological correlation and functional validation of
specific long non-coding RNAs for hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol
Cancer. 16:1642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang Y, Chen L, Gu J, Zhang H, Yuan J,
Lian Q, Lv G, Wang S, Wu Y, Yang YT, et al: Recurrently deregulated
lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 8:144212017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu FJ, Zheng JJ, Dong PH and Fan XM: Long
non-coding RNAs and hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Clin Oncol.
3:13–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang Z, Zhou L, Wu LM, Lai MC, Xie HY,
Zhang F and Zheng SS: Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
predicts tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
following liver transplantation. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1243–1250.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu S, Kong D, Chen Q, Ping Y and Pang D:
Oncogenic long noncoding RNA landscape in breast cancer. Mol
Cancer. 16:1292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu Y, Pan S, Liu L, Zhai X, Liu J, Wen J,
Zhang Y, Chen J, Shen H and Hu Z: A genetic variant in long
non-coding RNA HULC contributes to risk of HBV-related
hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese population. PLoS One.
7:e351452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lai MC, Yang Z, Zhou L, Zhu QQ, Xie HY,
Zhang F, Wu LM, Chen LM and Zheng SS: Long non-coding RNA MALAT-1
overexpression predicts tumor recurrence of hepatocellular
carcinoma after liver transplantation. Med Oncol. 29:1810–1816.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo S, Chen W, Luo Y, Ren F, Zhong T, Rong
M, Dang Y, Feng Z and Chen G: Clinical implication of long
non-coding RNA NEAT1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma
patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:5395–5402. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tu ZQ, Li RJ, Mei JZ and Li XH:
Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA GAS5 is associated with the
prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4303–4309. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan J, Zhou C, Guo K, Li Q and Wang Z: A
novel seven-lncRNA signature for prognosis prediction in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 120:213–223. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kong F, Deng X, Kong X, Du Y, Li L, Zhu H,
Wang Y, Xie D, Guha S, Li Z, et al: ZFPM2-AS1, a novel lncRNA,
attenuates the p53 pathway and promotes gastric carcinogenesis by
stabilizing MIF. Oncogene. 37:5982–5996. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Svensson EC, Tufts RL, Polk CE and Leiden
JM: Molecular cloning of FOG-2: A modulator of transcription factor
GATA-4 in cardiomyocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:956–961. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tevosian SG, Deconinck AE, Tanaka M,
Schinke M, Litovsky SH, Izumo S, Fujiwara Y and Orkin SH: FOG-2, a
cofactor for GATA transcription factors, is essential for heart
morphogenesis and development of coronary vessels from epicardium.
Cell. 101:729–739. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guo L, Wang J, Yang P, Lu Q, Zhang T and
Yang Y: MicroRNA- 200 promotes lung cancer cell growth through
FOG2-independent AKT activation. IUBMB Life. 67:720–725. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aumsuwan P, Khan SI, Khan IA, Ali Z, Avula
B, Walker LA, Shariat-Madar Z, Helferich WG, Katzenellenbogen BS
and Dasmahapatra AK: The anticancer potential of steroidal saponin,
dioscin, isolated from wild yam (Dioscorea villosa) root extract in
invasive human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 in vitro. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 591:98–110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tsang SY, Mei L, Wan W, Li J, Li Y, Zhao
C, Ding X, Pun FW, Hu X, Wang J, et al: Glioma association and
balancing selection of ZFPM2. PLoS One. 10:e01330032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hoene V, Fischer M, Ivanova A, Wallach T,
Berthold F and Dame C: GATA factors in human neuroblastoma:
Distinctive expression patterns in clinical subtypes. Br J Cancer.
101:1481–1489. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Laitinen MP, Anttonen M, Ketola I, Wilson
DB, Ritvos O, Butzow R and Heikinheimo M: Transcription factors
GATA-4 and GATA-6 and a GATA family cofactor, FOG-2, are expressed
in human ovary and sex cord-derived ovarian tumors. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 85:3476–3483. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Salonen J, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Mannisto S,
Nielsen JE, Graem N, Toppari J and Heikinheimo M: Differential
developmental expression of transcription factors GATA-4 and
GATA-6, their cofactor FOG-2 and downstream target genes in
testicular carcinoma in situ and germ cell tumors. Eur J
Endocrinol. 162:625–631. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Karlsson J, Holmquist Mengelbier L,
Elfving P and Gisselsson Nord D: High-resolution genomic profiling
of an adult Wilms' tumor: Evidence for a pathogenesis distinct from
corresponding pediatric tumors. Virchows Archiv. 459:547–553. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Virgone C, Cecchetto G, Ferrari A, Bisogno
G, Donofrio V, Boldrini R, Collini P, Dall'Igna P and Alaggio R:
GATA-4 and FOG-2 expression in pediatric ovarian sex cord-stromal
tumors replicates embryonal gonadal phenotype: Results from the
TREP project. PLoS One. 7:e459142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guan D and Tian H: Integrated network
analysis to explore the key genes regulated by parathyroid hormone
receptor 1 in osteosarcoma. World J Surg Oncol. 15:1772017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vastrad B, Vastrad C, Godavarthi A and
Chandrashekar R: Molecular mechanisms underlying gliomas and
glioblastoma pathogenesis revealed by bioinformatics analysis of
microarray data. Med Oncol. 34:1822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li L, Lv L, Liang Y, Shen X, Zhou S, Zhu J
and Ma R: Association of 8q23-24 region (8q23.3 loci and 8q24.21
loci) with susceptibility to colorectal cancer: A systematic and
updated meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:21001–21013.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Selenti N, Tzetis M, Braoudaki M, Gianikou
K, Kitsiou-Tzeli S and Fryssira H: An interstitial deletion at
8q23.1-q24.12 associated with langer-giedion
syndrome/trichorhinophalangeal syndrome (TRPS) type II and Cornelia
de Lange syndrome 4. Mol Cytogenet. 8:642015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Plaza-Benhumea L, Valdes-Miranda JM,
Toral-Lopez J, Perez- Cabrera A and Cuevas-Covarrubias S:
Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type II due to a novel 8q23.3-q24.12
deletion associated with imperforate hymen and vaginal stenosis. Br
J Dermatol. 171:1581–1583. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Win AK and Jenkins MA: Is the reported
modifying effect of 8q23.3 and 11q23.1 on colorectal cancer risk
for MLH1 mutation carriers valid? Int J Cancer. 133:1762–1763.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pereza N, Severinski S, Ostojic S, Volk M,
Maver A, Dekanić KB, Kapović M and Peterlin B: Third case of
8q23.3-q24.13 deletion in a patient with langer-giedion syndrome
phenotype without TRPS1 gene deletion. Am J Med Genet A.
158A:659–663. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Carvajal-Carmona LG, Cazier JB, Jones AM,
Howarth K, Broderick P, Pittman A, Dobbins S, Tenesa A, Farrington
S, Prendergast J, et al: Fine-mapping of colorectal cancer
susceptibility loci at 8q23.3, 16q22.1 and 19q13.11: Refinement of
association signals and use of in silico analysis to suggest
functional variation and unexpected candidate target genes. Hum Mol
Genet. 20:2879–2888. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Menyhart O, Nagy A and Gyorffy B:
Determining consistent prognostic biomarkers of overall survival
and vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. R Soc Open Sci.
5:1810062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1): D607–D613. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Roessler S, Jia HL, Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye
QH, Lee JS, Thorgeirsson SS, Sun Z, Tang ZY, Qin LX and Wang XW: A
unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor
relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer
Res. 70:10202–10212. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Seimiya M, Ohno S, Yamamoto H, Fujiwara K,
Yoshida T, Sawabe Y, Sogawa K, Matsushita K, Yokosuka O and Nomura
F: Child-Pugh score is altered by the albumin measurement method.
Hepatology. 57:2093–2094. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Taniai M, Tomimatsu M, Okuda H, Saito A
and Obata H: Immunohistochemical detection of proliferating cell
nuclear antigen in hepatocellular carcinoma: Relationship to
histological grade. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:420–425. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ghorbanoghli Z, Nieuwenhuis MH,
Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Jagmohan-Changur S, Hes FJ, Tops CM, Wagner
A, Aalfs CM, Verhoef S, Gómez García EB, et al: Colorectal cancer
risk variants at 8q23.3 and 11q23.1 are associated with disease
phenotype in APC mutation carriers. Fam Cancer. 15:563–570. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li M and Gu Y: Quantitative assessment of
the influence of common variation rs16892766 at 8q23.3 with
colorectal adenoma and cancer susceptibility. Mol Genet Genomics.
290:461–469. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Talseth-Palmer BA, Wijnen JT, Brenne IS,
Jagmohan-Changur S, Barker D, Ashton KA, Tops CM, Evans TJ,
McPhillips M, Groombridge C, et al: Combined analysis of three
Lynch syndrome cohorts confirms the modifying effects of 8q23.3 and
11q23.1 in MLH1 mutation carriers. Int J Cancer. 132:1556–1564.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wijnen JT, Brohet RM, van Eijk R,
Jagmohan-Changur S, Middeldorp A, Tops CM, van Puijenbroek M,
Ausems MG, Gómez García E, Hes FJ, et al: Chromosome 8q23.3 and
11q23.1 variants modify colorectal cancer risk in Lynch syndrome.
Gastroenterology. 136:131–137. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tomlinson IP, Webb E, Carvajal-Carmona L,
Broderick P, Howarth K, Pittman AM, Spain S, Lubbe S, Walther A,
Sullivan K, et al: A genome-wide association study identifies
colorectal cancer susceptibility loci on chromosomes 10p14 and
8q23.3. Nat Genet. 40:623–630. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Okamoto H, Yasui K, Zhao C, Arii S and
Inazawa J: PTK2 and EIF3S3 genes may be amplification targets at
8q23-q24 and are associated with large hepatocellular carcinomas.
Hepatology. 38:1242–1249. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Welter D, MacArthur J, Morales J, Burdett
T, Hall P, Junkins H, Klemm A, Flicek P, Manolio T, Hindorff L and
Parkinson H: The NHGRI GWAS catalog, a curated resource of
SNP-trait associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:(Database Issue).
D1001–D1006. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zheng R and Blobel GA: GATA transcription
factors and cancer. Genes Cancer. 1:1178–1188. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chou J, Provot S and Werb Z: GATA3 in
development and cancer differentiation: Cells GATA have it! J Cell
Physiol. 222:42–49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Albergaria A, Paredes J, Sousa B, Milanezi
F, Carneiro V, Bastos J, Costa S, Vieira D, Lopes N, Lam EW, et al:
Expression of FOXA1 and GATA-3 in breast cancer: The prognostic
significance in hormone receptor-negative tumours. Breast Cancer
Res. 11:R402009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Voduc D, Cheang M and Nielsen T: GATA-3
expression in breast cancer has a strong association with estrogen
receptor but lacks independent prognostic value. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 17:365–373. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kouros-Mehr H, Bechis SK, Slorach EM,
Littlepage LE, Egeblad M, Ewald AJ, Pai SY, Ho IC and Werb Z:
GATA-3 links tumor differentiation and dissemination in a luminal
breast cancer model. Cancer Cell. 13:141–152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Eeckhoute J, Keeton EK, Lupien M, Krum SA,
Carroll JS and Brown M: Positive cross-regulatory loop ties GATA-3
to estrogen receptor alpha expression in breast cancer. Cancer Res.
67:6477–6483. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gulbinas A, Berberat PO, Dambrauskas Z,
Giese T, Giese N, Autschbach F, Kleeff J, Meuer S, Büchler MW and
Friess H: Aberrant gata-3 expression in human pancreatic cancer. J
Histochem Cytochem. 54:161–169. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Parikh P, Palazzo JP, Rose LJ, Daskalakis
C and Weigel RJ: GATA-3 expression as a predictor of hormone
response in breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 200:705–710. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gong X, Liu W, Wu L, Ma Z, Wang Y, Yu S,
Zhang J, Xie H, Wei G, Ma F, et al: Transcriptional repressor GATA
binding 1-mediated repression of SRY-box 2 expression suppresses
cancer stem cell functions and tumor initiation. J Biol Chem.
293:18646–18654. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Xu K, Wang J, Gao J, Di J, Jiang B, Chen
L, Wang Z, Wang A, Wu F, Wu W, et al: GATA binding protein 2
overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in KRAS mutant
colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 36:1672–1678. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|