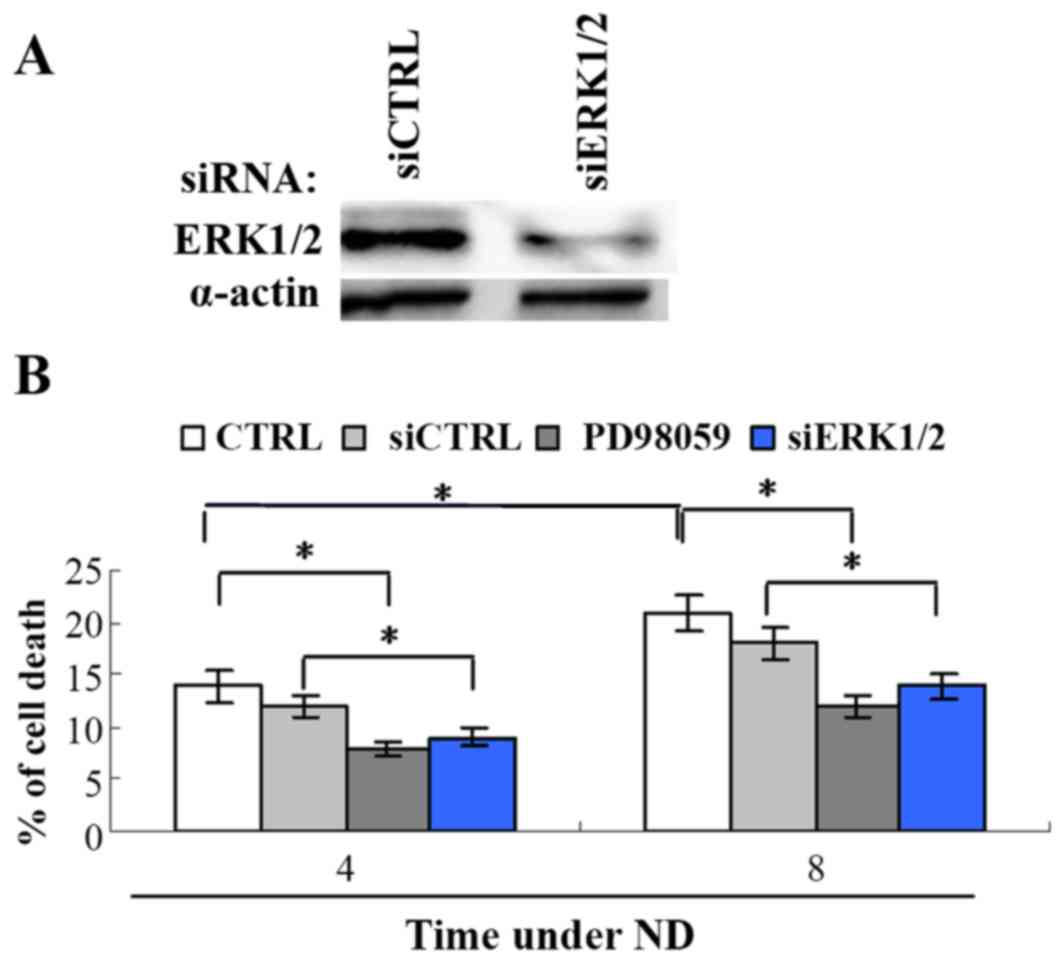
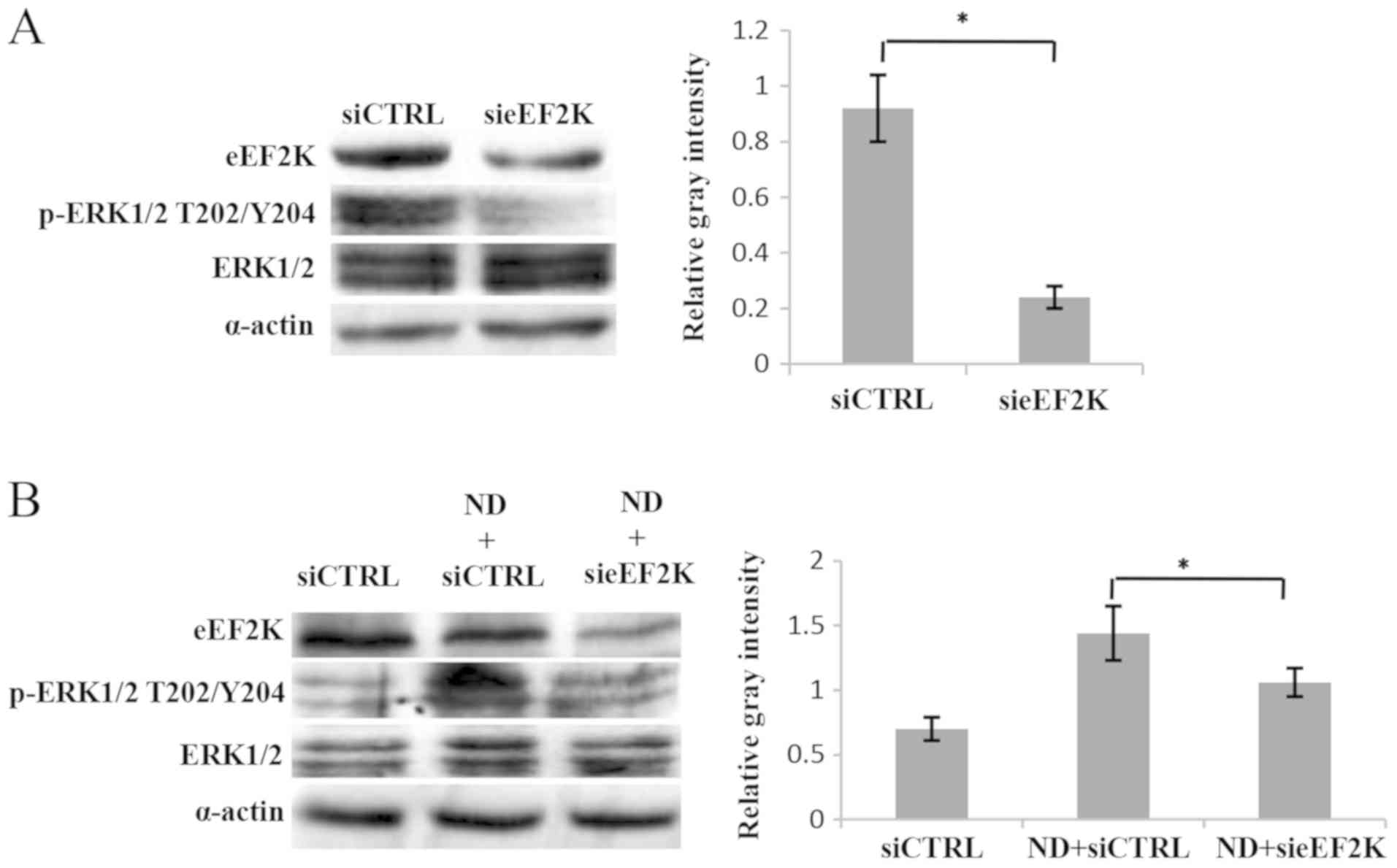
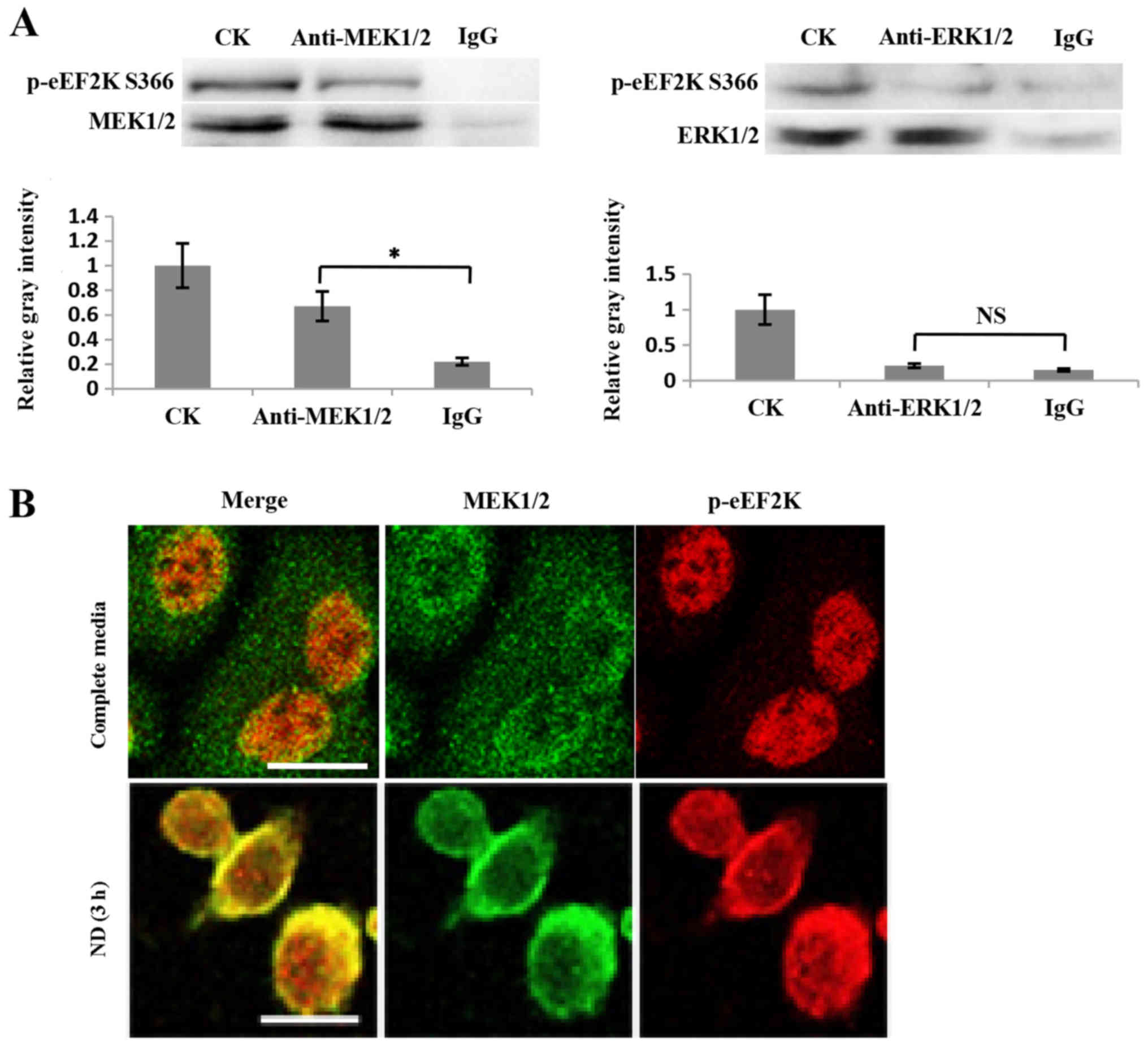
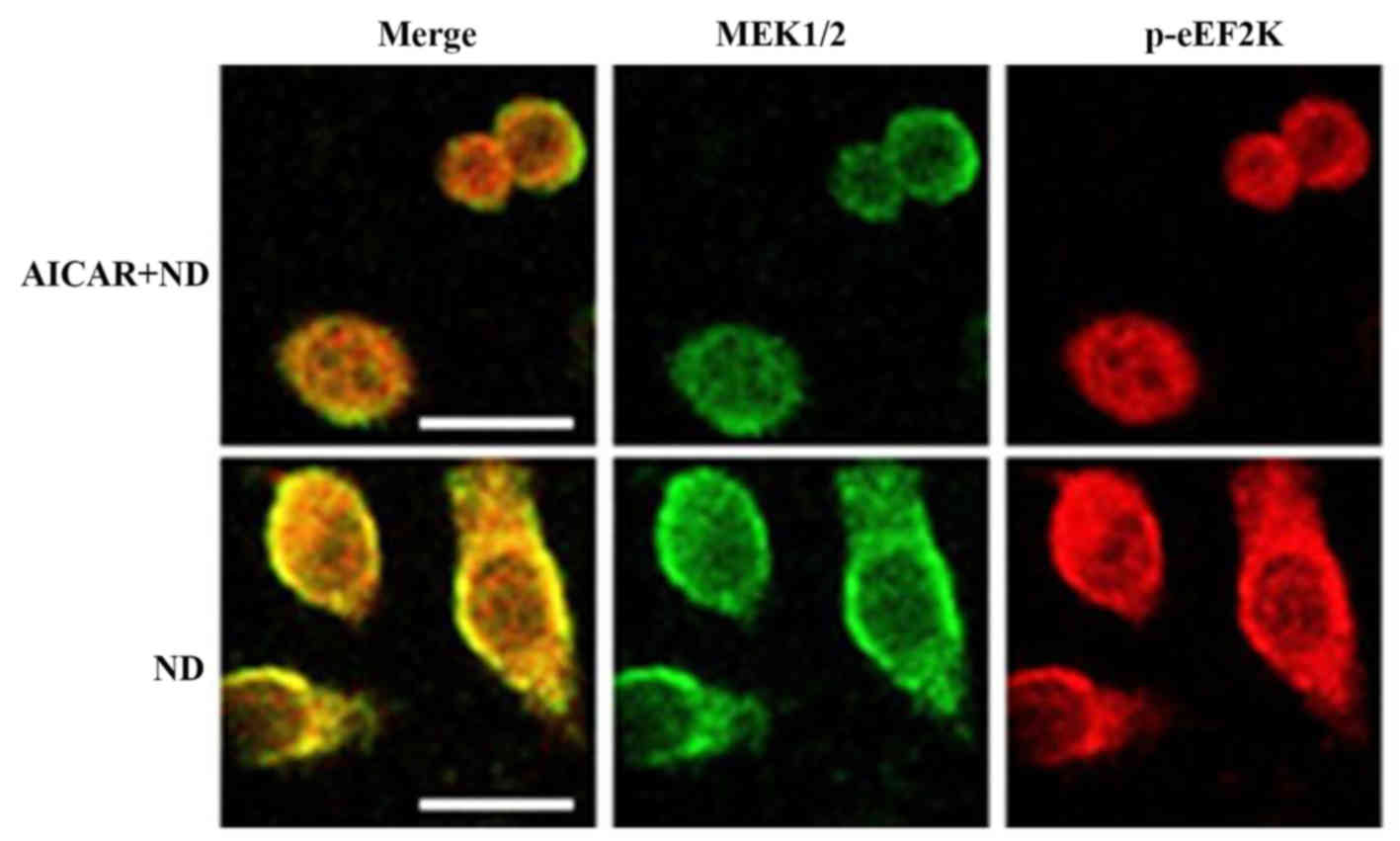
|
1
|
Caro-Maldonado A and Muñoz-Pinedo C: Dying
for something to eat: How cells respond to starvation. Open Cell
Signal J. 3:42–51. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jeon SM, Chandel NS and Hay N: AMPK
regulates NADPH homeostasis to promote tumour cell survival during
energy stress. Nature. 485:661–665. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hardie DG: Molecular pathways: Is AMPK a
friend or a foe in cancer? Clin Cancer Res. 21:3836–3840. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fu LL, Xie T, Zhang SY and Liu B:
Eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase (eEF2K): A potential
therapeutic target in cancer. Apoptosis. 19:1527–1531. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Johanns M, PyrDitRuys S, Houddane A,
Vertommen D, Herinckx G, Hue L, Proud CG and Rider MH: Direct and
indirect activation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase by
AMP-activated protein kinase. Cell Signal. 36:212–221. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meloche S and Pouysségur J: The ERK1/2
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway as a master regulator of
the G1- to S-phase transition. Oncogene. 26:3227–3239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lavoie JN, L'Allemain G, Brunet A, Muller
R and Pouyssegur J: Cyclin D1 expression is regulated positively by
the p42/p44MAPK and negatively by the p38/HOGMAPK pathway. J Biol
Chem. 271:20608–20616. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weinberg RA: The retinoblastoma protein
and cell cycle control. Cell. 81:323–330. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bracken AP, Ciro M, Cocito A and Helin K:
E2F target genes: Unraveling the biology. Trends Biochem Sci.
29:409–417. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zi X and Agarwal R: Modulation of
mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and cell cycle
regulators by the potent skin cancer preventive agent silymarin.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 263:528–536. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yuan HX, Xiong Y and Guan KL: Nutrient
sensing, metabolism, and cell growth control. Mol Cell. 49:379–387.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cagnol S and Chambard JC: ERK and cell
death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death-apoptosis, autophagy
and senescence. FEBS J. 277:2–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mebratu Y and Tesfaigzi Y: How ERK1/2
activation controls cell proliferation and cell death is
subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle. 8:1168–1175. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Li W, Williams M, Terada N, Alessi
DR and Proud CG: Regulation of elongation factor 2 kinase by
p90(RSK1) and p70 S6 kinase. EMBO J. 20:4370–4379. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Leprivier G, Remke M, Rotblat B, Dubuc A,
Mateo AR, Kool M, Agnihotri S, El-Naggar A, Yu B, Somasekharan SP,
et al: The eEF2 kinase confers resistance to nutrient deprivation
by blocking translation elongation. Cell. 153:1064–1079. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tang Q, Zhao S, Wu J, Zheng F, Yang L, Hu
J and Hann SS: Inhibition of integrin-linked kinase expression by
emodin through crosstalk of AMPKα and ERK1/2 signaling and
reciprocal interplay of Sp1 and c-Jun. Cell Signal. 27:1469–1477.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng F, Wu J, Zhao S, Luo Q, Tang Q, Yang
L, Li L, Wu W and Hann SS: Baicalein increases the expression and
reciprocal interplay of RUNX3 and FOXO3a through crosstalk of AMPKα
and MEK/ERK1/2 signaling pathways in human non-small cell lung
cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Browne GJ and Proud CG: A novel
mTOR-regulated phosphorylation site in elongation factor 2 kinase
modulates the activity of the kinase and its binding to calmodulin.
Mol Cell Biol. 24:2986–2997. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xie J, Mikolajek H, Pigott CR, Hooper KJ,
Mellows T, Moore CE, Mohammed H, Werner JM, Thomas GJ and Proud CG:
Molecular mechanism for the control of eukaryotic elongation factor
2 kinase by pH: Role in cancer cell survival. Mol Cell Biol.
35:1805–1824. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tavares CD, Ferguson SB, Giles DH, Wang Q,
Wellmann RM, O'Brien JP, Warthaka M, Brodbelt JS, Ren P and Dalby
KN: The molecular mechanism of eukaryotic elongation factor 2
kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 289:23901–23916. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Browne GJ, Finn SG and Proud CG:
Stimulation of the AMP-activated protein kinase leads to activation
of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase and to its phosphorylation
at a novel site, Serine 398. J Biol Chem. 279:12220–12231. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|