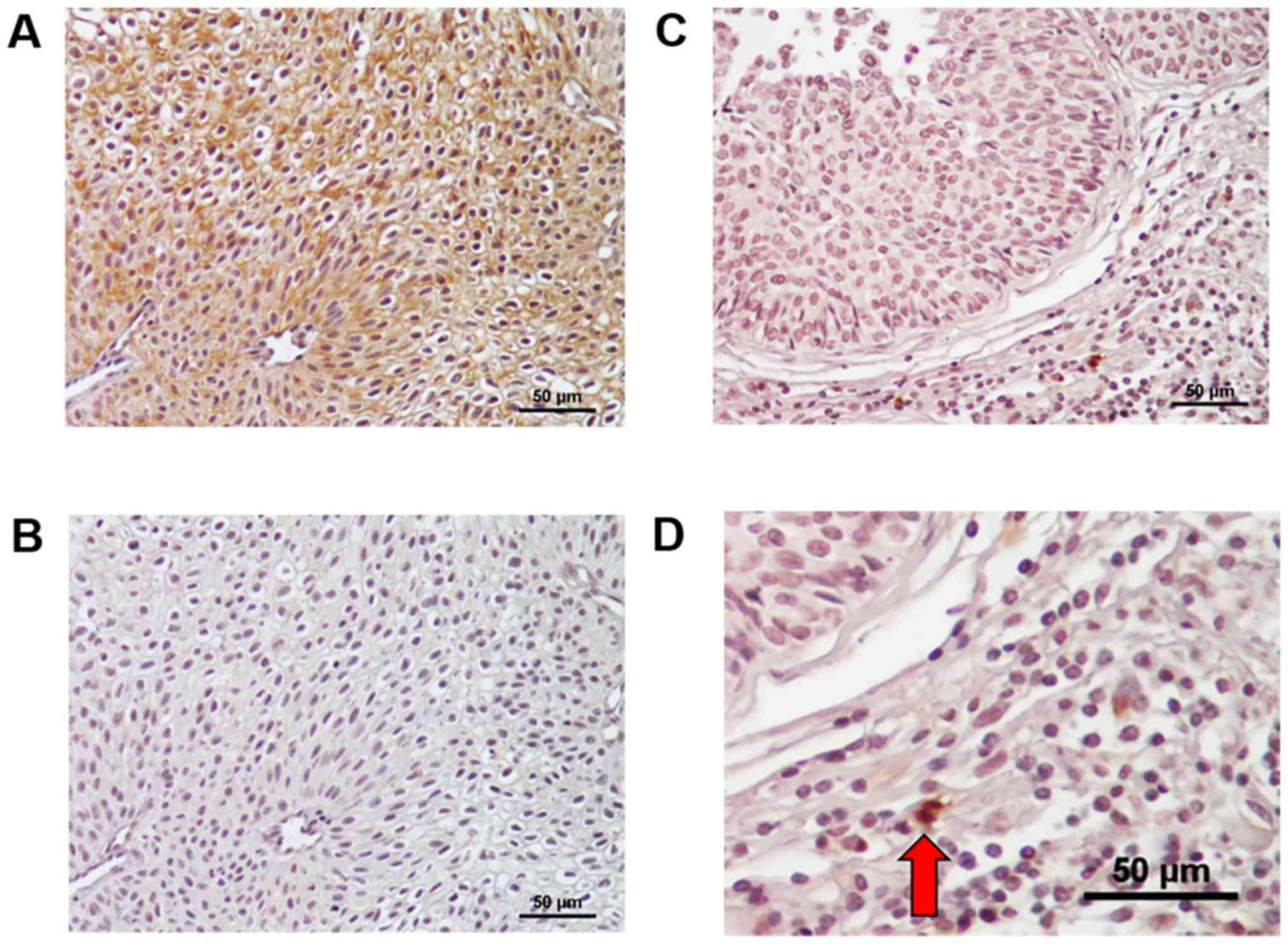
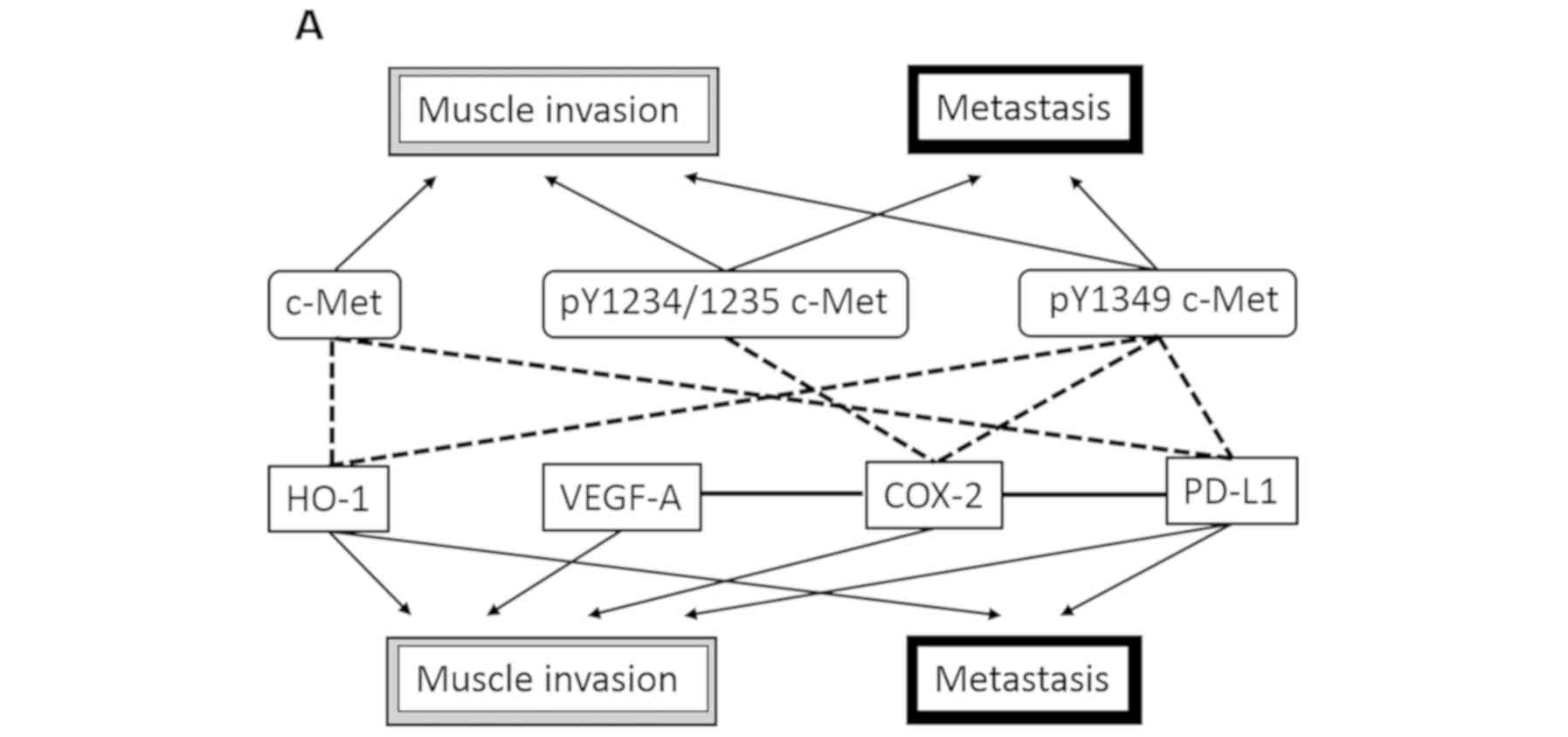
|
1
|
Gakis G: The role of inflammation in
bladder cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 816:183–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
von der Maase H, Hansen SW, Roberts JT,
Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, Bodrogi I, Albers P, Knuth A,
Lippert CM, et al: Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus methotrexate,
vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in advanced or metastatic
bladder cancer: Results of a large, randomized, multinational,
multicenter, phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 18:3068–3077. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Okabe K, Shindo T, Maehana T, Nishiyama N,
Hashimoto K, Itoh N, Takahashi A, Taguchi K, Tachiki H, Tanaka T
and Masumori N: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine and
cisplatin for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Multicenter
retrospective study. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 48:934–941. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arnold L, Enders J and Thomas SM:
Activated HGF-c-Met axis in head and neck cancer. Cancers (Basel).
9:E1692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu X, Zhang G, He L and Zhu Y:
Clinicopathological impacts of c-Met overexpression in bladder
cancer: Evidence from 1,336 cases. Onco Targets Ther. 12:2695–2702.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E and
Vande Woude GF: Met, metastasis, mortality and more. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 4:915–925. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miyata Y, Asai A, Mitsunari K, Matsuo T,
Ohba K, Mochizuki Y and Sakai H: Met in urological cancers. Cancers
(Basel). 6:2387–2403. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Noriega-Guerra H and Freitas VM:
Extracellular matrix influencing HGF/c-MET signaling pathway:
Impact on cancer progression. Int J Mol Sci. 19:E33002018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miyata Y, Ashida S, Nakamura T, Mochizuki
Y, Koga S, Kanetake H, Shuin T and Kanda S: Overexpression of
hepatocyte growth factor receptor in renal carcinoma cells
indirectly stimulates tumor growth in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 302:892–897. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Balan M, Mier y Teran E, Waaga-Gasser AM,
Gasser M, Choueiri TK, Freeman G and Pal S: Novel roles of c-Met in
the survival of renal cancer cells through the regulation of HO-1
and PD-L1 expression. J Biol Chem. 290:8110–8120. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Y, Sun Y, Zhang H, Liu X, Du W, Li Y,
Zhang J, Chen L and Jiang C: HGF/MET signaling promotes glioma
growth via up-regulation of Cox-2 expression and PGE2 production.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:3719–3726. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kammerer-Jacquet SF, Medane S, Bensalah K,
Bernhard JC, Yacoub M, Dupuis F, Ravaud A, Verhoest G, Mathieu R,
Peyronnet B, et al: Correlation of c-MET expression with PD-L1
expression in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated by
sunitinib first-line therapy. Target Oncol. 12:487–494. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Papaccio F, Della Corte CM, Viscardi G, Di
Liello R, Esposito G, Sparano F, Ciardiello F and Morgillo F:
HGF/MET and the immune system: Relevance for cancer immunotherapy.
Int J Mol Sci. 19:E35952018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu-Monette ZY, Zhang M, Li J and Young KH:
PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: Have we found the key to unleash the antitumor
immune response? Front Immunol. 8:15972017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lenouvel D, González-Moles MÁ, Talbaoui A,
Ramos-García P, González-Ruiz L, Ruiz-Ávila I and Gil-Montoya JA:
An update of knowledge on PD-L1 in head and neck cancers:
Physiologic, prognostic and therapeutic perspectives. Oral Dis.
26:511–526. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chun HW and Hong R: Significance of PD-L1
clones and C-MET expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol
Lett. 17:5487–5498. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hass R, Jennek S, Yang Y and Friedrich K:
c-Met expression and activity in urogenital cancers-novel aspects
of signal transduction and medical implications. Cell Commun
Signal. 15:102017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Miyata Y, Kanda S, Ohba K, Nomata K,
Hayashida Y, Eguchi J, Hayashi T and Kanetake H: Lymphangiogenesis
and angiogenesis in bladder cancer: Prognostic implications and
regulation by vascular endothelial growth factors-A, -C, and -D.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:800–806. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matsuo T, Miyata Y, Mitsunari K, Yasuda T,
Ohba K and Sakai H: Pathological significance and prognostic
implications of heme oxygenase 1 expression in non-muscle-invasive
bladder cancer: Correlation with cell proliferation, angiogenesis,
lymphangiogenesis and expression of VEGFs and COX-2. Oncol Lett.
13:275–280. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pichler R, Heidegger I, Fritz J, Danzl M,
Sprung S, Zelger B, Brunner A and Pircher A: PD-L1 expression in
bladder cancer and metastasis and its influence on oncologic
outcome after cystectomy. Oncotarget. 8:66849–66864. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Davick JJ, Frierson HF, Smolkin M and Gru
AA: PD-L1 expression in tumor cells and the immunologic milieu of
bladder carcinomas: A pathologic review of 165 cases. Hum Pathol.
81:184–191. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ferracini R, Longati P, Naldini L, Vigna E
and Comoglio PM: Identification of the major autophosphorylation
site of the Met/hepatocyte growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase.
J Biol Chem. 266:19558–19564. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bertotti A and Comoglio PM: Tyrosine
kinase signal specificity: Lessons from the HGF receptor. Trends
Biochem Sci. 28:527–533. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Raghav KP, Wang W, Liu S, Chavez-MacGregor
M, Meng X, Hortobagyi GN, Mills GB, Meric-Bernstam F, Blumenschein
GR Jr and Gonzalez-Angulo AM: cMET and phospho-cMET protein levels
in breast cancers and survival outcomes. Clin Cancer Res.
18:2269–2277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miyata Y, Sagara Y, Kanda S, Hayashi T and
Kanetake H: Phosphorylated hepatocyte growth factor receptor/c-Met
is associated with tumor growth and prognosis in patients with
bladder cancer: Correlation with matrix metalloproteinase-2 and −7
and E-cadherin. Hum Pathol. 40:496–504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamasaki K, Mukai S, Nagai T, Nakahara K,
Fujii M, Terada N, Ohno A, Sato Y, Toda Y, Kataoka H and Kamoto T:
Matriptase-induced phosphorylation of MET is significantly
associated with poor prognosis in invasive bladder cancer; an
immunohistochemical analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 19:E37082018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Miyata Y, Kanetake H and Kanda S: Presence
of phosphorylated hepatocyte growth factor receptor/c-Met is
associated with tumor progression and survival in patients with
conventional renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 12:4876–4881.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Morena D, Maestro N, Bersani F, Forni PE,
Lingua MF, Foglizzo V, Šćepanović P, Miretti S, Morotti A, Shern
JF, et al: Hepatocyte growth factor-mediated satellite cells niche
perturbation promotes development of distinct sarcoma subtypes.
Elife. 5:e121162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mitsunari K, Miyata Y, Asai A, Matsuo T,
Shida Y, Hakariya T and Sakai H: Human antigen R is positively
associated with malignant aggressiveness via upregulation of cell
proliferation, migration, and vascular endothelial growth factors
and cyclooxygenase-2 in prostate cancer. Transl Res. 175:116–128.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Le Goux C, Damotte D, Vacher S, Sibony M,
Delongchamps NB, Schnitzler A, Terris B, Zerbib M, Bieche I and
Pignot G: Correlation between messenger RNA expression and protein
expression of immune checkpoint-associated molecules in bladder
urothelial carcinoma: A retrospective study. Urol Oncol.
35:257–263. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Miyata Y, Kanda S, Nomata K, Eguchi J and
Kanetake H: Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and EP4 receptor in
transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. J Urol.
173:56–60. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jung I, Gurzu S, Turdean S, Ciortea D,
Sahlean DI, Golea M and Bela T: Relationship of endothelial area
with VEGF-A, COX-2, maspin, c-KIT, and DOG-1 immunoreactivity in
liposarcomas versus non-lipomatous soft tissue tumors. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:1776–1782. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu N, Zhou N, Chai N, Liu X, Jiang H, Wu
Q and Li Q: Helicobacter pylori promotes angiogenesis depending on
Wnt/beta-catenin-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor via
the cyclooxygenase-2 pathway in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer.
16:3212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Botti G, Fratangelo F, Cerrone M, Liguori
G, Cantile M, Anniciello AM, Scala S, D'Alterio C, Trimarco C,
Ianaro A, et al: COX-2 expression positively correlates with PD-L1
expression in human melanoma cells. J Transl Med. 15:462017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shirahama T, Arima J, Akiba S and Sakakura
C: Relation between cyclooxygenase-2 expression and tumor
invasiveness and patient survival in transitional cell carcinoma of
the urinary bladder. Cancer. 92:188–193. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim JH and Park J: Prognostic significance
of heme oxygenase-1, S100 calcium-binding protein A4, and
syndecan-1 expression in primary non-muscle-invasive bladder
cancer. Hum Pathol. 45:1830–1838. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ding X, Chen Q, Yang Z, Li J, Zhan H, Lu
N, Chen M, Yang Y, Wang J and Yang D: Clinicopathological and
prognostic value of PD-L1 in urothelial carcinoma: A meta-analysis.
Cancer Manag Res. 11:4171–4184. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mazzola CR and Chin J: Targeting the VEGF
pathway in metastatic bladder cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.
24:913–927. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bellmunt J, Powles T and Vogelzang NJ: A
review on the evolution of PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy for bladder
cancer: The future is now. Cancer Treat Rev. 54:58–67. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hori S, Miyake M, Tatsumi Y, Onishi S,
Morizawa Y, Nakai Y, Tanaka N and Fujimoto K: Topical and systemic
immunoreaction triggered by intravesical chemotherapy in an
N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl) nitorosamine induced bladder cancer
mouse model. PLoS One. 12:e01754942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Patel KR, Taylor BL, Khani F, Guzzo TJ,
Scherr DS, Ravishankar R, Lal P and Malkowicz SB: Impact of
neoadjuvant chemotherapy on concordance of PD-L1 staining fidelity
between the primary tumor and lymph node metastases in bladder
cancer. Urology. 131:150–156. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cesário JM, Brito RB, Malta CS, Silva CS,
Matos YS, Kunz TC, Urbano JJ, Oliveira LV, Dalboni MA and Dellê H:
A simple method to induce hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial
growth factor-A (VEGF-A) expression in T24 human bladder cancer
cells. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 53:272–276. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Patricia Moreno-Londoño A, Bello-Alvarez C
and Pedraza-Chaverri J: Isoliquiritigenin pretreatment attenuates
cisplatin induced proximal tubular cells (LLC-PK1) death and
enhances the toxicity induced by this drug in bladder cancer T24
cell line. Food Chem Toxicol. 109:143–154. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hurst EA, Pang LY and Argyle DJ: The
selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor mavacoxib (Trocoxil) exerts
anti-tumour effects in vitro independent of cyclooxygenase-2
expression levels. Vet Comp Oncol. 17:194–207. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Schwamborn K, Ammann JU, Knüchel R,
Hartmann A, Baretton G, Lasitschka F, Schirmacher P, Braunschweig
T, Tauber R, Erlmeier F, et al: Multicentric analytical
comparability study of programmed death-ligand 1 expression on
tumor-infiltrating immune cells and tumor cells in urothelial
bladder cancer using four clinically developed immunohistochemistry
assays. Virchows Arch. 475:599–608. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|