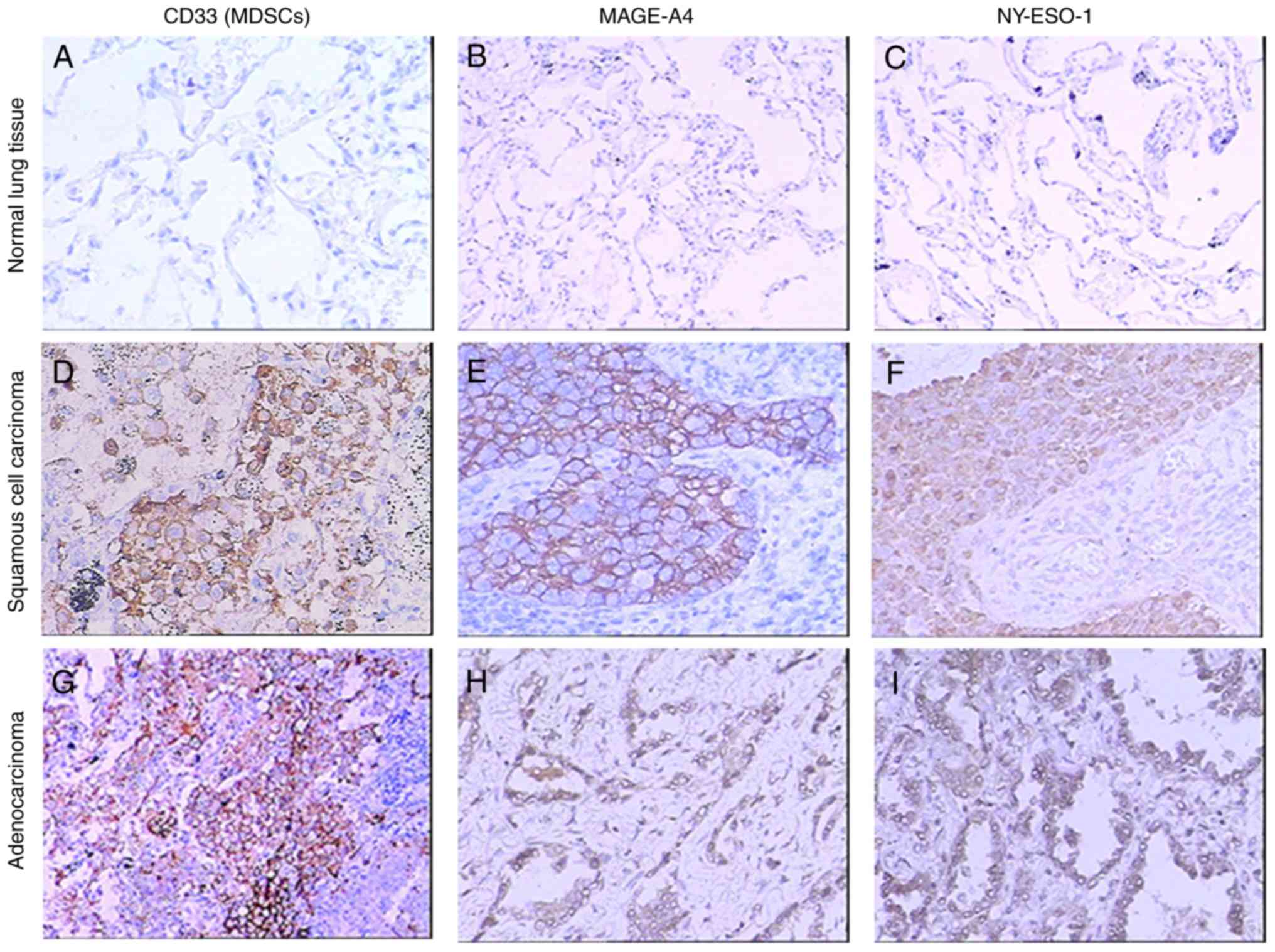
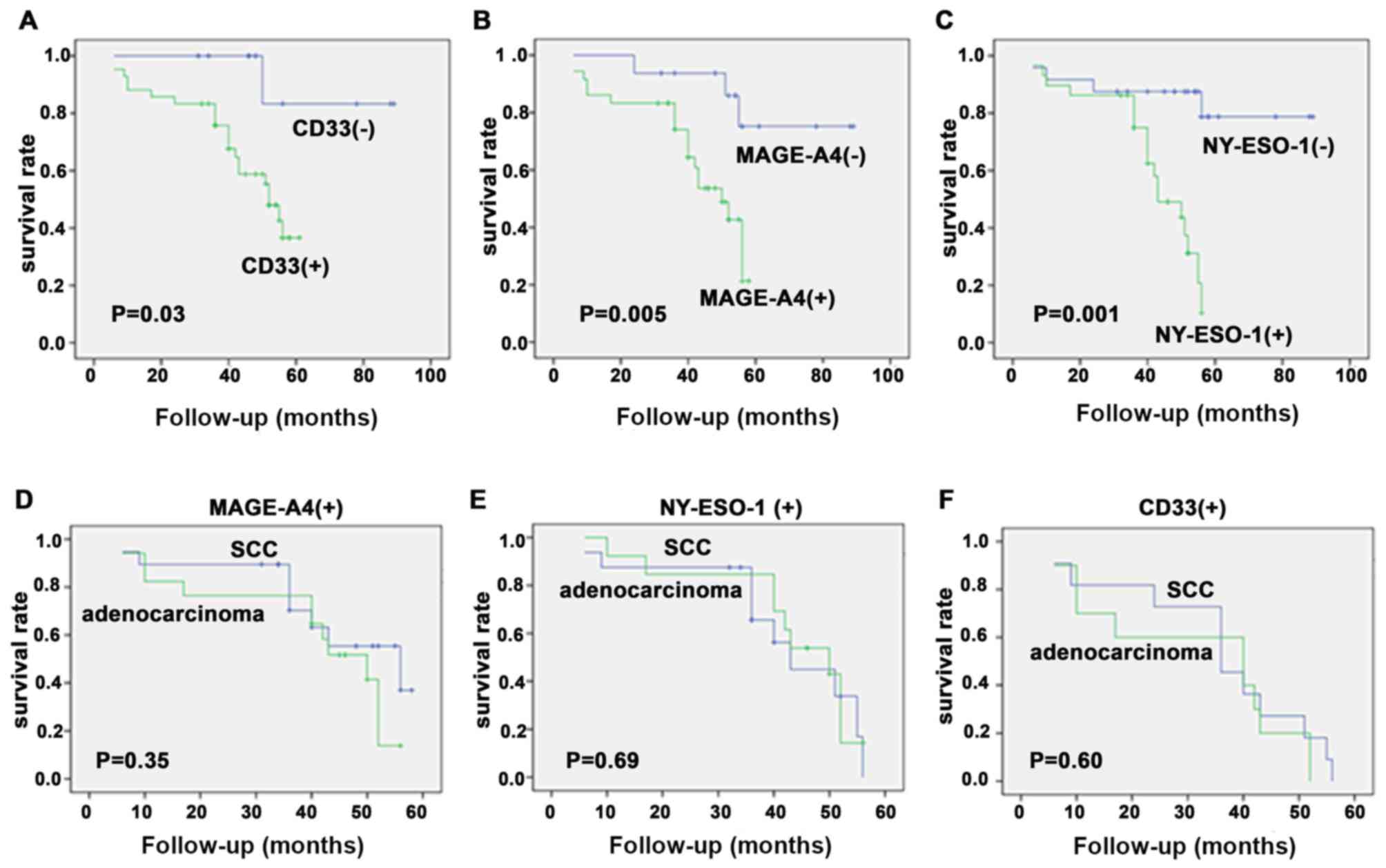
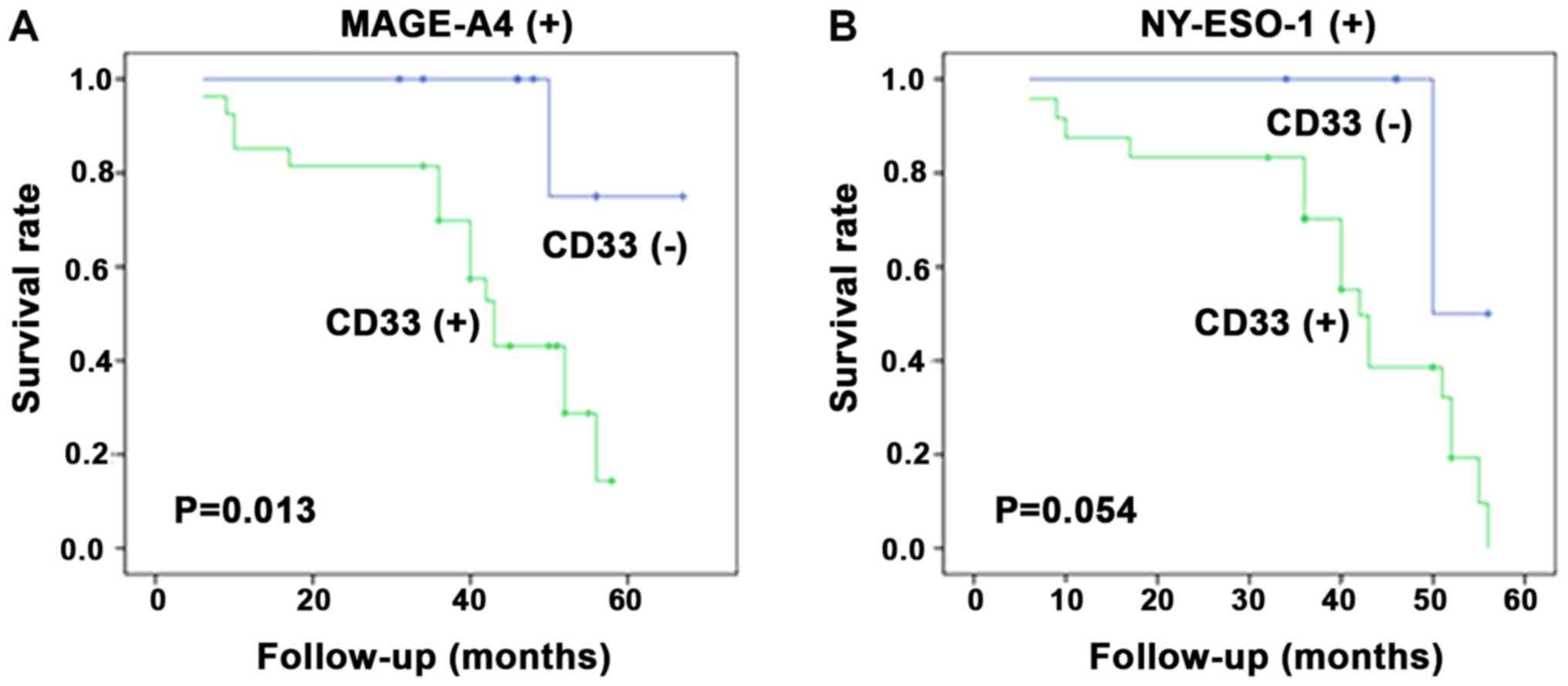
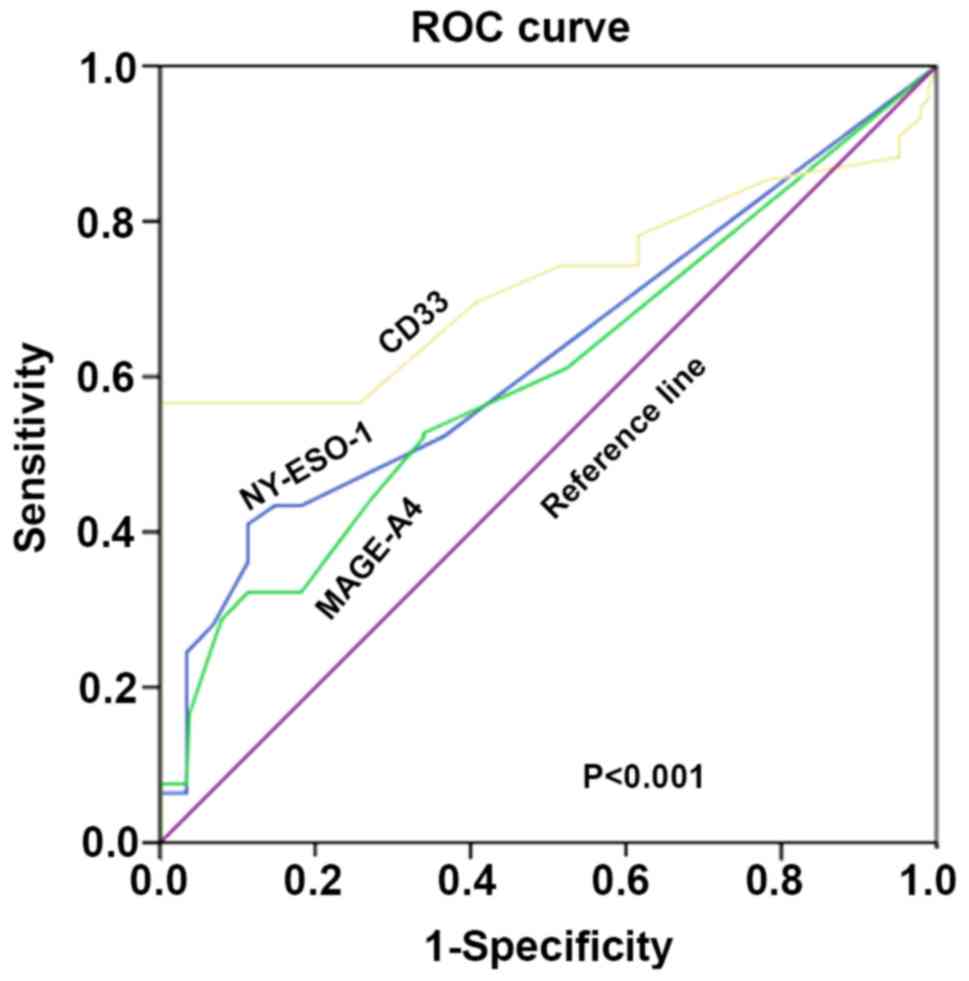
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carbone DP, Gandara DR, Antonia SJ,
Zielinski C and Paz-Ares L: Non-small-cell lung cancer: Role of the
immune system and potential for immunotherapy. J Thorac Oncol.
10:974–984. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zeltsman M, Dozier J, McGee E, Ngai D and
Adusumilli PS: CAR T-cell therapy for lung cancer and malignant
pleural mesothelioma. Transl Res. 187:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mayor M, Yang N, Sterman D, Jones DR and
Adusumilli PS: Immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer:
Current concepts and clinical trials. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
49:1324–1333. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shroff GS, de Groot PM,
Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Truong MT and Carter BW: Targeted therapy
and immunotherapy in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.
Radiol Clin North Am. 56:485–495. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Groeper C, Gambazzi F, Zajac P, Bubendorf
L, Adamina M, Rosenthal R, Zerkowski HR, Heberer M and Spagnoli GC:
Cancer/testis antigen expression and specific cytotoxic T
lymphocyte responses in non small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer.
120:337–343. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Adams S, Greeder L, Reich E, Shao Y,
Fosina D, Hanson N, Tassello J, Singh B, Spagnoli GC, Demaria S and
Jungbluth AA: Expression of cancer testis antigens in human
BRCA-associated breast cancers: Potential targets for
immunoprevention? Cancer Immunol Immunother. 60:999–1007. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Scanlan MJ, Gure AO, Jungbluth AA, Old LJ
and Chen YT: Cancer/testis antigens: An expanding family of targets
for cancer immunotherapy. Immunol Rev. 188:22–32. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stockert E, Jager E, Chen YT, Scanlan MJ,
Gout I, Karbach J, Arand M, Knuth A and Old LJ: A survey of the
humoral immune response of cancer patients to a panel of human
tumor antigens. J Exp Med. 187:1349–1354. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mahmoud AM: Cancer testis antigens as
immunogenic and oncogenic targets in breast cancer. Immunotherapy.
10:769–778. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gjerstorff MF, Andersen MH and Ditzel HJ:
Oncogenic cancer/testis antigens: Prime candidates for
immunotherapy. Oncotarget. 6:15772–15787. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Silina K, Zayakin P, Kalnina Z, Ivanova L,
Meistere I, Endzeliņš E, Abols A, Stengrēvics A, Leja M, Ducena K,
et al: Sperm-associated antigens as targets for cancer
immunotherapy: Expression pattern and humoral immune response in
cancer patients. J Immunother. 34:28–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cogdill AP, Frederick DT, Cooper ZA,
Garber HR, Ferrone CR, Fiedler A, Rosenberg L, Thayer SP, Warshaw
AL and Wargo JA: Targeting the MAGE A3 antigen in pancreatic
cancer. Surgery. 152 (3 Suppl 1):S13–S18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chew V, Chen J, Lee D, Loh E, Lee J, Lim
KH, Weber A, Slankamenac K, Poon RT, Yang H, et al:
Chemokine-driven lymphocyte infiltration: An early intratumoural
event determining long-term survival in resectable hepatocellular
carcinoma. Gut. 61:427–438. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Benchetrit F, Gazagne A, Adotevi O,
Haicheur N, Godard B, Badoual C, Fridman WH and Tartour E:
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes: Role in immunosurveillance and in
immunotherapy. Bull Cancer. 90:677–685. 2003.(In French).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Platsoucas CD, Fincke JE, Pappas J, Jung
WJ, Heckel M, Schwarting R, Magira E, Monos D and Freedman RS:
Immune responses to human tumors: Development of tumor vaccines.
Anticancer Res. 23:1969–1996. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yakirevich E, Sabo E, Lavie O, Mazareb S,
Spagnoli GC and Resnick MB: Expression of the MAGE-A4 and NY-ESO-1
cancer-testis antigens in serous ovarian neoplasms. Clin Cancer
Res. 9:6453–6460. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yoshida N, Abe H, Ohkuri T, Wakita D, Sato
M, Noguchi D, Miyamoto M, Morikawa T, Kondo S, Ikeda H and
Nishimura T: Expression of the MAGE-A4 and NY-ESO-1 cancer-testis
antigens and T cell infiltration in non-small cell lung carcinoma
and their prognostic significance. Int J Oncol. 28:1089–1098.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamauchi Y, Safi S, Blattner C,
Rathinasamy A, Umansky L, Juenger S, Warth A, Eichhorn M, Muley T,
Herth FJF, et al: Circulating and tumor myeloid-derived suppressor
cells in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 198:777–787. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ortiz ML, Lu L, Ramachandran I and
Gabrilovich DI: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the development
of lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2:50–58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schreiber RD, Old LJ and Smyth MJ: Cancer
immunoediting: Integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression
and promotion. Science. 331:1565–1570. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Zhang Y and Zhang L: Expression
of cancer-testis antigens in esophageal cancer and their progress
in immunotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 145:281–291. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Baran CA, Agaimy A, Wehrhan F, Weber M,
Hille V, Brunner K, Wickenhauser C, Siebolts U, Nkenke E, Kesting M
and Ries J: MAGE-A expression in oral and laryngeal leukoplakia
predicts malignant transformation. Mod Pathol. 32:1068–1081. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jin S, Cao S, Li J, Meng Q, Wang C, Yao L,
Lang Y, Cao J, Shen J, Pan B, et al: Cancer/testis antigens (CTAs)
expression in resected lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
11:4491–4499. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kakimoto T, Matsumine A, Kageyama S,
Asanuma K, Matsubara T, Nakamura T, Iino T, Ikeda H, Shiku H and
Sudo A: Immunohistochemical expression and clinicopathological
assessment of the cancer testis antigens NY-ESO-1 and MAGE-A4 in
high-grade soft-tissue sarcoma. Oncol Lett. 17:3937–3943.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ueda S, Miyahara Y, Nagata Y, Sato E,
Shiraishi T, Harada N, Ikeda H, Shiku H and Kageyama S: NY-ESO-1
antigen expression and immune response are associated with poor
prognosis in MAGE-A4-vaccinated patients with esophageal or
head/neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 9:35997–36011. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zimmermann AK, Imig J, Klar A, Renner C,
Korol D, Fink D, Stadlmann S, Singer G, Knuth A, Moch H and Caduff
R: Expression of MAGE-C1/CT7 and selected cancer/testis antigens in
ovarian borderline tumours and primary and recurrent ovarian
carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 462:565–574. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vetsika EK, Koinis F, Gioulbasani M,
Aggouraki D, Koutoulaki A, Skalidaki E, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V
and Kotsakis A: A circulating subpopulation of monocytic
myeloid-derived suppressor cells as an independent
prognostic/predictive factor in untreated non-small lung cancer
patients. J Immunol Res. 2014:6592942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lang S, Bruderek K, Kaspar C, Höing B,
Kanaan O, Dominas N, Hussain T, Droege F, Eyth C, Hadaschik B and
Brandau S: Clinical relevance and suppressive capacity of human
myeloid-derived suppressor cell subsets. Clin Cancer Res.
24:4834–4844. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Grauers Wiktorin H, Nilsson MS, Kiffin R,
Sander FE, Lenox B, Rydström A, Hellstrand K and Martner A:
Histamine targets myeloid-derived suppressor cells and improves the
anti-tumor efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint blockade. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 68:163–174. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barrera L, Montes-Servin E,
Hernandez-Martinez JM, Orozco-Morales M, Montes-Servín E,
Michel-Tello D, Morales-Flores RA, Flores-Estrada D and Arrieta O:
Levels of peripheral blood polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived
suppressor cells and selected cytokines are potentially prognostic
of disease progression for patients with non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 67:1393–1406. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rusch VW, Crowley J, Giroux DJ, Goldstraw
P, Im JG, Tsuboi M, Tsuchiya R and Vansteenkiste J; International
Staging Committee; Cancer Research and Biostatistics; Observers to
the Committee; Participating Institutions, . The IASLC Lung Cancer
Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the N descriptors in
the forthcoming seventh edition of the TNM classification for lung
cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2:603–612. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG,
Yatabe Y, Austin JHM, Beasley MB, Chirieac LR, Dacic S, Duhig E,
Flieder DB, et al: The 2015 world health organization
classification of lung tumors: impact of genetic, clinical and
radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol.
10:1243–1260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schacht V and Kern JS: Basics of
immunohistochemistry. J Invest Dermatol. 135:1–4. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Grah J, Samija M, Juretić A, Sarcević B
and Sobat H: Immunohystochemical expression of cancer/testis
antigens (MAGE-A3/4, NY-ESO-1) in non-small cell lung cancer: The
relationship with clinical-pathological features. Coll Antropol.
32:731–736. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hamilton G and Rath B: Immunotherapy for
small cell lung cancer: Mechanisms of resistance. Expert Opin Biol
Ther. 19:423–432. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wei X, Chen F, Xin K, Wang Q, Yu L, Liu B
and Liu Q: Cancer-Testis antigen peptide vaccine for cancer
immunotherapy: Progress and prospects. Transl Oncol. 12:733–738.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Grah JJ, Katalinic D, Juretic A, Santek F
and Samarzija M: Clinical significance of immunohistochemical
expression of cancer/testis tumor-associated antigens (MAGE-A1,
MAGE-A3/4, NY-ESO-1) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
Tumori. 100:60–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Smith SM and Iwenofu OH: NY-ESO-1: A
promising cancer testis antigen for sarcoma immunotherapy and
diagnosis. Chin Clin Oncol. 7:442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Su C, Xu Y, Li X, Ren S, Zhao C, Hou L, Ye
Z and Zhou C: Predictive and prognostic effect of CD133 and
cancer-testis antigens in stage Ib-IIIA non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:5509–5518. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
John T, Starmans MH, Chen YT, Russell PA,
Barnett SA, White SC, Mitchell PL, Walkiewicz M, Azad A, Lambin P,
et al: The role of Cancer-Testis antigens as predictive and
prognostic markers in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One.
8:e678762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ohue Y, Kurose K, Karasaki T, Isobe M,
Yamaoka T, Futami J, Irei I, Masuda T, Fukuda M, Kinoshita A, et
al: Serum antibody against NY-ESO-1 and XAGE1 antigens potentially
predicts clinical responses to anti-PD-1 therapy in non-small-cell
lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 14:2071–2083. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Giavina-Bianchi M, Giavina-Bianchi P,
Sotto MN, Muzikansky A, Kalil J, Festa-Neto C and Duncan LM:
Increased NY-ESO-1 expression and reduced infiltrating CD3+ T cells
in cutaneous melanoma. J Immunol Res. 2015:7613782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad E, Mohammadpour S,
Torshizi Esafahani A, Gharib E, Larki P, Moradi A, Amin
Porhoseingholi M, Asadzade Aghdaei H, Kuppen PJK and Zali MR:
Intratumoral infiltrating lymphocytes correlate with improved
survival in colorectal cancer patients: Independent of oncogenetic
features. J Cell Physiol. 234:4768–4777. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ostroumov D, Fekete-Drimusz N, Saborowski
M, Kühnel F and Woller N: CD4 and CD8 T lymphocyte interplay in
controlling tumor growth. Cell Mol Life Sci. 75:689–713. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li H, van der Leun AM, Yofe I, Lubling Y,
Gelbard-Solodkin D, van Akkooi ACJ, van den Braber M, Rozeman EA,
Haanen JBAG, Blank CU, et al: Dysfunctional CD8 T cells form a
proliferative, dynamically regulated compartment within human
melanoma. Cell. 176:775–789.e718. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Prall F, Dührkop T, Weirich V, Ostwald C,
Lenz P, Nizze H and Barten M: Prognostic role of CD8+
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in stage III colorectal cancer with
and without microsatellite instability. Hum Pathol. 35:808–816.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Knocke S, Fleischmann-Mundt B, Saborowski
M, Manns MP, Kühnel F, Wirth TC and Woller N: Tailored tumor
immunogenicity reveals regulation of CD4 and CD8 T cell responses
against cancer. Cell Rep. 17:2234–2246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Deschoolmeester V, Baay M, Van Marck E,
Weyler J, Vermeulen P, Lardon F and Vermorken JB: Tumor
infiltrating lymphocytes: an intriguing player in the survival of
colorectal cancer patients. BMC Immunol. 11:192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Simpson AJ, Caballero OL, Jungbluth A,
Chen YT and Old LJ: Cancer/testis antigens, gametogenesis and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:615–625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Atanackovic D, Arfsten J, Cao Y, Gnjatic
S, Schnieders F, Bartels K, Schilling G, Faltz C, Wolschke C,
Dierlamm J, et al: Cancer-testis antigens are commonly expressed in
multiple myeloma and induce systemic immunity following allogeneic
stem cell transplantation. Blood. 109:1103–1112. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Feng PH, Lee KY, Chang YL, Chan YF, Kuo
LW, Lin TY, Chung FT, Kuo CS, Yu CT, Lin SM, et al:
CD14(+)S100A9(+) monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells and
their clinical relevance in non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Respir
Criti Care Med. 186:1025–1036. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Li YD, Lamano JB, Lamano JB, Quaggin-Smith
J, Veliceasa D, Kaur G, Biyashev D, Unruh D and Bloch O:
Tumor-induced peripheral immunosuppression promotes brain
metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 68:1501–1513. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Almand B, Clark JI, Nikitina E, van Beynen
J, English NR, Knight SC, Carbone DP and Gabrilovich DI: Increased
production of immature myeloid cells in cancer patients: a
mechanism of immunosuppression in cancer. J Immunol. 166:678–689.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gabrilovich DI and Nagaraj S:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune
system. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:162–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Movahedi K, Guilliams M, Van den Bossche
J, Van den Bergh R, Gysemans C, Beschin A, De Baetselier P and Van
Ginderachter JA: Identification of discrete tumor-induced
myeloid-derived suppressor cell subpopulations with distinct T
cell-suppressive activity. Blood. 111:4233–4244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Nagaraj S and Gabrilovich DI:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 601:213–223.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kim SH, Lee S, Lee CH, Lee MK, Kim YD,
Shin DH, Choi KU, Kim JY, Park DY and Sol MY: Expression of
cancer-testis antigens MAGE-A3/6 and NY-ESO-1 in non-small-cell
lung carcinomas and their relationship with immune cell
infiltration. Lung. 187:401–411. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Haier J, Owzcareck M, Guller U, Spagnoli
GC, Bürger H, Senninger N and Kocher T: Expression of MAGE-A
cancer/testis antigens in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas.
Anticancer Res. 26:2281–2287. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Al-Khadairi G and Decock J: Cancer testis
antigens and immunotherapy: Where do we stand in the targeting of
PRAME? Cancers (Basel). 11:E9842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sigalotti L, Fratta E, Coral S, Tanzarella
S, Danielli R, Colizzi F, Fonsatti E, Traversari C, Altomonte M and
Maio M: Intratumor heterogeneity of cancer/testis antigens
expression in human cutaneous melanoma is methylation-regulated and
functionally reverted by 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine. Cancer Res.
64:9167–9171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Salmaninejad A, Zamani MR, Pourvahedi M,
Golchehre Z, Hosseini Bereshneh A and Rezaei N: Cancer/Testis
antigens: expression, regulation, tumor invasion, and use in
immunotherapy of cancers. Immunol Invest. 45:619–640. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Fratta E, Coral S, Covre A, Parisi G,
Colizzi F, Danielli R, Nicolay HJ, Sigalotti L and Maio M: The
biology of cancer testis antigens: putative function, regulation
and therapeutic potential. Mol Oncol. 5:164–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Almstedt M, Blagitko-Dorfs N, Duque-Afonso
J, Karbach J, Pfeifer D, Jäger E and Lübbert M: The DNA
demethylating agent 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine induces expression of
NY-ESO-1 and other cancer/testis antigens in myeloid leukemia
cells. Leuk Res. 34:899–905. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Song X, Song W, Wang Y, Wang J, Li Y, Qian
X, Pang X, Zhang Y and Yin Y: MicroRNA-874 functions as a tumor
suppressor by targeting cancer/testis antigen HCA587/MAGE-C2. J
Cancer. 7:656–663. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Thomas R, Al-Khadairi G, Roelands J,
Hendrickx W, Dermime S, Bedognetti D and Decock J: NY-ESO-1 based
immunotherapy of cancer: Current perspectives. Front Immunol.
9:9472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chinnasamy N, Wargo JA, Yu Z, Rao M,
Frankel TL, Riley JP, Hong JJ, Parkhurst MR, Feldman SA, Schrump
DS, et al: A TCR targeting the HLA-A*0201-restricted epitope of
MAGE-A3 recognizes multiple epitopes of the MAGE-A antigen
superfamily in several types of cancer. J Immunol. 186:685–696.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Peng JR, Chen HS, Mou DC, Cao J, Cong X,
Qin LL, Wei L, Leng XS, Wang Y and Chen WF: Expression of
cancer/testis (CT) antigens in Chinese hepatocellular carcinoma and
its correlation with clinical parameters. Cancer Lett. 219:223–232.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Nagorsen D, Scheibenbogen C, Marincola FM,
Letsch A and Keilholz U: Natural T cell immunity against cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:4296–4303. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chen YT, Chiu R, Lee P, Beneck D, Jin B
and Old LJ: Chromosome X-encoded cancer/testis antigens show
distinctive expression patterns in developing gonads and in
testicular seminoma. Hum Reprod. 26:3232–3243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Rivera MP and Stover DE: Gender and lung
cancer. Clin Chest Med. 25:391–400. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Barrera-Rodriguez R and Morales-Fuentes J:
Lung cancer in women. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 3:79–89. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hsu LH, Chu NM, Liu CC, Tsai SY, You DL,
Ko JS, Lu MC and Feng AC: Sex-associated differences in non-small
cell lung cancer in the new era: Is gender an independent
prognostic factor? Lung Cancer. 66:262–267. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Sakurai H, Asamura H, Goya T, Eguchi K,
Nakanishi Y, Sawabata N, Okumura M, Miyaoka E and Fujii Y; Japanese
Joint Committee for Lung Cancer Registration, : Survival
differences by gender for resected non-small cell lung cancer: A
retrospective analysis of 12,509 cases in a Japanese lung cancer
registry study. J Thorac Oncol. 5:1594–1601. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Shi G, Wang H and Zhuang X:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells enhance the expression of
melanoma-associated antigen A4 in a Lewis lung cancer murine model.
Oncol Lett. 11:809–816. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Perkins NJ and Schisterman EF: The
inconsistency of ‘optimal’ cutpoints obtained using two criteria
based on the receiver operating characteristic curve. Am J
Epidemiol. 163:670–675. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hajian-Tilaki K: Receiver operating
characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for medical diagnostic test
evaluation. Caspian J Intern Med. 4:627–635. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Obuchowski NA and Bullen JA: Receiver
operating characteristic (ROC) curves: Review of methods with
applications in diagnostic medicine. Phys Med Biol. 63:07TR012018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Carter JV, Pan J, Rai SN and Galandiuk S:
ROC-ing along: Evaluation and interpretation of receiver operating
characteristic curves. Surgery. 159:1638–1645. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kamarudin AN, Cox T and Kolamunnage-Dona
R: Time-dependent ROC curve analysis in medical research: Current
methods and applications. BMC Med Res Methodol. 17:532017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhang G, Huang H, Zhu Y, Yu G, Gao X, Xu
Y, Liu C, Hou J and Zhang X: A novel subset of
B7-H3(+)CD14(+)HLA-DR(−/low) myeloid-derived suppressor cells are
associated with progression of human NSCLC. Oncoimmunology.
4:e9771642015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Marvel D and Gabrilovich DI:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment:
Expect the unexpected. J Clin Invest. 125:3356–3364. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kaplan RM, Chambers DA and Glasgow RE: Big
data and large sample size: A cautionary note on the potential for
bias. Clin Transl Sci. 7:342–346. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Anderson SF, Kelley K and Maxwell SE:
Sample-size planning for more accurate statistical power: A method
adjusting sample effect sizes for publication bias and uncertainty.
Psychol Sci. 28:1547–1562. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Biau DJ, Kerneis S and Porcher R:
Statistics in brief: The importance of sample size in the planning
and interpretation of medical research. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
466:2282–2288. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|