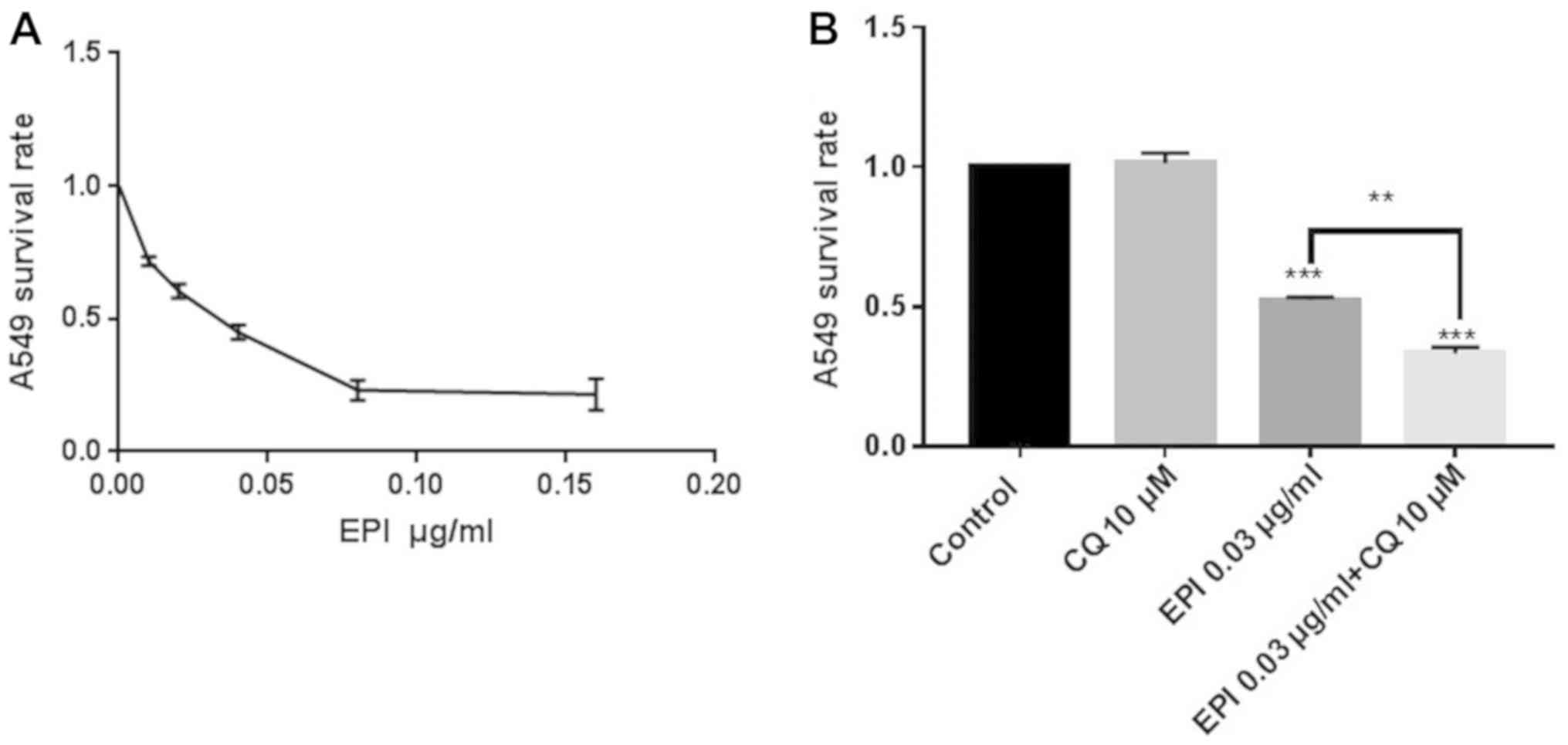
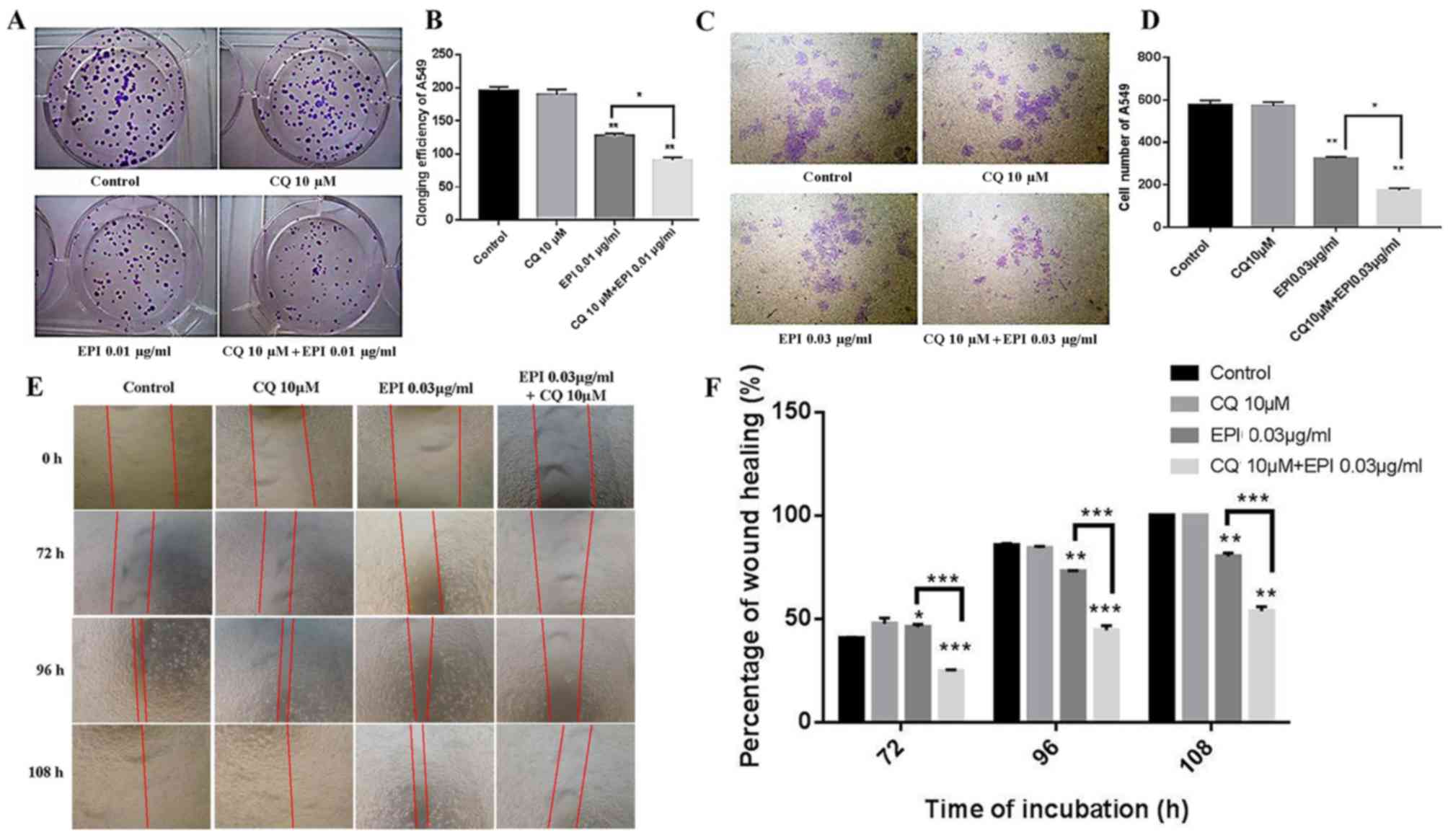
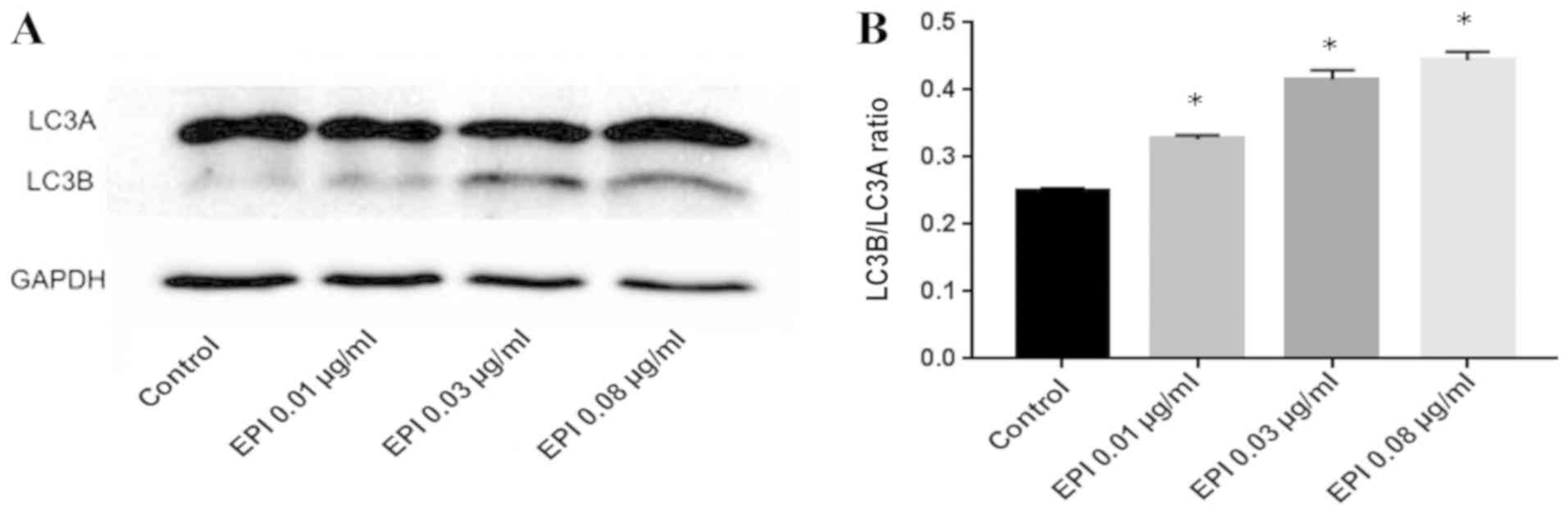
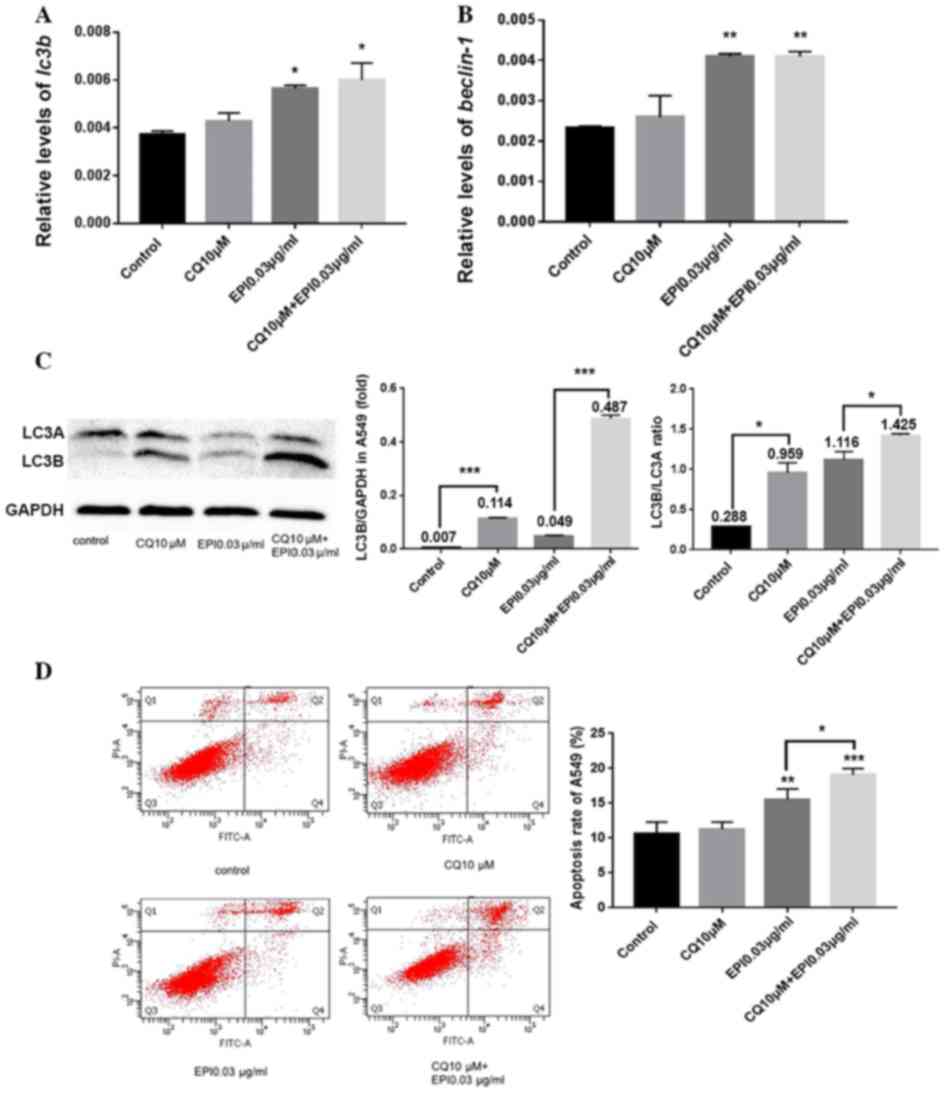
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sa H, Song P, Ma K, Gao Y, Zhang L and
Wang D: Perioperative targeted therapy or immunotherapy in
non-small-cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 12:8151–8159. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jacot W, Pujol JL, Chakra M, Molinier O,
Bozonnat MC, Gervais R and Quantin X: Epirubicin and ifosfamide in
relapsed or refractory small cell lung cancer patients. Lung
Cancer. 75:213–216. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen W, Yang Z, Deng G and Ye H: High-dose
epirubicin combination therapy in the treatment of 48 cases with
advanced chest malignant tumors. China Oncol. 11:355–356. 2001.(In
Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Plosker GL and Faulds D: Epirubicin. A
review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and
therapeutic use in cancer chemotherapy. Drugs. 45:788–856. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu F, Jin H, Shen J, Wu D, Tian Y and
Huang C: Gp130 degradation induced by epirubicin contributes to
chemotherapy efficacy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 519:572–578.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wachters FM, Van Putten JW, Kramer H,
Erjavec Z, Eppinga P, Strijbos JH, de Leede GP, Boezen HM, de Vries
EG and Groen HJ: First-line gemcitabine with cisplatin or
epirubicin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase III
trial. Br J Cancer. 89:1192–1199. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Owonikoko TK, Ramalingam SS and Belani CP:
Maintenance therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer:
Current status, controversies, and emerging consensus. Clin Cancer
Res. 16:2496–2504. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cianfanelli V, Fuoco C, Lorente M, Salazar
M, Quondamatteo F, Gherardini PF, De Zio D, Nazio F, Antonioli M,
D'Orazio M, et al: AMBRA1 links autophagy to cell proliferation and
tumorigenesis by promoting c-Myc dephosphorylation and degradation.
Nat Cell Biol. 17:20–30. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Koike M, Sou YS, Ueno
T, Hara T, Mizushima N, Iwata J, Ezaki J, Murata S, et al:
Homeostatic levels of p62 control cytoplasmic inclusion body
formation in autophagy-deficient mice. Cell. 131:1149–1163. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu JT, Li WC, Gao S, Wang F, Li XQ, Yu
HQ, Fan LL, Wei W, Wang H and Sun GP: Autophagy inhibition
overcomes the antagonistic effect between gefitinib and cisplatin
in epidermal growth factor receptor mutant non-small-cell lung
cancer cells. Clin Lung Cancer. 16:e55–e66. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Vander Heiden MG and
Kroemer G: Metabolic targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 12:829–846. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hale AN, Ledbetter DJ, Gawriluk TR and
Rucker EB III: Autophagy: Regulation and role in development.
Autophagy. 9:951–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu R, Chen Z, Yi X, Huang F, Hu G, Liu D,
Li X, Zhou H and Liu Z: 9za plays cytotoxic and proapoptotic roles
and induces cytoprotective autophagy through the PDK1/Akt/mTOR axis
in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Cell Physiol. 234:20728–20741.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy: Process and
function. Genes Dev. 21:2861–2873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Amaravadi RK, Yu D, Lum JJ, Bui T,
Christophorou MA, Evan GI, Thomas-Tikhonenko A and Thompson CB:
Autophagy inhibition enhances therapy-induced apoptosis in a
Myc-induced model of lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 117:326–336. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chou HL, Lin YH, Liu W, Wu CY, Li RN,
Huang HW, Chou CH, Chiou SJ and Chiu CC: Combination therapy of
chloroquine and C(2)-ceramide enhances cytotoxicity in lung cancer
H460 and H1299 cells. Cancers (Basel). 11:E3702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pan Y, Qian JX, Lu SQ, Chen JW, Zhao XD,
Jiang Y, Wang LH and Zhang GX: Protective effects of tanshinone IIA
sodium sulfonate on ischemia-reperfusion-induced myocardial injury
in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 20:308–315. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee JG, Shin JH, Shim HS, Lee CY, Kim DJ,
Kim YS and Chung KY: Autophagy contributes to the chemo-resistance
of non-small cell lung cancer in hypoxic conditions. Respir Res.
16:1382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pedrosa P, Corvo ML, Ferreira-Silva M,
Martins P, Carvalheiro MC, Costa PM, Martins C, Martins LMDRS,
Baptista PV and Fernandes AR: Targeting cancer resistance via
multifunctional gold nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci. 20:E55102019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu T, Wang MC, Jing L, Liu ZY, Guo H, Liu
Y, Bai YY, Cheng YZ, Nan KJ and Liang X: Autophagy facilitates lung
adenocarcinoma resistance to cisplatin treatment by activation of
AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:6421–6431.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sugita S, Ito K, Yamashiro Y, Moriya S,
Che XF, Yokoyama T, Hiramoto M and Miyazawa K: EGFR-independent
autophagy induction with gefitinib and enhancement of its cytotoxic
effect by targeting autophagy with clarithromycin in non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 461:28–34. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang MC, Wu MY, Hwang MH, Chang YT, Huang
HJ, Lin AM and Yang JC: Chloroquine enhances gefitinib cytotoxicity
in gefitinib-resistant nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One.
10:e01191352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sui X, Kong N, Zhu M, Wang X, Lou F, Han W
and Pan H: Cotargeting EGFR and autophagy signaling: A novel
therapeutic strategy for non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Clin
Oncol. 2:8–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chang CY, Kuan YH, Ou YC, Li JR, Wu CC,
Pan PH, Chen WY, Huang HY and Chen CJ: Autophagy contributes to
gefitinib-induced glioma cell growth inhibition. Exp Cell Res.
327:102–112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cheng Y, Li H, Ren X, Niu T, Hait WN and
Yang J: Cytoprotective effect of the elongation factor-2
kinase-mediated autophagy in breast cancer cells subjected to
growth factor inhibition. PLoS One. 5:e97152010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pietrocola F, Izzo V, Niso-Santano M,
Vacchelli E, Galluzzi L, Maiuri MC and Kroemer G: Regulation of
autophagy by stress-responsive transcription factors. Semin Cancer
Biol. 23:310–322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Klionsky DJ, Abeliovich H, Agostinis P,
Agrawal DK, Aliev G, Askew DS, Baba M, Baehrecke EH, Bahr BA,
Ballabio A, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of
assays for monitoring autophagy in higher eukaryotes. Autophagy.
4:151–175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Varbiro G, Veres B, Gallyas F Jr and
Sumegi B: Direct effect of Taxol on free radical formation and
mitochondrial permeability transition. Free Radic Biol Med.
31:548–558. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fulda S, Galluzzi L and Kroemer G:
Targeting mitochondria for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
9:447–464. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Namba T, Takabatake Y, Kimura T, Takahashi
A, Yamamoto T, Matsuda J, Kitamura H, Niimura F, Matsusaka T,
Iwatani H, et al: Autophagic clearance of mitochondria in the
kidney copes with metabolic acidosis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
25:2254–2266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Randow F and Youle RJ: Self and nonself:
How autophagy targets mitochondria and bacteria. Cell Host Microbe.
15:403–411. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boyer-Guittaut M, Poillet L, Liang Q,
Bole-Richard E, Ouyang X, Benavides GA, Chakrama FZ, Fraichard A,
Darley-Usmar VM, Despouy G, et al: The role of GABARAPL1/GEC1 in
autophagic flux and mitochondrial quality control in MDA-MB-436
breast cancer cells. Autophagy. 10:986–1003. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Karsli-Uzunbas G, Guo JY, Price S, Teng X,
Laddha SV, Khor S, Kalaany NY, Jacks T, Chan CS, Rabinowitz JD and
White E: Autophagy is required for glucose homeostasis and lung
tumor maintenance. Cancer Discov. 4:914–927. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo JY, Xia B and White E:
Autophagy-mediated tumor promotion. Cell. 155:1216–1219. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|