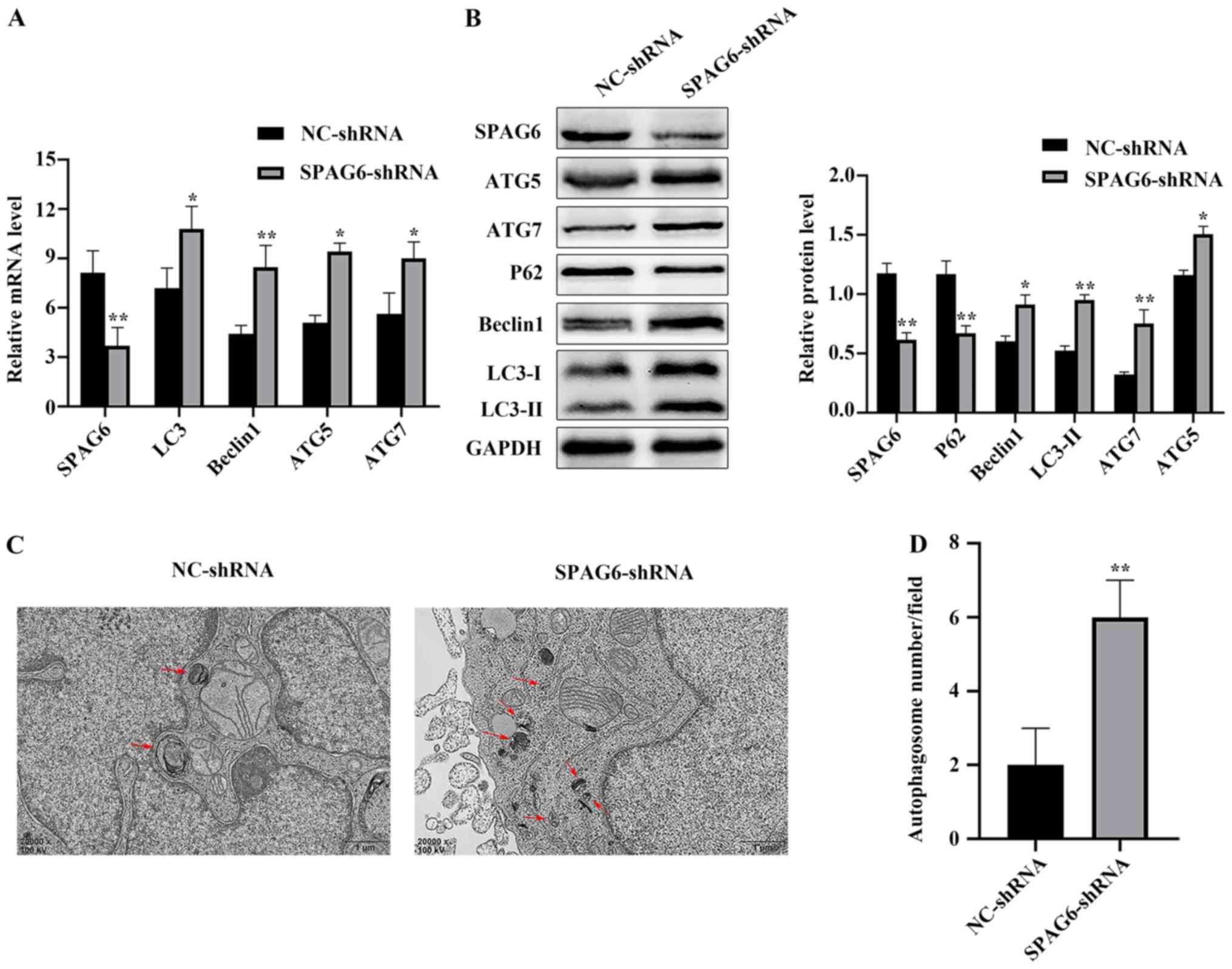
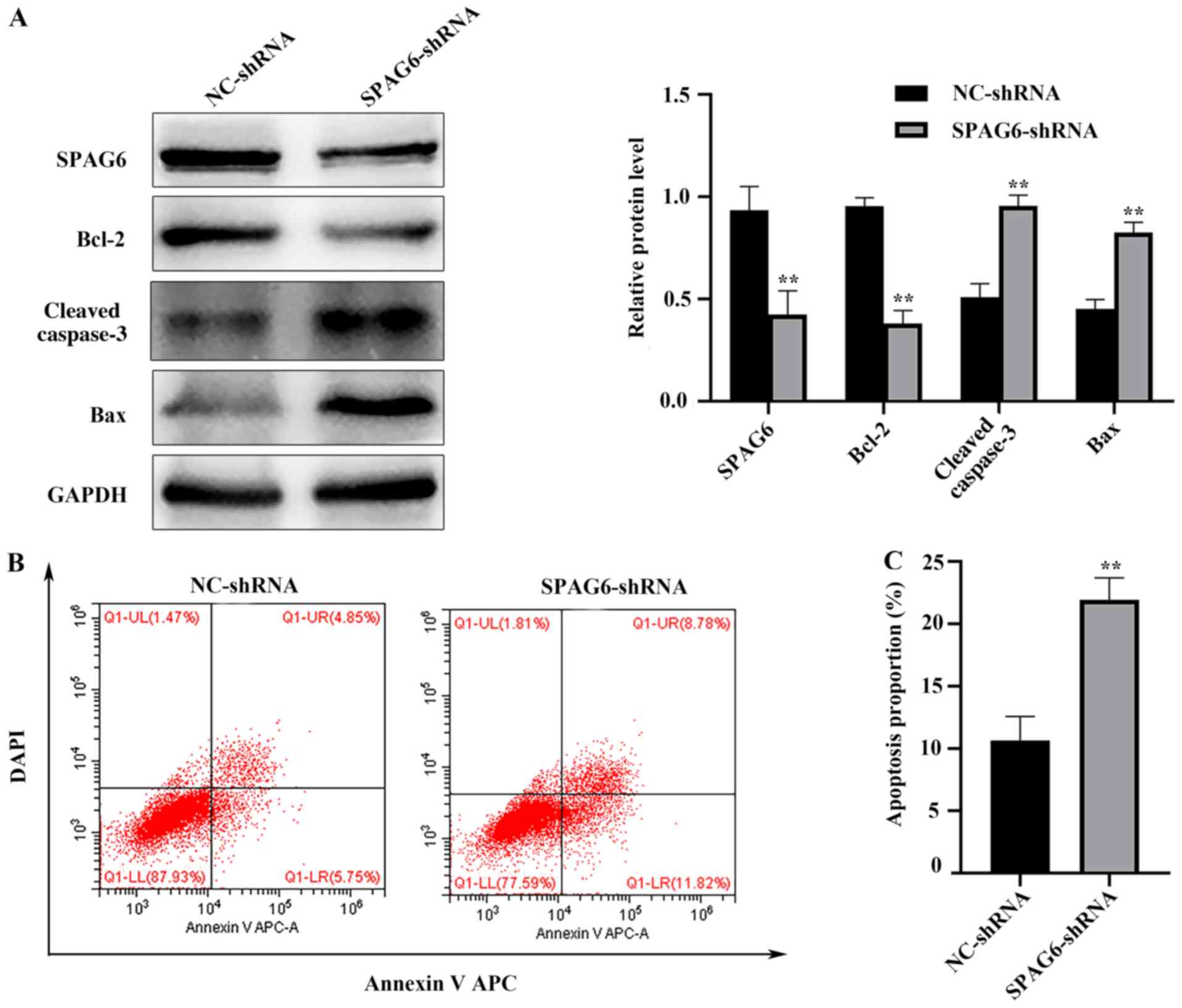
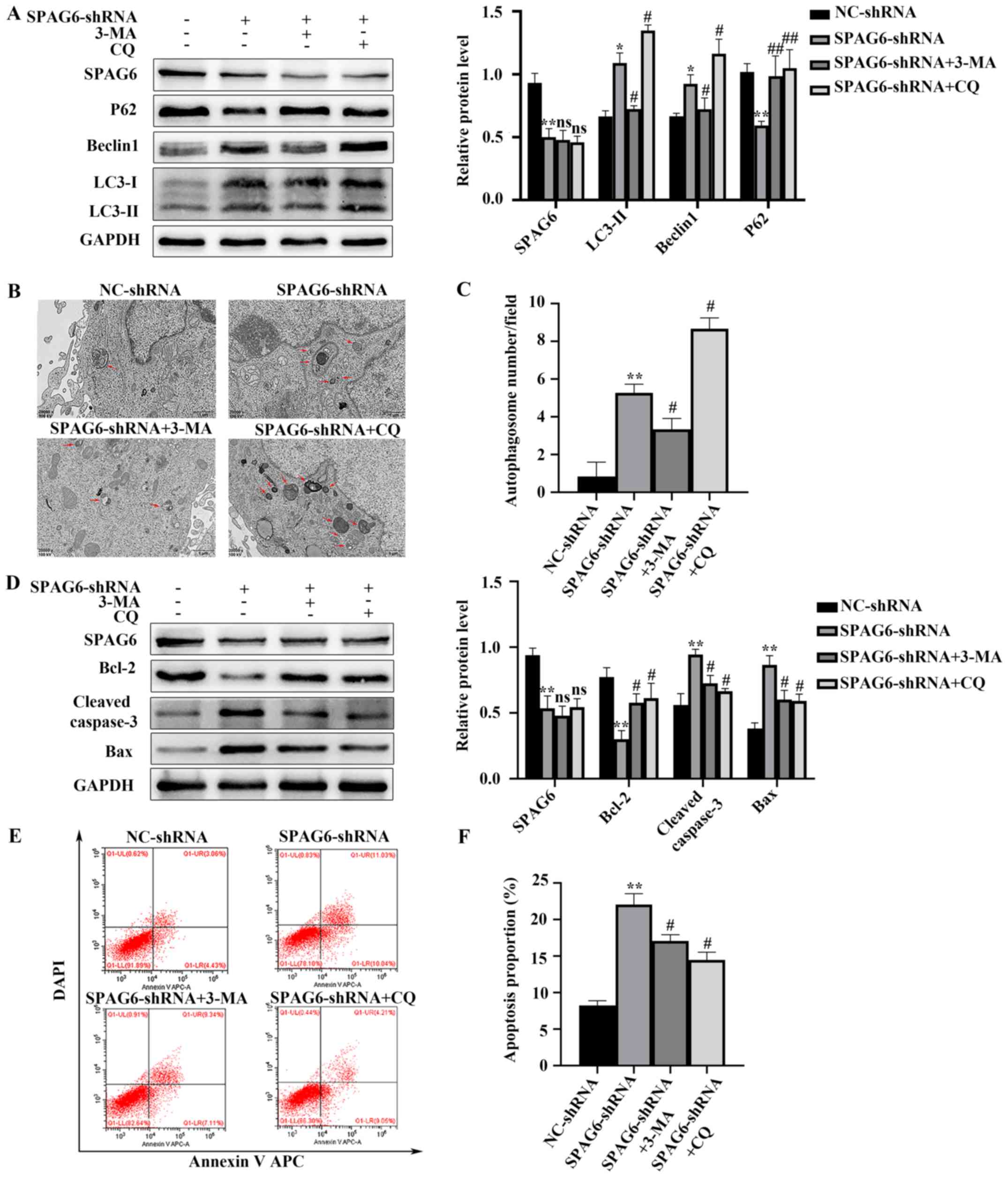
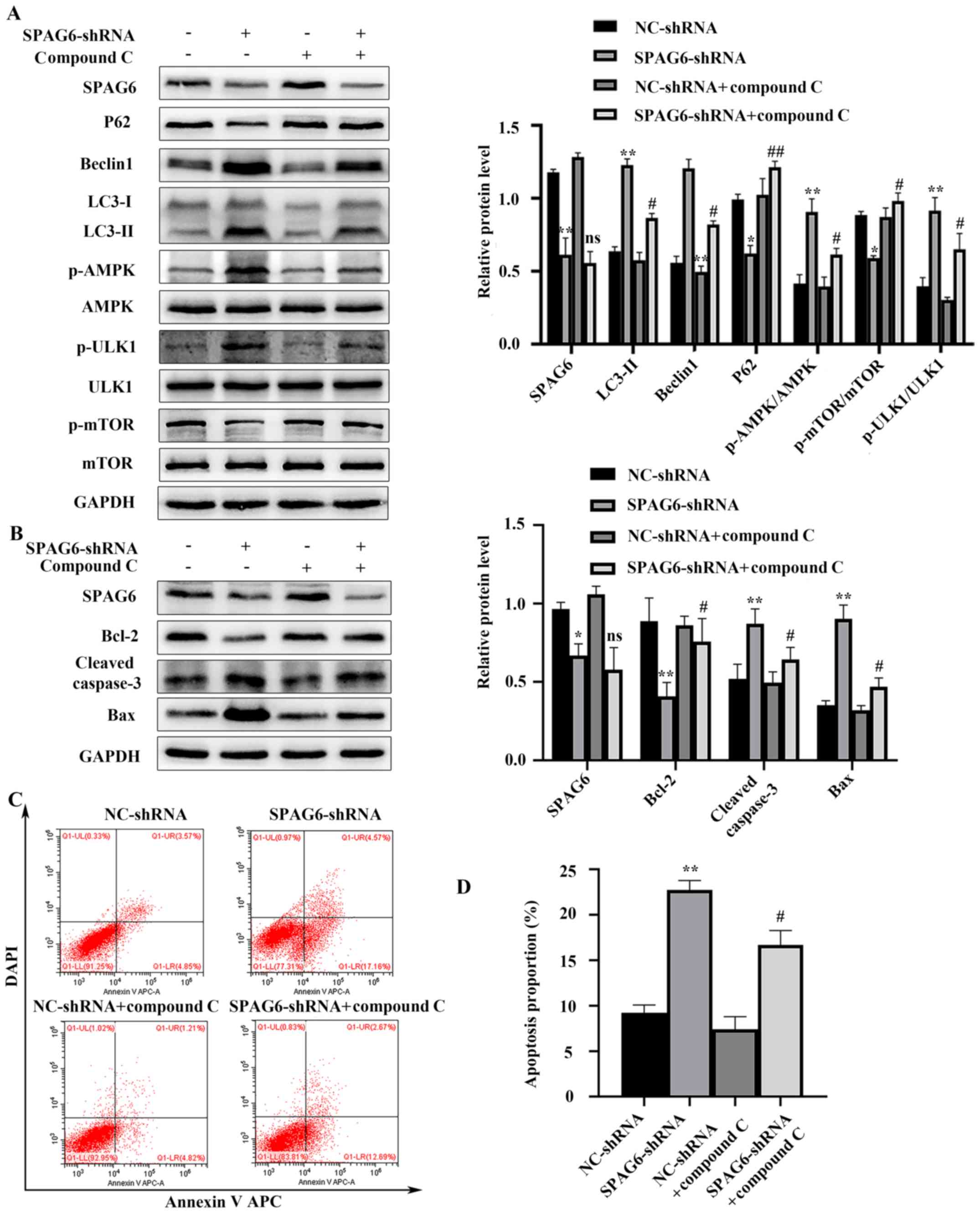
|
1
|
Corey SJ, Minden MD, Barber DL, Kantarjian
H, Wang JC and Schimmer AD: Myelodysplastic syndromes: The
complexity of stem-cell diseases. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:118–129. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Greenberg PL, Stone RM, Al-Kali A, Barta
SK, Bejar R, Bennett JM, Carraway H, De Castro CM, Deeg HJ, DeZern
AE, et al: Myelodysplastic syndromes, Version 2.2017, NCCN clinical
practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 15:60–87.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saber W, Cutler CS, Nakamura R, Zhang MJ,
Atallah E, Rizzo JD, Maziarz RT, Cortes J, Kalaycio ME and Horowitz
MM: Impact of donor source on hematopoietic cell transplantation
outcomes for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Blood.
122:1974–1982. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sapiro R, Kostetskii I, Olds-Clarke P,
Gerton GL, Radice GL and Strauss III JF: Male infertility, impaired
sperm motility, and hydrocephalus in mice deficient in
sperm-associated antigen 6. Mol Cell Biol. 22:6298–6305. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siliņa K, Zayakin P, Kalniņa Z, Ivanova L,
Meistere I, Endzeliņš E, Abols A, Stengrēvics A, Leja M, Ducena K,
et al: Sperm-associated antigens as targets for cancer
immunotherapy: Expression pattern and humoral immune response in
cancer patients. J Immunother. 34:28–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Steinbach D, Schramm A, Eggert A, Onda M,
Dawczynski K, Rump A, Pastan I, Wittig S, Pfaffendorf N, Voigt A,
et al: Identification of a set of seven genes for the monitoring of
minimal residual disease in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:2434–2441. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang M, Chen Y, Deng L, Luo X, Wang L and
Liu L: Upregulation of SPAG6 in myelodysplastic syndrome: Knockdown
inhibits cell proliferation via AKT/FOXO signaling pathway. DNA
Cell Biol. 38:476–484. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakagawa T, Matozaki S, Murayama T,
Nishimura R, Tsutsumi M, Kawaguchi R, Yokoyama Y, Hikiji K, Isobe T
and Chihara K: Establishment of a leukaemic cell line from a
patient with acquisition of chromosomal abnormalities during
disease progression in myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol.
85:469–476. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang B, Wang L, Luo X, Chen L, Yang Z and
Liu L: SPAG6 silencing inhibits the growth of the malignant myeloid
cell lines SKM-1 and K562 via activating p53 and caspase
activation-dependent apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 46:649–656. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li X, Yang B, Wang L, Chen L, Luo X and
Liu L: SPAG6 regulates cell apoptosis through the TRAIL signal
pathway in myelodysplastic syndromes. Oncol Rep. 37:2839–2846.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yin J, Li X, Zhang Z, Luo X, Wang L and
Liu L: SPAG6 silencing induces apoptosis in the myelodysplastic
syndrome cell line SKM-1 via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol. 53:297–306.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
White E and DiPaola RS: The double-edged
sword of autophagy modulation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5308–5316. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mortensen M, Ferguson DJ, Edelmann M,
Kessler B, Morten KJ, Komatsu M and Simon AK: Loss of autophagy in
erythroid cells leads to defective removal of mitochondria and
severe anemia in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:832–837. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Watson AS, Mortensen M and Simon AK:
Autophagy in the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndrome and acute
myeloid leukemia. Cell Cycle. 10:1719–1725. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mortensen M, Watson AS and Simon AK: Lack
of autophagy in the hematopoietic system leads to loss of
hematopoietic stem cell function and dysregulated myeloid
proliferation. Autophagy. 7:1069–1070. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ali AM and Raza A: Two different ‘tales’
of ATG7: Clinical relevance to myelodysplastic syndromes. Mol Cell
Oncol. 3:e12126862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jiang H, Yang L, Guo L, Cui N, Zhang G,
Liu C, Xing L, Shao Z and Wang H: Impaired mitophagy of nucleated
erythroid cells leads to anemia in patients with myelodysplastic
syndromes. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:63280512018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jacquel A, Luciano F, Robert G and
Auberger P: Implication and regulation of AMPK during physiological
and pathological myeloid differentiation. Int J Mol Sci.
19:E29912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao M and Klionsky DJ: AMPK-dependent
phosphorylation of ULK1 induces autophagy. Cell Metab. 13:119–120.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nieminen AI, Eskelinen VM, Haikala HM,
Tervonen TA, Yan Y, Partanen JI and Klefstrom J: Myc-induced
AMPK-phospho p53 pathway activates Bak to sensitize mitochondrial
apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E1839–E1848. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays
for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yim NH, Hwang YH, Liang C and Ma JY: A
platycoside-rich fraction from the root of Platycodon grandiflorum
enhances cell death in A549 human lung carcinoma cells via mainly
AMPK/mTOR/AKT signal-mediated autophagy induction. J
Ethnopharmacol. 194:1060–1068. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim HI, Hong SH, Ku JM, Lim YS, Lee SJ,
Song J, Kim TY, Cheon C and Ko SG: Scutellaria radix promotes
apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells via induction of
AMPK-Dependent autophagy. Am J Chin Med. 47:691–705. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu Y, Wang X, Guo H, Zhang B, Zhang XB,
Shi ZJ and Yu L: Synthesis and screening of 3-MA derivatives for
autophagy inhibitors. Autophagy. 9:595–603. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yin H, Yang X, Gu W, Liu Y, Li X, Huang X,
Zhu X, Tao Y, Gou X and He W: HMGB1-mediated autophagy attenuates
gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in bladder cancer cells involving JNK
and ERK activation. Oncotarget. 8:71642–71656. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xing JJ, Hou JG, Ma ZN, Wang Z, Ren S,
Wang YP, Liu WC, Chen C and Li W: Ginsenoside Rb3 provides
protective effects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via
regulation of AMPK-/mTOR-mediated autophagy and inhibition of
apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Cell Prolif. 52:e126272019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sperling AS, Gibson CJ and Ebert BL: The
genetics of myelodysplastic syndrome: From clonal haematopoiesis to
secondary leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:5–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schanz J, Tuchler H, Sole F, Mallo M, Luno
E, Cervera J, Granada I, Hildebrandt B, Slovak ML, Ohyashiki K, et
al: New comprehensive cytogenetic scoring system for primary
myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and oligoblastic acute myeloid
leukemia after MDS derived from an international database merge. J
Clin Oncol. 30:820–829. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li F, Zeng J, Gao Y, Guan Z, Ma Z, Shi Q,
Du C, Jia J, Xu S, Wang X, et al: G9a inhibition induces autophagic
cell death via AMPK/mTOR pathway in bladder transitional cell
carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01383902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mortensen M, Soilleux EJ, Djordjevic G,
Tripp R, Lutteropp M, Sadighi-Akha E, Stranks AJ, Glanville J,
Knight S, Jacobsen SE, et al: The autophagy protein Atg7 is
essential for hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. J Exp Med.
208:455–467. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu X, Yan R, Cheng X, Song L, Zhang W, Li
K and Zhao S: The function of sperm-associated antigen 6 in
neuronal proliferation and differentiation. J Mol Histol.
47:531–540. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li X, Xu L, Sun G, Wu X, Bai X, Li J,
Strauss JF, Zhang Z and Wang H: Spag6 mutant mice have defects in
development and function of spiral ganglion neurons, apoptosis, and
higher sensitivity to paclitaxel. Sci Rep. 7:86382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Maiuri MC, Criollo A and Kroemer G:
Crosstalk between apoptosis and autophagy within the Beclin 1
interactome. EMBO J. 29:515–516. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhuang L, Ma Y, Wang Q, Zhang J, Zhu C,
Zhang L and Xu X: Atg3 overexpression enhances bortezomib-induced
cell death in SKM-1 cell. PLoS One. 11:e01587612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Romano A, Giallongo C, La Cava P,
Parrinello NL, Chiechi A, Vetro C, Tibullo D, Di Raimondo F, Liotta
LA, Espina V and Palumbo GA: Proteomic analysis reveals autophagy
as pro-survival pathway elicited by long-term exposure with
5-azacitidine in high-risk myelodysplasia. Front Pharmacol.
8:2042017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gao L, Wang Z, Lu D, Huang J, Liu J and
Hong L: Paeonol induces cytoprotective autophagy via blocking the
Akt/mTOR pathway in ovarian cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
10:6092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Martelli AM, Evangelisti C, Chappell W,
Abrams SL, Basecke J, Stivala F, Donia M, Fagone P, Nicoletti F,
Libra M, et al: Targeting the translational apparatus to improve
leukemia therapy: Roles of the PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathway.
Leukemia. 25:1064–1079. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zeng J, Liu W, Fan YZ, He DL and Li L:
PrLZ increases prostate cancer docetaxel resistance by inhibiting
LKB1/AMPK-mediated autophagy. Theranostics. 8:109–123. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li TT, Zhu D, Mou T, Guo Z, Pu JL, Chen
QS, Wei XF and Wu ZJ: IL-37 induces autophagy in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol
Immunol. 87:132–140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chan EY, Kir S and Tooze SA: siRNA
screening of the kinome identifies ULK1 as a multidomain modulator
of autophagy. J Biol Chem. 282:25464–25474. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zheng Q, Zhao Y, Guo J, Zhao S, Fei C,
Xiao C, Wu D, Wu L, Li X and Chang C: Iron overload promotes
mitochondrial fragmentation in mesenchymal stromal cells from
myelodysplastic syndrome patients through activation of the
AMPK/MFF/Drp1 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 9:5152018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Basiorka AA, McGraw KL, Eksioglu EA, Chen
X, Johnson J, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Irvine BA, Cluzeau T, Sallman DA,
et al: The NLRP3 inflammasome functions as a driver of the
myelodysplastic syndrome phenotype. Blood. 128:2960–2975. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bullón P, Alcocer-Gómez E, Carrión AM,
Marín-Aguilar F, Garrido-Maraver J, Román-Malo L, Ruiz-Cabello J,
Culic O, Ryffel B, Apetoh L, et al: AMPK phosphorylation modulates
pain by activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Antioxid Redox Signal.
24:157–170. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|